Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Projection
Projection
Uploaded by
juncos0729Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Projection
Projection
Uploaded by
juncos0729Copyright:
Available Formats
MEMB113 Drawing 07 Multiview Projection
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Content
Projection Theory Multi-view Projection [Planes | Lines] Multi-view [6 principle views | View placement] Projection angle [1 angle | 3 angle] Detail drawing [1-view | 2-view | 3-view drawing] Creating multi-view drawing View selection Line convention Common feature in multi-view drawing
st rd
adzlyanuar 2004
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.1 Projection Theory
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Engineering and technical
graphics are dependent on projection methods 2 methods primarily used Parallel: object positioned at infinity & viewed from multiple points on an imaginary line parallel to the object Perspective: object position at finite distance & viewed from a single point
Parallel
Perspective
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.1 Projection Theory
Projection theory comprises of the principles used to graphically represent 3D objects on 2D media Based on 2 variables: Line of Sight (LOS): an imaginary ray of light between and observers eye and an object. Parallel all LOS are parallel; perspective all LOS start at a point Plane of projection: an imaginary flat plane where the image created by LOS is projected.
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
adzlyanuar 2004
adzlyanuar 2004
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.1 Projection Theory
Projections Perspective Projections Parallel Projections
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Linear Perspective
Aerial Perspective
Oblique Projections
Orthographic Projections Axonometric Projections Multiview Projections
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.1 Projection Theory: Multi-view
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
adzlyanuar 2004
adzlyanuar 2004
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.1 Projection Theory
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Orthographic projection: a parallel proj. technique where
the proj. plane is placed between observer and object and is perpendicular to the parallel lines of sight
Changing view point
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.2 Multi-view projection
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Multiview projection is an orthographic projection for
which the object is behind the plane of projection, and the object is orientated such that only two of its dimensions are shown.
object Projection plane
Orthographic projection Front View
adzlyanuar 2004
adzlyanuar 2004
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.2 Multi-view projection
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Multiview drawings
Employ multiview projection technique Generally three views of an object are drawn Each view is a 2D flat image
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.2 Multi-view projection
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Right side view
Top view
adzlyanuar 2004
adzlyanuar 2004
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.2 Multi-view projection
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Multiview drawing of an object
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.2 Multi-view: Lines
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Lines in multi-view
projection
adzlyanuar 2004
adzlyanuar 2004
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
5.2 Multi-view: Planes
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.2 Multi-view: Planes
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
adzlyanuar 2004
adzlyanuar 2004
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.3 Multi-view: The 6 principal views
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
The 6 principal views
are the six mutually perpendicular views that are produced by six mutually perpendicular planes of projection Imagine an object is suspended in a glass box, the 6 sides become projection plane showing the six views
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.3 Multi-view: The 6 principal views
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
The views are laid flat by unfolding the glass box This forms the basis of two
important multiview drawing standard
Top, front and bottom views are
all aligned vertically & share the same width dim. Rear, left, front and right side are aligned horizontally & share same height dim.
Alignment of views Fold lines
adzlyanuar 2004
adzlyanuar 2004
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.3 Multi-view: The 6 principal views
glass box
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Fold lines are the imaginary hinged edges of the
The fold line between the top & front views is labeled H/F The distance from a point in front view to the H/F is the same
as the distance from the corresponding point in the top view to the H/F fold line
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.4 Multi-view: View Placement
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
adzlyanuar 2004
adzlyanuar 2004
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.4 Multi-view: View Placement
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
The arrangement of views may vary as shown,
where the top view is considered the central view
Alternate view arrrangement
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.5
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
1st-
and
3rd-angle
projection
There are two standard
arrangement of all six views of an object First-angle projection Third-angle projection Each uses a different symbol The names are derived from the method used to view the object being drawn
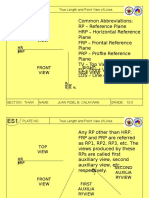
3rd angle projection
1st angle projection
adzlyanuar 2004
adzlyanuar 2004
10
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.5 1st- and 3rd-angle projection
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
In first-angle projection,
the object is placed in the first quadrant In third-angle projection, the object is placed in the third quadrant
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.5
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
1st-
and
3rd-angle
projection
Brief rules
1st angle projection View from above is placed underneath View from below is placed above View from left is placed on right View from right is placed on left
3rd angle projection View from above is place above View from below is placed below View from left is placed on left View from right is placed on right
Symbols
3rd angle projection 1st angle projection
adzlyanuar 2004
adzlyanuar 2004
11
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.5 1st- and 3rd-angle projection
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Third-angle projection
First-angle projection
adzlyanuar 2004
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.6 One-view & two-view drawings
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
One-view
Two-view
Three-view
adzlyanuar 2004
One-view
12
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.6 Two-view drawings
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Examples
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.6 Steps in creating multi-view drawing
READ H SKETC DRAW
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Decide: Projection angle, Location of view, Scale
Prepare paper
-> Draw border -> Title block -> etc.
Construct view (outline)
-> Using thin pencil -> Measure & place view -> Project all views -> Final lining: hidden & centre lines (thin), arcs & circles (thick)
TOP
depth
y Lining views
-> Line in the rest of the lines -> Start from top left -> Construction lines may be left if thin enough
FRONT
height
SIDE
y y = (total length height depth)/3
-> Dimension, notes, etc. -> Finish off title block, etc.
adzlyanuar 2004
Finish drawing
adzlyanuar 2004
Two-view
13
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.6 3-view dwg
Before start drawing, produce sketch on rough paper
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Decide on front view and projection angle Obtain the overall width, height and depth Place the views (in block) Determine approx. space between the views Sketch the component,
place dimensions
adzlyanuar 2004
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.6 Creating 3-view drawing
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
(1) Drawing of border/frame and location of view (2) Light construction of view (inc. title block frame) (3) Lining in the views (4) Dimensioning and inserting of any subtitles and notes (5) Drawing title block, parts list and revision table
adzlyanuar 2004
14
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.6 Creating 3-view drawing
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
(1) Draw border/frame, title block, etc.
Draw border, title block
title block revisions
revisions
parts list title block title block
Locating the view
should be approx. in centre distance between view =
(total length available view length) / 3
adzlyanuar 2004
Drawing projection lines
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.6 Creating 3-view drawing
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Projecting views
45O
TOP VIEW
TOP VIEW
SIDE VIEW
(a) FRONT VIEW TOP VIEW
SIDE VIEW
(b) FRONT VIEW TOP VIEW
45O
45O
SIDE VIEW
(c) FRONT VIEW
SIDE VIEW
(d)
FRONT VIEW
adzlyanuar 2004
15
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.6 Creating 3-view drawing
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
(2) Light construction of the views
Draw light/thin horizontal & vertical lines accordingly for front view Draw center lines and hidden lines as final Draw top (or side) view Project top view (or side) from front view using thin, light construction line Draw side (or top) view Project side view (or top) from front view and top (or side) view All arcs and circles should be lined (final) at this stage
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.6 Creating 3-view drawing
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
(3) Lining in of the views
To darken all visible edges (lines that represent a hard edge) Done using thick, black pencil (0.5mm, 2B) Should be done systematically for 3 views Start with horizontal line at the top of the
top/plan view, working down the page using T-square From left hand side, working across the page, line in all vertical lines, using Tsquare and set square Projection lines may be left on the drawing if they are very light
adzlyanuar 2004
adzlyanuar 2004
16
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.6 Creating 3-view drawing
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
(4) Write dimensioning, notes, annotation, etc. Be aware of redundant dimensioning
parts list & revision table, and others.
(5) Complete drawing by writing the rest of title block,
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.7 View Selection
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
4 basic decisions
(1) Determine the best position. The object must be positioned in such a way that the surface of major features are either perpendicular or parallel to glass planes.
(1)
adzlyanuar 2004
adzlyanuar 2004
17
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.7 View Selection
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
(2) Define the front view. Should show the object in natural state and show most features.
(2)
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.7 View Selection
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
(3) Determine the minimum number of views needed to completely describe the object. (4) Determine other views that have fewest number of hidden lines
(3) (4)
adzlyanuar 2004
adzlyanuar 2004
18
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.8 Line convention
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Hidden lines
Centre lines
Hidden features
adzlyanuar 2004
07 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION DRAWING
5.8 Line convention
MEMB113 | Dept. of Mechanical Engineering | UNITEN | 2005
Hidden
lines
Drawing conventions for hidden lines
adzlyanuar 2004
19
End of chapter [07] References: Engineering Drawing, A.W. Boundy, McGraw-Hill, 2000
- Fundamentals of Graphics Communication 3rd Edition, Gary Bertoline & Eric Weibe, McGraw-Hill
20
You might also like
- Aircraft Design (2011)Document271 pagesAircraft Design (2011)Elroy Christmas100% (2)
- Engineering-Graphics PDFDocument2 pagesEngineering-Graphics PDFbhargaviNo ratings yet
- School Earthquake DrillDocument22 pagesSchool Earthquake Drilljuncos0729No ratings yet
- Permit To Operate Application FormDocument2 pagesPermit To Operate Application Formjuncos072967% (6)
- Exam F4 C5 Paper2Document5 pagesExam F4 C5 Paper2Anonymous WA8soxk3xZNo ratings yet
- Engineering H191 Engineering Fundamentals and Laboratory IDocument33 pagesEngineering H191 Engineering Fundamentals and Laboratory Igunesh_10No ratings yet
- Week 4 - Orthographic ProjectionDocument29 pagesWeek 4 - Orthographic ProjectionNOR SYAKILA ALIA NATASYANo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing - Section and Auxiliary ViewsDocument18 pagesTechnical Drawing - Section and Auxiliary ViewsAdrian RajendraNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics (EG)Document8 pagesEngineering Graphics (EG)Sudalai MadanNo ratings yet
- Ge6152 Engineering Graphics L T P C 2 0 3 4Document3 pagesGe6152 Engineering Graphics L T P C 2 0 3 4balajimeieNo ratings yet
- 2.5third Angle ProjectionDocument6 pages2.5third Angle ProjectionSumeet Saini0% (1)
- Chapter 7: MultiviewsDocument10 pagesChapter 7: Multiviewsapi-25981522No ratings yet
- 03 Section ViewsDocument13 pages03 Section ViewsDita AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Orthographic ViewsDocument29 pagesOrthographic ViewsMelissa HuynhNo ratings yet
- Projections: Mechanical Engineering Drawing & Graphics Lecture # 5,& 6Document58 pagesProjections: Mechanical Engineering Drawing & Graphics Lecture # 5,& 6Mohammad SohaibNo ratings yet
- Sectional Views (Pandangan Potongan) : Gambar Teknik ?Document13 pagesSectional Views (Pandangan Potongan) : Gambar Teknik ?fjranggaraNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary View MergedDocument272 pagesAuxiliary View MergedTaha MisirliNo ratings yet
- 3D ProjectionDocument35 pages3D ProjectionjayNo ratings yet
- ENGR1025U - Winter 2023 Lecture 3Document51 pagesENGR1025U - Winter 2023 Lecture 3ronald.onyiorahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Auxiliary View - HandoutDocument25 pagesChapter 5 Auxiliary View - HandoutTeshome Bekele100% (1)
- Unit - 1 Basic DesignDocument20 pagesUnit - 1 Basic Design10rajNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4: Orthographic ProjectionDocument8 pagesUNIT-4: Orthographic Projectionsuresh DesaiNo ratings yet
- Acharya Polytechnic Parametric Modelling LabDocument56 pagesAcharya Polytechnic Parametric Modelling LabPraveen Kumar H GNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Teaching Made Esy by Use o Latest Educational TechnologyDocument8 pagesEngineering Drawing Teaching Made Esy by Use o Latest Educational TechnologySunil KhabiaNo ratings yet
- Design of Transmission SystemsDocument3 pagesDesign of Transmission Systemsgowrisankar32No ratings yet
- Engineering GraphicsDocument110 pagesEngineering GraphicsAkarshan upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Angel CG15Document23 pagesAngel CG15Hari HaraNo ratings yet
- CS 4204 Computer Graphics: 3D Views and ProjectionDocument36 pagesCS 4204 Computer Graphics: 3D Views and ProjectionAryaman TiwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document19 pagesChapter 5Hassan RashidNo ratings yet
- 2.4first Angle ProjectionDocument6 pages2.4first Angle Projectiondesign12No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer GraphicsDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Computer GraphicsringaudinisNo ratings yet
- MECH 211 - Mechanical Engineering Drawing: François TardyDocument83 pagesMECH 211 - Mechanical Engineering Drawing: François TardyFrancois TardyNo ratings yet
- Orthographic Projection 1Document46 pagesOrthographic Projection 1mohitreddy100% (1)
- GR 10 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS DESIGN TERM 2 REVISION Edited To Neil 2023Document12 pagesGR 10 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS DESIGN TERM 2 REVISION Edited To Neil 2023KelebogileNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing L Views 2ndDocument25 pagesTechnical Drawing L Views 2ndnguyen thi van dongNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics and VisualizationDocument35 pagesEngineering Graphics and Visualizationzain IshaqNo ratings yet
- 978 1 58503 562 5 4 PDFDocument47 pages978 1 58503 562 5 4 PDFJuan MartinezNo ratings yet
- CADM Lab ManualDocument16 pagesCADM Lab ManualRathnavel Ponnuswami100% (1)
- Ge6152 Engineering GraphicsDocument2 pagesGe6152 Engineering Graphicskb210538No ratings yet
- Mec339 - Rapid Prototyping and Reverse Engineering LaboratoryDocument3 pagesMec339 - Rapid Prototyping and Reverse Engineering Laboratorysunilsharma853380100% (1)
- WindshieldDocument4 pagesWindshieldapi-269424168No ratings yet
- Module 1 - 2 - 4ENME1011 - COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING DRAWING - 2023-24 - IISem - V6Document47 pagesModule 1 - 2 - 4ENME1011 - COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING DRAWING - 2023-24 - IISem - V6VaibhaviNo ratings yet
- ED4111 Cad and Design For Manufacture and Assembly LabDocument68 pagesED4111 Cad and Design For Manufacture and Assembly LabBoopathi KalaiNo ratings yet
- MC510 Mechanical Drawing IDocument2 pagesMC510 Mechanical Drawing IEduardo RNo ratings yet
- Standard Training Manual: CSC OrionDocument245 pagesStandard Training Manual: CSC OrionMasaba Solomon63% (8)
- Kamaraj College of Engineering & Technology, VirudhunagarDocument4 pagesKamaraj College of Engineering & Technology, VirudhunagardpksobsNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Meng 2203: Teshome Bogale May 2021Document41 pagesEngineering Drawing Meng 2203: Teshome Bogale May 2021Abdi ZerihunNo ratings yet
- Eg PDFDocument109 pagesEg PDFfahamith ahamedNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawings and Symbols: 16-1 © 2011 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights ReservedDocument41 pagesEngineering Drawings and Symbols: 16-1 © 2011 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights ReservedSrini KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering, E10. 1Document35 pagesIntroduction To Engineering, E10. 1Mani KandanNo ratings yet
- Semester 2, 2011/2012 Engineering Drawing (MME 1211) : Kulliyyah of Engineering International Islamic University MalaysiaDocument47 pagesSemester 2, 2011/2012 Engineering Drawing (MME 1211) : Kulliyyah of Engineering International Islamic University MalaysiaSarang Hae IslamNo ratings yet
- 16-1 © 2011 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights ReservedDocument41 pages16-1 © 2011 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights ReservedAyushmanNo ratings yet
- Engineering GraphicsDocument23 pagesEngineering Graphicsk4r7hyNo ratings yet
- Isometric ViewsDocument17 pagesIsometric Viewscoolboy_usamaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Design and CADDocument35 pagesEngineering Design and CADrika_efriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Solidworks Engineering Graphics With Sketching WorksheetsDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Solidworks Engineering Graphics With Sketching WorksheetsRicky SteeleNo ratings yet
- 2.8isometric ViewDocument9 pages2.8isometric ViewSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- ME6501 CAD 2marks Rejinpaul c1 PDFDocument13 pagesME6501 CAD 2marks Rejinpaul c1 PDFMonishaNo ratings yet
- A Parametric Strategy For Free-Form Glass Structures Using Quadrilateral Planar FacetsDocument16 pagesA Parametric Strategy For Free-Form Glass Structures Using Quadrilateral Planar FacetsStanislas PetitNo ratings yet
- Modernisation, Mechanisation and Industrialisation of Concrete StructuresFrom EverandModernisation, Mechanisation and Industrialisation of Concrete StructuresNo ratings yet
- Geometric Construction 2Document84 pagesGeometric Construction 2juncos0729100% (1)
- Voltage: AB BC CA AB BC CA AB BC CA AB BC CADocument2 pagesVoltage: AB BC CA AB BC CA AB BC CA AB BC CAjuncos0729No ratings yet
- ZebraDocument1 pageZebrajuncos0729No ratings yet
- Geometric Construction 1Document78 pagesGeometric Construction 1juncos0729No ratings yet
- Math 240: Inverses: Ryan BlairDocument19 pagesMath 240: Inverses: Ryan Blairjuncos0729No ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To ProjectionsDocument29 pages01 Introduction To Projectionsjuncos0729No ratings yet
- Cicm VisionmissionDocument1 pageCicm Visionmissionjuncos0729No ratings yet
- Math 240: The Divergence Theorem: Ryan BlairDocument9 pagesMath 240: The Divergence Theorem: Ryan Blairjuncos0729No ratings yet
- Water Pump ReportDocument1 pageWater Pump Reportjuncos0729No ratings yet
- Specifications Del RosarioDocument16 pagesSpecifications Del Rosariojuncos0729No ratings yet
- Hydrology Module 101Document18 pagesHydrology Module 101juncos0729No ratings yet
- Bill of Materials and Cost Estimate: Material Description Qty Unit of Measure Unit Cost Amount I. Concrete & MasonryDocument16 pagesBill of Materials and Cost Estimate: Material Description Qty Unit of Measure Unit Cost Amount I. Concrete & Masonryjuncos0729100% (1)
- Earthquake Preparedness Guide: What To Do Before, During, and After An EarthquakeDocument1 pageEarthquake Preparedness Guide: What To Do Before, During, and After An Earthquakejuncos0729No ratings yet
- Kra: Infrastructure DevelopmentDocument14 pagesKra: Infrastructure Developmentjuncos0729No ratings yet
- Math 240: More Power Series Solutions To D.E.s at Singular PointsDocument13 pagesMath 240: More Power Series Solutions To D.E.s at Singular Pointsjuncos0729No ratings yet
- Elementary MapupdatedDocument1 pageElementary Mapupdatedjuncos0729No ratings yet
- Ce ReviewDocument54 pagesCe Reviewjuncos0729No ratings yet
- Table of Specs in Hydro 402 - FinalsDocument2 pagesTable of Specs in Hydro 402 - Finalsjuncos0729No ratings yet
- TABLE of SPECS in Hydraulics - MidtermsDocument1 pageTABLE of SPECS in Hydraulics - Midtermsjuncos0729No ratings yet
- Lesson 10: Acceleration: A Change in SpeedDocument4 pagesLesson 10: Acceleration: A Change in SpeedGajendraNo ratings yet
- DP - Application of Derivatives PDFDocument38 pagesDP - Application of Derivatives PDFAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Towards an ω-groupoid model of Type Theory: Based on joint work with Ondrej RypacekDocument33 pagesTowards an ω-groupoid model of Type Theory: Based on joint work with Ondrej RypacekΓιάννης ΣτεργίουNo ratings yet
- The Schur Multiplier of An N-Lie Superalgebra: Hesam Safa April 14, 2020Document16 pagesThe Schur Multiplier of An N-Lie Superalgebra: Hesam Safa April 14, 2020picard82No ratings yet
- Vector 2021Document13 pagesVector 2021Mayank GoelNo ratings yet
- Gis Assignment 1Document7 pagesGis Assignment 1Yunus BadriNo ratings yet
- Quiz On IntegralsDocument7 pagesQuiz On IntegralsbalajiNo ratings yet
- A2 - (Sub 5,6,8) - Intan Sri Maharani - E1b120010Document7 pagesA2 - (Sub 5,6,8) - Intan Sri Maharani - E1b120010Intan MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Revised CBSE 10th Maths Syllabus 2020-21Document5 pagesRevised CBSE 10th Maths Syllabus 2020-21Kunsh WadheraNo ratings yet
- Duality Theory For Clifford Tensor PowersDocument47 pagesDuality Theory For Clifford Tensor PowersSergioGimenoNo ratings yet
- Integration: X XDX X XDX Marks)Document10 pagesIntegration: X XDX X XDX Marks)Norzulsuriana Binti YahayaNo ratings yet
- Emsyll 2Document4 pagesEmsyll 2Pareekshith KattiNo ratings yet
- Moment of A ForceDocument43 pagesMoment of A ForceJohn Kristoffer GimpesNo ratings yet
- UNIT 14 Volumes: CSEC Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesUNIT 14 Volumes: CSEC Multiple Choice QuestionsJoe EmanuelNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam 30 - 03 - 2021Document14 pagesCad Cam 30 - 03 - 2021Bharat GavaliNo ratings yet
- Plates PDFDocument13 pagesPlates PDFCRIISSY100% (1)
- Autocad NotesDocument59 pagesAutocad NotesMahesh PanditNo ratings yet
- Crain's Petrophysical Handbook - TRUE VERTICAL DEPTHDocument6 pagesCrain's Petrophysical Handbook - TRUE VERTICAL DEPTHMuhammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion - DinâmicaDocument32 pagesRotational Motion - DinâmicaRenan OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Kcet - Paper Analysis: - Total Number of Questions 60Document9 pagesKcet - Paper Analysis: - Total Number of Questions 60Kumkum KumbarahalliNo ratings yet
- ITFE1-Analytic Geometry SyllabusDocument5 pagesITFE1-Analytic Geometry Syllabusjason a. unNo ratings yet
- HW04 Columbia Modern Algebra 1Document2 pagesHW04 Columbia Modern Algebra 1Cecilia WangNo ratings yet
- Solves Problems Involving Sides and Angles of A PolygonDocument3 pagesSolves Problems Involving Sides and Angles of A PolygonRenante T. JosolNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Chapter 06 Triangles Practice Paper 06Document4 pagesMaths Class X Chapter 06 Triangles Practice Paper 06curiousnavinNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Quarter 4Document12 pagesMath 9 Quarter 4Maria Sadaran100% (1)
- 12 Rao Elements 2004Document9 pages12 Rao Elements 2004thesunbk25No ratings yet
- Theory of Machines Vibrations GATE 2020Document45 pagesTheory of Machines Vibrations GATE 2020Franklin ClintonNo ratings yet
- JEE 2021 REVISE Complete JEE MATHDocument4 pagesJEE 2021 REVISE Complete JEE MATHRaju GNo ratings yet
- Final DLP Valenzuela.11Document14 pagesFinal DLP Valenzuela.11elaine valenzuelaNo ratings yet