Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UP2 HW CH 19 S Temperature
Uploaded by
Vei AdoptanteOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
UP2 HW CH 19 S Temperature
Uploaded by
Vei AdoptanteCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYS-232
6: University Physics-II
HOMEWORK
PROBLEMS
Ch-19
Khalid Bukhari
Chapter 19: TEMPERATURE
Hand in your solutions in class, on:
Show the equations and calculations, and box your answer. Be sure to include
the units.
NOTE: Any four questions from this HW will be graded, and the marks for this HW will be
based on these only. (1, 5, 7, 9, 15, 19, 23, 24, 29, 35, 40, 62)
1.
Convert the following temperatures to their values on the Fahrenheit and Kelvin
scales:
(a) the sublimation point of dry ice, 78.5C; (b) human body temperature, 37.0C.
5.
Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of 195.81C at atmospheric pressure. Express this
temperature (a) in degrees Fahrenheit and (b) in kelvins.
7.
A copper telephone wire has essentially no sag between poles 35.0 m apart on a
winter day when the temperature is 20.0C. How much longer is the wire on a
summer day when the temperature is 35.0C?
9.
The active element of a certain laser is made of a glass rod 30.0 cm long and 1.50 cm
in diameter. Assume the average coefficient of linear expansion of the glass is equal
to 9.00 106 (C)1. If the temperature of the rod increases by 65.0C, what is the
increase in (a) its length, (b) its diameter, and (c) its volume?
PHYS-232
6: University Physics-II
Ch-19
Khalid Bukhari
15. A hollow aluminum cylinder 20.0 cm deep has an internal capacity of 2.000 L at
20.0C. It is completely filled with turpentine at 20.0C. The turpentine and the
aluminum cylinder are then slowly warmed together to 80.0C. (a) How much
turpentine overflows? (b) What is the volume of turpentine remaining in the cylinder
at 80.0C? (c) If the combination with this amount of turpentine is then cooled back to
20.0C, how far below the cylinders rim does the turpentines surface recede?
19. Gas is confined in a tank at a pressure of 11.0 atm and a temperature of 25.0C. If
two-thirds of the gas is withdrawn and the temperature is raised to 75.0C, what is
the pressure of the gas remaining in the tank?
PHYS-232
23.
6: University Physics-II
Ch-19
Khalid Bukhari
An auditorium has dimensions 10.0 m 20.0 m 30.0 m. How many molecules of
air fill the auditorium at 20.0C and a pressure of 101 kPa (1.00 atm)?
24. Q|C A container in the shape of a cube 10.0 cm on each edge contains air (with
equivalent molar mass 28.9 g/mol) at atmospheric pressure and temperature 300 K.
Find (a) the mass of the gas, (b) the gravitational force exerted on it, and (c) the force
it exerts on each face of the cube. (d) Why does such a small sample exert such a
great force?
29.
An automobile tire is inflated with air originally at 10.0C and normal atmospheric
pressure. During the process, the air is compressed to 28.0% of its original volume
and the temperature is increased to 40.0C. (a) What is the tire pressure? (b) After
the car is driven at high speed, the tires air temperature rises to 85.0C and the tires
interior volume increases by 2.00%. What is the new tire pressure (absolute)?
PHYS-232
6: University Physics-II
Ch-19
Khalid Bukhari
35. A spherical steel ball bearing has a diameter of 2.540 cm at 25.00C. (a) What is its
diameter when its temperature is raised to 100.0C? (b) What temperature change is
required to increase its volume by 1.000%?
40. The density of gasoline is 730 kg/m3 at 0C. Its average coefficient of volume
expansion is 9.60 104 (C)1. Assume 1.00 gal of gasoline occupies 0.003 80 m 3.
How many extra kilograms of gasoline would you receive if you bought 10.0 gal of
gasoline at 0C rather than at 20.0C from a pump that is not temperature
compensated?
PHYS-232
6: University Physics-II
Ch-19
Khalid Bukhari
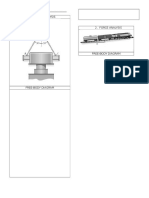
62. A cylinder that has a 40.0-cm radius and is 50.0 cm deep is filled with air at 20.0C
and 1.00 atm (Fig. P19.62a). A 20.0-kg piston is now lowered into the cylinder,
compressing the air trapped inside as it takes equilibrium height hi (Fig. P19.62b).
Finally, a 25.0-kg dog stands on the piston, further compressing the air, which
remains at 20C (Fig. P19.62c). (a) How far down (h) does the piston move when the
dog steps onto it? (b) To what temperature should the gas be warmed to raise the
piston and dog back to hi?
Figure P19.62
You might also like
- Time RatesDocument3 pagesTime RatesRonaldNo ratings yet
- ODE LargeFontDocument276 pagesODE LargeFontsticker592No ratings yet
- Thermo Chapter1Document11 pagesThermo Chapter1Mon Jhio San JuanNo ratings yet
- Updated Ee LPTR As of May 2019 (B)Document12 pagesUpdated Ee LPTR As of May 2019 (B)Broda de LeonNo ratings yet
- Ch. 11 Kinematics of ParticlesDocument90 pagesCh. 11 Kinematics of ParticlesMatt Finke100% (1)
- Integral Calculus: Engr. Anacleto M. Cortez JRDocument10 pagesIntegral Calculus: Engr. Anacleto M. Cortez JRPanfilo Diaz LacsonNo ratings yet
- 221HCh04 PDFDocument25 pages221HCh04 PDFisele1977No ratings yet
- Physics 1 Heat and TemperatureDocument52 pagesPhysics 1 Heat and TemperatureEazel SolanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 ProblemsDocument7 pagesChapter 15 ProblemsekojantiNo ratings yet
- Phys CH2Document37 pagesPhys CH2dockmom4100% (1)
- Uclm Cesafi QuestionsDocument1 pageUclm Cesafi QuestionsBeverly Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Problem - 3A PDFDocument14 pagesProblem - 3A PDFMonicaNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Thermal-ExpansionDocument14 pagesModule 1-Thermal-ExpansionHazel A. BelloNo ratings yet
- Paul Dawkins Calculus III - ThreeDimensions PDFDocument67 pagesPaul Dawkins Calculus III - ThreeDimensions PDFogasofotini100% (2)
- Introduction To Differential Equations: Jeffrey R. ChasnovDocument128 pagesIntroduction To Differential Equations: Jeffrey R. ChasnovMargono SoplantilaNo ratings yet
- FREE OSCILLATIONS: AN INTRODUCTIONDocument48 pagesFREE OSCILLATIONS: AN INTRODUCTIONShivang Mishra100% (1)
- (Ebook) - Engineering - Mechanical Engineering - Mechanics of Materials Solution Manual (3Rd Ed, by BeDocument78 pages(Ebook) - Engineering - Mechanical Engineering - Mechanics of Materials Solution Manual (3Rd Ed, by BeWesley SilvaNo ratings yet
- 02 KinematicsDocument17 pages02 KinematicsRonelle MaglayoNo ratings yet
- Curvilinear Motion PDFDocument49 pagesCurvilinear Motion PDFDaniel Naoe FestinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Kinematics of Particle Free Falling BodiesDocument15 pagesLecture 2 Kinematics of Particle Free Falling BodiesKRISTINE MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Problems Differential EquationsDocument121 pagesProblems Differential EquationsRazes50% (4)
- University Physics 13th Edition Solution Manual PDFDocument1 pageUniversity Physics 13th Edition Solution Manual PDFMohammed Rashwan32% (19)
- 2nd Law of ThermodynamicsDocument31 pages2nd Law of ThermodynamicsKazu YoshinagaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 2S AY2018-2019Document4 pagesProblem Set 2 2S AY2018-2019Allein Loisse EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5AnalysisofSeriesParallelSeries ParallelCircuitsDocument54 pagesChapter 5AnalysisofSeriesParallelSeries ParallelCircuitsLyssa ChoiNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - 3. ELMAG - 1 - Coordinate Systems and TransformationDocument44 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - 3. ELMAG - 1 - Coordinate Systems and TransformationDeni RistiantoNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of ParticlesDocument99 pagesKinematics of Particlesrevit37100% (3)
- Calculate the Volume of Solids of RevolutionDocument7 pagesCalculate the Volume of Solids of RevolutionhamxafarrukhNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Mechanical Engineering Principles John Bird 1Document24 pagesSolution Manual Mechanical Engineering Principles John Bird 1ridwansadelyNo ratings yet
- Related RatesDocument11 pagesRelated Ratesamitdeo99100% (1)
- Electric Charge, Forces and Fields Review Worksheet (Honors)Document2 pagesElectric Charge, Forces and Fields Review Worksheet (Honors)blackbutterflyNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Physics To SocietyDocument2 pagesThe Importance of Physics To SocietyBryan Ocampo Magculang100% (1)
- Ems TutorialDocument43 pagesEms TutorialJohn Eric Balarao Ferranco33% (3)
- Discrete Probability DistributionDocument5 pagesDiscrete Probability DistributionKent G NacaytunaNo ratings yet
- Graham's Law of Effusion WorksheetDocument2 pagesGraham's Law of Effusion WorksheetSheryl Renomeron MoralesNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument1 pageFluidsnico aspraNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument22 pagesGeometrycharles gueta100% (1)
- Money Time LowDocument41 pagesMoney Time LowChristian Sunga0% (2)
- Chapter 3 - Methods of Analysis PDFDocument47 pagesChapter 3 - Methods of Analysis PDFNisha Kamel100% (2)
- INTEGRAL CALCULUS Module 4Document12 pagesINTEGRAL CALCULUS Module 4Trazon Triestian Pedrera CardeñoNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge and Force Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesElectric Charge and Force Multiple Choice Questionsronaldo maanoNo ratings yet
- PHYS 211 Exam 1 Sample 2 With Key PDFDocument11 pagesPHYS 211 Exam 1 Sample 2 With Key PDFAndrew TrolioNo ratings yet
- AP Physics B - KinematicsDocument16 pagesAP Physics B - KinematicsPraba HarNo ratings yet
- Pasig Catholic College: Basic Calculus WorksheetDocument3 pagesPasig Catholic College: Basic Calculus WorksheetKkab ShiiiNo ratings yet
- Rectilinear Motion ExplainedDocument22 pagesRectilinear Motion ExplainedJamie MedallaNo ratings yet
- System+Dynamics+3+Edition+WillPALM (043 083)Document41 pagesSystem+Dynamics+3+Edition+WillPALM (043 083)Rosy Chávez Hernández100% (1)
- CH2 Describing Motion, Kinematics in One DimensionDocument38 pagesCH2 Describing Motion, Kinematics in One DimensionEpic WinNo ratings yet
- DE Midterm ExaminationDocument3 pagesDE Midterm ExaminationHades Vesarius RiegoNo ratings yet
- Review X DOT X Resultant of ForcesDocument44 pagesReview X DOT X Resultant of ForcesJohn Jim Paul DunesNo ratings yet
- Physics-II Ch-19: Solution To Similar Problems Chapter 19: TEMPERATURE 1Document5 pagesPhysics-II Ch-19: Solution To Similar Problems Chapter 19: TEMPERATURE 1James MondeloNo ratings yet
- Gas Thermometer Calibration & Pressure ProblemsDocument1 pageGas Thermometer Calibration & Pressure Problemsjason_cheong_6No ratings yet
- Temperatura EnglishDocument5 pagesTemperatura EnglishDiego AlonsoNo ratings yet
- NATIONAL CERTIFICATION EXAM GUIDE FOR ENERGY MANAGERSDocument18 pagesNATIONAL CERTIFICATION EXAM GUIDE FOR ENERGY MANAGERSzoom2No ratings yet
- PHYF144 Tutorial Questions UpdatedDocument16 pagesPHYF144 Tutorial Questions UpdatedAnonymous KUuLddnO98No ratings yet
- UP2 HW CH 20 S First Law ThermoDocument5 pagesUP2 HW CH 20 S First Law ThermoVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- 2004 Paper 2 Set BDocument6 pages2004 Paper 2 Set BNataraj Singh SardarNo ratings yet
- Khaire Sir Classes: All Imp Question of Unit 2 Sub: EtmDocument6 pagesKhaire Sir Classes: All Imp Question of Unit 2 Sub: EtmAkshay KhangreNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Key - 12th National Certification Exam for Energy ManagersDocument22 pagesPaper 2 Key - 12th National Certification Exam for Energy ManagersRichard RegidorNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Objective Type Paper - I: Key ConceptsDocument19 pagesMechanical Engineering Objective Type Paper - I: Key ConceptsVinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- IES Sample Paper - Mechanical EngineeringDocument19 pagesIES Sample Paper - Mechanical Engineeringravimech_86No ratings yet
- UP2 HW CH 24 S Gausss LawDocument3 pagesUP2 HW CH 24 S Gausss LawVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- Problem 9Document1 pageProblem 9Vei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- Ask Prob6Document1 pageAsk Prob6Vei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- SG GN SN - 1. Force AnalysisDocument15 pagesSG GN SN - 1. Force AnalysisVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- Phil Iri EnglishDocument2 pagesPhil Iri EnglishVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- CP S HW CH 9 DetailedDocument6 pagesCP S HW CH 9 DetailedVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- History of C Programming LanguageDocument1 pageHistory of C Programming LanguageVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- Nature of ElectricityDocument64 pagesNature of ElectricityVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- Computation of AgesDocument4 pagesComputation of AgesVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- UP HW CH 14 SDocument4 pagesUP HW CH 14 SVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- Civil Service Law OverviewDocument43 pagesCivil Service Law OverviewMark William S. MidelNo ratings yet
- UP2 HW CH 25 S Electric PotentialDocument4 pagesUP2 HW CH 25 S Electric PotentialVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- SchedDocument2 pagesSchedVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- MaslowDocument7 pagesMaslowVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- R A 9292 PDFDocument18 pagesR A 9292 PDFDaryl Langamon Uy CruzNo ratings yet
- PHYS-2325: Oscillatory Motion and Waves ProblemsDocument7 pagesPHYS-2325: Oscillatory Motion and Waves ProblemsVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- UP2 HW CH 19 S TemperatureDocument5 pagesUP2 HW CH 19 S TemperatureVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- 1.) Swap Two NumbersDocument10 pages1.) Swap Two NumbersVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 AP Practice 2D Motion With Answers Written in PDFDocument18 pagesChap 4 AP Practice 2D Motion With Answers Written in PDFVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- UP HW CH 17 SDocument2 pagesUP HW CH 17 SVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- Kinematics PracticeDocument6 pagesKinematics PracticeEdward GibsonNo ratings yet
- CP S HW CH 9 DetailedDocument6 pagesCP S HW CH 9 DetailedVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- PHYS-2325: Oscillatory Motion and Waves ProblemsDocument7 pagesPHYS-2325: Oscillatory Motion and Waves ProblemsVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- UP2 HW CH 20 S First Law ThermoDocument5 pagesUP2 HW CH 20 S First Law ThermoVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- UP2 HW CH 20 S First Law ThermoDocument5 pagesUP2 HW CH 20 S First Law ThermoVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- CP S HW CH 7 DetailedDocument9 pagesCP S HW CH 7 DetailedVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- UP HW CH 18 SDocument1 pageUP HW CH 18 SVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- E15 Newtons 2nd LawDocument5 pagesE15 Newtons 2nd LawVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- Class Schedule by Period and DayDocument3 pagesClass Schedule by Period and DayVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet