100% found this document useful (2 votes)
5K views3 pagesPlug Flow Reactor Design
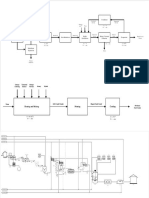
This document discusses the design of a plug flow reactor for a transalkylation reaction. It provides equations to calculate the volume of reactor required based on the initial reactant concentration, flow rate, specified conversion, catalyst voidage fraction, and catalyst density. The steps involve:
1) Calculating the weight of catalyst needed
2) Determining the volume of catalyst
3) Calculating the volume of reactor required using the specified conversion
4) Adding a 10% allowance to the volume for reactor heads
5) Determining reactor diameter and length based on a diameter to length ratio of 5.
Uploaded by
Passmore DubeCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
5K views3 pagesPlug Flow Reactor Design
This document discusses the design of a plug flow reactor for a transalkylation reaction. It provides equations to calculate the volume of reactor required based on the initial reactant concentration, flow rate, specified conversion, catalyst voidage fraction, and catalyst density. The steps involve:
1) Calculating the weight of catalyst needed
2) Determining the volume of catalyst
3) Calculating the volume of reactor required using the specified conversion
4) Adding a 10% allowance to the volume for reactor heads
5) Determining reactor diameter and length based on a diameter to length ratio of 5.
Uploaded by
Passmore DubeCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd