Professional Documents
Culture Documents
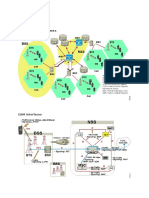
GSM Network Elements
Uploaded by
sibongile0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagestransmission microwave
Original Title
Doc1...
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenttransmission microwave
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesGSM Network Elements
Uploaded by
sibongiletransmission microwave
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
GSM Network Elements
GSM Interfaces
GSM Data Services
GSM networks handle both voice and data traffic requirements of the mobile
communication by providing two modes of operation:
Circuit switched (high-speed circuit switched data)
Packet switched (GPRS)
Circuit switching provides the customer with a dedicated channel all the way to
the destination. The customer has exclusive use of the circuit for the duration of
the call, and is charged for the duration of the call.
With packet switching, the operator assigns one or more dedicated channels
specifically for shared use. These channels are up and running 24 hours a day,
and when you need to transfer data, you access a channel and transmit your
data. Packet switching is more efficient than circuit switching.
The standard data rate of a GSM channel is 22.8 kbps.
GPRS Interfaces
GPRS Tunneling Protocol
GTP Packet Structure
You might also like
- Functionality MCBSC NokiaDocument6 pagesFunctionality MCBSC NokiaAlieNo ratings yet
- CHE504 - Lab Report On Gas Absorption L8 PDFDocument23 pagesCHE504 - Lab Report On Gas Absorption L8 PDFRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- GSM To 3G: A Journey of Wireless CommunicationDocument45 pagesGSM To 3G: A Journey of Wireless Communicationsrshelke100% (1)
- Week 7 GSM Enhancements: - HSCSD - GprsDocument21 pagesWeek 7 GSM Enhancements: - HSCSD - GprsConor O 'ReganNo ratings yet
- Module 5 GPRS and EdgeDocument37 pagesModule 5 GPRS and EdgeSwapnil NageNo ratings yet
- EDGE Technology: Prepared byDocument17 pagesEDGE Technology: Prepared bySantosh NayakNo ratings yet
- GPRS LecDocument37 pagesGPRS LecRussell F PhiriNo ratings yet
- GPRSDocument18 pagesGPRSpapayee lakshmananNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument19 pagesFinalVepin VydulaNo ratings yet
- New LTEDocument33 pagesNew LTEVikash YadavNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Data - Rates For GSM Evolution (Document16 pagesEnhanced Data - Rates For GSM Evolution (kiranmannNo ratings yet
- Assalm-O-Alikum: Group MembersDocument21 pagesAssalm-O-Alikum: Group MembersHassan AminNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GPRS: General Packet Radio System (GPRS)Document5 pagesIntroduction To GPRS: General Packet Radio System (GPRS)Arinjay BishtNo ratings yet
- Evolution From GSM To UMTSDocument32 pagesEvolution From GSM To UMTSnattynafNo ratings yet
- DE1.1 6th Sem.08 WirelessDocument202 pagesDE1.1 6th Sem.08 WirelessgpsonlineNo ratings yet
- On The Road To UMTS: Hongyi Wu Xiaojun CaoDocument56 pagesOn The Road To UMTS: Hongyi Wu Xiaojun CaoBirckof PearceNo ratings yet
- What Is 3GDocument15 pagesWhat Is 3GShampad AyanNo ratings yet
- Ac RE56 41 GSM Data SecondDocument7 pagesAc RE56 41 GSM Data SecondCedrik PendjiNo ratings yet
- By: Richa SachdevDocument18 pagesBy: Richa SachdevRicha SachdevNo ratings yet
- Sunny GprsDocument18 pagesSunny GprsSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 2Document27 pagesLecture # 2Shah Zeb YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 13 14 15 16 17 Winter 2023 2024Document97 pagesLecture 12 13 14 15 16 17 Winter 2023 2024ritamonde4No ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 PDFDocument29 pagesLecture - 3 PDFLatera FekedeNo ratings yet
- All Rights Reserved - Group: A AhmedDocument27 pagesAll Rights Reserved - Group: A AhmedMohamedSalahNo ratings yet
- Mobile and Wireless Communication Complete Lecture Notes #2Document28 pagesMobile and Wireless Communication Complete Lecture Notes #2Student Lecture NotesNo ratings yet
- Mobile Devices and Systems: Handheld Pocket ComputersDocument125 pagesMobile Devices and Systems: Handheld Pocket ComputersChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Gprs Interview QuestionsDocument2 pagesGprs Interview Questionssindhur6938No ratings yet
- 3GEVOLDocument33 pages3GEVOLNavaneeth KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Cdma2000 1xRTTDocument19 pagesCdma2000 1xRTTsubashkuruppathNo ratings yet
- What Is GPRS ?: Main Features of GPRSDocument5 pagesWhat Is GPRS ?: Main Features of GPRSMayank BansalNo ratings yet
- A Mobile & Cellular Communication Assignment On: Opic No: 46Document16 pagesA Mobile & Cellular Communication Assignment On: Opic No: 46Gulshan PrakashNo ratings yet
- Gprs CodingDocument4 pagesGprs CodingPuneet GuptaNo ratings yet
- HSPA For Improved Data TransferDocument21 pagesHSPA For Improved Data TransferAmine InpticNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Fast Access Technologies: By:-Gurpreet RathoreDocument25 pagesPresentation On Fast Access Technologies: By:-Gurpreet RathoreDaljit SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SGSNDocument79 pagesIntroduction To SGSNge01109100% (3)
- 2.5 G SystemsDocument10 pages2.5 G SystemsdeardestinyNo ratings yet
- 2.75 G & 3GDocument14 pages2.75 G & 3GSaad KhaliqNo ratings yet
- Traning Pre (Ashi)Document27 pagesTraning Pre (Ashi)poonamshallyNo ratings yet
- Module 01 - Introduction To EDGE PDFDocument17 pagesModule 01 - Introduction To EDGE PDFRomi StepanusNo ratings yet
- Mobile GenerationDocument24 pagesMobile GenerationPhantom FireNo ratings yet
- 3G TrainingDocument359 pages3G TrainingVikash Yadav100% (3)
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Is A: Services OfferedDocument5 pagesGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Is A: Services Offeredrenuka_ec694456No ratings yet
- Unit - IvDocument73 pagesUnit - Ivdeecodes13No ratings yet
- Module 3 (Cellular Communication)Document128 pagesModule 3 (Cellular Communication)anu molNo ratings yet
- Telecom PresentationDocument33 pagesTelecom PresentationGamme T MijanNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communications 3G Systems: by Sheharyar ZahidDocument38 pagesWireless Communications 3G Systems: by Sheharyar ZahidDanish RazaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document57 pagesUnit 4Utsav SoniNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Wireless Data CommunicationsDocument63 pagesAn Overview of Wireless Data CommunicationsebinVettuchirayilNo ratings yet
- 21 Final 3GDocument41 pages21 Final 3GMosab MohammadNo ratings yet
- Click To Edit Master Subtitle Style General Packet Radio ServiceDocument16 pagesClick To Edit Master Subtitle Style General Packet Radio ServiceFahad JamilNo ratings yet
- Copy (2) of GPRS2Document14 pagesCopy (2) of GPRS2saha_debajyoti0No ratings yet
- Multi-Channel Multipoint Distribution Service (MMDS)Document19 pagesMulti-Channel Multipoint Distribution Service (MMDS)Rahul SinghalNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: UNIT: 4 Third Generation CommunicationDocument65 pagesGujarat Technological University: UNIT: 4 Third Generation CommunicationUtsav SoniNo ratings yet
- General Packet Radio ServiceDocument9 pagesGeneral Packet Radio ServicemsthenmozhiNo ratings yet
- MCN Unit 4.2Document18 pagesMCN Unit 4.2venkatNo ratings yet
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Is ADocument8 pagesGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Is AAjay AryaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Comm Short NoteDocument8 pagesMobile Comm Short NoteSarthak BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- 1 1.1 DevelopmentDocument39 pages1 1.1 DevelopmentPaniqsNo ratings yet
- CVDocument3 pagesCVsibongileNo ratings yet
- 1Document88 pages1sibongileNo ratings yet
- GSM Network ElementsDocument3 pagesGSM Network ElementssibongileNo ratings yet
- GSM Network ElementsDocument3 pagesGSM Network ElementssibongileNo ratings yet
- Sony HCD Zx30avDocument80 pagesSony HCD Zx30avrrobles8777No ratings yet
- Chloride LINEAR MK II - Service ManualDocument32 pagesChloride LINEAR MK II - Service Manualfabio.perazzoloNo ratings yet
- File: OPL3.java Software Implementation of The Yamaha YMF262 Sound Generator. Version 1.0.6Document18 pagesFile: OPL3.java Software Implementation of The Yamaha YMF262 Sound Generator. Version 1.0.6mendofriulNo ratings yet
- Detail of Earthing Lug Detail-A Base Plate Detail (Bp-1)Document1 pageDetail of Earthing Lug Detail-A Base Plate Detail (Bp-1)saravqwertyNo ratings yet
- Geomechanics & ERDDocument18 pagesGeomechanics & ERDRene Torres HinojosaNo ratings yet
- SSC Scientific Assistant Answer Key For Electronics & Telecommunication 2017Document14 pagesSSC Scientific Assistant Answer Key For Electronics & Telecommunication 2017Shrishanti Kale100% (1)
- ErrorsDocument498 pagesErrorsIsmael DiasNo ratings yet
- PRINCIPLES OF SURGERY (James R. Hupp Chapter 3 Notes) : 1. Develop A Surgical DiagnosisDocument5 pagesPRINCIPLES OF SURGERY (James R. Hupp Chapter 3 Notes) : 1. Develop A Surgical DiagnosisSonia LeeNo ratings yet
- How Torque Converters Work - HowStuffWorksDocument7 pagesHow Torque Converters Work - HowStuffWorksKrishanu ModakNo ratings yet
- DWL-3200AP B1 Manual v2.40 PDFDocument83 pagesDWL-3200AP B1 Manual v2.40 PDFFrank Erick Soto HuillcaNo ratings yet
- SmartPRO 5000U Plus ManualDocument10 pagesSmartPRO 5000U Plus ManualMugiranezaNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet: Control Unit Micrologic 5.0 A, For Masterpact NT/ NW, LSI ProtectionsDocument3 pagesProduct Data Sheet: Control Unit Micrologic 5.0 A, For Masterpact NT/ NW, LSI ProtectionsEvandro PavesiNo ratings yet
- SMD TR60-1.0mm With 12mm Bar (Office Floor 3.64m Span) PDFDocument2 pagesSMD TR60-1.0mm With 12mm Bar (Office Floor 3.64m Span) PDFabhijitkolheNo ratings yet
- Daatabase AssignmentDocument4 pagesDaatabase AssignmentIshani Puvimannasinghe100% (1)
- Installation and Operation Manual: 3161 GovernorDocument48 pagesInstallation and Operation Manual: 3161 GovernorMiguel Sotelo100% (1)
- Lecture 4 Maps Data Entry Part 1Document80 pagesLecture 4 Maps Data Entry Part 1arifNo ratings yet
- Flanges: SI SMEDocument16 pagesFlanges: SI SMEbalaNo ratings yet
- Correlational ResearchDocument10 pagesCorrelational ResearchSari100% (1)
- Research MethodsDocument10 pagesResearch MethodsAhimbisibwe BenyaNo ratings yet
- 1-A Survey On Mobile Edge Computing: TheCommunication Perspective PDFDocument37 pages1-A Survey On Mobile Edge Computing: TheCommunication Perspective PDFDHRAIEF AmineNo ratings yet
- Running EventStatsticsUtil To Understand How Events Are Stored in The OBM DatabaseDocument5 pagesRunning EventStatsticsUtil To Understand How Events Are Stored in The OBM DatabaseChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Vessel Support: Vertical Saddle ReactionsDocument12 pagesHorizontal Vessel Support: Vertical Saddle ReactionsSanket BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMDocument7 pagesIMMUNOHISTOCHEMJadys Merill DiezNo ratings yet
- Hook Height With Drawwork SensorDocument3 pagesHook Height With Drawwork SensorJose PalumboNo ratings yet
- A Proof of The Black and Scholes Formula: Claudio Pacati May 30, 2012Document3 pagesA Proof of The Black and Scholes Formula: Claudio Pacati May 30, 2012AndresC.MedinaSanhueza100% (1)
- Sap PP 01 Organizational Structure Overview PDFDocument52 pagesSap PP 01 Organizational Structure Overview PDFMahesh KamdeyNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 01 Basic Geometry Concepts PDFDocument16 pagesAnswer Key - CK-12 Chapter 01 Basic Geometry Concepts PDFValery Liz0% (1)
- Fa4 Webinar Wincc Unified CompressedDocument56 pagesFa4 Webinar Wincc Unified CompressedNeuron StimNo ratings yet
- Free Electricity From The Earth Rotating Through Its Own Magnetic Field Using The Homopolar Generator EffectDocument3 pagesFree Electricity From The Earth Rotating Through Its Own Magnetic Field Using The Homopolar Generator EffectmarcelogiovaneNo ratings yet