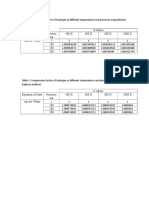
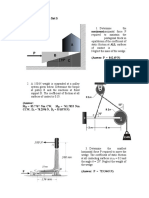
Review.
Limit of a Function
Evaluate the following limits or explain why it does not exist.
lim 4 x 2 3 f 1
x1
x
x 1
lim
1 2 x 1 x 3
lim
x 2
4 x2 0 g 2
�Review. Limit of a Function
Evaluate the following limits or explain why it does not exist.
x2 1
h x x 5
3
5
4
x
lim h x does not exist
x0
lim h x 2 h 1
x1
1 x
1 x 0
x0
�CONTINUITY OF A FUNCTION
�Definition
A function f is continuous at a number a
if all of the following are satisfied:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
exists;
exists; and
�Remarks
If at least one of the conditions is not
satisfied, then the function f is
discontinuous at a.
If condition (ii) is not satisfied, the
discontinuity is said to be essential.
If condition (ii) is satisfied and either (i) or
(ii) is not satisfied, the discontinuity is said
to be removable.
�Definition
A function f is continuous at a number a
if all of the following are satisfied:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
exists;
exists; and
Essential
�Definition
A function f is continuous at a number a
if all of the following are satisfied:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
exists;
exists; and
Removable
�Theorems
A polynomial function is continuous
everywhere.
A rational function is continuous at
every number in its domain.
�Example
Since this is a polynomial function, then it
is continuous everywhere.
�Example
Since this is a rational function, then it is
continuous in its domain, i.e. it is
continuous at every real number except 2.
�Example
Note that
does not exist.
Then, the discontinuity is essential.
�Example
This rational function is continuous at
every real number except at 1 and 3.
�Example
This is an infinite limit, i.e. the limit does not
exist.
Hence, the function h has an essential
discontinuity at 1.
�Example
Hence, the function h has a removable
discontinuity at 3.
�Example
h has a removable discontinuity at 3.
h1 x
x2 9
x2 4 x 3
3
,x 3
,x 3
�Example
The function is possibly discontinuous only at
2.
(i)
does not exist.
Then, F is indeed discontinuous at 2.
�Example
Hence, the discontinuity at 2 is removable.
�Example
F has a removable discontinuity at 2.
�Exercise.
Identify, if any, the points of
discontinuity of the given functions.
f x 2 x3 4 x 2 1
g x x 1 x x 1
2
The above functions do not have points of
discontinuity.
�Exercise.
Identify, if any, the points of
discontinuity of the given functions.
x 5 3 x 1
F x
x 5 x 1
F is discontinuous at -5 and at 1.
F has a essential discontinuity at 1 and
a removable discontinuity at -5.
�Exercise.
Identify, if any, the points of
discontinuity of the given functions.
G x
2 x
x2 1
G is discontinuous at -1 and at 1.
G has a essential discontinuity at -1 and
a essential discontinuity at 1.
�Exercise.
Identify, if any, the points of
discontinuity of the given functions.
x2 1
h x x 5
3
5 4 x
1 x
1 x 0
x0
h is discontinuous at 0.
h has a essential discontinuity at 0.
�Definition
A function f is continuous from the right
at a number a if all of the following are
satisfied:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
exists;
exists; and
�Definition
A function f is continuous from the left at
a number a if all of the following are
satisfied:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
exists;
exists; and
�Example
The function is possibly discontinuous at -2
and 0.
(i)
�Example
Hence, the function has an essential
discontinuous at -2.
�Example
But
Thus, the function is continuous from the
right at -2.
�Example
The function has an essential discontinuity
at 0.
�Example
But
so the function is continuous from the left at
0.
�Definition
A function is continuous on an open
interval
if it is continuous at every
number in the interval.
�Example
We know that f is discontinuous at -2 and
0.
f is continuous on any open interval that
does not contain -2 and 0.
�Definition
A function f is continuous on a closed
interval
if the following are satisfied:
(i) f is continuous on the open interval
(ii) f is continuous from the right at a;
(iii) f is continuous from the left at b.
�Definition
A function f is continuous on an interval
if the following are satisfied:
(i) f is continuous on the open interval
(ii) f is continuous from the right at a.
�Definition
A function f is continuous on an interval
if the following are satisfied:
(i) f is continuous on the open interval
(ii) f is continuous from the left at b.
�Example
f is continuous from the right at -2.
f is continuous from the left at 0.
�Example
f is continuous on this interval since
it is continuous on
it is continuous from the right at -2 and
it is continuous from the left at 0.
�Example
f is not continuous on
since it is
not continuous from the left at -2.
�Example
f is not continuous on
since f is not
continuous on
since 0, a point of
discontinuity, is in the open interval.
�Example
f is continuous on
since
it is continuous on
and
it is continuous from the left at 3.
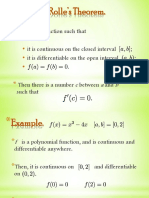
�Intermediate Value Theorem
If the function f is
continuous on the closed interval
and
then for any number k between
and
there exists a number c between a and b
such that
�Example
f is a polynomial function and is continuous
anywhere.
Then it is continuous on the given interval.
The conditions of the IVT are satisfied.
�Example
By IVT, there exists a c between 0 and 3
such that
.
The value of c satisfying IVT is 2.