Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine System Organ Actions
Uploaded by
Flordeliza Santos MagalonaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System Organ Actions
Uploaded by
Flordeliza Santos MagalonaCopyright:
Available Formats
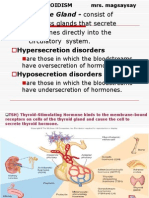
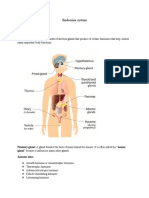
MAGALONA, JANNEL S. Pharma 1Y2-1 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ORGAN ACTION HYPOSECRETION 1.PITUITARY GLAND A.
Anterior pituitary gland It is a major Dwarfism participant in control of several complex physiologic processes, including growth and metabolism. Stimulates the thyroid gland to release thyroid hormone. Stimulates adrenal glands to produce hormones. isa trophicpeptide hor mone responsible for the release of folliclestimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary stimulates mammary gland growth and milk production 1.PITUITARY GLAND Myxedema crentenism Addisonss disease Kallmann syndrome, HYPERSECRETION
Growth hormone (GH)
anterior pituitary
Gigantism Acromegaly
Thyrotropin (TSH) Corticotropin (ACTH) Gonadotropins
thyroid adrenal glands ovaries and testes
Thyrotoxicosis Crushings disease
Hyperglycemia
Prolactin (PRL)
ovaries
Inability to produce milk after pregnancy.
Amenorrhea Galactorrhea.
Antidiurtic hormones (ADH) Oxytocin
Thyroxine (T4) Triiodothyronine (T3) Calcitonin
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Glucocorticoids
B. Posterior pituitary gland kidneys Regulates water Diabetes insipidus balance mammary Induces milk Low blood pressure glands and movement and uterine uterine inertia uterus contractions during child birth 2.THYROID GLAND thyroid Stimulates metabolic lethargy, weight gain rate for growth, cell metabolism thyroid cell metabolism, blood Myxedema levels Hashimotos disease thyroid Inhibits breakdown of hypercalcemia bone and causes decreases in blood calcium concentrations 3. PARATHYROID GLAND Skeletal Bone resorption Tenany system/bones Decreased urinary hypocalcemia ,kidneys excretion of calcium ,small gastrointestinal intestine absorption of calcium (vitamin D) Hypercalcemia Increased 4. ADRENAL GLAND liver cells Increases blood Addison disease glucose level by (muscle weakness stimulating liver cells, fatigue, weight loss) reduce inflammation.
abnormal water retention Impotence
hyperthyroidism Grave's disease hypocalcemia
Polyuria Polydipsia hypercalcemia
Crushing syndrome (moon face, red stretch marks, thin skin)
Mineralocorticoids Epinephrine/ Norepinephrine Gland
Kidney cells sympathetic nerve, heart, blood vessels, airways(brac hial tubes), and liver cells
retention of ions Intensifies and prolongs the sympathetic response during stress.
Decrease in water in blood low blood pressure. no problems
Conns syndrome Increased BP, increased HR, increased Cardiac force, increased Breathing rate, DECREASE in metabolism in digestive system, anxiety, sweating, exhaustion Premature male sexual development
Testosterone
Testes
5. GONADS A. Male Gonads Maturation of male reproductive organs 5. GONADS B. Female Gonads Promotes development and maintenance of female sexual characteristics Promotes conditions needed for pregnancy 6. PANCREATIC ISLET Stimulates glycogenolysis causing increase in blood glucose concentration Promotes glucose entry into cells causing
Lack of sexual development gynecomastia lack of female sexual development, infertility and osteoporosis Sterility Uncertain
Estrogen
Ovaries
premature sexual development in females and infertility
Progesterone Glucagon
Ovaries
pancreatic islets
Uncertain
Insulin
pancreatic islets
diabetes mellitus
severe insulin shock or hypoglycemia
Thymosin
Bone marrow
decrease in blood glucose concentration 7. THYMUS Promotes development of immune system cells
immune system
Maturation of T lymphocytes involved in immune response
You might also like
- List of Hormones - Hypersecretion and HyposecretionDocument11 pagesList of Hormones - Hypersecretion and HyposecretionAngeli Jean Koreen Corpuz88% (48)
- Uworld EndocrineDocument211 pagesUworld Endocrineهنادي رازمNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Glands and HormonesDocument213 pagesThe Endocrine System: Glands and HormonesRosita Antiquina Elopre100% (1)
- Endocrine ChartDocument7 pagesEndocrine Chartwjg2882No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine SystemAnne Jillian83% (6)
- 40.43.function of Endocrine - Pptx?targetDocument28 pages40.43.function of Endocrine - Pptx?targetAnnemerline RavixNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Endocrine SystemDocument64 pagesPathophysiology of Endocrine SystemTess MohamedNo ratings yet
- 10 Endocrine SystemDocument35 pages10 Endocrine SystemALICIA GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Hormones: Prof. Dr. V P SoniDocument21 pagesHormones: Prof. Dr. V P SoniPadma VishwanathNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism 2011Document30 pagesHyperthyroidism 2011Elyza MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Baluga, Basa, Ong: A concise guide to endocrine glands and hormonesDocument6 pagesBaluga, Basa, Ong: A concise guide to endocrine glands and hormonesdave_1128No ratings yet
- Review Endocrine Disorders FINALDocument166 pagesReview Endocrine Disorders FINALmeranith100% (10)
- Function Hormone Endocrine Gland: Collecting Tubule Antidieuretik)Document7 pagesFunction Hormone Endocrine Gland: Collecting Tubule Antidieuretik)ridwan100% (1)
- The Endocrine System (Notes)Document4 pagesThe Endocrine System (Notes)Wasim HakimNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument25 pagesEndocrine Systemangel_maui100% (13)
- Thyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!From EverandThyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Diseases of The Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesDiseases of The Endocrine SystemMichelle HuangNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Review NotesDocument8 pagesEndocrine System Review Notesjeshema100% (1)
- Endocrine DiseasesDocument170 pagesEndocrine DiseasesJustin Ahorro-DionisioNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Study: Endocrinology Physician: EndocrinologistDocument5 pagesEndocrine System: Study: Endocrinology Physician: EndocrinologistSakshi BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Endocrine and Metabolic SystemDocument21 pagesStructure and Function of The Endocrine and Metabolic Systemcoy008No ratings yet
- Kuliah PituitariDocument48 pagesKuliah PituitariLona Veronika HutajuluNo ratings yet
- WorkshopBIO 12 CH. 50Document5 pagesWorkshopBIO 12 CH. 50JISAS CLIMAXNo ratings yet
- HypopituitarismDocument2 pagesHypopituitarismAnne de VeraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Hormones and Their FunctionDocument1 pageEndocrine Hormones and Their FunctionDee RavalNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 018 Chapter 14Document3 pagesZoology Notes: 018 Chapter 14humanupgrade100% (1)
- NM 24 Endohypothapituit 2007Document71 pagesNM 24 Endohypothapituit 2007api-26938624No ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFDocument8 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFSaurav SoniNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E: Nursing Care of The Client: Endocrine SystemDocument29 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E: Nursing Care of The Client: Endocrine SystemWilbert Antonino CabanbanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 pagesEndocrine SystemLen Len Ochinang OchinangNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: One of Us, and I'm Not Certain Which, Has A Glandular DisorderDocument10 pagesEndocrine System: One of Us, and I'm Not Certain Which, Has A Glandular Disorderroserem2000No ratings yet
- Week 2 Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology Review & Pituitary DisturbancesDocument27 pagesWeek 2 Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology Review & Pituitary DisturbancesZiqri Dimas SandyNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System: Central Nervous System Hypothalamus Pituitary Ovaries Uterus, Breasts, Skin, VaginaDocument44 pagesFemale Reproductive System: Central Nervous System Hypothalamus Pituitary Ovaries Uterus, Breasts, Skin, VaginayeandunNo ratings yet
- Endo EndoDocument45 pagesEndo EndomaoNo ratings yet
- Marieb Endocrine System SummaryDocument8 pagesMarieb Endocrine System SummaryLezahbef Neaj SollogonNo ratings yet
- S9 Q4 M2 Body Regulators and Reproduction and Development LectureDocument21 pagesS9 Q4 M2 Body Regulators and Reproduction and Development LectureJermae DizonNo ratings yet
- Hormone Regulation & Endocrine StructuresDocument28 pagesHormone Regulation & Endocrine StructuresFujoshiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Physiology of The Endocrine System: Geofrey S. SevillenoDocument55 pagesAnatomy, Physiology of The Endocrine System: Geofrey S. Sevillenocoral jade cuaNo ratings yet
- ArainDocument71 pagesArainAllah Bux KhosoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy EndocrineDocument2 pagesAnaphy EndocrineJoey MagnoNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Anatomy PhysiologyDocument60 pagesEndocrinology Anatomy PhysiologyhamidNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusRohan Sahu0% (1)
- The Endocrine SystemDocument52 pagesThe Endocrine Systemone nurcahyonoNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3_ the Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesTOPIC 3_ the Endocrine SystemKaren Pearl TagleNo ratings yet
- Patologia EndocrinaDocument6 pagesPatologia EndocrinaDamaryNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland DisordersDocument80 pagesPituitary Gland DisordersNang KhamNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - Class - 10 - Icse.Document2 pagesEndocrine System - Class - 10 - Icse.zoha afshanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of The Endocrine System. Violation of Hypophysis, Thyroid and Adrenal Glands. General Adaptation SyndromeDocument123 pagesPathophysiology of The Endocrine System. Violation of Hypophysis, Thyroid and Adrenal Glands. General Adaptation SyndromeAyman RehmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 12.6 and 12.7Document16 pagesChapter 12 12.6 and 12.7Omkara HiteshNo ratings yet
- endocrine-diseases-1Document66 pagesendocrine-diseases-1Nathaniel BudayNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Reviews UndanaDocument132 pagesEndocrine Reviews UndanaAndi Suchy Qumala SarieNo ratings yet
- Pituitary GlandDocument30 pagesPituitary GlandAnurag MahawarNo ratings yet
- Developmental Aspects of the Endocrine System ExplainedDocument70 pagesDevelopmental Aspects of the Endocrine System ExplainedKevinNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine SystemBenjamin CristobalNo ratings yet
- Presentation 6Document26 pagesPresentation 6555556666667777777No ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument4 pagesEndocrine System NotesSashaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument4 pagesChapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationanuminiatureNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Notes - NCERT BasedDocument8 pagesEndocrine System Notes - NCERT Basedpallab mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders and Their PharmacotherapyDocument4 pagesEndocrine Disorders and Their PharmacotherapyYemaya84No ratings yet
- Thyroid Diet: How to improve and cure thyroid disorders, lose weight, and improve metabolism with the help of food!From EverandThyroid Diet: How to improve and cure thyroid disorders, lose weight, and improve metabolism with the help of food!No ratings yet
- Certificate of Participation: Flordeliza S. MagalonaDocument1 pageCertificate of Participation: Flordeliza S. MagalonaFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Participation: Flordeliza S. MagalonaDocument1 pageCertificate of Participation: Flordeliza S. MagalonaFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Participation: Flordeliza S. MagalonaDocument1 pageCertificate of Participation: Flordeliza S. MagalonaFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Participation: Flordeliza S. MagalonaDocument1 pageCertificate of Participation: Flordeliza S. MagalonaFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Participation: Flordeliza S. MagalonaDocument1 pageCertificate of Participation: Flordeliza S. MagalonaFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Participation: Flordeliza S. MagalonaDocument1 pageCertificate of Participation: Flordeliza S. MagalonaFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Participation: Flordeliza S. MagalonaDocument1 pageCertificate of Participation: Flordeliza S. MagalonaFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Certificate awarded for webinar participationDocument1 pageCertificate awarded for webinar participationFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Certificate earned for online art webinarDocument1 pageCertificate earned for online art webinarFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Certificate earned for remote learning webinarDocument1 pageCertificate earned for remote learning webinarFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Certificate earned for online learning eventDocument1 pageCertificate earned for online learning eventFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Kinds of ThermometerDocument10 pagesKinds of ThermometerFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Oral Drug BioavailabilityDocument15 pagesOral Drug BioavailabilityFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Seven Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument8 pagesSeven Habits of Highly Effective PeopleFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Seven Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument8 pagesSeven Habits of Highly Effective PeopleFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Organ ActionsDocument4 pagesEndocrine System Organ ActionsFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and EstersDocument22 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Estersapi-3706290100% (2)
- Vowel sounds A-E-I-O-UDocument2 pagesVowel sounds A-E-I-O-UFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- IliadDocument6 pagesIliadFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Vector AnalysisDocument10 pagesVector AnalysisFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNo ratings yet