Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diagram" Add With Power Supply
Uploaded by
Jonathan F. CardinalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diagram" Add With Power Supply
Uploaded by
Jonathan F. CardinalCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Network is the
interconnection of electrical
components
To: analyze, design, and measure.
Quantities number ex. Current
voltage.
EE sub disciplines:
Power
Electromagnetics
Communication / Signal
processing
Digital control
Control
Solid state
AM radio
EE disciplines:
C/SP (frequency domain
analysis)
ElectroMag (antennas,
high frequency circuits)
Power (battery,power
supplies)
SS (minaturation, lowpower electronics)
System: Transmitter, Receiver
Signal is a quantity may vary
with time.
Voltage or current
Sound (pressure wave
travelling through air or
water)
Light/radio waves
(electromagnetic energy
traveling through free
space)
Frequency
analysis and design of
AM radios
- using Fourier analysis (
combinations of
sinusoids( sines and
cosines)
- is the rate which
signal oscillates
Electromagnetic Waves visible
light within 380thz 860thz
Red- 460thz green-570thz blue630thz
AM radio limit: 500khz 1.8mhz
Sound waves pitch of the sound
(frequency) clear whistle(sound)
Static(sound) many frequency
Fourier analysis mathematical
analysis of signals
- weighted sum of sine
and cosine
- ex. Square wave
AM transmitter 10khz (transmit
signal)
Signal broadcast: 605khz 615khz
Transmitter input(signal source) =
audio signal
Ex. Signal source -> modulator ->
power amplifier -> antenna
Modulator convert frequency
into input signal to audio range (05khz)
Power amplifier am station:
50kw(class I or II stations) ,
5KW(class III) , 1kw(class IV)
Antenna Frequency
domain(ouput), converts current
or voltage signal to
electromagnetic signal(radiated
through space)
Am receiver ex. superhetrodyne
receiver (use most modern radio
and t.v)
- desired signal - first
translated into
IF(intermediate
frequency)
o recovered by
demodulator
Receiver block diagram:
Antenna -> RF(amplifier) ->
IF(mixer) -> IF(amplifier) ->
Envelope detector) -> audio
amplifier -> speaker.
RF amplifier: (radio frequency),
amplifies small signals from
antenna
- performs band pass
filter operation
band pass filter
(attenuated)frequency outside the
frequency band.
IF mixer: shift input frequency
domain to carrier frequency to
intermediate frequency (455 kHz)
IF amplifier: bandpass filter the
output of the IF mixer, eliminating
undesired signals.
Envelope Detector: computes the
envelope of its input signal
Audio amplifier: amplifies signal
from ED, provides power to drive
the speaker.
Hierarchal system models:
Modelling at different
levels of abstraction.
Divide and conquer
Higher level model(
describe overall function)
Lower level model
(describe detail necessary
to implement the system)
Systems in EE:
- Electrical or mechanical
device
- Process, mathematical
model relates input to
output
Am receiver:
Antenna (input)
Sound energy (output)
Top level model:
Input signal -> am receiver ->
sound
Second level model:
the same as receiver block
diagram add with power supply
in the middle.
Low level model: ED
Halfwave -> low-pass filter
->
Telephone system:
EE disciplines:
Signal processing
o speech compression
o noise reduction
o A/D and D/A
conversion
Communication and
networking
o Transmission
o Network architectures
o Protocols
Digital and computer
o Configurable switching
hardware
Electromagnetics
o Microwave
transmission(hardwar
e)
Solid state
o Miniaturization
o Integration of complex
system
Power electronics
o Extremely reliable
power supplies
POTS- plain old telephone service
Voice transmission (early
telephone system)
Host of other services (modern
telephone system)
Data transmission and
video transmission
Billing and features
capabilities (call waiting/
call forwarding)
Early telephone system:
Switch board l power supply ->
speakerlmic (3x)
Carbon microphone (major
components)
Speaker (made from
electromagnetic and
paramagnetic)
Twisted pair wires ( connected
through central office)
Early phone circuit:
Telephone
handset(earphonelcarbon
microphone) -> central
office(battery) -> Telephone
handset(earphonelcarbon
microphones)
Phone circuit:
From battery(central
office) through the
components of
2telephones(speaker and
microphone) and back
into the battery
Series connection (phone
circuit)
All current flow in the
battery flows also through
the components in
2telephones.
Microphone:
Compost of carbon
granules in a box with
diaphragm
Converts changes in
pressure to change
resistance
Modeled electrically as a
variable resistor
Speaker:
Made from
electromagnetic and
paramagnetic diaphragm
Convert changes in
current to move a
diaphragm produces
sound energy
As inductor
Central office:
Switch board(connects
2telephones electrically)
Battery(provides power to
create electrical current
loop)
Modern Telephone System:
Ex
- Digital data, video. Signal
transmitted along with speech
- Calls routed
automatically(softwar
e control)
- Transmission is digital
Analog -> pcm encoder <- pcm
decoder -> switching network <pcm decoder -> pcm encoder <analog
Analog continuous-time signal
Digital signal sequence 1s and
0s
Can mix many types of
information
Less expensive
Can be encrypted
PCM pulse Code modulation
PCM encoder: converts analog
signal to digital signal
PCM decoder: converts digital
signal to analog signal
- One form of
quantization
- AD / DA conversion
PCM Encoder- continuous signal is
converted to bit stream
Operation: quantization, encoding
Sampling - value of the signal at
equally spaced points in time
Quantizer quantized to one of a
finite number of values
Encoding pattern of bits
assigned to each level of quantizer
- n bits can represent
2n quantizer output
levels
PCM Decoder digital to analog
(D/A converter)
Telephone network:
Subscriber (house or
business)
Twisted pair wire
connections (common)
Subscribers analog
connected to RT( Regional
Terminal) or Co(Central
Office)
RT/CO signal converted
to digital signal
Network Architecture:
4xSubscriber -> 2xRT -> CO <->Long distance network
You might also like
- Lecture02 Spring04Document56 pagesLecture02 Spring04Jonathan F. CardinalNo ratings yet
- Dictionary For Phone RepairingDocument104 pagesDictionary For Phone RepairingJean Paul Muvara Kabiligi100% (1)
- Comsats Institute of Information Technology: EEE 352 Analog Communication SystemsDocument35 pagesComsats Institute of Information Technology: EEE 352 Analog Communication Systemsali_rehman87No ratings yet
- Comsats Institute of Information Technology: EEE 352 Analog Communication SystemsDocument44 pagesComsats Institute of Information Technology: EEE 352 Analog Communication SystemsUsman Ullah AsifNo ratings yet
- Ec 352 DceDocument88 pagesEc 352 DceTanvi BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Electrical DictionaryDocument91 pagesElectrical DictionaryQudratullah EhsanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To CommDocument32 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To CommhaftamunigusNo ratings yet
- Module 5 NewDocument43 pagesModule 5 NewMythri RangaswamyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication SystemDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Communication SystemJon AbNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Communication Lab Manual PDFDocument41 pagesElectronics and Communication Lab Manual PDFtesterNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication Systems: Lesson-1Document26 pagesIntroduction To Communication Systems: Lesson-1Kennedy MutaiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Digital CommunicationDocument14 pagesUNIT 5 Digital CommunicationSunithaNo ratings yet
- Signal Processing and SensorsDocument51 pagesSignal Processing and SensorsKassimNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication SystemsDocument30 pagesAnalog Communication SystemsNeelamAsifNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital Communication SystemsDocument25 pagesAnalog and Digital Communication SystemsGourav100% (1)
- Channel DistortionDocument3 pagesChannel DistortionBlessonThomasNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Introduction To CommunicationDocument58 pagesCHAPTER 1 Introduction To CommunicationadibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document35 pagesChapter 01Syed Ariful Islam EmonNo ratings yet
- Methods of CommunicationDocument3 pagesMethods of CommunicationCwezy ZhoorNo ratings yet
- Elements of Communication System:: Communication: It Is The Process of Conveying orDocument168 pagesElements of Communication System:: Communication: It Is The Process of Conveying orsakthiNo ratings yet
- Unit I Audio Compression Audio Types: Speech Signals and Music-Quality AudioDocument5 pagesUnit I Audio Compression Audio Types: Speech Signals and Music-Quality AudioVicky HavNo ratings yet
- WTM Microwave DigitalDocument16 pagesWTM Microwave DigitalrrohuuNo ratings yet
- Team Luger: Laser Guided Energy ReceiverDocument34 pagesTeam Luger: Laser Guided Energy ReceivertecnicodeprimeraNo ratings yet
- Electronics ReviewerDocument5 pagesElectronics ReviewerTristeine MorattiNo ratings yet
- PCM (Pulse code modulation) : -Teacher: Masters Nguyễn Thanh Đức -Group memberDocument77 pagesPCM (Pulse code modulation) : -Teacher: Masters Nguyễn Thanh Đức -Group memberTao Thích Màu ĐenNo ratings yet
- Munications Basic PrinciplesDocument10 pagesMunications Basic Principleseslamcowboy3No ratings yet
- Teacher's Introduction: Dr. Salman Abdul GhafoorDocument11 pagesTeacher's Introduction: Dr. Salman Abdul GhafoorMohammad NaumanNo ratings yet
- Thermal EngineeringDocument17 pagesThermal EngineeringJagpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Communication SystemsDocument15 pagesCommunication SystemsMuhammad AdeelNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication SystemsDocument169 pagesAnalog Communication SystemsVenkateswara RajuNo ratings yet
- LAB 1.cDocument13 pagesLAB 1.cMUHAMMAD AMMARNo ratings yet
- Pulse Modulation Consists Essentially of Sampling Analog Information Signals and Then ConvertingDocument40 pagesPulse Modulation Consists Essentially of Sampling Analog Information Signals and Then ConvertingDaniel LoNo ratings yet
- Ece 104 Chapter 1Document31 pagesEce 104 Chapter 1YUUYANo ratings yet
- Ansari VaqarDocument31 pagesAnsari VaqarKate AllenNo ratings yet
- Mixed Signals and SensorsDocument27 pagesMixed Signals and SensorsT ENGANo ratings yet
- 4.5.4 Pulse Code Modulation PDFDocument40 pages4.5.4 Pulse Code Modulation PDFFirdausNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Communication SystemsDocument59 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Communication Systemswleum100% (1)
- ESAT FormulaDocument11 pagesESAT FormulaSKYE LightsNo ratings yet
- DDC ReviewerDocument15 pagesDDC ReviewerKimmy WadeNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response of Switching Power SuppliesDocument2 pagesFrequency Response of Switching Power SuppliesRicardo SouzaNo ratings yet
- Carrier RecoveryDocument4 pagesCarrier RecoveryYsrael M. TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document91 pagesModule 4mahendra naikNo ratings yet
- Telephony Part 3 RevDocument125 pagesTelephony Part 3 RevKairosNo ratings yet
- Dasar - Dasar ElektronikaDocument12 pagesDasar - Dasar ElektronikaMuhammad SyawalNo ratings yet
- RF Oscillator and Its NeeedsDocument4 pagesRF Oscillator and Its NeeedsArnab PalNo ratings yet
- Communication Theory Lecture NotesDocument120 pagesCommunication Theory Lecture NotesAnup KumarNo ratings yet
- Superheterodyne Group: N The ChannelDocument23 pagesSuperheterodyne Group: N The ChannelSunghoonie KangNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1: Superheterodyne GroupDocument12 pagesQuiz 1: Superheterodyne GroupSunghoonie KangNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument2 pagesCommunicationJohn Lester Laurentino RamirezNo ratings yet
- S-72.245 Transmission Methods in Telecommunication Systems (4 CR)Document28 pagesS-72.245 Transmission Methods in Telecommunication Systems (4 CR)Sandra JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication Systems 1: Prof. Dr. Tayfun AkgülDocument46 pagesTelecommunication Systems 1: Prof. Dr. Tayfun Akgülabdullahsaeed47No ratings yet
- Instrumentationamplifier ECGDocument35 pagesInstrumentationamplifier ECGRoiNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code ModulationDocument78 pagesPulse Code ModulationHamid HussainNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Analog CommunicationsDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Analog CommunicationsAnonymous G5D0xzq2No ratings yet
- Intro To Electronic Communication SystemDocument17 pagesIntro To Electronic Communication SystemRyan Anthony AndalNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication Standardization BureauDocument5 pagesTelecommunication Standardization BureauabcedeNo ratings yet
- David FinalDocument46 pagesDavid Finaljoshua olayinkaNo ratings yet
- Hamdard-HIIT Communication SystemDocument13 pagesHamdard-HIIT Communication Systemshakr123No ratings yet
- Intro To DISH Pro TechDocument20 pagesIntro To DISH Pro TechdknightcoNo ratings yet
- AX-70T 130T AnE SpecDocument2 pagesAX-70T 130T AnE SpecrodrigoaranhaNo ratings yet
- Microphone Sans Fil Akg Wms 450 - CutsheetDocument6 pagesMicrophone Sans Fil Akg Wms 450 - Cutsheetbenblidia.zineddine02No ratings yet
- Selection of NDT Techniques For Inspection of Heat Exchanger TubingDocument7 pagesSelection of NDT Techniques For Inspection of Heat Exchanger Tubingநந்த குமார் சம்பத் நாகராஜன்100% (1)
- Department of Electrical and Information Engineering (Eie) : Staff ListDocument32 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Information Engineering (Eie) : Staff ListtemitopefunmiNo ratings yet
- Given: System Gain 105 DB RX Input NF 3.75 DB N - 115 DBW, S/N 50 Db. DetermineDocument8 pagesGiven: System Gain 105 DB RX Input NF 3.75 DB N - 115 DBW, S/N 50 Db. DetermineBrey ZNo ratings yet
- Electronic Warfare: October 2019Document13 pagesElectronic Warfare: October 2019Deepak LohknaNo ratings yet
- Bitx20A Bidirectional SSB Transceiver by Ashhar FarhanDocument9 pagesBitx20A Bidirectional SSB Transceiver by Ashhar FarhanDARU WIRANTONo ratings yet
- Laser Communication SystemDocument4 pagesLaser Communication Systemjose273No ratings yet
- Thomas Barber JR., Phil Carvey, Anantha Chandrakasan: BBN's 141. ForDocument5 pagesThomas Barber JR., Phil Carvey, Anantha Chandrakasan: BBN's 141. FormharitmsNo ratings yet
- Icom IC-M45 Service ManualDocument30 pagesIcom IC-M45 Service ManualGanifianto RasyidNo ratings yet
- ETSI TS 138 215: 5G NR Physical Layer Measurements (3GPP TS 38.215 Version 15.2.0 Release 15)Document18 pagesETSI TS 138 215: 5G NR Physical Layer Measurements (3GPP TS 38.215 Version 15.2.0 Release 15)Chetan BhatNo ratings yet
- Pana Bežični Manujal kx-tcd150FXDocument77 pagesPana Bežični Manujal kx-tcd150FXi4004No ratings yet
- KX1 Data Sheet NP 0706 RevCDocument2 pagesKX1 Data Sheet NP 0706 RevCzascribdotNo ratings yet
- Citylink Manual RevDDocument153 pagesCitylink Manual RevDVassiliy PevnevNo ratings yet
- pulseEKKO PRO Brochure 1Document6 pagespulseEKKO PRO Brochure 1Levent AkcaylarNo ratings yet
- 2 Ericsson Rrus12 b4 2100mhz Tda 2015 TocDocument7 pages2 Ericsson Rrus12 b4 2100mhz Tda 2015 TocOrizaNo ratings yet
- Model RT-U50DSR: Universal Remote ControlDocument8 pagesModel RT-U50DSR: Universal Remote ControlJose Luis Camargo PonceNo ratings yet
- Open ROADM MSA Specification Ver 3 01Document91 pagesOpen ROADM MSA Specification Ver 3 01mcclaink06No ratings yet
- Novel Sat NS2000 Web UGDocument46 pagesNovel Sat NS2000 Web UGTechne PhobosNo ratings yet
- Decibel NotationDocument7 pagesDecibel NotationRyan Anthony AndalNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communications and Networks PDFDocument192 pagesWireless Communications and Networks PDFDilpalNo ratings yet
- 1410 Records - TelecommunicationDocument142 pages1410 Records - TelecommunicationPatentYogiNo ratings yet
- Coverage Analysis of LTE CAT M1 White PaperDocument20 pagesCoverage Analysis of LTE CAT M1 White PaperoskcarrasquiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Objectives:: Ee 171 Lecture Notes Chapter 1: Introduction To Communication Systems (Rev 1) 1.1Document6 pagesChapter Objectives:: Ee 171 Lecture Notes Chapter 1: Introduction To Communication Systems (Rev 1) 1.1Rosendo J. BaronNo ratings yet
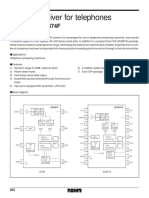
- DTMF Receiver For Telephones: BU8874 / BU8874FDocument10 pagesDTMF Receiver For Telephones: BU8874 / BU8874FYazan HaidarNo ratings yet
- Radio CodesDocument237 pagesRadio CodesMartina Sigmi100% (1)
- BEAM1224 Data SheetDocument2 pagesBEAM1224 Data SheetWilliam DiasNo ratings yet
- AR8000 Operating ManualDocument115 pagesAR8000 Operating Manualaar9smNo ratings yet
- See Through Walls With Wi-FiDocument12 pagesSee Through Walls With Wi-Fislysoft.20009951No ratings yet
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonFrom EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceFrom EverandThe Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tFrom EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- Retro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsFrom EverandRetro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsNo ratings yet
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (331)
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...From EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...No ratings yet
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosFrom EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power System Control and ProtectionFrom EverandPower System Control and ProtectionB. Don RussellRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesFrom EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)From EverandGuide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Build Your Own Electronics WorkshopFrom EverandBuild Your Own Electronics WorkshopRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsFrom EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionFrom EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Digital Transformation: Survive and Thrive in an Era of Mass ExtinctionFrom EverandDigital Transformation: Survive and Thrive in an Era of Mass ExtinctionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Empires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldFrom EverandEmpires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (87)