Professional Documents
Culture Documents
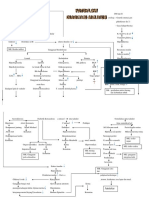
Properties and Changes
Uploaded by
Shine GatilloCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Properties and Changes
Uploaded by
Shine GatilloCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Changes
Chemical changes take place on the molecular level. A chemical change
produces a new substance. Examples of chemical changes include
combustion (burning), cooking an egg, rusting of an iron pan, and mixing
hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide to make salt and water.
Physical Changes
Physical changes are concerned with energy and states of matter. A physical
change does not produce a new substance. Changes in state or phase
(melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, sublimation) are physical
changes. Examples of physical changes include crushing a can, melting an
ice cube, and breaking a bottle.
How to Tell Chemical & Physical Changes Apart
A chemical change makes a substance that wasn't there before. There may
be clues that a chemical reaction took place, such as light, heat, color
change, gas production, odor, or sound. The starting and ending materials of
a physical change are the same, even though they may look different.
A physical property is an aspect of matter that can be observed or measured
without changing it. Examples of physical properties include color, molecular
weight and volume.
A chemical property may only be observed by changing the chemical identity
of a substance. This property measures the potential for undergoing a
chemical change. Examples of chemical properties include reactivity,
flammability and oxidation states.
Chemical vs Physical Properties
Chemical Properties: properties that describe how one substance reacts
with another substance. Chemical properties may only be observed by
reacting one chemical with another.
Examples of Chemical Properties:
flammability
oxidation states
reactivity
Here are some examples of chemical properties.
reactivity with other chemicals
toxicity
coordination number
flammability
enthalpy of formation
heat of combustion
oxidation states
chemical stability
types of chemical bonds that will form
Physical Properties: properties used to identify and characterize a
substance. Physical properties tend to be ones you can observe using your
senses or measure with a machine.
Examples of Physical Properties:
density
color
melting point
Examples of Physical Properties
Any property you can see, smell, touch, hear or otherwise detect and
measure without performing a chemical reaction is a physical property.
color
shape
volume
density
Chemical vs Physical Changes
Chemical Changes: result from a chemical reaction and make a new
substance.
Examples of Chemical Changes:
burning wood (combustion)
rusting of iron (oxidation)
cooking an egg
Examples of Chemical Properties
Physical Changes: involve a change of phase or state and do not produce
any new substance.
Examples of Physical Changes:
melting an ice cube
crumpling a sheet of paper
boiling water
You might also like
- Aminoglycoside Side EffectsDocument2 pagesAminoglycoside Side EffectsShine GatilloNo ratings yet
- A Slight Smile Is Very CharmingDocument220 pagesA Slight Smile Is Very CharmingShine Gatillo100% (14)
- Answer SheetDocument1 pageAnswer SheetShine GatilloNo ratings yet
- Pharinfo - PrelimsDocument22 pagesPharinfo - PrelimsShine GatilloNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy MeasurementsDocument5 pagesPharmacy MeasurementsShine GatilloNo ratings yet
- WJPPS 661Document18 pagesWJPPS 661Shine GatilloNo ratings yet
- AntidotesDocument2 pagesAntidotesYemaya84No ratings yet
- Molisch Test: Name of Test Reagent Used Positive Result Use of The Test Additional InformationDocument3 pagesMolisch Test: Name of Test Reagent Used Positive Result Use of The Test Additional InformationShine GatilloNo ratings yet
- General Properties of CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesGeneral Properties of CarbohydratesShine GatilloNo ratings yet
- Blaise PascalDocument2 pagesBlaise PascalShine GatilloNo ratings yet
- AkapulkoDocument9 pagesAkapulkoShine GatilloNo ratings yet
- Beautiful WordsDocument3 pagesBeautiful WordsShine GatilloNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- LinkageDocument47 pagesLinkageTony BernardNo ratings yet
- Spoilage of Frozen Chicken Nuggets by Toxigenic Psycrophilic FungiDocument16 pagesSpoilage of Frozen Chicken Nuggets by Toxigenic Psycrophilic FungiNIDHI BARINo ratings yet
- Mechanical Operation Slurry TransportDocument113 pagesMechanical Operation Slurry TransportIsrarulHaqueNo ratings yet
- NURS FPX 6410 Assessment 2 Executive Summary To AdministrationDocument7 pagesNURS FPX 6410 Assessment 2 Executive Summary To Administrationzadem5266No ratings yet
- E 23 Fuel System Schaffer 4350ZDocument3 pagesE 23 Fuel System Schaffer 4350ZSergeyNo ratings yet
- Natural Medicine - 2016 October PDFDocument100 pagesNatural Medicine - 2016 October PDFDinh Ta HoangNo ratings yet
- IWGIA Book The Indigenous World 2021 ENGDocument824 pagesIWGIA Book The Indigenous World 2021 ENGREy FOxNo ratings yet
- RPLB NewDocument22 pagesRPLB NewMeta learnNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument3 pagesProposalAbdullahAlmasNo ratings yet
- Operations Manual: Conical Burr Coffee GrinderDocument15 pagesOperations Manual: Conical Burr Coffee Grindercherrera73No ratings yet
- Book Review - Black Skin, White MasksDocument9 pagesBook Review - Black Skin, White MasksKaren A. LloydNo ratings yet
- Med Mantra Hospital Management Solution 0813 1Document4 pagesMed Mantra Hospital Management Solution 0813 1vvr_9No ratings yet
- SM - Business PoliciesDocument46 pagesSM - Business PoliciesPrithvi AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Animal Death Unknown 2010Document57 pagesAnimal Death Unknown 2010Vincent J. CataldiNo ratings yet
- MOLYKOTE 1000 Paste 71-0218H-01Document2 pagesMOLYKOTE 1000 Paste 71-0218H-01Victor PomboNo ratings yet
- 3 D7 QC Physical and Chemical Tests Ok For EmailDocument17 pages3 D7 QC Physical and Chemical Tests Ok For EmailUbaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Brown Wolf ExerciseDocument8 pagesBrown Wolf ExerciseAarnav kumar0% (1)
- Memorandum - World Safety Day "2023''Document2 pagesMemorandum - World Safety Day "2023''attaullaNo ratings yet
- Patoflow DMDocument2 pagesPatoflow DMAngel da CostaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Fitness Training PrinciplesDocument80 pagesChapter 10 Fitness Training Principlesapi-115744109No ratings yet
- Invoice, packing list mẫuDocument2 pagesInvoice, packing list mẫuPHI BUI MINHNo ratings yet
- Dow Corning Corporation Material Safety Data SheetDocument9 pagesDow Corning Corporation Material Safety Data Sheetgazwang478No ratings yet
- Korean Wellhead KWM-2014-Revision0Document20 pagesKorean Wellhead KWM-2014-Revision0DrakkarNo ratings yet
- Key MechanicalDocument72 pagesKey MechanicalDasuki FahmiNo ratings yet
- DS 1 CatDocument38 pagesDS 1 CatMuhammad Bilal Khattak100% (1)
- PFI Freediver ManualDocument69 pagesPFI Freediver ManualLuca MariniNo ratings yet
- A Rare Peripheral Odontogenic Keratocyst in Floor of Mouth: A Case ReportDocument6 pagesA Rare Peripheral Odontogenic Keratocyst in Floor of Mouth: A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Production & Downstream Processing of Baker's Best FriendDocument26 pagesProduction & Downstream Processing of Baker's Best FriendMelissaNo ratings yet
- First Communion: You Are The VoiceDocument10 pagesFirst Communion: You Are The VoiceErnesto Albeus Villarete Jr.No ratings yet
- Oil Palm Fractions Derivatives Web PDFDocument6 pagesOil Palm Fractions Derivatives Web PDFIan RidzuanNo ratings yet