Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bili Near Transformation
Uploaded by
Juan BoggianoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bili Near Transformation
Uploaded by
Juan BoggianoCopyright:
Available Formats
Page 1
Bilinear Transformation
Control Engineering
by Dr. L. K. Wong
Page 2
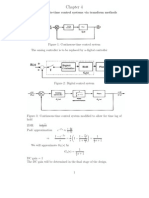
A Control System
Most plants are continuous-time systems
Power supply, power amplifier, motor
Digital controllers are in discrete-time
Implemented by micro-controller
Controller Plant
Reference
Output
+
Page 3
Continuous-time Signals
f(t)
t
Page 4
Discrete-time Signals
f*(t)
t
T
2T
3T
4T
'
Otherwise 0
), (
) (
*
nT t t f
t f
Page 5
Transformation
Convert a continuous-time transfer function
to a discrete-time transfer function
H(s) H(z)
Page 6
Methods of Transformation
Backward difference
Forward difference
Bilinear transformation
z-transform
Page 7
Theoretical Background
a s
b
s R
s Y
s H
+
) (
) (
) (
) ( ) ( ) ( t br t ay t y +
!
) ( ) ( ) (
1
t br t ay t y +
dt t y t y t y
t
t
+
2
1
) ( ) ( ) (
1 1 2
Let
T k t ) 1 (
1
kT t
2
Page 8
Theoretical Background
[ ] ) 1 ( ) (
2
) 1 ( ) (
1 1
+ + k y k y
T
k y k y
y
1
(t)
t
t
1
=(k1)T t
2
=kT
Page 9
Theoretical Background
[ ] ) 1 ( ) (
2
) 1 ( )
2
1 ( ) ( )
2
1 ( + + k r k r
bT
k y
aT
k y
aT
[ ]
1 1
) ( ) (
2
) ( )
2
1 ( ) ( )
2
1 (
+ + z z R z R
bT
z z Y
aT
z Y
aT
[ ] ) 1 ( ) (
2
) 1 ( ) (
1 1
+ + k y k y
T
k y k y
Page 10
Theoretical Background
a
z
z
T
b
aT
z
z
bT
aT
z
z z
bT
z
z aT
bT
z z
aT aT
z
bT
z
aT aT
z
bT
z R
z Y
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ + +
+
+
+
) 1 (
1 2
2 ) 1 (
1
2
2 ) 1 (
2 1
2
) 1 (
2
)
2
1 (
2
2 )
2
1 ( )
2
1 (
) 1 (
2
)
2
1 ( )
2
1 (
) 1 (
2
) (
) (
1
1
1
1
1
1 1
1
1
1 1
1
1
1
Page 11
Theoretical Background
a
z
z
T
b
z R
z Y
z H
+
+
) 1 (
1 2 ) (
) (
) (
1
1
a s
b
s R
s Y
s H
+
) (
) (
) (
1
1 2
+
z
z
T
s
Compare
Page 12
Example 1
Find a digital replacement of the following
continuous-time plant by bilinear
transformation with sampling period of
T = 0.1s.
100 10
100 2 . 0
) (
2
2
1
+ +
+ +
s s
s s
s H
Page 13
Answer
1
1
20
1
1 2
+
z
z
z
z
T
s
4286 . 0 8571 . 0
7086 . 0 8571 . 0 7200 . 0
300 600 700
496 600 504
) (
2
2
2
2
1
+
+
+
+
z z
z z
z z
z z
z H
Page 14
Frequency (rad/sec)
P
h
a
s
e
(
d
e
g
)
;
M
a
g
n
i
t
u
d
e
(
d
B
)
Bode Diagrams
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
From: U(1)
10
-1
10
0
10
1
10
2
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
T
o
:
Y
(
1
)
Frequency Warping
10
5
) (
2
+
s
s H
9048 . 0
) 1 ( 0238 . 0
) (
2
z
z
z H
Page 15
Frequency Warping
Approximation has been taken place
use a trapezoidal to approximate the area under
a curve
Frequency response of H(s) deviates from
that of H(z)
Significant if it lies in critical frequency
e.g. 3dB cut-off frequency
Page 16
Analytical Derivation
1
1 2
+
z
z
T
s
T j
A
D
e z j s
and Substitue
T
T j
T
e e
e e
T
e
e
T
j
D
D
T j T j
T j T j
T j
T j
A
D D
D D
D
D
2
1
cos
2
1
sin
2
2
1
1 2
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
into
Page 17
Analytical Derivation
T
T
D A
2
1
tan
2
D A
D D
D
T T
2
1
2
1
tan
small, is If
Page 18
Frequency Pre-warping
Modify H(s) before applying transform
Cancel out the warping effect exactly at a
frequency
Same frequency response of H(s) and H(z)
at
Page 19
Step 1
Calculate the pre-warped frequency
T
T
P
2
1
tan
2
Page 20
Step 2
Replace by
P
p
p
p
p
s
s
s
s
Page 21
Step 3
Applying bilinear transformation
1
1 2
+
z
z
T
s
P
Page 22
Example 2
Apply bilinear transformation with
frequency pre-warping at = 10 rad s
1
to
the following continuous-time plant with
sampling period of T = 0.1s. Calculate the
magnitude and phase angle at for both
continuous-time and discrete-time plant.
100 10
100 2 . 0
) (
2
2
3
+ +
+ +
s s
s s
s H
Page 23
Answer
Step 1
Step 2
926 . 10
1 . 0 10
2
1
tan
1 . 0
2
P
p
s
s
s 915 . 0
926 . 10
10
100 15 . 9 84 . 0
100 183 . 0 84 . 0
) (
2
2
3
+ +
+ +
P P
P P
P
s s
s s
s H
Page 24
Answer
Step 3
Substitute s= j to H
3
(s) and z= e
jT
to H
3
(z),
Magnitude = 0.02
Phase = 0 rad
4077 . 0 7606 . 0
6979 . 0 7606 . 0 7098 . 0
) (
2
2
3
+
+
z z
z z
z H
Page 25
Question
Can we select two frequencies to pre-warp?
Page 26
w-transform
Transform a z-plane transfer function into a
so-called w-plane transfer function
Inverse process of bilinear transformation
w
w
z
1
1
Page 27
Design on the w-plane
Employ s-plane design
velocity error constant
gain and phase margin
No need to tackle the irrational function
z= e
jT
Page 28
Further Modification
Large frequency distortion in w-transform
Modify the w-transform as follows
2
1
2
1
wT
wT
z
Page 29
Example 3
Transform H
4
(z) into a transfer function
H
4
(w) in w-plane by the given bilinear
transformation. Sketch the bode plot of
H
4
(w).
) 8187 . 0 )( 1 (
9356 . 0
03746 . 0 ) (
4
+
z z
z
z H
w
w
z
1 . 0 1
1 . 0 1
Page 30
Answer
,
_
,
_
,
_
997 . 0
1
300
1
10
1 2
) (
4
w
w
w w
w H
Page 31
Conclusion
Bilinear transformation
Frequency pre-warping
w-transform
Page 32
Reference
M. Gopal, Digital Control Engineering.
J ohn Wiley & Sons.
I.J . Nagrath and M. Gopal, Control Systems
Engineering. 2nd edition. J ohn Wiley &
Sons.
You might also like
- The Handbook of Formulas and Tables For Signal ProcessingDocument8 pagesThe Handbook of Formulas and Tables For Signal ProcessingPrakash BachaniNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response AnalysisDocument33 pagesFrequency Response AnalysisShiraz HusainNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response Analysis: Section 6Document45 pagesFrequency Response Analysis: Section 6Ahmed HassanNo ratings yet
- Wavelets (Chapter 7) : CS474/674 - Prof. BebisDocument109 pagesWavelets (Chapter 7) : CS474/674 - Prof. Bebissrc0108No ratings yet
- 110 Semiconductor Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Semiconductor Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Discrete-Time IIR Filter Design From Continuous-Time FiltersDocument16 pagesDiscrete-Time IIR Filter Design From Continuous-Time FiltersstudentNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Mapping Between Z Plane and S PlaneDocument15 pagesMapping Between Z Plane and S Planeamanpanghal67% (3)
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Equation Form RomerDocument23 pagesEquation Form Romerfarsad1383No ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Introduction To Discrete Time Systems and The Z TransformDocument93 pagesIntroduction To Discrete Time Systems and The Z TransformRaufzha AnandaNo ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Frequency ResponseDocument30 pagesFrequency ResponseGovind KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Retiming: 1 ECE734 VLSI Arrays For Digital Signal ProcessingDocument24 pagesChapter 4 Retiming: 1 ECE734 VLSI Arrays For Digital Signal ProcessingaravinthcpNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - 2Document68 pagesModule 2 - 2abcdNo ratings yet
- ECEN5807Document32 pagesECEN5807Mike WongNo ratings yet
- Lecture7 Ee689 Eq Intro TxeqDocument27 pagesLecture7 Ee689 Eq Intro TxeqdogudoguNo ratings yet
- 446-05 Laplace II (N) - HandoutDocument8 pages446-05 Laplace II (N) - HandoutIrfan MahyunisNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Formula SheetDocument12 pagesControl Systems Formula SheetliamhrNo ratings yet
- Interpolation & Decimation: - Sampling Period at The OutputDocument32 pagesInterpolation & Decimation: - Sampling Period at The OutputAnand Krishna GhattyNo ratings yet
- 14 Interpolation DecimationDocument32 pages14 Interpolation DecimationSanjay BalwaniNo ratings yet
- Wavelet TransformDocument27 pagesWavelet TransformMuhammad Salman100% (1)
- ControlSystem2 PDFDocument40 pagesControlSystem2 PDFBùi MTriếtNo ratings yet
- RetimingDocument24 pagesRetiminggalaxystarNo ratings yet
- Course 18.327 and 1.130 Wavelets and Filter BanksDocument12 pagesCourse 18.327 and 1.130 Wavelets and Filter Banksdjoseph_1No ratings yet
- Stata Lab4 2023Document36 pagesStata Lab4 2023Aadhav JayarajNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Modeling: Finite Element MethodDocument32 pagesGroundwater Modeling: Finite Element Methodmaribo2005No ratings yet
- COMM 602: Digital Signal ProcessingDocument32 pagesCOMM 602: Digital Signal ProcessingMohamed YaseenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Equalization: Guy Wolf Roy Ron Guy ShwartzDocument50 pagesIntroduction To Equalization: Guy Wolf Roy Ron Guy ShwartzShilpi RaiNo ratings yet
- Modern Control Sys-Lecture Vi PDFDocument46 pagesModern Control Sys-Lecture Vi PDFMtanzania MtanzaniaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Discrete Wavelet TransformsDocument36 pagesAn Introduction To Discrete Wavelet TransformsAtacan ÖzkanNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 4: Communication SystemsDocument17 pagesLecture # 4: Communication SystemsKhalid MajeedNo ratings yet
- DigitalControlSystems Lecture 1 PDFDocument50 pagesDigitalControlSystems Lecture 1 PDFShafayet UddinNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Systems and Their Representations Unit-1: Ms. P. Geethanjali Asst. Professor (SR) SelectDocument72 pagesControl Systems Systems and Their Representations Unit-1: Ms. P. Geethanjali Asst. Professor (SR) SelectVijay IndukuriNo ratings yet
- ELEC4410 Control System Design Revision NotesDocument10 pagesELEC4410 Control System Design Revision Notescjman404No ratings yet
- Chapter 2.2 Response Ist Order SystemsDocument30 pagesChapter 2.2 Response Ist Order SystemsSyed AliNo ratings yet
- EPM 4056 Feedback Control Analysis and Design: Trim. 48-Trimester 2 2011/2012 Ching Seong Tan Multimedia UniversityDocument58 pagesEPM 4056 Feedback Control Analysis and Design: Trim. 48-Trimester 2 2011/2012 Ching Seong Tan Multimedia UniversityTan Yong LiangNo ratings yet
- FIR and IIR Filter AsdsaDocument55 pagesFIR and IIR Filter AsdsaShanmuka ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8: From Analog To Digital Controllers, PID Control Design ApproachesDocument10 pagesLecture 8: From Analog To Digital Controllers, PID Control Design ApproachesarafatasgharNo ratings yet
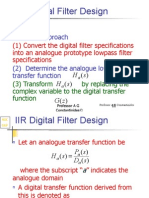
- IIR Digital Filter Design: Standard ApproachDocument27 pagesIIR Digital Filter Design: Standard ApproachAshok GadhwalNo ratings yet
- I. Concepts and Tools: Mathematics For Dynamic SystemsDocument48 pagesI. Concepts and Tools: Mathematics For Dynamic SystemsRaveendhra IitrNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics and Control SolutionsDocument22 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control Solutionsciotti620988% (8)
- First Order and Integrator Dynamical System: Laboratory Experiment No.1Document8 pagesFirst Order and Integrator Dynamical System: Laboratory Experiment No.1Rodrigo TavarezNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Response.: S A S XDocument15 pagesSinusoidal Response.: S A S XManidhar ThulaNo ratings yet
- The Ramsey-Cass-Koopmans Model: Romer (2001), Ch. 2, Part ADocument8 pagesThe Ramsey-Cass-Koopmans Model: Romer (2001), Ch. 2, Part ATan AdelineNo ratings yet
- Z Transform 2 of 3Document18 pagesZ Transform 2 of 3Gilbert SigalaNo ratings yet
- 2D and 3D TransformationDocument42 pages2D and 3D Transformationachintya0105No ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document35 pagesLecture 14AhsabNo ratings yet
- 3d TransformationDocument33 pages3d TransformationMd Minhazur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 5-1 Introduction: Chapter 5 The Laplace TransformDocument29 pages5-1 Introduction: Chapter 5 The Laplace TransformRatna Priya SinghNo ratings yet
- SignalsDocument3 pagesSignalsBerentoNo ratings yet
- Notes 03 - Nyquist PlotsDocument3 pagesNotes 03 - Nyquist PlotsJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics and Control, Ch. 8 Solution ManualDocument12 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control, Ch. 8 Solution ManualBen SpearmanNo ratings yet
- The Convolution Integral: D T H X T H T X T yDocument39 pagesThe Convolution Integral: D T H X T H T X T yshahriaraustNo ratings yet
- 12-Bit, 500-/550-MSPS Analog-to-Digital Converters: FeaturesDocument49 pages12-Bit, 500-/550-MSPS Analog-to-Digital Converters: FeaturesJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- 12-Bit, 500-/550-MSPS Analog-to-Digital Converters: FeaturesDocument49 pages12-Bit, 500-/550-MSPS Analog-to-Digital Converters: FeaturesJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Ad8646 8648 PDFDocument18 pagesAd8646 8648 PDFJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Adc14x250 PDFDocument70 pagesAdc14x250 PDFJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- tps768 q1 PDFDocument28 pagestps768 q1 PDFJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Adc12j2700 PDFDocument100 pagesAdc12j2700 PDFJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Isl71026m PDFDocument32 pagesIsl71026m PDFJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Adc14x250 PDFDocument70 pagesAdc14x250 PDFJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Adc12j2700 PDFDocument100 pagesAdc12j2700 PDFJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Ad8646 8648 PDFDocument18 pagesAd8646 8648 PDFJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Design - Consideratons Design Note 9Document4 pagesDesign - Consideratons Design Note 9Juan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- SoC RfPIC12F675 Data SheetDocument136 pagesSoC RfPIC12F675 Data SheetJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Technical Article: How To Connect and Test A Proportional ModelDocument2 pagesTechnical Article: How To Connect and Test A Proportional ModelJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- JWE08 Series XXX Series: 8 WattsDocument3 pagesJWE08 Series XXX Series: 8 WattsJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- 15/20 Watts JCM Series: SpecificationDocument2 pages15/20 Watts JCM Series: SpecificationJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- 5-30 Watts MTC Series: SpecificationDocument5 pages5-30 Watts MTC Series: SpecificationJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- RFSAS20EDRMDocument76 pagesRFSAS20EDRMJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Signal Chain For Noise Figure AnalysisDocument14 pagesSignal Chain For Noise Figure AnalysisJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- IEC 60870-5-104 - The New Solution For Communication in SubstationsDocument5 pagesIEC 60870-5-104 - The New Solution For Communication in SubstationsrmbalcobiaNo ratings yet
- Product Description ED1608 v1.06Document10 pagesProduct Description ED1608 v1.06Juan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Ad8646 8648 PDFDocument18 pagesAd8646 8648 PDFJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- DDS FundamentalsDocument9 pagesDDS Fundamentalsdeval_kumarNo ratings yet
- Signal Chain For Noise Figure AnalysisDocument14 pagesSignal Chain For Noise Figure AnalysisJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- 3HE06623AAAATQZZA01 - V1 - Alcatel-Lucent 7705 SAR Command Line Interface Quick Reference CardDocument2 pages3HE06623AAAATQZZA01 - V1 - Alcatel-Lucent 7705 SAR Command Line Interface Quick Reference CardJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Frequency Allocation ChartDocument1 pageFrequency Allocation Chartravifireblade8402No ratings yet
- 3HE06603AAABTQZZA01 - V1 - Alcatel-Lucent 7705 SAR Release 5.0 Read Me First - Documentation Set OverviewDocument6 pages3HE06603AAABTQZZA01 - V1 - Alcatel-Lucent 7705 SAR Release 5.0 Read Me First - Documentation Set OverviewJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Tms 320 F 28 PLC 83Document132 pagesTms 320 F 28 PLC 83Juan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Smart Grid SolutionsDocument19 pagesSmart Grid SolutionsJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8: FM DemodulatorDocument20 pagesExperiment 8: FM Demodulatorslay17No ratings yet
- DWDMDocument45 pagesDWDMJuan BoggianoNo ratings yet
- Length and Time-NotesDocument6 pagesLength and Time-NotesBalasbramani ThangavelNo ratings yet
- BRAUN A5S0-Manual ENDocument20 pagesBRAUN A5S0-Manual ENSureshNo ratings yet
- JEE Class Companion Physics: Module-2Document167 pagesJEE Class Companion Physics: Module-2The IndianNo ratings yet
- RadioisotopeDocument10 pagesRadioisotopeSuba SriNo ratings yet
- HVAC Handbook HVAC Design Brief (Singapore)Document26 pagesHVAC Handbook HVAC Design Brief (Singapore)Sam Wing Hong50% (2)
- Volcanic Plumes PDFDocument254 pagesVolcanic Plumes PDFmichgeb100% (1)
- AIR BEARINGS - Review and ApplicationsDocument25 pagesAIR BEARINGS - Review and ApplicationsSubhamMohantyNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab - A Velocity Constant TitrationDocument6 pagesChem Lab - A Velocity Constant TitrationMiguel Ackah-Yensu50% (2)
- Eriez Sl08 Lifting Magnets BrochureDocument24 pagesEriez Sl08 Lifting Magnets Brochuredante224No ratings yet
- PowerGen Europe Final PDFDocument24 pagesPowerGen Europe Final PDFAnonymous knICaxNo ratings yet
- L Inverted Siphon 3rd CDocument6 pagesL Inverted Siphon 3rd CPreston VargheseNo ratings yet
- Random Variables and Stochastic Processes - April-2016Document4 pagesRandom Variables and Stochastic Processes - April-2016rajeshkumar_niceNo ratings yet
- Desain Dan Simulasi Elemen Hingga Gantry Crane Kapasitas 9 Ton Menggunakan Autodesk Inventor 2017Document9 pagesDesain Dan Simulasi Elemen Hingga Gantry Crane Kapasitas 9 Ton Menggunakan Autodesk Inventor 2017Samuel Panda PotanNo ratings yet
- Cae Analysis and Structure Optimization Design of Injection Mold For Charge Upper Cover IJERTV8IS110007Document4 pagesCae Analysis and Structure Optimization Design of Injection Mold For Charge Upper Cover IJERTV8IS110007mubarakNo ratings yet
- Mm326 System Dynamics Hw3 SolutionDocument7 pagesMm326 System Dynamics Hw3 SolutionOğulcan AytaçNo ratings yet
- Loading VSP As A SyntheticDocument2 pagesLoading VSP As A SyntheticAlfian AminNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Perlite and RDocument8 pagesMechanical and Thermal Properties of Perlite and RSheilaNo ratings yet
- Venus 001Document21 pagesVenus 001Abinava ChandrikaNo ratings yet
- Adsorption by BhanuDocument20 pagesAdsorption by BhanuHiren vaghaniNo ratings yet
- Directions For Howard Miller Weather Instruments: Barometer ThermometerDocument2 pagesDirections For Howard Miller Weather Instruments: Barometer ThermometerJaime FuentesNo ratings yet
- Addressing Some Issues in Drop Weight Testing - A Material Science ApproachDocument16 pagesAddressing Some Issues in Drop Weight Testing - A Material Science ApproachManish BhadauriaNo ratings yet
- Ef 402 IntroDocument2 pagesEf 402 Introuwang uwangNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Revision (2020) : Prepared by T. PondoDocument7 pagesDifferentiation Revision (2020) : Prepared by T. PondoCourteney LungileNo ratings yet
- Turning On A PivotDocument12 pagesTurning On A PivotMinahil WaqarNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 3-HIDROGRAFIDocument16 pagesKuliah 3-HIDROGRAFIaizatNo ratings yet
- Questions and Speculation On Learning and Cohomology, Version 3Document136 pagesQuestions and Speculation On Learning and Cohomology, Version 3Hrittik RoyNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of High Pressure Door With Stiffened PlateDocument12 pagesDesign and Analysis of High Pressure Door With Stiffened PlateSyed Faiz Quadri100% (1)
- Introduction To Atomic and Quantum Physics - Sommerfeld TheoryDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Atomic and Quantum Physics - Sommerfeld TheorySrinivas SaiNo ratings yet
- Corrosion MonitoringDocument8 pagesCorrosion MonitoringEleonoraNo ratings yet
- Stability of Slopes: Dr. Sayed Mohamed ElarabyDocument38 pagesStability of Slopes: Dr. Sayed Mohamed ElarabyTân BùiNo ratings yet