Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Degree of Protec
Uploaded by
Hari Krishna.M0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views11 pagesperot
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentperot
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views11 pagesDegree of Protec
Uploaded by
Hari Krishna.Mperot
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
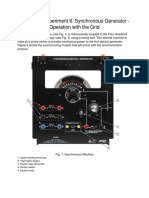
Alternator (Generator) is a rotating
machine, which converts available mechanical
energy into electrical energy as per Faradays
laws of electro magnetic induction.
We have installed a 30MW, 4-pole,
rotating magnetic field 3-phase synchronous
turbo generator with brush less excitation
system supplied by M/s TD power System for
our captive requirement
I. Specification of the Generator:
Type
: TC210
Out put KVA
: 37500
Power Factor
: 0.8 lag
Voltage
: 11KV
Armature current
: 1968.3A
Frequency
: 50Hz.
Speed
: 1500rpm
Number of poles
: 4
Number of phases
: 3
Insulation Class
: F
Temperature rise
: class B limits
Rating
: Continuous
Degree of protection
: IP54
Over Speed
: 20% for 2 minutes.
Excitation method
: Brush less excitation with AVR control.
II. OFF LOAD SYNCHRONISATION:
A. Check list:
1. Ensure that space heaters are in off
position.
2. Ensure that Generator master trip relays
86GHA & 86GHB are in reset position
and except turbine trip & AVR trip all
other protections are in reset position.
3. Ensure that no line clearance on
generator breaker and it is in service /
remote.
4. Ensure that Generator coolers inlet and
out let valves are in open position.
B. Procedure:
1. Off load synchronization means
synchronization of the generator with
grid when it is at no load (Here
synchronization of the Generator
breaker).
2. After starting the turbine, clear the
turbine trip alarm in REM relays and
reset the master trip relays (86 M1A &
86 M1B).
3. After attaining 1500-rpm speed of the
generator, select the excitation in Auto
and Switch on the excitation from AVR
panel. Observe the generator voltage
raise it gradually rises upto 95% of the
rated voltage (10450V).
4. Reset the AVR trip alarm in REM relays
and reset the master trip relays (86 M2A
& 86 M2B).
5. Select the synchronization breaker (CB
1) and observe the remote and open
feedback.
6. Select the mode of synchronization
(Dead bus / Live bus). For off load
synchronization of generator breaker
we have to select only live bus. Live
bus means supply is available for both
sides of the CB and Dead bus means
supply is available for only one side of
the CB. Ensure the available feedback
indication.
7. Select the synchronization mode
(Manual or Auto).
8. Press start command.
9. Manual mode: Adjust the generator
voltage and frequency equal to the grid
parameters.
10. Switch on the synchro scope
11. Close CB at 12O clock position (SKE
relay also should act at the same time).
12. Auto mode: Generator voltage and
frequency will be made equal to the grid
parameters by Wood ward auto
synchronizer and CB also closes in auto
at 12Oclock position of the synchro
scope also with SKE permission.
13. After the synchronization immediately
observe the power factor, if it is tending
to leading side increase the MVAR by
increasing the Generator voltage to
maintain the power factor in lagging
side in between 0.85 to 0.95.
14. After synchronization, maintain the
generation at least more than 4 MW.
There is low forward power protection
at 2.5% of the rated load.
III. ON LOAD SYNCHRONIZATION:
1. On load synchronization means
synchronization of the generator with
grid at load or in Island mode. (Here
synchronization of the PP tie feeder, S/S
tie feeder and grid breaker).
2. Select the CB to be synchronized and
observe the Remote / open status of the
selected C.B. (C.B 2 : Grid breaker,
C.B 3 : Power Plant Tie feeder, C.B
4: Spare & C.B 5: Substation tie
feeder).
3. Select the Live bus.
4. Select the synchronous mode (Auto or
manual).
5. Press synchro start
6. Adjust the voltage and frequency of the
generator to match the grid parameters
if it is manual selection. If it is auto
selection, auto synchronizer it self
adjusts these parameters.
7. Switch on the synchro scope
8. Close CB at 12O clock position (SKE
relay also should act at the same time)
in manual mode. In Auto mode breaker
will be closed it self thru auto
synchronizer.
Note:
1. In dead bus selection there is no
need of synchro scope, we can select
the breaker to be closed in dead bus
selection and switch on it directly as
there is no voltage at second end.
2. We cannot synchronize the generator
by closing the grid breaker in dead bus
selection (in island mode) as it is not
suggestible, to feed power to 132KV
side (grid) when there is no supply
available at 132KV side from grid.
IV. Controls
Salient Features in Generator Control
panel:
1. Auto / manual synchronization of grid
breaker, generator breaker, power plant
tie feeder and substation tie feeder
breaker with check synchronization relay
and synchro scope.
2. Micro scan: Temperature monitoring for
Generator R-ph, Y-ph & B-ph windings,
Generator front bearing & rear bearing
temperatures, generator coolers hot air
& cold air temperatures and tripping of
the generator on these parameters high
level.
3. Programmable Display Unit (MMI): For
annunciation of the light faults (alarms)
& heavy faults (trips) and monitoring of
the active power, reactive power,
apparent power, generator voltage in
three lines, current in three phases,
power factor and frequency.
4. Power quality meter: For monitoring the
line voltages, phase voltages, line
currents, power factor, harmonic
component and energy.
5. Frequency control of the generator if it
is in island mode.
6. Load control of the generator if it is
synchronized with grid
7. Voltage / power factor control of the
Generator.
Automatic Power control (APC):
We have APC provision between 6MW &
30MW of the generation. In APC mode, we can
vary the set point with 0.1 to 1MW variation
from Generator Control panel as per the boiler
steam availability and load requirement. APC
tries to maintain the power out put of the
generator nearly the set point.
APC / APFC enable limit
: 6000KW
Dead band
: 200KW
KW increase/ decrease
: 100KW
On pulse duration (1/10
th
sec)
: 2 sec
Off Pulse duration (1/10
th
sec)
: 20 sec
Automatic Power factor Control (APFC):
We have APFC provision between 6MW & 30MW
of the generation. In APFC mode, we can vary
with set point from Generator Control panel or
from excitation panel as per the reactive power
requirement. APFC tries to maintain the power
factor of the generator nearly the set point by
altering the generator voltage with in the range.
APFC set point will be displayed in the excitation
system front panel screen.
Power factor to be maintained in Auto = (100
% set point)/100
The same APFC increase / decrease push
buttons can be used for the generator voltage
increase / decrease.
Note:
1. Both APC & APFC will be disabled by
themselves when unit turned into island
mode or generation decreased to below
6MW.
2. APFC will be disabled itself if excitation
turned into manual from auto.
Manual control of power factor
In manual control of power factor, to reduce the
power factor increase the reactive power by
increasing the generating voltage (By increasing
the Excitation) or reduce the power transformer
tap position at substation.
To increase the power factor decrease the
reactive power by decreasing the generating
voltage (by reducing the excitation) or increase
the power transformer tap position.
Note: Dont allow running the generator in
leading power factor.
V. Inter locks:
1. To switch on excitation, generator rpm
should be above 95% of the rated.
2. Excitation could not be switched off
when generator breaker is in closed
position.
3. APC & APFC should be active at more
than 6MW of the generator output.
4. APC & APFC should be inactive when
unit is in island mode.
5. No dead bus selection for the grid
breaker.
6. Dead bus selection for the generator
breaker is only with generator supply is
available and idle 11KV bus.
7. Selected furnace will trip it self if unit
turns into island mode (This interlock
will be useful if unit is running at low
load or with single boiler) such that to
avoid sudden increase of the load on
generator and tripping of generator on
under frequency or under voltage.
Furnace trip selector switch:
Position 1 : First furnace will trip in Island mode.
Position 2 : Second furnace will trip in Island
mode.
Position 0 : No furnace will trip.
VI. Generator protections:
Protection & codes in REM relays:
The following are the protections covered in the
Generator protection relay (REM 543)
Code
Protection
1. DIFF 6G
Generator Differential
2. DEF
Sensitive Directional Earth fault
3. VOC6 low
Voltage restrained over current
4. FREQ1 ST_1 Under
frequency tripping of the Gen
5. FREQ1 ST_2 Over frequency
tripping of the Gen
6. UV3 low Under
Voltage
7. OV3 low
Over Voltage
8. NOC3 low
IDMT Over current
9.
NOC3 inst Inst over current
10.UE6 low Loss of
excitation
11. UPOW6ST_1 Low
forward power
12.OPOW6ST_2 Reverse active
power
13.NPS3low
Negative phase sequence current
14.FREQ1 ST_3 Under
frequency tripping of the Grid
(REM 1)
15.FREQ1 ST_3 Over frequency
tripping of the Grid
(REM 2)
16.FREQ1 ST_4 df/dt grid
breaker trip
17. Fuse fail protection
Protections covered other than the REM
relays are
18. Rotor earth fault relay
19. Stator earth fault relay.
20. Generator winding
temperature high
21. Generator bearing
vibrations high
22. Back up earth fault
relay
VII. INSTRUCTIONS
1) When the following protections are
operated, the Generator should not be
excited until the fault is cleared.
a. Generator differential
protection.
b. Stator Earth fault
protection (100 % &
95%).
c. Voltage restraint over
current protection.
d. Backup impedance
protection
e. Local breaker backup
relay / Circuit breaker
failed to protect
f. AVR trip.
g. Instantaneous over
current.
h. Rotor Earth Fault
2. Analyze the root cause in
coordination with the Electrical
maintenance wing and excite the
Generator after clearing the fault.
For the protection operation on the
generator, the following actions are to be
taken.
1. IDMT Over current.
Operating mode :
Normal inverse
Start current
: 1.0I
n
Time multiplier : 0.1
If this NOC3 low annunciation appears,
reduce the load on the Generator.
The Generator will be tripped as per the
normal inverse characteristics.
2. Under frequency
Voltage limit
: 0.3U
n
Start Frequency :
47.5Hz.
Operating time : 3sec
If unit is running with grid and there is any
frequency drop in grid then our machine
frequency will also drop accordingly. Before
this frequency of generator tripping, at
48Hz unit will come to island mode on
tripping of grid breaker on under frequency
tripping then control room engineers should
control the generator load according to
avoid further fall in frequency and tripping
of the generator.
(If load on the generator more than the
steam availability, by coordinating with FAP
control room engineers reduce the load if
still it is not possible to control then trip one
furnace either from PP control room or from
FAP control room)
If already unit is running in Island mode at
rated frequency, then both load on the
generator and steam input to the turbine
should be maintained equal to avoid
variation in turbine speed further generator
frequency.
3. Over frequency
Voltage limit
: 0.3U
n
Start Frequency :
52.5Hz.
Operating time : 5sec
If unit is running with grid if there is any
frequency rise in grid then our machine
frequency also rise accordingly. At 51.5Hz
unit will come to island mode on tripping of
grid breaker on over frequency tripping then
control room engineers should control the
generator load according to the steam
availability to avoid further rise in frequency
and tripping of the generator.
(If steam generation is more than the load
on the generator then vent out the steam)
4. Field Failure / Loss of Excitation.
Circle off set
: 0.19 PU
Circle diameter 2.88
PU
Circle displacement
: 0 PU
Operating time : 2sec
In absence of excitation generator will
run in asynchronous mode as a
induction generator by drawing reactive
power from system instead of feeding
the reactive power into system.
Operation in asynchronous mode is
harm full for the generator
When this protection operates, check up
the excitation circuits of the generator &
rectify the problem then only
synchronize the machine to grid.
5. Negative phase sequence
Operating mode :
Inverse time
Start value
: 0.14I
n
K
: 20
Start delay
: 2 sec
Maximum time : 500
sec
Cooling time
: 60 sec
When the generator is connected to a
balanced load, the phase currents are
equal in magnitude and displaced
electrically by 120
0.
The ampere-turns
wave produced by the stator currents
rotates synchronously with the rotor and
no eddy currents are induced in the
rotor.
Unbalanced loading gives rise to a
negative sequence component in the
stator current. The negative sequence
current produces an additional wave
which rotates backward, hence it
rotates twice the synchronous speed
relatively to the rotor. The double
frequency eddy currents induced in the
rotor may cause excessive heating.
Negative Phase Sequence Current high
protection operates when the unbalance
on the Generator currents is more due
to unbalance loading of the furnaces, so
minimize the unbalance in coordination
with the substation and furnace
operators. This relay operates with
inverse characteristics, so with in the
stipulated period respond immediately
and control the unbalance. If at all, it is
not possible to control the unbalance
current switch off the unbalance-loading
furnace with the coordination of furnace
operator.
When this protection operates as per
the inverse characteristics, Generator
will be tripped then wait for the time
equivalent to cooling time constant of
the Generator and reset the relay. Relay
will not be reset unless the cooling time
constant of the generator reached.
6. Local breaker backup protection
(LBB or CBFP)
This protection operates when the
generator breaker fails to open even
after the master trip relays operated.
This is sensed by the LBB protection and
trips the power plant tie feeder in 11KV
switchgear.
After checking the generator breaker
physically and rectify the problem,
synchronize the generator grid.
7. Generator winding temperature
high.
At the winding temperature of 120
o
C
alarm annunciates, immediately reduce
the generator current by decreasing the
reactive power or active power or both.
Mean while cross check with the
remaining temperature tags.
At winding temperature of 135
o
C
generator will trip.
Please note that temperature rise limits
to Class B insulation limits.
We have monitoring of generator
temperatures in generator control panel
Programmable Display Unit & Micro
scan and tripping thru later one.
8. Under voltage & Over Voltage
Under Voltage
Operating mode : Definite time
Start voltage : 0.9U
n
Operating time : 3sec
Over voltage
Operating mode : Definite time
Start voltage : 1.1U
n
Operating time : 3sec
Automatic Voltage regulator controls
generator voltage between 90% & 110% of
the rated voltage to maintain the power
factor.
If there is any short circuit in the load side it
may lead to voltage dip at that time AVR
tries to boost the voltage if the fault
intensity is more than that of AVR response
& capability or faulty system is not isolated
then generator will trip on under voltage
protection.
If there is sudden impact load on the
generator in Island mode it may lead to
both voltage and frequency drop. So, dont
allow sudden impact loading on the
generator in island mode.
If any sudden load thrown off in Island
mode then there are chance to acting of
over voltage protection. Over voltage
protection may also act when generator is
running at very low lagging power factor set
point with high voltage and if there is any
voltage sudden voltage shoot in grid.
9. Low forward power and Reverse
power.
Low forward power:
Power setting :
2.5%S
n
Operation mode : Under
power
Wait time
: 5 sec
Reverse power:
Power setting : 2%S
n
Operation mode : Under
power
Operation time : 3 sec
If turbine inlet steam is not available to generate
the power or turbine stop valves closed / turbine
tripped then low-forward protection operates
and trip the generator.
When there is any reverse power from 11KV bus
to generator then Generator will operate as a
synchronous motor then, reverse power
protection operates and trip the generator to
avoid motoring of the generator.
10. Stator Earth fault protection:
Earth faults normally occur in the armature
slots. They are more likely to happen when
there are voltage surges or sustained over
voltages at the generator terminals
100% stator ground fault relay can be used
in generators that produces third harmonic
at all service conditions. This type of relay
protects the entire stator winding upto the
neutral point. This scheme includes a 95%
stator earth fault unit which covers 95% of
stator winding from 5% of the neutral and a
third harmonic voltage unit which covers 5%
portion from the neutral.
When the generator is in operation and
there is no ground fault near the neutral,
the third harmonic as well as the voltage
check unit pickup and tripping is blocked.
When a ground fault near the neutral
occurs, the third harmonic unit will drop-of
and tripping obtained.
In our system present is kept at minimum
level. In full load of the generator 3
rd
harmonic component is to be measured and
setting will be made according to that level.
11. Generator Differential protection:
Basic Setting : 5%
Starting ratio : 10%I
n
Turn point1 : 0.5I
n
Turn point2 : 1.5I
n
Inst setting : 5.0I
n
The differential protection is that which
responds to the vector difference between two
or more similar electrical quantities. On
Generator, the current transformers are
provided at each end of the generator armature
windings. When there is no fault in the windings
and for through faults, the currents in the CT
secondary are equal. The difference current is
zero. When fault occurs inside the protected
winding, the balance is disturbed and the
differential current flows through the operating
coil of relays causing relay operation. Thereby
generator circuit breaker is tripped.
VIII. Excitation system:
Excitation system regulates the terminal voltage
and the reactive power flow of the alternator by
altering the field current with the aid of
Thyristor converters. We have installed the AVR
cum Excitation panel for our 30MW generator
supplied by M/s TDPS of M/s ABB make Unitrol
F system for rotating rectifier brush less
excitation system. The rotary rectifier rectifies
AC electric source that comes from three-phase
AC exciter to DC. Then that DC electric source
excites the field coil of generator. Therefore, the
generator does not have brush and slip ring.
Exciter rating:
1. Excitation system type
: Brush less
2. Excitation supply
: PMG
3. Excitation field voltage at rated load
:119V DC
4. Excitation field current at rated load
: 25A DC
5. Maximum exciter field current
: 40A DC
6. Minimum exciter field current
: 5A DC
7. Maximum exciter field voltage
: 180V DC
8. Minimum exciter field voltage
: 20V DC
9. Exciter rating
:230KW
10. AVR make
: ABB
11. Exciter output Voltage
: 331V
12. Exciter out put Current
:499A
13. Frequency
:150Hz
14. Revolutions
:1500rpm
15. No. of phases
:3
16. No. poles
:12
17. Power factor
:0.95 lag
18. Insulation class
: F
19. Armature :
Revolving armature type
Pre checks for switching on the excitation:
1. Ensure that space heater is in off
position.
2. No line clearance should be pending.
3. Control supplies are available (230V UPS
& 110V DC).
4. Ensure that excitation system is in
remote mode.
5. No alarm and trip codes are displaying.
6. Generator speed should be at rated.
Start up:
1. After reaching the rated rpm of the
generator and getting clearance for
synchronization, switch on excitation in
Auto mode and observe that voltage
rise. Generator voltage will raise upto
95% of the rated (10450V).
2. Clear the AVR trip alarm in REM relays
and reset the master trip relays 86M2A
& 86M2B.
3. Increase the generator voltage manually
to 11KV.
4. After switching on the synchro scope,
adjust the generator voltage equal to
the grid voltage.
5. After synchronizing adjust the generator
voltage such that to maintain lagging
power factor and to meet the reactive
power requirement.
6. After achieving the 6MW generation
keep the power factor control in Auto.
Interlocks:
1. Excitation will not switch on below 95%
of the rated speed of the generator.
2. Excitation could not be switched off
manually when generator breaker is in
ON position.
3. At fuse fail protection excitation will be
turned into manual mode it self.
4. To keep excitation system in Automatic
Power Factor Control excitation should
be in Auto.
3. Schematic Diagram of Synchronizing
Breakers
Grid PT
Gen Bus PT
Grid
bus PT
Power Plant 11KV Bus
Substation 11KV Bus
CB1
CB 3 CB 5
CB 2
Gen PT
Tie
Breaker PT
11KV Cable
30MW Generator
CB1 : Generator Breaker
CB2 : Grid Breaker
CB3 : Power Plant Tie BreakerCB4 : Spare
CB5 : Substation
~
You might also like
- Specifications of Avr - SMR (Mosfet)Document4 pagesSpecifications of Avr - SMR (Mosfet)Александр ЩеблыкинNo ratings yet
- Generator Protection SchemesDocument7 pagesGenerator Protection Schemesabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Avr 100s IngleseDocument65 pagesAvr 100s IngleseVedran GaćeNo ratings yet
- Ses-12 TDPSDocument31 pagesSes-12 TDPSbaljeetjatNo ratings yet
- Benn Machine Lab ManualDocument14 pagesBenn Machine Lab ManualRahatullah Khan100% (1)
- 660 Generator Protection SchemesDocument9 pages660 Generator Protection SchemesshashankNo ratings yet
- VVF Drive Induction Motor Specs CHD - 02Document10 pagesVVF Drive Induction Motor Specs CHD - 02Sanjeev DhariwalNo ratings yet
- Automatic Voltage Regulator AVR100S Operation, Use and Maintenance InstructionsDocument65 pagesAutomatic Voltage Regulator AVR100S Operation, Use and Maintenance InstructionsYassine.G ChipLabNo ratings yet
- UH60 Electrical SystemDocument12 pagesUH60 Electrical SystemKiriti Satyanarayana100% (2)
- Automatic Voltage RegulatorDocument5 pagesAutomatic Voltage Regulatorvirendkumar50% (2)
- AUTO CONTROLLER FOR PETROL (Revised)Document25 pagesAUTO CONTROLLER FOR PETROL (Revised)Hamed RazaNo ratings yet
- EEE 458 - Power System Protection LaboratoryDocument12 pagesEEE 458 - Power System Protection LaboratoryAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Gen ProtectionDocument33 pagesGen Protectionhafiz_hazreen100% (1)
- A Guide On Load Flow Analysis Using ETAPDocument20 pagesA Guide On Load Flow Analysis Using ETAPMalik EltayiebNo ratings yet
- Excitation System - 11.05.2011Document52 pagesExcitation System - 11.05.2011vijayrajuNo ratings yet
- EE 340L Experiment 6 Synchronous Generator Operation GridDocument6 pagesEE 340L Experiment 6 Synchronous Generator Operation GridMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Motor Control Instruction Manual C880800-00Document12 pagesMotor Control Instruction Manual C880800-00RICHIHOTS2No ratings yet
- Manual OmbiraDocument16 pagesManual Ombirazz2nktNo ratings yet
- Synchronization of MSEB With GeneratorDocument2 pagesSynchronization of MSEB With GeneratorSarah FrazierNo ratings yet
- 220 KV Switchyard ConfigurationDocument7 pages220 KV Switchyard ConfigurationIrfan UllahNo ratings yet
- Mx341 Avr Newage StamfordDocument4 pagesMx341 Avr Newage Stamfordabuzer1981No ratings yet
- Static Excitation SystemDocument36 pagesStatic Excitation Systemlrpatra100% (1)
- Generator TroubleshootingDocument22 pagesGenerator TroubleshootingMichael Cabrera Rabino100% (1)
- Specifications of Avr - Uvr7Document4 pagesSpecifications of Avr - Uvr7Александр ЩеблыкинNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Universal AVR Operation GuideDocument6 pagesHybrid Universal AVR Operation Guideabuzer1981No ratings yet
- The Following Are The Main Protection Schemes Adopted For Our GeneratorDocument8 pagesThe Following Are The Main Protection Schemes Adopted For Our GeneratorBhargav PuraniNo ratings yet
- Excitation System of Generator: Presented By: Niaz Akhtar Gte-ElectDocument40 pagesExcitation System of Generator: Presented By: Niaz Akhtar Gte-Electrk250No ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Uh60 Electrical SystemDocument12 pagesDokumen - Tips Uh60 Electrical SystemJosef SafioniNo ratings yet
- AVC63-7F Voltage Regulator - Instructions - 9302800994-D - March 2012 - BASLER ELECTRIC PDFDocument4 pagesAVC63-7F Voltage Regulator - Instructions - 9302800994-D - March 2012 - BASLER ELECTRIC PDFpevareNo ratings yet
- Static Excitation SystemDocument44 pagesStatic Excitation Systemgigelu79No ratings yet
- SX440 Automatic Voltage Regulator Operation ManualDocument4 pagesSX440 Automatic Voltage Regulator Operation ManualMuhammad Sajjad ShadNo ratings yet
- MX321 ManualDocument4 pagesMX321 ManualFernando MendozaNo ratings yet
- EA15A Generator AVR Manual: Self-Excited 15A Automatic Voltage RegulatorDocument6 pagesEA15A Generator AVR Manual: Self-Excited 15A Automatic Voltage RegulatorVijays HiremathNo ratings yet
- Control 3-Phase AC Drive with DSPDocument5 pagesControl 3-Phase AC Drive with DSPaman srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Generator ProtectionDocument5 pagesGenerator ProtectionThirumalNo ratings yet
- Generator ProtectionDocument10 pagesGenerator ProtectionRam SinghNo ratings yet
- VSOP For Unit Synchronization.Document15 pagesVSOP For Unit Synchronization.pradeep1987coolNo ratings yet
- AVR341 Generator Automatic Voltage Regulator Operation ManualDocument6 pagesAVR341 Generator Automatic Voltage Regulator Operation ManualEmanuel Arguiñarena100% (1)
- Ea341 Manual enDocument6 pagesEa341 Manual enVishnu VardhanNo ratings yet
- Generator Automatic Voltage Regulator Operation ManualDocument6 pagesGenerator Automatic Voltage Regulator Operation ManualSabyasachi KarNo ratings yet
- SS15A3P ManualDocument6 pagesSS15A3P ManualBurce MherjheNo ratings yet
- Handout - ElectricDocument12 pagesHandout - Electric김종환No ratings yet
- Load Characteristics of Separately and Self-Excited Generators LabDocument17 pagesLoad Characteristics of Separately and Self-Excited Generators LabPinky EceNo ratings yet
- Automatic Panel Control GuideDocument5 pagesAutomatic Panel Control GuideНиколай Белый100% (2)
- Ensure generator synchronization in 12 stepsDocument1 pageEnsure generator synchronization in 12 stepsDebabrata TantubaiNo ratings yet
- C C!C C "#C$%&C'%C C (' C +, ( - (,! (./ C: C C C CCDocument12 pagesC C!C C "#C$%&C'%C C (' C +, ( - (,! (./ C: C C C CCMarcos TapiaNo ratings yet
- Submittal - LS Power Chambersburg - G3096 - 5.15.20Document419 pagesSubmittal - LS Power Chambersburg - G3096 - 5.15.20kohatian27796105100% (2)
- Sx440, STAMFORD ManualDocument4 pagesSx440, STAMFORD ManualSarawut PipeNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Transformer Insulating Oil and Types of Transformer OilDocument7 pagesTransformer Insulating Oil and Types of Transformer OilHari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- Transformer Insulating Oil and Types of Transformer OilDocument8 pagesTransformer Insulating Oil and Types of Transformer OilHari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- AmendmentFY2017-18 24.10.17Document2 pagesAmendmentFY2017-18 24.10.17Hari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- Energy Auditors and Maintenance of Their ListDocument8 pagesEnergy Auditors and Maintenance of Their ListINDIRAKALYANINo ratings yet
- Static Excitation Systems Sppa s3000Document2 pagesStatic Excitation Systems Sppa s3000Hari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- CT Failure Diagnostic Paper ITMF 2011 JunaidiDocument6 pagesCT Failure Diagnostic Paper ITMF 2011 JunaidiHari Krishna.M100% (1)
- 261Document11 pages261Solaiappan KtNo ratings yet
- Transformer Insulating Oil and Types of Transformer OilDocument8 pagesTransformer Insulating Oil and Types of Transformer OilHari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- Vesta Partners Benchmarking WorkshopDocument58 pagesVesta Partners Benchmarking WorkshopHari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- Vacon NX Service Manual Appendix FR9Document96 pagesVacon NX Service Manual Appendix FR9Hari Krishna.M100% (1)
- Air Circuit Breakers: CG International DivisionDocument9 pagesAir Circuit Breakers: CG International DivisionHari Krishna.M100% (2)
- AC Drive Motors - Influence of Drive On Acoustical Noise: Technical Guide No. 105Document9 pagesAC Drive Motors - Influence of Drive On Acoustical Noise: Technical Guide No. 105Hari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- MiCOM P122 & P123Document3 pagesMiCOM P122 & P123Hari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- Amiad Self-Cleaning Strainers For Water FiltrationDocument10 pagesAmiad Self-Cleaning Strainers For Water FiltrationHari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- Testing Procedure For Shaft Voltage and Discharges Using A Fluke 190-204 ScopeMeterDocument41 pagesTesting Procedure For Shaft Voltage and Discharges Using A Fluke 190-204 ScopeMeterHari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- IEEMA-Basics of Dual Ratio TransformersDocument3 pagesIEEMA-Basics of Dual Ratio TransformersHari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- CEA Metering RegulationsDocument20 pagesCEA Metering RegulationsRavi GoyalNo ratings yet
- Realistic CT SpecsDocument7 pagesRealistic CT Specskapil100% (6)
- Merne JediniceDocument12 pagesMerne JediniceDarko Vasic Wood ProcessingNo ratings yet
- Enter Values in Boxes for IEC Curve Overcurrent Relay SettingsDocument1 pageEnter Values in Boxes for IEC Curve Overcurrent Relay SettingsHari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- CommissioningDocument65 pagesCommissioningMourad Benderradji100% (1)
- Electrical Plant ChecklistDocument5 pagesElectrical Plant ChecklistAjish Rajan TNo ratings yet
- Awt S 91Document8 pagesAwt S 91Donatas BertasiusNo ratings yet
- Busbar ConfiguarationsDocument41 pagesBusbar ConfiguarationsRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation Act Amendments & RulesDocument150 pagesEnergy Conservation Act Amendments & Rulesranjish_007No ratings yet
- PAT RulesDocument98 pagesPAT RulesHari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- Lossofexcitation 130805045350 Phpapp01Document52 pagesLossofexcitation 130805045350 Phpapp01ahvaz1392bNo ratings yet
- AP 02713001 eDocument12 pagesAP 02713001 eabhijit_wceNo ratings yet
- Bentonite IS.12446.2007Document14 pagesBentonite IS.12446.2007azher03No ratings yet
- PAT Rules Amendmends WS - 0Document18 pagesPAT Rules Amendmends WS - 0Hari Krishna.MNo ratings yet