Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson Plan Conditional Probability
Uploaded by
Jonathan RobinsonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Plan Conditional Probability
Uploaded by
Jonathan RobinsonCopyright:
Available Formats
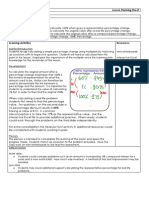
Lesson Planning Sheet Title: Conditional Probability Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson: All students should
be able to draw a tree diagram for conditional events. Most students should be able to calculate the probability for two conditional events using a tree diagram. Some students should be able to calculate the probability for two or more conditional events using a tree diagram. Key words: Conditional Events, Tree Diagram, Branch Learning Activities Starter/Introduction Students recap drawing tree diagrams for independent events. Encourage the class to consider the total of each branch as this is prerequisite knowledge for the main learning objective. Using mini-whiteboards would ensure the teacher is able to assess each students prior understanding of using tree diagrams. Development For the first question on the second slide, encourage the class to consider how this question is different to the one they experienced at the start. The ideal response would be to indicate that the second event is dependent on the first event. This makes the two conditional. Carefully work through the labelling of the tree diagram since once this is understood the calculations arising from it should be fairly simple. The third slide is an opportunity for students to practise for themselves. Plenary The plenary provides an opportunity for students create their own probability tree with the correct labelling. Students may need to work in pairs to ensure they fully understand the problem and how to translate that understanding to the creation of the tree diagram. Differentiation More able: Students could work with three or more conditional events. Probabilities could be given as algebraic expressions so that quadratics arise. Less Able Students may need to have the tree diagram labelled for them so they only focus on the probabilities of each event. Resources: Mini-whiteboards Calculators maybe of benefit for some calculations
You might also like
- Sat Lesson Plan BiconditionalDocument6 pagesSat Lesson Plan Biconditionalapi-526889056No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics For Grade 10Document21 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics For Grade 10Cathline AustriaNo ratings yet
- Unit Circle Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesUnit Circle Lesson Plankcarr13100% (1)
- Math 10 Sample Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesMath 10 Sample Lesson PlanAce SundiamNo ratings yet
- PNHS LP 2ndDEMODocument7 pagesPNHS LP 2ndDEMOBen Joseph Capistrano100% (1)
- DAILY LESSON LOG OF M11GM-Ih-i-1 (Week Nine - Day One)Document2 pagesDAILY LESSON LOG OF M11GM-Ih-i-1 (Week Nine - Day One)Nelson MaraguinotNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesSample Lesson PlanMenchie AnieteNo ratings yet
- Counting The Number of Occurences of An Outcome in An ExperimentDocument5 pagesCounting The Number of Occurences of An Outcome in An ExperimentNiña Romina G. NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesGrade 7 Lesson PlanShara Mae PicardalNo ratings yet
- Statistics WEEK 7Document18 pagesStatistics WEEK 7Elvin PretencioNo ratings yet
- PDF A Detailed Lesson Plan in General Mathematics - CompressDocument4 pagesPDF A Detailed Lesson Plan in General Mathematics - CompressMary bethany ocampoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Final DemoDocument10 pagesLesson Plan For Final DemoJinky CanitanNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics Grade 7 (Algebra) : I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics Grade 7 (Algebra) : I. ObjectivesNick GuevarraNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 8Document6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 8Roldan CaroNo ratings yet
- Mastery Test in Mathematics 10 Quarter 3 Weeks 1 & 2: San Guillermo National High SchoolDocument9 pagesMastery Test in Mathematics 10 Quarter 3 Weeks 1 & 2: San Guillermo National High SchoolSheila Mauricio GarciaNo ratings yet
- Learning Competencies Lesson No. 1: Quadratic Equations: What You'll LearnDocument2 pagesLearning Competencies Lesson No. 1: Quadratic Equations: What You'll LearnRonald AlmagroNo ratings yet
- Week 3-Day2 DLP (Asuncion, Alwin C.)Document12 pagesWeek 3-Day2 DLP (Asuncion, Alwin C.)Chello Ann Pelaez AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Rational Equations LemonsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Rational Equations LemonsJam Marie Antolin100% (1)
- LP PermutationDocument7 pagesLP PermutationAlexis Jon Manligro NaingueNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 8Document3 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics 8Kristhel Pecolados Rombaoa100% (1)
- Mathematics 9 - Week 5 Q4Document2 pagesMathematics 9 - Week 5 Q4Angel EjeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Final DemoDocument10 pagesLesson Plan For Final DemoMichelle Felipe NavarroNo ratings yet
- Range and Standard Deviation Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesRange and Standard Deviation Lesson Planapi-266325800No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 4Document20 pagesMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 4Cillian ReevesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ProbabilityDocument11 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in ProbabilityChristine Grace IlanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (Domain and Range)Document8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (Domain and Range)Jeanelyn SegotierNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - PROBABILITY OF UNION OF TWO EVENTS-Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesWeek 7 - PROBABILITY OF UNION OF TWO EVENTS-Lesson PlanAubrey Elaine MagpusaoNo ratings yet
- 13 DLP Fundamental Counting PrincipleDocument4 pages13 DLP Fundamental Counting PrincipleWilson MoralesNo ratings yet
- Math 10 - DLL - March 20 March 24 2023Document9 pagesMath 10 - DLL - March 20 March 24 2023Ian Paul CauguiranNo ratings yet
- K To 12 Curriculum Guide: MathematicsDocument18 pagesK To 12 Curriculum Guide: Mathematicseiz catNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN IN Probability of Simple Events: March 2019Document9 pagesLESSON PLAN IN Probability of Simple Events: March 2019Tintin SaintsNo ratings yet
- Permutation CombinationDocument2 pagesPermutation CombinationSabariah OsmanNo ratings yet
- Probability of A Simple EventDocument5 pagesProbability of A Simple EventKaye Celino100% (1)
- Special AnglesDocument38 pagesSpecial AnglesPrincess Clarina Catina JavierNo ratings yet
- PermutationsDocument15 pagesPermutationsironickNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsHazel Recites Bernaldez100% (1)
- Qdoc - Tips Dlp-PermutationsDocument8 pagesQdoc - Tips Dlp-PermutationsMargelene Mejido MaritoNo ratings yet
- SSS Congruence PostulateDocument6 pagesSSS Congruence Postulaterowel saloriaNo ratings yet
- Lessom Plan in RadicalsDocument4 pagesLessom Plan in RadicalsJay Andalicio Delideli100% (1)
- IV-Day 39Document4 pagesIV-Day 39Florita LagramaNo ratings yet
- Basic Triangle Congruence Lesson PlanDocument1 pageBasic Triangle Congruence Lesson Planapi-219434647No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics For DemoDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics For DemoLA Lloyd Arvin MontesNo ratings yet
- Khai Lesson Plan 2Document10 pagesKhai Lesson Plan 2api-299009301100% (1)
- Lessonplaninmathematics10permutations 1Document2 pagesLessonplaninmathematics10permutations 1Edwin SartinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Probability BingoDocument4 pagesLesson 1 Probability Bingoapi-253261408No ratings yet
- DAILY LESSON LOG OF M8AL-Ig-1 (Week Seven-Day One) : Possible ResponsesDocument3 pagesDAILY LESSON LOG OF M8AL-Ig-1 (Week Seven-Day One) : Possible ResponsesFlorita Lagrama100% (1)
- PROBABILITYDocument9 pagesPROBABILITYMarjorie MalvedaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument7 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityJay ReyesNo ratings yet
- Final DLP Gr. 10 Faftors PolynomialDocument4 pagesFinal DLP Gr. 10 Faftors PolynomialAljohaila GulamNo ratings yet
- DLP - Measure of Position QuartileDocument11 pagesDLP - Measure of Position QuartileJohn Michael TismoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning Sheet BisectorsDocument1 pageLesson Planning Sheet BisectorsJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Scatter GraphsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Scatter GraphsJonathan Robinson100% (2)
- BC Iii-3Document4 pagesBC Iii-3Erick EstiraNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math - FactoringDocument4 pagesGrade 9 Math - FactoringJerson Yhuwel100% (1)
- DLP Math 8.3Document8 pagesDLP Math 8.3Val Daryl AnhaoNo ratings yet
- DLP CombinationDocument10 pagesDLP CombinationAlexis Magana100% (1)
- Polynomials FunctionsDocument6 pagesPolynomials FunctionsJerson Yhuwel100% (2)
- Department of Education: A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Statistics and ProbabilityDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Statistics and ProbabilityJoanMurilloSimanganNo ratings yet
- I-Day 34Document11 pagesI-Day 34Rainman InsanityNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plann Mutually ExcDocument1 pageLesson Plann Mutually ExcJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Reverse PercentagesDocument1 pageLesson Plan Reverse PercentagesJonathan Robinson100% (1)
- Time Lesson PlanDocument1 pageTime Lesson PlanJonathan Robinson100% (4)
- Tables of Functions Lesson PlanDocument1 pageTables of Functions Lesson PlanJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Ordering NegativesDocument1 pageLesson Plan Ordering NegativesJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Venn Diagrams StarterDocument1 pageVenn Diagrams StarterJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan MetricDocument1 pageLesson Plan MetricJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan SpeedDocument2 pagesLesson Plan SpeedJonathan Robinson100% (8)
- Lesson Plan Similar AreasDocument1 pageLesson Plan Similar AreasJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Travel GraphsDocument1 pageLesson Plan Travel GraphsJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Conversion GraphsDocument1 pageLesson Plan Conversion GraphsJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Similar VolumesDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Similar VolumesJonathan Robinson100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Simlar LengthsDocument1 pageLesson Plan Simlar LengthsJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Imperial Lesson PlanDocument1 pageImperial Lesson PlanJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Similar CalculationsDocument1 pageLesson Plan Similar CalculationsJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Excel TrigDocument3 pagesExcel TrigJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Trig IntroDocument1 pageLesson Plan Trig IntroJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Trig LengthsDocument1 pageLesson Plan Trig LengthsJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan HypotenuseDocument1 pageLesson Plan HypotenuseJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- 3D Trig WorksheetDocument4 pages3D Trig WorksheetJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Trig AnglesDocument1 pageLesson Plan Trig AnglesJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3D TrigDocument1 pageLesson Plan 3D TrigJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Proof of Pythagoras' TheoremDocument1 pageProof of Pythagoras' TheoremJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Basic Rotation WorksheetDocument4 pagesBasic Rotation WorksheetJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Pythagoras 3Document1 pageLesson Plan Pythagoras 3Jonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Pythag IntroDocument1 pageLesson Plan Pythag IntroJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet For Basic EnlargementDocument3 pagesWorksheet For Basic EnlargementJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Basic EnlargementsDocument1 pageLesson Plan Basic EnlargementsJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Rotation WorksheetDocument3 pagesRotation WorksheetJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Rotational Symmetry WorksheetDocument4 pagesRotational Symmetry WorksheetJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Reflection Grid WorksheetDocument4 pagesReflection Grid WorksheetJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet