Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pile Design PDF
Uploaded by
Khusairy AhmadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pile Design PDF
Uploaded by
Khusairy AhmadCopyright:
Available Formats
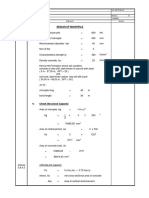
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Sample Design Calculations
For Micropiles in Kenny
Hill Formation
Generalized Subsoil Profile
-
Generally flat terrain
Subsoil profile:
0-3m, silty SAND, SPT=1- 5
3-6m, silty SAND, SPT= 15 - 50
6-20m, highly weathered sandstone
Schematic Detail
Soil becoming
weathered rock
Mild Steel Capping Plate
L
=
350mm
B
=
350mm
Thickness
=
10mm
Mild Steel Stiffeners
Thickness =
10mm
Pile Boring
Diameter = 200mm
L = 20.0m
API Pipe
O.D.
Thickness
fy (min)
Grade
=
=
=
=
127.0mm
9.2mm
552 Mpa
N-80
Cementitious Grout
W/c
=
0.45
Fcu
=
25 Mpa
Safe Working Load
Pa
=
80 tonnes
Lsocket
=
20m
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 1
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Subject : Micropile Design
1.0
Material Properties
1.1
Basic Dimensions and Properties
1.1.1
1.1.2
1.1.3
Micropile Diameter, D
Pile Composite Modulus Ep
Moment of Inertia, Ip
1.2
Cementitious Grout
1.2.1
1.2.2
1.2.3
1.2.4
1.2.5
1.2.6
Max. water/cement ratio
Anti-shrink / Additives
Grout Area. Ac
28 day Comp. Strength, Fcu'
Density
Elastic Modulus. Ec
1.3
API Pipe Reinforcement
1.3.1
1.3.2
1.3.3
1.3.4
1.3.5
1.3.6
1.3.7
1.3.8
1.3.9
Source
Outer Diameter, OD
Wall Thickness. t
Inner Diameter. ID
Cross Sectional Area, As
API Specification
Grade Designation
Mm. Yield Strength, fy
Elastic Modulus. Es
1.4
Compliance with British Standards Designed
1.4.1
1.4.2
1.4.3
1.4.4
Working Grout/API Pipe Bond (MPa)
0.8
12
Grout Characteristic Strength, fcu (MPa)
25
20
Cement content (kg/m"3)
400
00
Grout working compressive stress,0.4fcu/FoS 0.2 x fcu 0.25 x fcu
1.5
Minimum Factors of Safety
1.5.1
1.5.2
1.5.3
1.5.4
Against Structural Failure
Against Buckling Failure
Against Geotech. Failure
Against Geotech. Failure
2.0
Structural Design
Assuming that the applied vertical load is carried by the API Pipe alone.
Ultimate Load Capacity Pu
= 0.87 x fy x As
= 1633450 N
= 1633.5 kN
= 163.3 tonnes
Use the Factor of Safety prescribed in Section 1.5 on Plate 2
Allowable Load Capacity Pa
= 82 tonnes
2.1
2.2
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
= 200mm
= 41
GPa
= 7.85E+07 mm^4
=
=
=
=
=
=
0.45
Adogroud 100g 150kg bag
45686
mm"2
25
MPa
2000
kg /M^3
28
GPa
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
127
9.19
108.62
3401
5A-80
N-80
552
210
=
=
=
=
2.00
1.60
2.00
2.50
mm
mm
mm
mm^2
MPa
GPa
Req. Min.
(Max)
Source
BS8110
BS8004
BS8004
BS8004
Skin Friction
End Bearing
Page 2
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
2.3
Design Safe Working Load SWL
= 80 tonnes
3.0
Geotechnical Design
Refer Piler Analysis for derivation of Geotechnical Safe Working Load -Appendix ......
3.1
Design Length
3.1.1
3.1.2
3.1.3
Safe Working Load per Pile
Nominal Diameter
Embedment
3.2
Grout l API Pipe Bond
3.2.1
3.2.2
3.2.3
3.2.4
Ultimate Grout Pipe - Bond Stress, t (u)
Factor of Safety
Working Bond Stress, t (w)
Req'd API Pipe Embedment in Grout
P
D
Ls
Therefore, adopted socket length is
= 800
= 200
= 20.0 m
kN
mm
= 2.0
= 2.5
= 0.8
= 2.5
< 20.0 m
OK
MPa
MPa
m
4.0
Buckling (Pile Slenderness)
4.1
Pile End Conditions (Unfilled Cavities)
4.1.1
4.1.2
4.1.3
4.1.4
Pile Top (at Pilecap Level)
Pile Base (at Rock Head Level)
Ass. length in unfilled cavity L assumed
Effective Length - 0.7 x L L eff.
4.2
Eucler's Buckling Load (Unfilled Cavities)
4.2.1
4.2.2
Effective radius
Euler Critical Load
4.3
Elastic Buckling Load of Pile embedded in Overburden (ie Winkler Medium)
4.3.1
4.3.2
4.3.3
4.3.4
Average SPT in Overburden soils, N
Est. Und. Cohesion Overburden soils, Cu
Modulus of Horiz. Subgrade Reaction, kh'c
20100 kPa
Elastic Buckling Load, Pcr
4.3.5
FOS available
5.0
Rate of Corrosion of Reinforcement
5.1
Ex Oil Drill API Pipe Reinforcement
5.1.1
5.1.2
5.1.3
5.1.4
5.1.5
5.1.6
5.1.7
Outer Diameter
Wall Thickness
Internal Diameter
Cross sectional Area
API Specification
Grade Designation
Min Yield Strength
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Analysis not appropriate
for Kenny Hill Formation
r
Pe
FOS available
O.D.
t
I.D.
As
fy
=
=
=
=
Fixed
Fixed
1m
0.7 m
=41.8
=@pi^2 - Ep l(Lelr)^2 = 1428 kN
=9.78
OK
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
50
6 ' N kPa 300 kPa
67*Cu
20.1 MPa
2 x @sgrt (Ep x Ip x kh x d)
16014 kN
20.02 OK
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
127.0
9.2
108.6
3401
5A-80
N-80
552
mm
mm
mm
mm^2
MPa
Page 3
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
5.1.8
5.1.9
Elastic Modulus Es
=
210
GPa
Allowable Axial Working Stress (Clause 7.4.6.3.1 BS8004)
Fa
=
50% of Yield Strength
=
276 MPa
5.2
Design for allowable corrosion as for sheetpiles w/o grout/
concrete protection
5.2.1
5.2.2
5.2.3
5.2.4
5.2.5
Allowable corrosion rate
Max. pile axial load Pa
Req'd Steel Area
Min. OD of API Pipe
Allowable Corrosion Period
=
=
=
=
=
Asc
O.D.
Tc
0.01
800
2899
124.5
255
mm/year
kN
mm^2
mm
years
Summary
No additional reinforcement required, Tc > Design Life of 50 years.
6.0
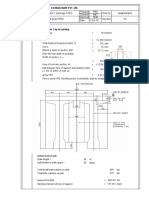
Pilehead Capping Details
Safe Working Load
800
kN
=
=
=
x
25
6.85
116800
350
MPa
MPa
mm^2
OK
155
MPa
6.1
Capping Plate Size
6.1.1
6.1.2
6.1 3
Assume characteristic strength of pileca f cu
Permissible direct compressive stress fcu13.65
Req'd bearing area of capping plate
Adopt plate of dimmensions (mm)
350
6.2
Thickness of Stiffners
6.2.1
Allowable Axial Compressive Stress
=
(Table 17 (a). BS449 : Part 2: 1969)
Contact Area of API Pipe on Capping Plate
=
Stiffener projection beyond API pipe OD
=
Required thickness of MS Stiffeners
t(s) =
Adopt
6.2.2
6.2.3
6.2.4
6.3
Thickness of Capping Plate
6.3.1
6.3.2
Allow Shear Stress on Capping Plate
(Table 10. BS449:Part 2:1969)
Effect. Punching Shear Shear Perimeter
6.3.3
Required Thickness of Capping Plate
125
OD of API Pipe + Perimeter
- 8 x thickness of stiffeners
1599 mm
4.0
mm
10
mm
=
=
Adopt
6.4
Allowable Bearing Stress on Capping Plate
6.4.1
Allow. Bearing Stress on Capping Plate
(Table 9. BS449:Part 2:1969)
Proj. Bearing Area (API + Stiffeners)
Actual Bearing Stress
6.4.2
6.4.3
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
3401 mm^2
184
mm
2.4
mm
10
mm
(4No. MS Stiffeners)
MPa
210
MPa
=
=
10761 mm^2
74
MPa
< All. Bearing Stress, OK
Page 4
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
6.5
Check Stiffeners for Buckling
6.5.1
6.5.2
Bearing Area of API Pile
=
3401 mm^2
Bearing Area of 4No. Stiffeners
=
7359 mm^2
Assume uniform distribution of Pile Axial Load,
Compressive Load per Stiffener
=
136.8 kN
Pile head Embedment into Pilecap
=
150
mm
Assume Stiffener Depth, d
=
140
mm
(Conservative Estimate)
Slenderness Ratio of Stiffener
d ' @sgrt(3)1 thickness of stiffener
=
24.2
Allow. Compressive Stress
=
146
MPa
(Table 17(a). BS449)
Allow. Buckling Load on Stiffener
=
268.6 kN '
> Compressive Load of Stiffener, OK
6.5.3
6.5.4
6.5.5
6.5.6
6.5.7
6.5.8
6.6
Check Bearing on API Pipe
6.6.1
6.6.2
6.6.3
6.6.4
Moment equilibrium about intersection of Capping Plate and API Pipe,
Bearing Force on API Pipe
=
180
kN
Assume material for API Pipe to be equivalent to G55 steel,
Allow. Bearing Stress
=
320
MPa
Allow Bearing Load
=
448
kN
> Actual Bearing Force, OK
6.7
Fillet Weld Design (Stiffener to API Pipe)
6.7.1
Weld Length per Stiffener
6.7.2
Req'd Shear Load Capacity for weld
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
=
=
=
Adopt
2xd
280
0.49
7
mm per stiffener
kN/mm
mm Fillet Weld
Page 5
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Design Report
1.
Introduction
This report presents the design criteria and design calculations for pile foundation for
Interchange 3 of Project B 15 Road Upgrading Works.
Interchange 3 is a cloverleaf interchange with arch shaped R.C bridge as shown below
From structural analysis the compression load coming over the piles from one half of the
bridge is 12600 ton while the other half is 2800 ton in tension.
2.
Site Condition
The topograph of the site is rolling to undulating. The subsoil condition is generalized as
shown above.
The top 12m to 16m from the OGL of the residual soil is clayey silt with SPT 6-39 (aver
age SPT=20): This is underlain by hard clayey silt sith SPT exceeding 50 up to 28m bgi.
3.
4.
Analysis
Shallow foundation is not suitable because part of the formation is on filled ground and also
part of the foundation is in tension or high compression.
Driven spun piles cannot or not practical to provide adequate tension required. Large diam
eter bored piles are suitable for high compression and tension required.
Design Calculations
4.1
Compression piles
The allowable compression load carrying capacity of the single pile has been cal
culated based on the SPT 'N" values, using the following formula.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 6
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Allowable load
Ab
Ab, af + As,fs
3
2
2
base area (m )
qf
=
=
unit base resistance
400 Nb (in SI-unit), Meyerhof's Empirical Formula
Nb
average 'N' over 5m above and 3m below depth
being considered (< 50)
As
Pile circumference area (m2)
fs
=
=
unit skin friction
2 Nave (in SI-unit)
Nave
= Average SPT value with depth
Factor of safety of base resistance
= 3 to control settlement
Factor of safety of friction resistance = 2
The detailed pile calculations are given in Appendix B.
4.2
Tension piles
The allowable tension load carrying capacity of single pile has been calculated
based on SPT 'N' values, using following formula
Allowable load
=
As . fs 2
As
Pile circumference area
fs
=
=
Unit skin friction
2 Nave (in SI-unit)
Nave
Average SPT 'N' value with depth
Factory of safety against friction resistance = 2
The detailed pile calculations are given in Appendix B.
5.
Design Calculations
5.1
General
Diameter of Compression pile : 1500 mm with design load of 900 ton
Diameter of Tension piles : 1200m with design load of 400 ton
Estimated pile length = 19m socketing 3 times diameter into hard stratum of SPT> 50
5.2
Preliminary Load Tests Analysis
Compression load tests and pull out tests were carried out at the Interchange bridge site to
assess the performance of the piles installed to the design lengths.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 7
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
(a)
West Abutment
The tension Test Piles (No.81) located on the west abutments satisfied the per
formance criteria. Based on Prof Chin's Stability Plot:
Ultimate load
: 1141 tonne
Average Unit Shaft Friction
16 tonne/m2
The compression Test Pile No. 15 located ont the west abutments satisfied crite
ria at work load and 2 x work load but just failed to satisfy the recovery criteria.
Based on stability plot.
Ultimate capacity
: 2,490 tonne
Ultimate Shaft capacity
1,945 tonne
Mobilised Toe capacity
548 tonne
Ultimate Unit Shaft Resistance
39 tonne/m2
Mobilised Unit Toe Resistance
310 tonne/m2
Based on these assessment, piles were constructed to following toe elevations:
Compression Piles
: RL 33.00
(5m longer than Test Piles)
Tension Piles
(same length as Test Pile)
(b)
RL 31.00
East Abutment
Tension Pile No. 71 was tested. Pile satisfy the deflection criteria at working load
but however failed to attain the 2 x working load without excessive movement.
Based on Stability Plot, the following capacitities can be estimated:
Ultimate Shaft capacity
624 tonne
Unit Shaft Resistance
9 tonne/m2
This is much less than the 16.0 tonne/m2 value of tension pile No. 81. Based on
the evaluated value of 9.0 tonne/m2, all remaining working tension
piles are installed to RL 21.00 toe level, l O.Om longer than the test pile.
Compression pile No. 65 was first tested. It failed to satisfy the performance cri
teria. Estimated capacities are:
Ultimate capacity
: 1600 tonne
Ultimate Shaft capacity
625 tonne
Ultimate Toe capacity
1041 tonne
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 8
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Unit Shaft Resistance
12 tonne/m2
Mobilised Unit Toe Resistance589 tonne/m2 Based on above results, Test Pile
No. 2 (Pile No.66) located 4.50m from P65 was installed to toe level RL 33.00
(5.Om longer). Theoretical ultimate capacity should be of the order of 1,900
tonnes. The test showed the following:
Ultimate capacity
: 1520 tonne
Ultimate Shaft capacity
730 tonne
Mobilised Toe capacity
790 tonne
Ultimate Unit Shaft Resistance
10 tonne/m2
Mobilised Unit Shaft Resistance
447 tonne/m2
These are less than values obtained from P65, indicating significant variation in the sub
soil strength. Concreting procedures are satisfactory and concrete batch records
and test indicate supplied concrete complied with the requirements of the specification.
Concreting volume of pile does not indicate occurrence of collapse of borehole or neck
ing. Since the pile was concrete immediately after boring, strength relaxation due to
aging should not occured.
Based on above, all remaining piles are to be installed to toe levels 23. Pile No. P52 will
be test to assess amount of pile head movement at working load and 2 x working load.
Estimated ultimate capacity of piles to toe level RL 23.00 is order 2,100 tonnes.
(c)
Results of loads tests carried out at Interchange No. 3 are shown in Figure T1 to
T.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 9
Road B -15
= 2*Nave (SI-Unit s)
fs
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
62
61
60
59
58
57
26
27
28
29
30
39
38
37
36
35
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
47
47
32
32
28
28
31
31
29
29
23
23
17
17
16
16
16
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
32.5
32.5
32.5
32.5
31
31
23.5
23.5
21.5
21.5
23
23
22
22
19
19
16
16
15.5
15.5
15.5
C o r r ect ed
37.53
36.28
34.95
33.52
31.98
30.33
28.54
26.6
24.5
22.2
21.71
21.18
20.58
19.92
19.26
18.53
18.2
17.82
17.54
17.21
16.68
16.05
15.39
14.56
13.93
13.08
12.5
11.63
10.33
7.75
N ave
A ver ag e
75.06
72.57
69.9
67.04
63.96
60.65
57.08
53.21
49
44.41
43.43
42.35
41.16
39.83
38.53
37.06
36.4
35.64
35.08
34.42
33.36
32.1
30.78
29.13
27.86
26.17
25
23.25
20.67
15.5
f s=2 N
141.37
136.66
131.95
127.23
122.52
117.81
113.1
108.38
103.67
98.96
94.25
89.54
84.82
80.11
75.4
70.69
65.97
61.26
58.55
51.84
47.12
42.41
37.7
32.99
28.27
23.56
18.85
14.14
9.42
4.71
As
10612
9917
9223
8529
7837
7146
8456
5767
5080
4395
4093
3792
3491
3191
2905
2620
2401
2184
1984
1784
1572
1361
1160
961
788
817
471
329
195
73
Qs
U LT I M A T E S HA F T R E S I S T A N C E
1. Correct ed N = 15 + 0.5 (N-15), f or N up t o and equal t o 4 t imes N=50
25
Not e:
24
20
45
41
19
40
18
47
46
23
17
48
42
16
49
21
15
51
50
22
14
52
43
13
53
44
11
12
54
63
10
64
55
65
56
D ep t h
Level ( m)
SPT
B ored pile diamet er
Db
2.00
1.20 met ers
FS f or f rict ional res
FS f or base resist ain 3.00
A llowable load = A b*qf / 3 + A s*f s/ 2
A llowable load = Ult imat e load along base/ 3.0 + Ult imat e load along shaf t / 2.0
Nave = average spt value wit h dept h
= SPT value at base
= pile circumf erence (m^2)
As
= 400*Nb(SI-Unit s)
qf
Nb
= base area (m^2)
Ab
R ed uced
where
(WEST SIDE OF THE CENTRE LINE OF THE ROA D)
P ILE LE N G T H E S T IM A T IO N A LO N G T H E IN T E R C H A N G E # 3
75
75
75
75
70
64
59
54
48
43
36
30
29
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
21
20
19
18
17
15
14
13
13
12
10
Nb
30000
30000
30000
30000
27875
25750
23625
21500
19300
17100
14525
11950
11400
10850
10375
9900
9450
9000
8775
8550
8275
8000
7625
7250
6925
5825
5571
5233
5000
4650
4133
q f =4 0 0 N b
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
1.767
Ab
53014
53014
53014
53014
49259
45504
41749
37994
34106
30218
25668
21117
20145
19174
18334
17495
16700
15904
15507
15109
14623
14137
13474
12812
12237
10294
9846
9248
8836
8217
7304
Qb
U LT I M A T E E N D B E A R I N G R E S I S T A N C E
17671
17671
17671
17671
16420
15168
13916
12665
11369
10073
8556
7039
6715
6391
6111
5832
5567
5301
5169
5036
4874
4712
4491
4271
4079
3431
3282
3083
2945
2739
2435
B ase
5306
4958
4611
4265
3918
3573
3228
2883
2540
2197
2047
1896
1746
1596
1453
1310
1201
1092
992
892
786
681
580
480
394
308
236
164
97
37
S haf t
22977
22630
22283
21936
20338
18741
17144
15548
13909
12270
10602
8935
8461
7987
7564
7141
6767
6393
6161
5928
5660
5393
5072
4751
4473
3739
3517
3247
3043
2776
2435
T o t al ( kN )
A LLO W A B LE LO A D
B oring B H-11(West side)
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 47
V .Sof t clayey silt SPT 2
V .Sof t clayey silt SPT 2
V .Sof t clayey silt SPT 2
St if f clayey silt SPT 29
St if f clayey silt SPT 23
M ed clayey silt SPT 17
M ed clayey silt SPT 16
B oring
B H-13(Eest side)
24
26
2
0
22
20
16
14
12
10
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
V .St if f clayey silt SPT
V .St if f clayey silt SPT
V .St if f clayey silt SPT
St if f clayey silt SPT 11
St if f clayey silt SPT 7
M ed clayey silt SPT 9
M ed clayey silt SPT 6
Dept h(m) RD Level 25.75m
6
4
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
V .St if f clayey silt SPT 39
V .St if f clayey silt SPT 39
St if f clayey silt SPT 12
M ed clayey silt SPT 11
M ed clayey silt SPT 10
Soil Invest igat ion Ph:l
28
26
24
22
20
18
16
14
12
10
RD Level 66.50m
B H-13(West side)
Dept h(m)
B oring
18
Soil Invest igat ion Ph:ll
28
26
24
22
20
18
16
14
12
10
Dept h(m) RD Level 64.89m
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
34
36
38
40
42
44
46
48
50
52
54
56
58
60
62
64
66
68
Level(m)
Reduced
S UB S O IL P R O F ILE A LO N G T H E B R ID G E LO C A T IO N
A ppe ndix B
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
Page 10
Road B -15
= 2*Nave (SI-Unit s)
fs
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
26
27
28
29
30
-1
-2
-3
-4
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
38
38
32
31
21
21
11
11
11
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
32.5
32.5
32.5
32.5
26.5
26.5
23.5
23
18
18
11
11
11
C o r r ect ed
39.82
38.65
37.4
36.05
34.61
33.06
31.38
29.56
27.59
25.43
23.07
20.48
17.61
16.78
15.85
14.81
13.63
12.71
11.65
10.67
9.55
8.7
7.67
7.25
6.71
5.4
4.5
N ave
A ver ag e
79.65
77.3
74.79
72.11
69.22
66.12
62.76
59.13
55.17
50.86
46.14
40.95
35.21
33.56
31.71
29.63
27.27
25.43
23.31
21.33
19.09
17.4
15.33
14.5
13.43
12
10.8
f s=2 N
113.1
109.33
105.56
101.79
98.02
94.25
90.48
86.71
82.94
79.17
75.4
71.63
67.86
64.09
60.32
58.55
52.78
49.01
45.24
41.47
37.7
33.93
30.16
26.39
22.62
18.85
15.08
11.31
7.54
3.77
As
9008
8451
7895
7340
6785
6231
5678
5127
4576
4027
3479
2933
2389
2151
1912
1675
1439
1246
1054
885
720
590
462
383
304
226
163
102
60
23
Qs
U LT I M A T E S HA F T R E S I S T A N C E
1. Correct ed N = 15 + 0.5 (N-15), f or N up t o and equal t o 4 t imes N=50
25
Not e:
24
20
19
18
23
17
16
10
21
15
11
22
14
12
13
13
11
12
15
14
10
17
18
16
22
19
23
24
25
21
26
20
D ep t h
Level ( m)
SPT
B ored pile diamet er
Db
2.00
1.20 met ers
FS f or f rict ional res
FS f or base resist ain 3.00
A llowable load = A b*qf / 3 + A s*f s/ 2
A llowable load = Ult imat e load along base/ 3.0 + Ult imat e load along shaf t / 2.0
Nave = average spt value wit h dept h
= SPT value at base
= pile circumf erence (m^2)
As
= 400*Nb(SI-Unit s)
qf
Nb
= base area (m^2)
Ab
R ed uced
where
(WEST SIDE OF THE CENTRE LINE OF THE ROA D)
P ILE LE N G T H E S T IM A T IO N A LO N G T H E IN T E R C H A N G E # 3
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
70
64
59
54
48
42
35
29
27
25
22
20
18
16
14
12
10
Nb
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
27875
25750
23625
21500
19075
16650
14075
11475
10750
10025
8950
7875
7100
6225
5500
4650
4050
3450
2900
2686
2400
2160
1800
1600
q f =4 0 0 N b
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
Ab
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
31528
29123
26719
24316
21573
18831
15918
12978
12158
11338
10122
8906
8030
7040
6220
5259
4580
3902
3280
3037
2714
2443
2036
1810
Qb
U LT I M A T E E N D B E A R I N G R E S I S T A N C E
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
10509
9708
8906
8105
7191
6277
5306
4326
4053
3779
3374
2969
2677
2347
2073
1753
1527
1301
1093
1012
905
814
679
603
B ase
4504
4226
3947
3670
3393
3116
2839
2563
2288
2013
1740
1467
1195
1075
956
838
720
623
527
442
360
295
231
191
152
113
81
51
30
11
S haf t
15814
15535
15257
14980
14702
14425
14149
13072
11996
10920
9845
8658
7472
6381
5282
4890
4499
3997
3496
3119
2707
2369
1984
1718
1452
1206
1094
956
844
690
603
T o t al ( kN )
A LLO W A B LE LO A D
B oring B H-11(West side)
M ed clayey silt SPT 16
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 47
V .Sof t clayey silt SPT 2
V .Sof t clayey silt SPT 2
V .Sof t clayey silt SPT 2
St if f clayey silt SPT 29
St if f clayey silt SPT 23
M ed clayey silt SPT 17
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
V .St if f clayey silt SPT 39
V .St if f clayey silt SPT 39
St if f clayey silt SPT 12
B oring
B H-13(Eest side)
24
26
2
0
22
18
16
14
12
10
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
V .St if f clayey silt SPT
V .St if f clayey silt SPT
V .St if f clayey silt SPT
St if f clayey silt SPT 11
St if f clayey silt SPT 7
M ed clayey silt SPT 9
M ed clayey silt SPT 6
Dept h(m) RD Level 25.75m
20
4
M ed clayey silt SPT 10
M ed clayey silt SPT 11
Soil Invest igat ion Ph:l
28
26
24
22
20
18
16
14
12
10
RD Level 66.50m
B H-13(West side)
Dept h(m)
B oring
Soil Invest igat ion Ph:ll
28
26
24
22
20
18
16
14
12
10
Dept h(m) RD Level 64.89m
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
34
36
38
40
42
44
46
48
50
52
54
56
58
60
62
64
66
68
Level(m)
Reduced
S UB S O IL P R O F ILE A LO N G T H E B R ID G E LO C A T IO N
A ppe ndix B
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
Page 11
Road B -15
= 2*Nave (SI-Unit s)
fs
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
29
30
19
18
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
32.5
32.5
32.5
32.5
32.5
C o r r ect ed
68.15
67.92
67.67
67.41
67.13
66.83
66.5
66.15
65.76
65.34
64.88
64.38
6..82
63.19
62.5
61.72
60.83
59.82
58.65
57.29
55.68
53.75
51.39
48.44
44.64
39.58
32.5
32.5
32.5
32.5
32.5
N ave
A ver ag e
136.29
135.83
135.34
134.82
134.26
133.65
133
132.29
131.52
130.68
129.76
128.75
127.63
126.39
125
123.44
121.67
119.64
117.31
114.58
111.36
107.5
102.78
96.88
89.29
79.17
65
65
65
65
65
f s=2 N
113.1
109.33
105.56
101.79
98.02
94.25
90.48
86.71
82.94
79.17
75.4
71.63
67.86
64.09
60.32
56.55
52.78
49.01
45.24
41.47
37.7
33.93
30.16
26.39
22.62
18.85
15.08
11.31
7.54
3.77
As
15414
14850
14287
13723
13160
12597
12034
11471
10908
10346
9784
9222
8661
8100
7540
6980
6421
5864
5307
4752
4198
3647
3100
2558
2020
1492
980
735
490
245
Qs
U LT I M A T E S HA F T R E S I S T A N C E
1. Correct ed N = 15 + 0.5 (N-15), f or N up t o and equal t o 4 t imes N=50
28
20
Not e:
26
27
21
25
22
24
23
20
28
24
19
29
23
18
30
25
17
31
21
16
32
22
15
33
27
14
34
26
12
13
35
11
37
36
10
38
40
39
41
45
44
46
47
42
48
43
D ep t h
Level ( m)
SPT
B ored pile diamet er
Db
2.00
1.20 met ers
FS f or f rict ional res
FS f or base resist ain 3.00
A llowable load = A b*qf / 3 + A s*f s/ 2
A llowable load = Ult imat e load along base/ 3.0 + Ult imat e load along shaf t / 2.0
Nave = average spt value wit h dept h
= SPT value at base
= pile circumf erence (m^2)
As
= 400*Nb(SI-Unit s)
qf
Nb
= base area (m^2)
Ab
R ed uced
where
(WEST SIDE OF THE CENTRE LINE OF THE ROA D)
P ILE LE N G T H E S T IM A T IO N A LO N G T H E IN T E R C H A N G E # 3
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
75
70
64
59
54
48
45
40
33
33
33
Nb
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
30000
27875
25750
23625
21500
19375
17857
15833
13000
13000
13000
q f =4 0 0 N b
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
1.131
Ab
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
33929
31526
29123
26719
24316
21913
20196
17907
14703
14703
14703
Qb
U LT I M A T E E N D B E A R I N G R E S I S T A N C E
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
11310
10509
9708
8906
8105
7304
6732
5969
4901
4901
4901
B ase
7707
7425
7143
6662
6580
6298
6017
5735
5454
5173
4892
4611
4330
4050
3770
3490
3211
2932
2653
2376
2099
1824
1550
1278
1010
746
490
368
245
123
S haf t
19017
18735
18453
18171
17890
17608
17327
17045
16764
16483
16202
15921
15640
15360
15080
14800
14520
14242
13963
13686
13409
12332
11257
10185
9115
8050
7222
6337
5146
5023
4901
T o t al ( kN )
A LLO W A B LE LO A D
M ed clayey silt SPT 16
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 47
V .Sof t clayey silt SPT 2
V .Sof t clayey silt SPT 2
V .Sof t clayey silt SPT 2
St if f clayey silt SPT 29
St if f clayey silt SPT 23
M ed clayey silt SPT 17
B oring
B H-13(Eest side)
24
26
2
0
22
18
16
14
12
10
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
V .St if f clayey silt SPT
V .St if f clayey silt SPT
V .St if f clayey silt SPT
St if f clayey silt SPT 11
St if f clayey silt SPT 7
M ed clayey silt SPT 9
M ed clayey silt SPT 6
Dept h(m) RD Level 25.75m
20
4
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
Hard clayey silt SPT 50
V .St if f clayey silt SPT 39
V .St if f clayey silt SPT 39
St if f clayey silt SPT 12
M ed clayey silt SPT 11
M ed clayey silt SPT 10
RD Level 66.50m
Soil Invest igat ion Ph:l
28
26
24
22
20
18
16
14
12
10
Soil Invest igat ion Ph:ll
28
26
24
22
20
18
16
14
12
10
Dept h(m)
B H-13(West side)
B oring
B oring B H-11(West side)
Dept h(m) RD Level 64.89m
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
34
36
38
40
42
44
46
48
50
52
54
56
58
60
62
64
66
68
Level(m)
Reduced
S UB S O IL P R O F ILE A LO N G T H E B R ID G E LO C A T IO N
A ppe ndix B
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
Page 12
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Pile Design Report
Page 13
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Pile Design Report
Page 14
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Pile Design Report
Page 15
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Pile Design Report
Page 16
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
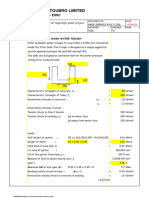
5)
Check for buckling load
Qub
Where
Qub
Allowable Qb
Cu El
CU
=
=
10
15 kPa
210 kN/mm2
1/64 B (d14 - d24)
15 x 210 x
B (101.64 - 85.444)
64
106
10
907 kN
907
___
2
454 kN > 300 kN
OK
6) Check for elastic compression
e
PL
P
L
=
=
300 kN
10m
EP
31416 mm2
Ep
= 35.3 kN/mm2
300 x10 x103
31416 x 35.3
3 mm
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 17
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Sample Pile Design Calculations
1.
Project :
KKS Road Project
Piled Embankment for the approaches to Sg. Likas
Bridge.
2.
Generalized subsoil profile.
Piled embankment
Sand Lenses
C
L
Bridge
V.soft to soft clay
Stiff to hard
Sandstone/shale
3.
Flat alluvial formation
Top 24m consists of soft to very soft alluvium with few localized sandy lenses (Cu =
10-20 kPa with an average of about 15 kPa except at lenses of sand). Stiff to hard
strata of about 2 - 4m thick overlying on highly to moderately weathered
sandstone/shale bedrock. WT is near the ground surface.
Analysis
Stability and settlement analysis have concluded that simple ground treatments by partial
sand replacement with high strength woven polyester geotextile reinforcement or vertical
drains are not possible to achieve FOS = 1.5 and or post construction settlement to be less
than 200mm for the first 5 years of service if height of embankment exceeds 4.2m.
Piled raft embankment is adopted in preference to EPS, elevated structure and stone column
treatment because:
a)
EPS embankment is technically not acceptable because the site is subject to flooding
& the cost is high.
4.
b)
Elevated structure is about 30% more expensive (separate analysis)
c)
Though treatment by stone columns is cheaper, it requires longer time to consolidate
and technically less superior
Design calculation
Analysis has shown that driven R.C piles will be the most cost effective.
The site has no vibration or noise or ground heave constraints. Pile capacity of about
600 kN is chosen to get optimum pile spacing of 2 to 3m and raft thickness of 350 450mm for pile depth of about 30m.
Use 250X250 R.C piles at spacing "x" bothways Max design capacity - 625 kN.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 18
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Load on each pile = x2.d.h, where
625
= x2.20.h
x
For h
For h
For h
For h
For h
=
=
=
=
=
=
x
d
=
=
=
=
spacing
soil density
20kN/m3 h
embankment height
(31.25/h)1/2
6.5m, x = 2.19m, say 2.0m
6.0m, x = 2.2m, say 2.0m
5.5m, x = 2.38m, say 2.25m
5.0m, x = 2.50m, say 2.25m
4.5m, x = 2.64m, say 2.25m (allow some traffic load of 10 kPa)
Conclusion:
Use 250x250 R.C x 30m long at 2.0m spacing for h=6.5 - 6.0m & 2.25m spacing for h = 4-6m
(Pile capacity calculations enclosed).
R.C piles (MS 1314, Class 1) are designed as end bearing piles driven to set.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 19
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Pile Design Report
Page 20
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Design of Micropile
a) Design load per pile
b) Diameter of micropile
c) Main reinforcement
= 800kN
= 200mm
= 3 Nos of 50mm diam. deformed bars of yield
stress fy = 410N/mm2.
d) Factor of safety
= 2.5 (min)
= 20N/mm2.
e) Grout characteristic strength, fcu
Check Structural Capacity
= B/4 x 502 x 3
= 5892mm2
= 20N/mm2
Area of reinf, Asc
fcu
= B /4 x 2002
= 31,416mm2
= 31,416 - 5892
= 25,524mm2
Area of grout, Ag
..Area of net grout
According to BS 8110, clause 3.8. 4.3
Ultimate axial load, Pu = 0.4 fcu Ac + 0.75Asc fy
= 0.4x20x25,524 + 0.75x5892x410
= 2,016kN.
.. Factor of safety
= Pu/800
= 2.53
> 2.5 O.K.
Check Bond Length Required
- Depth of micropile = 20m
At least l0m will be embedded in very hard decomposed granite SPT, N > 50.
-
Bond between grout & hard formation = 0.4N/mm2
..
Min required bond length in hard
formation, Ib = 800 x 2.5 x l 000N
B x 200 x 0.4
= 7958mm
= 8.0m.
< 10m provided O.K.
Design of M.S. Plate for Pile Head
Use 250mm x 250mm x 20mm M.S. plate
Stress on plate
= 800 x l03N
250 x 250
= 12.8N/mm2
< 155N/mm2 O.K.
(allowable stress BS449)
Details of Micropiles & works specification are encl
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 21
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
Works Specification for Design and Installation of
200mm Diameter Micropiles
1.
Scope of work shall include design & installation of 200mm diam micropiles of 20m provi
sional length. The micropiles shall be reinforced with 3 Nos. of 50mm diam deformed bars
(fy = 410N/mm2) The working load of the micropile is 800KN.
2.
Drilling
Initial drilling involves installation of 242mm diam conductor casing through loose soil
(about 1.5m) by means of rotary boring or equivalent. Upon reaching hard/stiff formation
down the hole hammer will be used to advance the borehole till a minimum penetration of
10m in very hard decomposed granite. The drilled hole will be flush clean by compressed
air before the reinforcement bars are inserted into the hole. Suitable coupling device will be
used. During drilling, a complete record of soil strata will, be taken for Engineer's inspec
tion.
3.
Grout Mix
Ordinary Postland cement with water cement ratio of 0.5 will be used Non-shrink cement
admixture will be added to improve bonding.
4.
Grouting Procedure
A high speed Koken grout mixer is used for the mixing of the cement grout. The capacity
of the grout mixer is about 25-0 litres.
For grout mixing, 100 litres of water with some non shrink admixture is poured into the
mixer follow by 4 bags of 50 kg. ordinary Portland cement then allow to mix throughly,
normally a few minutes. After mixing, the cement grout, a pressure hose is connected to the
grouting pipe which acts as tremie pipe for grouting. The other end of the pressure hose is
connected to a diesel engine high pressure pump.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 22
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Pile Design Report
Page 23
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Micropile Design Calculations
Micropile design for underpinning works for an old building is shown as follows. The subsoil consists of about 3m of very soft clay, 5m to 8m of stiff to hard sandy clay with gravels (SPT = 11 to
42). The bedrock generally consists of highly weathered and fractured sandstone/shale (RQD = 0 25%, UCS = 7.5 Mpa).
1)
Micropile details
Diameter of micropile
Design load of micropile
Pipe diameter
Pipe wall thickness
Steel grade (API pipe)
=
=
=
=
=
Yield strength
= 500 N/mm2
(a)
200 mm
300 kN
101.6 mm
8.08 mm
N80
Check for structural capacity
Ultimate structural capacity
PU = B (101.62 -85.44 2) X 500 kN
4
1000
= 1187 kN
Applying factor of safety of 2.5.
Allowable structural capacity.
PA
= 1187
2.5
= 475 kN > 300 kN
OK
(b)
Check for geotechnical capacity
Based on boreholes BH1 and BI-12, the depth of bedrock (sandstone/shale) varies
from 8.7 m to 11.0 m b.g.l. Since the overburden soil consists of about 3.0 m of very
soft soil, the shaft friction on the remaining overburden soil (5 to 8 m) with N value
of 11 to 42 should be ignored and the micropiles are designed to be socketed into the
bedrock.
The socketing length in rock, L, is worked out as follows:
FS Qa
0.05 qa B D x L + 0.5qa B D2
4
where FS is the factor of safety
=
2.5
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 24
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Qa
qa
= Allowable geotechnical capacity
= Unconfined compressive strength of rock
= 7.5 Mpa for sandstone/shale
Bond stress
D
2.5 x 300
= 5% of UCS of rock
= Diameter of micropile hole
= 0.05 x 7.5 x 103 x B x0.2 L +
0.5 x 7.5 x 103 x B x 0.22
4
750
L
= 235.6 L + 117.8
= 2.68 m
Designed socketing length of pile = 3.0 m
2)
Check overall underpinning pile support
Estimated total load of the whole building (3 storey).
=
2,000 tons
No. of micropile points
Load on each pile
= 95
= 2,000
95
= 21 tons
Working load for each micropile provided = 30 tons
OK
3)
Check for anchorage bond between underpinning pile and the existing foundatic
Since epoxy grout is used to fill the hole formed by the micropile in the existir foundation
and the strength of epoxy grout is much higher than the concrete strength, it can be consid
ered as monolithic for the whole foundation.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 25
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Critical section
for shear check
Existing
Column
Stump
650mm
Proposed 200mm
micropile
100
mm
1900mm
4)
Check for shear failure of existing foundation.
Perimeter for shear check, p
= 1900 mm
Effective depth of foundation, d = 1050-50-10
= 990 mm
Maximum reaction load,
Shear stress, V
= 300 kN
= V
Pd
= 300 x 103
1900 x 990
= 0.16 N/mm2
From Table 3.9, BS 8110 for d > 400 mm and
100As/bd = 0.25 (nominal reinforcement), allowable shear stress Vc = 0.40 N/mm2
V<Vc
OK
In grouting operation, the cement grout is pumped into the borehole through the pipe by
tremie method. All loose material, cuttings and water in the borehole are displaced by the
cement grout. Pressure applied should be just adequate to displace the cutting and water
from the borehole. Temporary casings should be withdrawn where cement grout overflow
from the casing and top up cement grout if necessary.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 26
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Item
No.
A.
Description
Quantity Unit
Rate
Design and install cast in-situ 800kN working
capacity micropiles complete with
reinforcement as shown on the drawings in
provisional lengths 20.0m and pressuregrouted with and including approved grouting
material, drilling in all types of soils and
rock and all coring casings, linings, plugs,
etc. and disposal of all excavated material
and debris from site.
Design information:a)
b)
c)
d)
Diameter of piles: 200mm
Main bars: 3Y50
Links: R05 helical link @ 100mm c/c
Steel casings: 292mm O.D x 9mm thick
e) Grout: Cement grout, w/c = 0.5, fcu = 20N/m2
f) Grout additives: Non shrink admixture
g) Factor of safety : 2.5
h) Bond strength: 0.9N/mm2
i) Bond length: 10m
j) Ultimate load: 2016kN
k) Capacity: 800kN
l) Working load: 800kN
m) etc
Design and install all capping plates and
starter bars
Design information:-
B.
Plate size: 250 x 250mm
Plate thickness: 25mm
Starter bar size: 3Y50 or 8Y25
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 27
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Projek :
Cadangan Blok Tambahan pada Hospital
Bersalin di Hospital Besar, K.Lumpur.
1.0
Tujuan
Laporan ini bertujuan untuk menyampaikan laporan penyiasatan tanah dan syor-syor
asas yang sesuai bagi:Projek blok tambahan pada hospital bersalin, Kuala Lumpur.
2.0
Skop Projek
Perlaksanaan projek ini melibatkan pembinaan blok tambahan 2 tingkat di Hospital
Bersalin. Blok yang dicadangkan ini dikelilingi oleh bangunan sedia ada.
3.0
Keadaan Tanah
3.1 Sebanyak 3 ujian gerekan dalam telah dijalankan. Hasil ujian menunjukkan
keadaan lapisan tanah seperti berikut :Jenis Tanah
SPT (blows/ft.)
Ukurdalam(m)
0 - 4.5
Very soft CLAY
0-4
4.5 - 9/10.5
Loose SAND
1-7
9/10.5-13.5/16.0
Stiff silt or CLAY
1-9
13.5/16.0
Limestone
RQD = 73 - 100%.
>16.0
Limestone
3.2
4.0
Kedudukan aras air bawah tanah ialah 1.45m.
syor-syor Asas
4.1 Penapak konkrit tetulang adalah tidak sesuai kerana keupayaan galas yang rendah
dan jugs paras air bawah-tanah adalah tinggi.
"Driven R.C. or steel piles" adalah juga tidak sesuai kerana masalah "noise &
vibration" dikawasan Hospital sukar diterima. "Inclined bedrock" juga mungkin
mengakibat "excessive pile deviations".
Syor-syor asas yang dicadangkan adalah seperti berikut :-
Jenis Bangunan
Jenis Asas
Saiz Panjang Keupayaan
(mm)
(m) galas yg
dibenarkan
Blok Tambahan Cerucuk
200
16.5-19 200kN mikro
with 102
(micropile) API paip
(4)
Geseran
Kulit
negatif
Beba
Ujian
400kN
4.2
Cerucuk mikro hendaklah digerudi sehingga ke paras batukapur dan dikunci
(key) minima 3m ke dalam batukapur.
4.3
Sekurang-kurangnya 2 bilangan cerucuk digunakan untuk setiap tiang.
4.4
Jack pile (200x200xl5m) juga boleh diterima sebagai cerucuk gantian.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 28
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
5.0
Syor-syor Tambahan
5.1 Jika rongga (cavity) ditemui, cerucuk hendaklah dipanjangkan
melebihi rongga dan dikunci (keyed) minima 3m ke dalam batukapur
tanpa rongga. (rujuk Fig. 1).
5.2
6.0
Pile Design Report
Untuk mengatasi masalah penanaman micropile dirongga, penender mestilah
diarah mengemukakan cadangan sistem 'micropile installation' dan teknik-teknik
'grouting' dirongga semasa tawaran dibuat.
Hal-hal lain
Satu set rekod penanaman cerucuk-cerucuk yang diuji berserta ujian beban hendaklah
dihantar ke Unit Makmal bagi tujuan dokumentasi.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 29
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Lampiran A
Micropile Specfication
1.
General
The work involves the construction of 200mm (8") diameter micropile. The micropile shall
be fabricated using steel tube and the bond length of micropile shall be 16m or directed
by the S.O. The working load of micropile is 200 kN and factor of safety used in design is
2.0. The whole of work and materials shall be in, accordance with curreht Malaysian or
British Standard or other National Standards approved by the S.O.
2.
Reinforcement
Steel grade - HFS 16 (BS: 1775 - 1964)
External diameter 139mm (51/2)
Thickness - 9.5mm (3/8") 2
Yield strength - 250 N/mm (16 Tsi)
3.
Grout
The grout shall be thcFoughly mixed with Ordinary Portland Cement (MS522) and water
(MS28). The grout shall be Antishrink cement grout. The water cement ratio shall be 0245 0.50. The 28 days. Strength for cement grout shall be 25N/mm (3570 psi). The representa
tive cubes shall be collected on each day of grouting works for testing on the 28th days.
Details of admixture shall be submitted to the S.O. for approval before commencement of
works. The use of the admixture shall comply with instruction by the manufacturer & MS
922. The grout shall be free from segregation, slumping, & bleeding of water and fine
materials during and after placing.
4.
Installation
a)
Drilling
The drilling for installation of micropile shall guarantee the absence of Vibration
which may cause damage to the existing building. Adequate precaution must be
taken to ensure boreholes for micropile do not collapse during drilling.
If necessary, temporary casing shall be used. During drilling of borehole, the con
tractor shall maintain complete record of soil profile. The logging shall include
depth of soil and water table. This drilled hole Viand! soil bore log shall be
signed by contractor's site representative and a copy of which shall be deposited
with the S.O. The contractor shall be required to keep representative sample of
soil for each soil profil in plastic bag for inspection by.the S.O. Sample may only
be disposed after the S.O. is satisfied that the logging has been properly done.
The type-of drilling equipment shall be approved by the S.O. The drilled hole
shall be flushed ckean.with air or water.
b)
Fabrication of micro pile
Method of splicing of bars or pipes shall be approved by the S.O. Centralisers at
about 3m centre must be used to ensure a minimum cover of 25mm or directed
by the S.O.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 30
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
c)
Pile Design Report
Grouting
The contractor shall also provide details on method and equipment used in grout
mixing. Further information such as grouting pressure, grouting procedure, grout
ing equipment and techniques employed in grouting under water shall also be
furnished and approved by the S.O.
'To prevent deterioration of strength of soil, soil coring, installation of reinforce
ment and cement grouting shall be carried out in one continous operation.
5.
Load Testing
Micro-pile shall be load tested to 2 times design load using the Maintain Load Test.
Minimum of one (1) load test shall be carried out. The contractor shall also specify and pro
vide details of the method of load testing. Micropile shall be constructed only after the pre
liminary pile pass the load test requirements of JKR standard specification for building
Works.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 31
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Contoh Jadual Sebut Harga
Bil.
1
Description
Unit
Quantity
Rate
MICROPILES
(ALL PROVISIONAL)
A.
B.
Allow for Preliminaries
Item
Provide all necessary piling
equipment on site, maintain on site,
dismantle and remove from site on
completion, allow for all standing
or idling time and cost of operation
for the whole of piling works.
C.
Item
Installation of 200mm diameter
Micropiles in soil, including coring,
4" diameter pipe, steel plate head,
jointing and extension and grouting
MR
in cement, all as specified (50
positions)
D.
Provide all necessary pile testing
equipment on site, dismantle and
remove from site on completion.
T est 200mm diameter Micropiles in soil
as specified.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
NO
Page 32
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Lampiran E1
Pile Design
for
SMK (Perempuan Raja Zarina)
Kelang
1.
This project consists of construction of one additional 3-storey school block.
2.
Max column load = 57 ton
3.
This is a typical coastal alluvium site where first 60ft to 100 ft consists of very soft clay
4.
Deep Sounding is very suitable and 4 nos of D/S results give consistent results as shown in
Lampiran E-1
5.
The site is a flat land and the first 4 ft is imported fill (about 5 years ago) Negative friction
has to be checked.
6.
Selection of piles (Refer to Fig. 1)
6.1 Non displacement piles not suitable because of low column load and very soft clay
near the first 100 ft.
7.
6.2
Timber pile also not suitable bacause its max length is about 40 ft. only.
6.3
Use 12" x 12" x 100 ft R.C. piles Design load = 30 Ton/pile (max)
Check Pile Capacity (Refer to Lampiran E-1)
From D/S results
Qu
= Qs + Qp
where Qu
= ultimate capacity
Qs
= skin friction
Qp
= end resistance
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 33
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
7.1
Skin friction, Qs
Based on total friction (remoulded)
At 30m (100ft), total friction = 3,000 kg.
Qs
= tube friction x-pile perimeter
tube perimeter
= 3,000 x (12" x 2.54 x 4)
11.3
= 32,300 kg
= 30 Ton.
Based on local friction (undisturbed)
Qs
= (8.5 x 0.05 + 7.5 x 0.13 + 13 x 0.27 + 0.9) x 3.28 x 4 x 0.92
= 70 Ton
Sensitivity = Qs (undisturbed)
Qs (remoulded)
= 70
30
= 2.3, within usual range
Q's = " Qs, where " = 0.7 (Bjerrum)
= 0.7 x 70
= 49 Ton
7.2
End Resistance, Qp,
Qp = 80 (kg/cm2) x 1 ft2 x 0.92
= 73.6 Ton
Qu = 49 + 73.6
= 122.6 Ton
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 34
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
7.3
Negative friction
Negative friction for piles at spacing more than 3 x diameters is
fn
0.2 Po (Bjerrum)
where Po
= effective overburden
= h
= 100' (100psf - 62.4 psf)
= 3760 psf
Max. fn
= 0.2 Po
= 0.2 x 3760
= 752 psf
Average fn
= (0 + 752)/2
= 376 psf
Total negative friction
7.4
=
=
=
=
fn x As
376 x (100 x 4)
150,400 lb
67 Ton
Allowable load, Qs
The negative skin friction, QN should only considered in combination with dead
load because QN acts mainly at the lower portion of the pile and would only affect
the settlement.
2.5 QD.L = Qu - QN
QD.L = 70% Qa
2.5 x 0.7Qa = Qu - QN
Qa
= (Qu - QN) /1.75
= (122.6 - 67)/1.75
= 31 Ton
say 30 Ton/pile
Notes :
The filling is done about 5 years ago. At least 60 - 70% consolidation com
pleted.
fn used is about the same as the undrained shear strength. Hence QN estimated is on the
light side.
To prevent tensile stress and buckling during driving, free drop hammers is preferred.
8.
Recommendation
Use 12" x 12" x 100 ft R.C. piles
Friction piles, driven to the required pene:,tration and load test to verify the capacity. (No
"set" required).# Load tests after 4 weeks of driving.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 35
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Pile Design Report
Page 36
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Memo
Daripada:
Penolong Pengarah Makmal,Caw. Rekabentuk & Penyelidikan, IP. JKR
Kepada:
Penolong Pengarah(Binaan), Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L.
Bil surat:
(X) dlm. PKR.RB 4112
Tarikh :
26.3.1983
Per: Cadangan Masjid Baru di Batu 31/2, Jalan Cheras, K.L.
Berhubung dengan perkara yang tersebut di atas, sukacita dimaklumkan bahawa cadan
gan asas yang disyorkan adalah seperti berikut:1.
Keputusan penyiasatan tanah
Sebanyak 28 Nos. Proba JKR dan 5 Nos. Deep Boring telah dijalankan ditapak projek
itu. Keputusan - keputusan yang diterima menunjukkan bahawa kawasan projek ini
adalah terdiri daripada batu kapur. Paras batu kapur adalah daripada 2.5m hingga 14m
daripada paras permukaan tanah sedia ada. Oleh kerana keadaan batu dasar yang susah
untuk diramalkan, langkah-langkah pengawasan dan faktor keselamatan yang lebih
tinggi perlu diambil di dalam rekabentuk asas.
2.
2.1
Syor-syor asas
Jenis - jenis asas yang disyorkan adalah seperti dicatitkan di dalam Lampiran A.
Sebelum kerja - kerja piling dimulakan sekurang - kurangnya satu ujian Proba JKR
perlu dijalankan di setiap kedudukan tiang untuk menentukan paras batu dasar (>400
blows/kaki). Sekiranya paras batu dasar didapati kurang daripada 4.5m dibawah per
mukaan bumi, adalah dicadangkan supaya menggunakan R.C.cylinder foundation
(sila lihat Lampiran A & B)
2.2
Sekurang - kurangnya 2 cerucuk perlulah digunakan ditiap-tiap kedudukan tiang
kecuali jika R.C.cylinder foundation digunakan. Tiap - tiap tiang hendaklah diikat den
gan rasak bawah dikedua - dua arah. Ini adalah sebagai langkah awas oleh kerana terda
pat rongga - rongga dan kemungkinan masalah surutan.
2.3
Untuk memperolehi pengawasan yang lebih baik semasa memacu cerucuk tukul jatuh
bebas(free drop hammer) dicadangkan supaya digunakan. Ini ialah supaya cerucuk tidak
menerima hentaman dan menyimpang berlebihan (overdriving and excessive deviation)
oleh kerana keadaan batu dasar yang mencerun (inclined bedrock surfaces).
2.4
Hujung cerucuk keluli hendaklah dikelulikan dengan plat yang lebih. Ini adalah perlu
untuk menahan tegasan yang berlebihan (withstand overstressing) apabila cerucuk sam
pai ke paras batu dasar.
2.5
Sekurang - kurangnya 2 nos. kumpulan cerucuk (pile group, NCT single pile) perlulah
dipilih untuk ujian beban. Satu set driving records dan keputusan ujian beban hendak
lah dihantar kepada Unit Makmal ini untuk analisa dan sebagai rekod di Unit Makmal.
2.6
Perhatian hendaklah diberi kepada pengalaman yang lepas iaitu cerucuk - cerucuk tam
bahan mungkin diperlukan untuk menggantikan cerucuk - cerucuk yang menyimpang
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 37
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
berlebihan dan cerucuk - cerucuk yang masih tidak set diparas yang dalam (>10m).
Adalah dicadangan supaya tambahan sebanyak 25m disertakan didalam B.Q.
2.7
Oleh kerana keadaan tanah yang rumit (tricky) jurutera tapak bina hendaklah selalu
rujuk kepada keputusan penyelidikan tapak semasa menyelia kerja - kerja pembinaan
asas. Apabila cerucuk dijangka sampai paras batu dasar, kejatuhan pemukul (drop of
hammer) hendaklah dikurangkan. Tujuan langkah ini ialah untuk better keying & bed
ding effect on rock surface. Langkah ini juga akan mengurangkan cerucuk daripada
menyimpang berlebihan.
Sekian disampaikan ulasan kami untuk tindakan tuan selanjutnya.
Berkhidmat Untuk Negara
......................................................
(Ir. Neoh Cheng Aik),
Jurutera Kerja Kanan (R1),
bp. Penolong Pengarah (Makmal),
Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 38
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Lampiran A
Cadangan Asas Untuk Pro jek
Mas jid Batu 31/2, Jalan Cheras,K.L.
1.
Bangunan Masjid (13T - 105T)
Sila gunakan cerucul; keluli 203mm x 203mm x 45kg/m (Grade 43A9 BS 4360) den
gan beban keupayaan 210 0/eerucuk. Untuk tujuan tawaran, panjang cerucuk ialah 8.5m
(27ft) ATAU "R-C- cylinder foundation".Sila lihat Para 2.1
2.
Bangunan Quarters Kelas G(9T - 16T)
Sila gunakan eerucuk I-,yu berubat (treated timber pile) 125m x 125m dengan beban
keupayaan 5W/oerucuk. Untuk tujuan taviarany panjang cerucuk ialah 8.5m (27 ft).
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 39
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Pile Design Report
Page 40
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
Lampiran E 5
Extension of Terminal Building, Subang Airport
1.
General
The project consists of extension of International and Domestic Transper Corridor for
Subang International Airport. The proposed-site is situated approximately 13 miles west of
Kuala Lumpur.
Due to the close proximity of the proposed site to the existing terminal building v where the
Control Tower for the airport is located, severe vibration such as driving piles is unaccept
abldo Bored and Cast-in-situ piles were considered most suitable.
2.
Soil Condition
The site consists of residual soils of granite.
Lampiran E5-1 represents the generalised poil profile. The top layer of the soil consists of
brown firm sandy silty clay with some organic matters. The depth of this top soil varies
from 6" to 2ft. Beneath this top soil underlies the yellowish with patches of grey medium
sandy clayey silt with some gravelse This medium sandy clayey silt extend to a depth of 40
to 85 ft. below R.L. 86.00'. Between these layers of medium sandy clayey silt and the frac
tured or slightly weathered granite bedrocksq lies the greyish very stiff decomposed granite
residual soil. The thickness of this decomposed granite residual soil varies. Water table is
about Oft. b.g.l.
3.
Load Settlement Criteria
The system of piling to be designed shall meet the followings:a) Safety Factor
The factor of safety for the purpose of computing the working load shall be taken
as 2.5.
b) Working Load
The working load adopted for single pile shall not be greater than the ultimate
load divided by the safety factor of 2.5 and the ultimate load is defined as:
(i)
Load at which the gross settlement continues to increase without any further
increase in load.
(ii)
Load at which gross settlement is 10% of the pile diameter.
c) Settlement Criteria
(i)
Gross settlement of the pile at working load during the first cycle of load
ing, loading to one time working load, shall not exceed 0.5".
(ii)
The residual settlement of the pile at the end of the first cycle of loading
shall not exceed 0.10".
(iii)
The gross settlement of the pile at twice the working load shall not exceed
1.5"
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 41
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
d) Group Effect
Negligible because of small group (2 or 3 pile per group) & large spacing 2.5 .
4.
Structural Capacity of Piles
Since piles are not fully reinforced, the structural capacity of the piles will be solely depend
on the concrete section of the piles* In this case, the pile is reinforced for the top 40ft.
only for the dispersion of the possible slight bending moment elperienced at the pile top.
The piles will be designed as short columns. According to CP 2004, the structural carrying
capacity of Cast-in-situ concrete pile, that is, the safe working load per pile, W
W - 1/4 (Acc.Uw)
5.
Where Acc
Uw
=
=
=
Gross cross section of the area of concrete
Specified cube crushing strength at 28 days.
3000 psi.
For d
d
d
=
=
=
18, max. structural load =
24, max. structural load =
30, max structural load =
80 Ton.
150 Ton
230 Ton.
Check Pile Capacity
Use 18" bored piles x85 ft max. Meyerhofs formula (modified) is applicable for bored
piles in residual soil
Qu
Qs + Qp
=
=
fs As.+ Op Ap
N As + N. Ap
50
where N =
average SPT along pile shaft
average SPT near pile base (4 above pile base & 2 below pile base).
As
pile shaft area (ft2)
As
pile base area (ft2)
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 42
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Based on DB12
18" x 75'
= 0.32 TSF
16
fs = N
50
50
qp = 50 TSB
Qs
=
=
fs As
0.32 x (1.5' x 3.1416 x 75) = 113 Ton
Qp
50 x (1/4 x 1.52 x 3.1416) = 88 Ton
Qa
=
Qs/20 + Qp/3.0
=
56.5 + 29.3
=
85.8 Ton
say 80 Ton
Based on DB 10
18" x 55ft
N
20
fs
= 0.4 TSF
=
=
80
qp
= 80 TSF
0-4 x (1o5 x 301416 x 55)
Qp
80 x (1/4 x 1o5 x 1o5 x 3o1416) = 141 Ton
Qa
Qs/2.0 + Op/3.0 = 52 + 47
=104 Ton
= 99 Ton
say 80 Ton.
Based on DB 13
18 x 80ft.
N
23
fs
= 0.46 TSF
35
qp
= 35 TSF
Qs
0.46 x (1.5 x 3.1416 x 80)
Qp
35 x (1/4 x 3o1416 x 1o5 x 145) =62 Ton
Qa
Qs / 2.0 + Qp / 3.0
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
=173 Ton
=173/2 + 62/3.0
= 86 + 31
= 117 Ton
> 80 Ton.
Page 43
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
6.
Founding Level
Founding level should be determined by observing the soil type from the boring. Suitable
founding soil should be weathered granite bedrock or oompacted/cemented clayey silt with
gravels, or up to a max depth of eft'. In case of dou7gt, SPT should be carried in the bored
base.
7.
Recommendation
Use 18 bored pile Vrith max capacity 80 Ton per pile. Site engineer should use the DB
results to determine the founding level. Para 6 above can be used as a guide. 4 Nos load
tests should be carried out to verify the capacity.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 44
DB 13
DB 12
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
DB 10
DB 9
Loose clayey, silty sand
Hard, Fractured, Weathered granite
Stiff sandy clayey silt with gravels
Compact clayey silty sand with gravels
Sandy silty clay
Hard surface tarmac
DB 11
DB 8
Scale: Horizontal 3/16 to 480
Fig. 1 Soil Profile
DB 7
DB 6
DB 5
DB 4
DB 3
DB 2
DB 1
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
Page 45
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Lampiran E 6
1.
Objective
To design the foundation system for the proposed Dewan Orang Ramai in Kampung
Cheras Baru
2.
Introduction
2.1 The proposed.structure is a one-storey assembly-hall'situated on Lot 405 in
Kampung Ceras Baru, M11rim Ampang, Daerah Hulu Langat
2.2
Column loads
Maximum
Minimum
3.
- 68T
- 30T
Site Condition
3.1
Surface Condition
The terrain is generally flat. It was formerly an old building site that has been
cleared. Springs of water are visible which suggest the ground water table is
very near the ground surface. The only visible form of undergrowth are bushes
and shrubs.
3.2
Subsurface Condition
3.2.1
Referring to the geological map of Kuala Lumpur District (after Ting
and Ooi 1972)2, Kampung Cheras Baru is located in the Granite
region. Hence the soil is residual Gradite soil.
3.2.2
Scope of Site Investigation.
Initially 6 Nos of JKR Probes were performed by the district office of
JKR Hulu Langat. Due to the inconsistency of the probe results, a
more elaborate method of sub-soil exploration in the form of 3 Nos.
Deep Boring was done by the Unit Makmal Ibu Pejabat JKR.
Borehole positions are as indicated in Appendix B. From the borelog
results (APPENDIX C) the soil profile is not consistent along the three
boreholes. Generally) though, the sub-soil eonsists of interlayer
between sand, clay and stilt. The first 9 metres Appears to be com
prised of loose to medium dense sand and very soft-to firm clays (the
variation occuring with depth). Below 9m the soil seems to improve
from medium dense to very dense silts and sands as well as stiff to
very hard clays. The groundwater is very near to the surface and the
subsoil is assumed to be fully saturated.
3.2.3
Other Relevant Information.
Near to the proposed site of the hall, in a north, easterly direction is sit
uated a quarry. There is an access-road leading to the intended site but
it is in a bad state.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 46
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
4.
Foundation Analysis and Recommendation
4.1
Selection of type of foundation
With reference-to the results obtained from the S.I. done the first 5 metres com
prises of compressible material which is of insufficient strength to sustain the
intended imposed loads. Hence an ordinary shallow foundation in the form of a
pad footing would not suffice. A piled foundation system is warranted here in
order to transfer the loads to the stronger material found below 15m of the
ground-level. In selecting the particular type of pile'to be used, particular consid
eration has been made to
(a)
Cost.
(b)
Driving lengths
(c)
Resistance to hard driving.
(d)
Strength mf pile as structural member
(e)
Effectiveness in mobilising friction and end-bearing
(see T able 1)
Table 1 : Selection of Pile Type
T ype
Max. length
Resistance
Structural
Merit as
Merit as
Cost
of
of
to Hard
Capacity
frictional
end
(per m run)
pile
Driving possible
Driving
pile
bearing
(18m)
R.C.
Steel
pile
T imber X
Figures in box represents order of choise
e.g. 3 third choice
From Table 1, the most apparent' choice would be to use steel piles. However,
based on the soil variation (profile) and the intended loading system which is rel
atively small, the .use of steel' piles is overly conservative. Furthermore hard
driving is not expected.RC piles would be more appropriate in this case because;
(a)
it is more economical
(b)
RC piles would be able to mobilise sufficient safe end-bearing resistance
at a much shallower depth than would be necessary fdv its steel counter
part.
(c)
Due to its rougher surface texture RC piles can mobilise frictional resist
ance better than steel piles
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 47
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Hence RC Piles would serve better and cheaper than-steel piles as both a friction
al and end-bearing pile in this particular sub-soil condition.
4.2
Estimation of Ultimate Loads
4.2.1 Design Assumptions
(a)
The soil is fully saturated. In calculating the effective overburden pressure,
Pd, the values of X sat for the various soil categories are obtained from
Appendix B in Ref. 1 (Pg. 397).
(b)
For an SPT value of N 11p the undrained cohesion Cu, is assumed
approximately to be 125 lbs/ft ,
(c)
Due to the inconsistency in the soil variation for the three boreholes, the
piles were designed based on each individual borehole result and the worst
(or lowest)' calculated working load per pile was adopted for use.
(d)
The criteria for design was only to consider both frictional and end-bear
ing piles. Totally frictional or totally end-bearing-piles were not consid
ered.
(e)
Assumed that piles would achieve safe and bearing resistance in soil lay
ers with SPT values of N-~ 15 i.e. in medium dense coesionless soils or
stiff cohesive layers.
(f)
Factor of safety adopted is 2.5 (para 4.6 pg. 149 of. ref. 1)
(g)
Lower values of were assumed for silts as compared to sands.Generally,
(h)
Type of Silts
V.loose to loose
0 - 10
27 - 29
Medium Dense
10 - 30
29 - 34
Dense to V.Dense
30
34 - 39
In obtaining the end-bearing resistance in cohesion soils, the bearing
capacity factor No is taken to be 9 (Para 2 Pg. 122 Ref. 1)
4.2.2 Formulae Used in the Estimation of the Ultimate Loads
4.2.2.1 In Cohesionless Soil.
For frictional resistance
*Qs Avg. uni akin friction = is (1.) Ref. 1 Pg. 137 Para 4)
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 48
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
where
Qs a Ultimate akin resistance
As = .Area, of shaft
.
Avg. unit skin friction is obtained from Fig. 4.19
Pg. 139 of Ref. 1)
*The foriaula (Ref. 1 Pg. 136 Eln. 4.13)
Qs = 1/2 K, Pd tan As is not applicable in this
particular case because it becomes invalid for
penetration depths/width ratios 10-20 for straight
sided piles (Ref. 1 Pg. 137)
For End-Bearing
Qb = Pd Nq Ab
(2) (Ref. 1 Pg. 135 Eqn.4.12)
where
Qs = Ultimate End,-Bearing Resistance.
Pd = Effective Overburden Pressure
Nq = Bearing Capacity Factor
(obtained from Berezantsevs' Curves in Ref. 1 Pg 134
Fig. 4.14 (b) )
Ab = Area of pile base
It should be noted that value of Qb at penetration depths of 20
diameters is taken as the peak value for ultimate end bearing
resistance but shall not exceed 100 tons/ft2.
4.2.2.2
In Cohesive Soil
For frictional resistance
Qs = Cu As
- (3) (Ref. 1 Pg. 123 Eqn. 4o5) ,
where
Qs = Ultimate skin resistance
= adhesion factor (taken - 1)
Cu = Average undisturbed undrained cohesion of
soil surrounding pile shaft
As = Area of shaft
For End-bearing resistance
Qs = No Cb Ab - (4)(Ref. 1 Pg. 122 Eqn. 4.2)
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 49
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
where
No = Bearing Capacity factor (taken = 9)
Cb = Undisturbed undrained cohesion of soil at pile
toe
Ab = Area of pile base
4.2.3 Recommendation
Scope of work done on S.I. were 6 Nos. JO -Probes and 3 Nos. Deep
Boring. On compilation of the results, the soil profile was generalized as
Table 2 : Generalized Soil Profile
Soil Type and Condition
Depth (m)
0-9
Loose sand and soft clay
9 - 13
M. Dense Silts and firm clay
> 13
Dense/V.Dense silts and
firm /stiff/v.stiff clays
follows:A piled foundation system was selected instead. of shallow foundation in
order to transfer the loads onto the stronger layers at the lower depths.
RC piles were chosen and- designed to be partly frictional and partly endr
bearing. Trids were done with 15" s 15", 12" z 12" and 10" = 10" RC
Pile size
Penetration
Working loads (Tons/pile)
Depth (m)
BH 1
BH 2
BH 3
15" x 15"
21.5
101
12" x 12"
20
69
37
42
21.5
70
40
52
16.5
32
28
31
19.5
42
26
31
10" x 10"
Table 3 : Summary of Analysis
piles. The results are summarised in the table below.
It should be noted that due. to the inconsistency of the soil variation of the
three boreholes done, the design was based on each individual borehole.
From the analysis done, it was decided to use a combined system of RC
piles driven to a depth of 2090m below formation level in order to opti
mise the cost of pile installation and prevent the problem of eccentricity
between columns and single pile foundation system during construction.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 50
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Hence the recommended system is as follows:For the-loading range of
(a)
30T - 40T - Use 10" _ .10" RC pile with a working load of
20T/pile driven to a depth of 20m below forma
tion level.
(b)
4.3
40T - 70T
- Use a minimum of 2 Nose 12" = 12" piles with a
working load of 35T/pile driven to a depth of 20m
below formation level.
Settlement Analysis
In this particular project, the concern for settlement would be over
(a) settlement of the pile toe
(b) settlement of the sub-soil due 'to the surcharge weight of the fill material.
4-3.1
In the case of (a), settlement checks were not done as the piles are not totally fric
tional and generally the recommended foundation system would result in only 2
Nos* of piles to a . group. Furthermore, work done by X.Je Tomlinson have
shown that for piles of small to medium (up to 600mm) diameter the settlement
under the working load will not exceed 10mm or 3/8" if the safety factor is not
lower than 2.500..-00.00. (Ref- 1 Pg. 149)
4.3.2
Settlement. of tho sub-soil due to the surcharge weight of the fill material
4.3.2.1 Essumptions made
(a)
Soil layers with an SPT value of N48 were taken as compressible lay
ers
(b)
Depth of compressible layer = 12m,
(c)
Effective area of fill was approximated to be the same as the plan area
of the proposed Dewan Orang Ramai
i.e. B - 17m and L . 321x.
(d)
Depth of fill was not constant throughout the site. This is because the
original ground level is not the same over the intended site.
0.3m
Plane DB 2
qf2
DB 2
Plane DB 3
0.6m
qf3
Formation Level
DB 3
1m
O.G.L
qf1
DB 1
Fill Material
12m
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Compressible Layer
Page 51
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Below is a schematic presentation of the fill depth and area.
(e)
The bulk density of the fill material was assumed to be 18 bulk
(f)
The borehole positions were taken as the points of consideration in
estimating the settlement of the soft layer due to the surcharge weight
of the fill, i.e. Points DB1,'DB2 and DB3
(g)
With regards to (e), the generalized surcharge weights over the'respeo
tive points in a plane orientation (see Fig. 1) areaPlane DB1; qf1 - 18 kN/m2
Plane DB2; qf2 - 6 kN,/m2
Plane DB3; qf3 - 12 kN/m2
(h)
The compressible soil was classified as type CL under the Casagrande
classification system
(i)
Liquid Limit of the soil was assumed to be 35%
(j)
Voids ratio assumed to be 0.7
(k)
The Compression Inde= Cc was obtained from the relationship cc o 0.009
(Lw - 10%)
where Lw = liquid limit-of the clay
(Eqn. 2.24 Ref. 3 Pg. 128)
4.3.2.2
Estimation of settlement
To obtain the average immediate _settlement the method of Janbu, Jerrum and
Kjaernsli was adopted where
Average settlement = p1 = U1 U1 of B ....(5)
E
U1 Uo are obtained from Refs 1 Pg. 180 Fig. 5.10
qf = net surcharge of the fill
B = width of fill area
E = Modulus of Elasticity of clay
Values of E were obtained from Ref. 1 Pg. 186 BU- 5 .17
For Consolidation Settlement, Terzaghils conventional 1-D consolidation theory
was used.
So = Co
1 t e,
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
H. Log Po +z ......(6)
Po
Page 52
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
where,
Co = Compression Index
Eo = Initial voids ratio
H = Thickness of compressible layer (m)
Po = Effective overburden pressure (kN/m2)
z =
Value of vertical stress at depth considered (kN/m2)
Values of were obtained from
z = qfI o
.... (7) (Ref. 4 Pg. 223)
Where qf = surcharge of fill
Io = Influence factors obtained from Padumts Chart (Ref. 4 .Fgi 224 Fig.
7.2)
4.3.2.3
From the settlement analysis. done on the effect of the surcharge weight of the fill material, the following were obtained
settlement under plane DB1 - 92mm (3.6")
settlement under plane DB2 - 30am (1.2")
settlement under plane DB3 - 232 am (9")
(centre of fill)
Obviously, there is substantial total and differential settlement of the soft layer
due to the effect of the fill surcharge.
In the light. of this estimation, it is advisable to design a suspended floor for the
proposed structure and to use tie-beams (ground beams) for the foundation sys
tem (tied in two cUreotions) in order to have a more rigid structure.
4.4
Load Testing Requirement
4.4.1
2 nos. of load tests are recommended in accordance with JKt siandard
specificationsiUnit Malarial are to be advised of the date the loading
tests are to be done and copies of the results are to be cent to Unit
Makmal for purposes of monitoring and records.
4.4.2
The test loadings should be done at least 4 weeks after the test piles are
driven, to fully mobilise frictional resistance between soil and pile
interface.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 53
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
4.5
Associated Designs
4.5.1
Requirements of fill material and its commotion Soil should be of suit
able selected fill material. The H.S. 1377 s 1972 method shall be used
as the standard compaction test for determining the moisture density
relationship of the soil. The selected material should have liquid limit
values less than 35 (LL 35) and values of plasticity index less than 55
(Pole L 55)-The -field density after compaction shall be determined in
accordance with the "Band Replacement Method" or AASHO T205-64
(Rubber Balloon Method). The fill shall be compacted to a density of
not less than 95% of the ma3d!m,m dry density as determined by the
Standard Compaction Test.
The type of compacting equipment to be used shall be subject to the
approval of the Superintending Officer.
4.5.2
Structural Recommendations
In order to deal with the expected settlement of the soft sub-soil due to
the surcharge of the fill material, it is advisable to design a suspended
floor system for the structure.
Further precautions should be taken in the form of tying the columns
in two-directions with ground beams so as to' haves. more rigid struc
ture.
5.
Conclusion
From the-analysis done based on assumptions laid down in Clause ~4.2.1, the recommen
dations are
i) For the load range of
30T - 40T Use 10'1 x 10" RC piles with a working load of 20T/pile
40T - 702'
Use a minimum of 2 Nos 12" x 12" piles with a working load of
35T/pile:
ii) The piles shall function as partly frictional and partly end-bearing.
iii) Piles are to be driven to set below the formation level
iv) Specify tender lengths to be 20m and an additional 10% should be added to the number
of piles specified in the BQ or summary of tender to cater for pile deviations during
driving.
v) Use suspended floor and tie beams are to be provided in two directions between the col
umn positions.
6.
Appendices
Appendix A : Location Plan
Appendix B :
Layout plan showing locations of site investigation
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 54
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Appendix C :
7.
Generalized soil profile Borelog Results
Bibliography
Ref. 1
:
PILE DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION PRACTICE M. J. TOAIIINSON
VIEWPOINT PUBLICATION
Ref. 2
MALAYSIAN SOILS AND ASSOCIATED PROBLEKS
- DR. 001 TECK AUN
Ref. 3
FOUNDATION RESIGN AND CONS'T'RUCTION
- M.J. TOMLINSON
PITMAN INTEMATIONAL TEXT 3rd Edition
Ref. 4
ELEMENT OF SOIL MECHANICS - G. N. SMITH
CROSBY LOW00D STAPLES 4th Edition
'
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 55
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
33.05
28.5
22.5
13.5
9.0
6.0
4.0
5.0
Hard silty clayey
Basalt(Boulder)
Hard clayey silt
-32.1
-30.6
Hard clayey silt N=50
V.Stiff clayey silt N=35
Stiff clayey silt N=18
Firm silty clay N=8
Soft silty clay N=4
Med. dense silty sand N=21
Loose silty sand N=2
V.soft silty clay N=1
25.50
19.50
15.00
13.50
12.00
9.00
7.50
5.00
6.00
2.45
3.15
29.45
Med. dense to loose silty sand
Proposed Pile
Granite
V.dense silty sand N>50
Hard clayey silt N=40
Hard silty clay N=30
Stiff silty clay N=15
Firm silty clay N=7
Firm silty clay N=14
Firm silty clay N=5
Sofy sandy silt N=4
V.Loose silty sandy N=2
Loose silty sand N=2
V.soft silty clay N=2
V.soft silty clay N=0
V.Loose silty sandy N=2
-34.25
-21.6
28.70
27.00
18.00
18.00
4.50
2.00
3.00
Granite
Sandy silt N>50
Quartzite and decomposed granite
Hard clayey silt N>50
V.stiff clayey silt N=24
Stiff clayey silt N=15
Firm clayey silt N=4
V.loose silty sand N=1
Loose silty sand N=5
V.soft silty clay N=2
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
Page 56
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
Cadangan Syor asas untuk Projek Rumah
Kediaman Kelas 'G' Penjara Penor, Kuantan, Pahang.
1.
Introduction
The project site is located off the Pekan - Kuantan trunk road. From the site plan an earth
filling of 1' to 5' is proposed for the whole site. The project consists of construction of
6 Blocks of JKR Standard 5-storey Class G Quarters.
2.
Site Conditions
6 nos of boreholes were carried out to determine the subsoil conditions. The sub soil con
sists of soft silty clay with organic matters from ground level to 6m below ground level.
From 6m to 12m below ground level the soil consists of loose silty sand with decayed mat
ters and from 12m to 28m the soil is of loose to medium stiff sandy clay with SPT N aver
ages from 6 to 12. From 28m_to,36m the soil strata consists of dense sandy'silt with traces
of gravel. SPT N ranges from 18 to 50.
3.
Geotechnical Evaluation
Due to the 1' to 5' of fill, consolidation settlement may occur for the compressible layers of
soil. Hence negative skin friction on piles is to be accounted for.
12" x 12" r.c. piles are evaluated for the bearing capacities. It is found that the founding
depths of the piles varies from 28.5m to 36m.
The following table is abstracted from the calculations for which the estimated founding
depths Ultimate loads (Qu) and allowable loads (Qa) are tabulated. A factor of safety of 2.5
and negative skin friction of 16 tons are used in the calculations.
BH nos.
Estimated depths
Ultimate load
Allowable load
(m)
Qu (tons)
Qa = Qu/2.5 - Qn
1
33
197.54
65.59
2
31.5
178.65
55.03
3
28.5
166.84
50.31
4
28.5
183.87
57.12
5
36
208.56
67.00
6
35
204.62
65.42
From the above it is noted that the calculated bearing capacities of the 12" x 12" r.c. piles
ranges from 50.00 to 67 tons. Hence it is proposed that 12" x 12" JKR r.c: piles of Grade 40
concrete be used.
The allowable working load of the 12" x 12" JKR r.c. piles shall be 49 tons per pile.
Calculations for the geotechnical evaluations for the 6 boreholes are attached.
4.
Conclusion
12" x 12" JKR Standard R.C. piles grade 40 with tender length of 36m shall be used.
Allowable load per pile is 49 tons.The estimated negative friction load is 16 Ton per pile.
Hence the test load shall 2 x (49 + 16) = 130 Tons. At least 4 piles shall be selected for load
tests.
All piles are designed as end bearing piles. All piles shall be driven to set which can be
achieved at about 28.5m to 36m below ground level.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 57
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cadangan Kelas G, Penjara Penoh, Kuantan, Pahang.
Evaluation of 12 x 12 reinforced concrete pile.
Borehole 1
Depth
(m)
Soil Description
Top soi l, soft
clayey silt
1.5
Loose clayey silt
Ditto
4.5
6
S.P.T
(Na)
Fs
Ap
(ft)
Qs
(Tons)
Qs
(tons)
Fb
Ab
(sq ft)
Qb (tons)
Qu
(tons)
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Loose clayey silt
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
7.5
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
10.5
Soft silty clay,
traces of sand
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
12
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
13.5
Ditto
2.5
0.05
0.98
0.98
20
20.00
20.98
8.39
15
Stiff silty clay,
traces of sand
5.5
0.11
2.16
3.15
24
24.00
27.15
10.86
16.5
Ditto
0.14
2.76
5.90
32
32.00
37.90
15.16
Qa
(tons)
18
Ditto
7.5
0.15
2.95
8.86
28
28.00
36.86
14.74
19.5
Ditto
0.14
2.76
11.61
28
28.00
39.61
15.84
21
Ditto
6.5
0.13
2.56
14.17
24
24.00
38.17
15.27
22.5
Ditto
7.5
0.15
2.95
17.12
36
36.00
53.12
21.25
24
Ditto
18
13.5
0.27
5.31
22.44
72
72.00
94.44
37.77
25.5
Ditto
16
17
0.34
6.69
29.13
64
64.00
93.13
37.25
27
Ditto
30
23
0.46
9.05
38.18
120
120.00
158.18
63.27
28.5
Dense silty sandy
gravel
25
27.5
0.55
10.82
49.00
100
100.00
149.00
59.60
30
Ditto
24
24.5
0.49
9.64
58.65
96
96.00
154.65
61.86
31.5
Ditto
21
22.5
0.45
8.86
67.50
84
84.00
151.50
60.60
33***
*
Ditto
30
25.5
0.51
10.04
77.54
120
120.00
197.54
79.02
34.5
Ditto
50
40
0.80
15.74
93.28
200
200.00
293.28
117.31
36
Ditto
50
50
1.00
19.68
112.96
200
200.00
312.96
125.19
To calc. negative skin friction (Qn)
Qn = fn x As, where fn = 0.25 x Po /2
Po = (110 -62.5) x H x 3.28, where H = 12m =
Qn = 0.25 x Po /2 x As x H x 3.28/2240
1869.6
Allowable load Qa = (Qu/2.5 Qn) =
79.02
16.43
62.59
*** from borelog N = 50, use N = 3D only
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 58
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cadangan Kelas G, Penjara Penoh, Kuantan, Pahang.
Evaluation of 12 x 12 reinforced concrete pile.
Borehole 2
Fs
Ap
(ft)
Qs
(Tons)
Qs
(tons)
Fb
Ab
(sq ft)
Qb
(tons)
Qu
(tons)
Qa
(tons)
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Depth
(m)
Soil Description
Top soi l, soft
clayey silt
1.5
Loose clayey silt
S.P.T
(Na)
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
4.5
Loose clayey silt
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
7.5
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
10.5
Soft silty clay,
traces of sand
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
12
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
13.5
Ditto
0.04
0.79
0.79
16
16.00
16.79
6.71
15
Stiff silty clay,
traces of sand
11
7.5
0.15
2.95
3.74
44
44.00
47.74
19.10
16.5
Ditto
12
11.5
0.23
4.53
8.27
48
48.00
56.27
22.51
18
Ditto
9.5
0.19
3.74
12.00
28
28.00
40.00
16.00
19.5
Ditto
0.12
2.36
14.37
20
20.00
34.37
13.75
21
Ditto
4.5
0.09
1.77
16.14
16
16.00
32.14
12.86
22.5
Ditto
0.10
1.97
18.11
24
24.00
42.11
16.84
24
Ditto
0.12
2.36
20.47
24
24.00
44.47
17.79
25.5
Ditto
5.5
0.11
2.16
22.63
20
20.00
42.63
17.05
27
Ditto
24
14.5
0.29
5.71
28.34
96
96.00
124.34
49.74
28.5
Dense silty sandy
gravel
26
25
0.50
9.84
38.18
104
104.00
142.18
56.87
30
Ditto
24
25
0.50
9.84
48.02
96
96.00
144.02
57.61
31.5
Ditto
30
27
0.54
10.63
58.65
120
120.00
178.65
71.46
33****
Ditto
50
40
0.80
15.74
74.39
200
200.00
274.39
109.76
34.5
Ditto
50
50
1.00
19.68
94.07
200
200.00
294.07
117.63
36
Ditto
50
50
1.00
19.68
113.75
200
200.00
313.75
125.50
To calc. negative skin friction (Qn)
Qn = fn x As, where fn = 0.25 x Po /2
Po = (110 -62.5) x H x 3.28, where H = 12m = 1869.6
Qn = 0.25 x Po /2 x As x H x 3.28/2240
Allowable load Qa = (Qu/2.5 Qn) =
71.46
16.43
55.03
*** from borelog N = 50, use N = 3D only
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 59
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cadangan Kelas G, Penjara Penoh, Kuantan, Pahang.
Evaluation of 12 x 12 reinforced concrete pile.
Borehole 3
S.P.T
Depth
(m)
Soil Description
0
1.5
Fs
Ap
(ft
)
Qs
(Tons)
Qs
(tons)
Fb
Ab
(sq ft)
Qb
(tons)
Qu
(tons)
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
(Na)
Top soil , soft clayey
silt
Loose clayey silt
Qa
(tons)
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
4.5
Loose clayey s and
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
7.5
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
10.5
Soft silty clay, traces
of sand
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
12
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
13.5
Ditto
0.08
1.57
1.57
32
32.00
33.57
13.43
15
Stiff silty clay, traces
of sand
8.5
0.17
3.35
4.92
36
36.00
40.92
16.37
16.5
Ditto
12
10.5
0.21
4.13
9.05
48
48.00
57.05
22.82
18
Ditto
10.5
0.21
4.13
13.19
36
36.00
49.19
19.67
19.5
Ditto
11
10
0.20
3.94
17.12
44
44.00
61.12
24.45
21
Ditto
9.5
0.19
3.74
20.86
32
32.00
52.86
21.14
22.5
Ditto
0.14
2.76
23.62
24
24.00
47.62
19.05
24
Ditto
5.5
0.11
2.16
25.78
20
20.00
45.78
18.31
25.5
Ditto
5.5
0.11
2.16
27.95
24
24.00
51.95
20.78
27
Ditto
30
18
0.36
7.08
35.03
120
120.00
155.03
62.01
28.5
Dense silty sandy
gravel
30
30
0.60
11.81
46.84
120
120.00
166.84
66.74
30
Ditto
50
40
0.80
15.74
62.58
200
200.00
262.58
105.03
31.5
Ditto
50
50
1.00
19.68
82.26
200
200.00
282.26
112.90
33
Ditto
50
50
1.00
19.68
101.94
200
200.00
301.94
120.78
34.5
Ditto
50
50
1.00
19.68
121.62
200
200.00
321.62
128.65
36
Ditto
50
50
1.00
19.68
141.30
200
200.00
341.3 0
136.52
To calc. negative skin friction (Qn)
Qn = fn x As, where fn = 0.25 x Po /2
Po = (110 -62.5) x H x 3.28, where H = 12m = 1869.6
Qn = 0.25 x Po /2 x As x H x 3.28/2240
Allowable load Qa = (Qu/2.5 Qn) =
66.74
16.43
50.31
*** from borelog N = 50, use N = 3D only ddedit
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 60
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cadangan Kelas G, Penjara Penoh, Kuantan, Pahang.
Evaluation of 12 x 12 reinforced concrete pile.
Borehole 4
Depth
(m)
Soil Description
Top soil , soft
clayey silt
1.5
Loose clayey silt
S.P.T
(Na)
Fs
Ap
(ft)
Qs
(Tons)
Qs
(tons)
Fb
Ab
(sq ft)
Qb
(tons)
Qu
(tons)
Qa
(tons)
4.5
0.08
1.51
1.51
36
36.00
37.51
15.00
Ditto
15
12
0.20
4.01
5.52
60
60.00
65.52
26.21
4.5
Loose clayey
sand
11
0.19
3.68
9.20
28
28.00
37.20
14.88
Ditto
0.09
1.67
10.87
12
12.00
22.87
9.15
7.5
Ditto
3.5
0.06
1.17
12.04
16
16.00
28.04
11.22
Ditto
0.00
0.67
12.71
0.00
12.71
5.09
10.5
Soft silty clay,
traces of sand
0.03
0.00
12.71
0.00
12.71
5.09
12
Ditto
2.5
0.00
0.84
13.55
20
20.00
33.55
13.42
13.5
Ditto
5.5
0.04
1.84
15.39
24
24.00
39.39
15.76
15
Stiff silty clay,
traces of sand
0.09
2.01
17.40
24
24.00
41.40
16.56
16.5
Ditto
0.10
2.34
19.74
32
32.00
51.74
20.70
18
Ditto
0.12
2.34
22.08
24
24.00
46.08
18.43
19.5
Ditto
10
0.12
2.68
24.76
40
40.00
64.76
25.90
21
Ditto
11
10.5
0.14
3.51
28.27
44
44.00
72.27
28.91
22.5
Ditto
10
10.5
0.18
3.51
31.78
40
40.00
71.78
28.71
24
Ditto
0.18
3.01
34.79
32
32.00
66.79
26.72
25.5
Ditto
0.15
2.68
37.47
32
32.00
69.47
27.79
27
Ditto
35
21.5
0.14
7.19
44.66
140
140.00
184.66
73.87
28.5
Dense silty sandy
gravel
32
33.5
0.37
11.21
55.87
128
128.00
183.87
73.55
30
Ditto
50
41
0.57
13.72
69.59
200
200.00
269.59
107.84
31.5
Ditto
50
50
0.70
16.73
86.32
200
200.00
286.32
114.53
33
Ditto
50
50
0.85
16.73
103.04
200
200.00
303.04
121.22
34.5
Ditto
50
50
0.85
16.73
119.77
200
200.00
319.77
127.91
36
Ditto
50
50
0.85
16.73
136.50
200
200.00
336.50
134.60
To calc. negative skin friction (Qn)
Qn = fn x As, where fn = 0.25 x Po /2
Po = (110 -62.5) x H x 3.28, where H = 12m = 1869.6
Qn = 0.25 x Po /2 x As x H x 3.28/2240
Allowable load Qa = (Qu/2.5 Qn) =
73.55
16.43
57.12
*** from borelog N = 50, use N = 3D only
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 61
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cadangan Kelas G, Penjara Penoh, Kuantan, Pahang.
Evaluation of 12 x 12 reinforced concrete pile.
Borehole 5
Depth
(m)
Soil Description
Top soil , soft
clayey silt
1.5
Loose clayey silt
S.P.T
(Na)
Fs
Ap
(ft)
Qs
(Tons)
Qs
(tons)
Fb
Ab
(sq ft)
Qb
(tons)
Qu
(tons)
Qa
(tons)
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
4.5
Loose clayey
sand
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
7.5
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
10.5
Soft silty clay,
traces of sand
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
12
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
13.5
Ditto
0.08
1.57
1.57
32
32.00
33.57
13.43
15
Stiff silty clay,
traces of sand
7.5
0.15
2.95
4.53
28
28.00
32.53
13.01
16.5
Ditto
6.5
0.13
2.56
7.08
24
24.00
31.08
12.43
18
Ditto
0.12
2.36
9.45
24
24.00
33.45
13.38
19.5
Ditto
6.5
0.13
2.56
12.00
28
28.00
40.00
16.00
21
Ditto
6.5
0.13
2.56
14.56
24
24.00
38.56
15.43
22.5
Ditto
0.12
2.36
16.92
24
24.00
40.92
16.37
24
Ditto
10
0.16
3.15
20.07
40
40.00
60.07
24.03
25.5
Ditto
13
11.5
0.23
4.53
24.60
52
52.00
76.60
30.64
27
Ditto
28
20.5
0.41
8.07
32.67
112
112.00
144.67
57.87
28.5
Dense silty sandy
gravel
32
30
0.60
11.81
44.48
128
128.00
172.48
68.99
30
Ditto
18
25
0.50
9.84
54.32
72
72.00
126.32
50.53
31.5
Ditto
22
20
0.40
7.87
62.19
88
88.00
150.19
60.08
33
Ditto
20
21
0.42
8.27
70.45
80
80.00
150.45
60.18
34.5
Ditto
21
20.5
0.41
8.07
78.52
84
84.00
162.52
65.01
36
Ditto
30
25.5
0.51
10.04
88.56
120
120.00
208.56
83.42
To calc. negative skin friction (Qn )
Qn = fn x As, where fn = 0.25 x Po /2
Po = (110 -62.5) x H x 3.28, where H = 12m = 1869.6
Qn = 0.25 x Po /2 x As x H x 3.28/2240
Allowable load Qa = (Qu/2.5 Qn) =
83.42
16.43
67 .00
*** from borelog N = 50, use N = 3D on ly
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 62
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cadangan Kelas G, Penjara Penoh, Kuantan, Pahang.
Evaluation of 12 x 12 reinforced concrete pile.
Borehole 6
Depth
(m)
Soil Description
Top soi l, soft
clayey silt
1.5
Loose clayey silt
S.P.T
(Na)
Fs
Ap
(ft)
Qs
(Tons)
Qs
(tons)
Fb
Ab
(sq ft)
Qb
(tons)
Qu
(tons)
Qa
(tons)
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
4.5
Loose clayey
sand
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
7.5
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
10.5
Soft silty clay,
traces of sand
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
12
Ditto
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
13.5
Ditto
10
0.10
1.97
1.97
40
40.00
41.97
16.79
15
Stiff silty clay,
traces of sand
8.5
0.17
3.35
5.31
28
28.00
33.31
13.33
16.5
Ditto
6.5
0.13
2.56
7.87
24
24.00
31.87
12.75
18
Ditto
6.5
0.13
2.56
10.43
28
28.00
38.43
15.37
19.5
Ditto
0.12
2.36
12.79
20
20.00
32.79
13.12
21
Ditto
4.5
0.09
1.77
14.56
16
16.00
30.56
12.23
22.5
Ditto
4.5
0.09
1.77
16.33
20
20.00
36.33
14.53
24
Ditto
11
0.16
3.15
19.48
44
44.00
63.48
25.39
25.5
Ditto
15
13
0.26
5.12
24.60
60
60.00
84.60
33.84
27
Ditto
27
21
0.42
8.27
32.87
108
108.00
140.87
56.35
28.5
Dense silty sandy
gravel
26
26.5
0.53
10.43
43.30
104
104.00
147.30
58.92
30
Ditto
16
21
0.42
8.27
51.56
64
64.00
115.56
46.22
31.5
Ditto
20
18
0.36
7.08
58.65
80
80.00
138.65
55.46
33
Ditto
18
19
0.38
7.48
66.12
72
72.00
138.12
55.25
34.5
Ditto
23
20.5
0.41
8.07
74.19
92
92.00
166.19
66.48
36
Ditto
30
26.5
0.53
10.43
84.62
120
120.00
204.62
81.85
To calc. negative skin friction (Qn)
Qn = fn x As, where fn = 0.25 x Po /2
Po = (110 -62.5) x H x 3.28, where H = 12m = 1869.6
Qn = 0.25 x Po /2 x As x H x 3.28/2240
Allowable load Qa = (Qu/2.5 Qn) =
81.85
16.43
65.42
*** from borelog N = 50, use N = 3D only
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 63
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Design Calculations of Bored Piles
& Pile Caps for Proposed SK
Taman Segar Cheras
1.
Introduction
The project consists of construction of 2 blocks. of 4-storey JKR Std. School buildings. The
site is generally flat with about 2m fill some 5 years ago. The generalized subsoil proper
ties are as follows:0 - 12m
:
loose clayey sand with localized very dense layer. Average SPT, N = 5.
12m - 17m :
medium to dense silty clayey sand, N = 16
17m - 27m :
very dense grey spotted yellowish fine to coarse silty sand with gravel
(N = 40 - 50). Water table 15m bgl.
No of colums per block is 44 and the columnload is about 78 Ton (max.)
Due to presence of localized very. dense cemented clayey sand with gravels at shallow
depth, very hard driving will encountered at shallow depth if driven piles are used.
Bored piles are considered more cost effective piling system in this case when compared
with other suitable piling system such as H piles (R.C. piles are Not suitable). Though the
site consists of sandy soil, the bored piles are considered suitable because water.table is low
and the residual soil is usually quite impermeable.
2.
Design Calculations
460mm diameter bored piles are proposed.
2.1
Design Criteria
2.2
Concrete Grade 25 for piles & caps
Design compressive stress = 4.8N/mm sq.
< fcu/4.
Longitudinal reinf provided is 1.0% for full bored shaft, i.e. 6Y20 & R9
@ 300mm c/c as helical reinforcement.
Installation procedure according to JKR spec (KPKR 6/1989).
max design load = 80 Ton.
max test load = 2 X design load.
Geotechnical Capacity
Use modified Meyerhof s equation:
Ultimate capacity, Qu = N1 As + K2 Ab
K1
K2
Where
N1
K1
K2
N2
As
Ab
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
=
=
=
=
average SPT value for shaft
50
1
average SPT valug at base
= surface area(ft2)
= base area (ft2)
Page 64
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Generalised Design SPT
0 - 17m, average SPT = 8
17m - 24m,average SPT = 40
Average SPT @ 24M = 50
.'. Total ultimate frictional resistance
Qs- Spx52x1.5xi1 +540 0 x22 x1.5xi1
= 39.2 + 82.9
= 122.1 Ton
Total ultimate end bearing
Qb = 50 x 1.52 x 11 /4 = 88.3 Ton
:. Qu =12.2.1+88.3 = 210.4 Ton
.'. Safe load Qa = 210.4/2.5 = 84.1 Ton
Say 80 Ton per bored pile (18" diam x 24m)
3.
Pilecap Design
Single Pilecap for Pile Diameter 460mm (18" Diam x 24m Bored Pile)
No. of Pile
Pile Diameter
=
1
= 460mm
Size of Pilecap
= 660 x 660 x 900mm
Steel Reinforcement
Main Bars
= 0.15% x b x d = 792mm2
.. Provide 4 Y 16 Bothways
Horizontal Links
.: Provide 3 Y 10
= 0.25% OF Main Steel Area = 100mm2
Quantities Per Cap
Excavation
Volume of Concrete
= 0.41 m3
= 0.39 m3
WT. of Reinforcement = 26.6 kg. (Y 16)
= 4.8 kg. (Y 10)
Lean Concrete
= .44 m2
Formwork
= 2.38 m2
Steel Content
= 134 lb/yd3
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 65
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Pile Design Report
Page 66
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
LAPORAN GEOTEKNIK
MAKTAB PER GUR UAN SRI PIN ANG ,
BUKIT MIER TAJAM,
SEBERANG PERA1,
PULAU PIN ANG
DISEDIAKAH OLEH :
IR. ANNIES MD. ARIFF
EH. AHMAD AZLAN AHMAD
(INSTITUT LATIHAN & PENYELIDIKAN JKR)
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 67
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pendahuluan
Laporan ini adalah 'bertujuan untuk menyampaikan keterangan ringkas sumbangan yang
telah diberi oleh Pusat ini di dalam menentukan
pemilihan asas-asas yang sesuai bagi bangunan-bangunan yang dicadangkan untuk projek
yang disebut di atas. Sumbangan ini. adalah
bersesuaian dengan peranan utama pusat ini
sebagai satu organisasi.sokongan kepada semua
cawangan di dalam JKR dalam hal- hal yang
bersangkut-paut dengan bidang geoteknikal.
Laporan ini akan' ketengahkan juga masalahmasalah parancangan yang dihadapi semasa
pusat ini menjalankan kerja penyiasatan -tapak
dan kerja merekabentuk asas yang sesuai bagi
bangunan bangunan yang terlibat
Bagi 'projek ini permintaan untuk menjalankan
penyiasatan tapak dan seterusnya'pen gesyoran
syor-syor asas telah dikemukakan oleh
Cawangan Kerja Pendidikan melalui surat
PKR(KP)MP/PP/87/17(102) bertarikh
27/02/1989.
Skop Projek
Pelaksanaan projek ini melibatkan pembinaan
32 bush bangunan dengan ketinggian bangunan-bangunan di antara 1-tingkat hingga 4tingkat. Lingkungan beban-beban tiang pula
adalah dari serendah-rendah 50.0 kN sehingga
setinggi 1800.0 kN. Penyediaan tapak melibatkan kerja-kerja pemotongan se dalam di
antara 0.0 hingga 6.Om dan penimbusan setinggi di antara 0.0 hingga 6.0m.
Butiran bangunan mengikut bilangan tingkat
adalah seperti berikut:1-tingkat
- 16 unit
2-tingkat
- 7 unit
4-tingkat
- 8 unit
Tangki Air - 1 unit
Skop Penyiasatan Tapak/Tanah
Berpandukan lukisan punca tatatur yang dikemukakan, satu skop kerja penyiasatan tapak,
berupa 33 bil. ujian gerekan dalam, 3 bil. ujian
gerimit tangan dan 89 bil. ujian proba
Mckintosh, telah dirancangkan. Perancangan
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
skop kerja penyiasatan tersebut dibuat
mengambilkira faktor-faktor berikut:i) Jenis bangunan serta beban-beban tiang yang
terlibat,
ii) Kegunaan bangunan,
iii) Ciri-ciri geology kawasan,
iv) Keadaan kawasan tapak,
v) Kerja-kerja tanah - potongan dan penimbu
san.
Selain dari perancangan skop kerja penyiasatan
kedudukan lokasi ujian-ujian juga dibuat dengan mengambilkira faktor-faktor yang disebutkan di atas.
Adalah dimaklumkan bahawa perkara (v) di
atas hanya dapat dibuat andaian sahaja semasa
perancangan skop penyiasatan tapak kerana
paras formasi tidak dinyatakan di dalam lukisan tatatur tersebut.
Oleh kerana projek ini telah dikelaskan sebagai
projek SEGERA dan memandangkan beban
kerja semasa unit penyiasatan tapak pusat ini
pada masa itu adalah terlalu banyak maka
keputusan telah dibuat supaya kerja-kerja
penyiasatan tapak ini dijalankan secara kontrak.
Juga bagi menjimatkan masa telah dipersetujui
bahawa tender kerja ini dilakukan secara lantikan terus. Kontraktor yang telah dilantik'
untuk menjalankan kerja-kerja ini adalah
Sekata Bina Sdn. Bhd. dengan kos kontrak
kerja terhad tidak melebihi $50,000-00.
Oleh yang demikian, kawalan kos yang ketat
telah dilakukan semasa kerja-.kerja penyiasatan
sedan& dijalankan bagi memastikan kos
keseluruhan kontrak ini tidak melebihi
$50,000-00.
Keputusan Penyiasatan Tapak
Berpandukan kepada peta Hydrogeologi
Semenanjung Malaysia tapak projek ini, iaitu
daerah Bukit Mertajam, adalah terletak di atas
formasi batu GRANIT yang diselubungi oleh
tanah jenis KELODAK/BERLIAT. Ini adalah
Page 68
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
berpadanan dengan keputusan penyiasatan
tapak/tanah yang diperolehi di mana tanah
bawahan adalah jenis tanah LIAT/KELODAK
dan berpasir. Tanah adalah dalam keadaan
sederhana kental hingga sangat kental di antara
paras dalaman 0.0 hingga 35.0m, dan keras
sehingga sangat keras pada -dalaman lebih dari
18.0m.
Kedudukan paras air bawah tanah semasa kerja
penyiasatan dijalankan (bulan Mac, 1989)
adalah di antara 1.55m hingga kering.
Rekabentuk Syor Asas
Pada amnya pemilihan jenis sistem asas adalah
berdasarkan kepada faktor-faktor berikut:a) kemampuan tanah bawahan menanggung
beban yang akan ditanggung berdasarkan
keupayaan galas yang dibenarkan yang '
dikira bersesuaian dengan keadaan tanah
bawahan dan juga ciri-ciri geologi
kawasan.
b) beban tiang dan jarak antara tiang
c) faktor keselamatan terhadap kegagalan dan
enapan yang dapat diterima pada beban
kerja struktur bagi memenuhi kehendak
'servicibilty limit state'
d) Kawalan mutu semasa pembinaan
Pile Design Report
tusan ujian-ujian tanah yang dibuat ditempat
kedudukan atau berdekatan dengan bangunan
yang terlibat. Walaubagaimanapun disebabkan
pindaan ke atas pelan punca projek ini, di mana
lokasi kebanyakan bangunan telah dialihkan,
maka terdapat bebarap ujian gerekan dalam
berada diluar kawasan tapak bangunan, malahan terdapat juga beberapa bangunan yang
tidak ada sebarang ujian penyiasatan tapak
dijalankan. Dalam hal demikian, pusat ini telah
membuat ekstrapolasi kepada keputusan-keputusan ujian tanah yang paling berdekatan dengan bangunan yang tiada sebarang ujian tanah,
dan mengunakan maklumat tersebut berserta
pengetahuan geologi kawasan bagi membuat
penganalisa geoteknik.
Berpandukan faktor-faktor di atas dan juga
keputusan penyiasatan tapak yang telah dibuat,
dua (2) jenis sistem asas telah direkabentuk
bagi projek ini. Dua (2) jenis sistem asas yang
dimaksudkan itu ialah asas penapak konkrit
dan alas cerucuk. Bagi sistem asas cerucuk dua
jenis cerucuk telah direkabentuk iaitu cerucuk
konkrit tetulang dan cerucuk kayu berubat.
Bagi sistem asas cerucuk daya tanggung cerucuk-cerucuk yang direkabentuk adalah dari
separa geseran badan (frictional) dan separa
tangouno hujung (end bearing) dan faktor keselamatan yang telah digunakan di dalam perkiraan adalah.2.0 serta menggunakan kekuatan
tanah dalam lingkungan batasan rendah.
e) Jenis struktur
f) tapak timbusan atau potongan
g) ekonomik
Oleh yang demikian sebelum menentukan
sebarang sistem asas yang hendak digunakan,
faktor-faktor di atas perlu diteliti terlebih dahulu bagi setiap bangunan supaya satu sistem asas
yang sesuai dan ekonomik dapat ditentukan.
Perlu dinyatakan disini bahawa di dalam hal
membuat perkiraan rekabentuk geoteknik
adalah mustahak ciri-ciri jenis tanah serta butiran kekuatan tanah-tanah yang dipilih di dalam
perkiraan rekabentuk diperolehi daripada kepuCawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Apa yang dimaksudkan dengan geseran badan
ialah beban yang ditanggung oleh cerucuk
berkenaan akan dipindahkan ke tanah melalui
rintangan geseran (frictional resistance) di
antara permukaan badan cerucuk dan tanah,
dan ini akan hanya terjadi sekiranya cerucul:
tersebut mengalami mendapan lebih dari mendapan tanah (relative settlement of pile is
greater than that of the soil). Maksud tanggung
hujung pula ialah beban yang ditanggung oleh
cerucuk akan dipindahkan ke tanah melalui
penghujung cerucuk (base of pile).
Contoh-contoh perkiraan rekabentuk kedua-dua
jenis sistem, asas ada seperti di dalam lampiran-lampiran 'A' dan 'B'.
Page 69
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
Bagi bangunan-bangunan yang mana telah
disyorkan lantai gantung keputusan-ini adalah
berdasarkan kepada beberapa faktor yang mana
adalah seperti di bawah:a) timbusan Yang akan dilakukan adalah ter
lalu tinggi,
b) Kegunaan bangunan.
Contoh perkiraan anggaran enapan tanah timbusan adalah seperti di dalam -Lampiran 'E'.
Senarai Lampiran
Lampiran 'A' - CONTOH PERKIRAAN
REKABENTUK GEOT
EKNIK BAGI CERU
CUK KONKRIT TETU
LANG
Lampiran 'B' - CONTOH PERKIRAAN
REKABENTUK GEOT
EKNIK BAGI PENAPAK
Lampiran 'C' -
SURAT SYOR ASAS
YANG TELAH DIKE
MUKAKAN KEPADA
CAW. KERJA PEN
DIDIKAN
Lampiran 'D'-
LAPURAN PENYIASA
TAN TAPAK YANG
TELAH DIJALANKAN
Lampiran 'E' - CONTOH PERKIRAAN
ANGGARAN ENAPAN
TANAH TIMBUSAN
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 70
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Lampiran 'A'
Pile Foundation Design for Administration Blocks (4-Storey)
Northern Block :
F.F.L. = 16.0m;
Fill = 0.5 to 1.0m
Central Block
F.F.L. = 17.5m;
Fill = 0.0 to 1.5m
Cut = 0.0 to 1.0m
Southern Block :
F.F.L. = 19.0m;
Fill = 0.0 to 2.0m
Cut = 0.0 to 1.5m
Column Load
755.OkN (83 numbers); 700.OkN (83 numbers)
Deep Boring
DB/3, DB/4 and DB/G (Refer sketch attached)
Shaft Resistance Formulae
a) CLAY
Q =
*Cu*A. where = adhesion factor
Cu = undisturbed undrained cohesion '
A. = surface area of pile
b) SILT
Q = N/60*A. where N = Standard Penetration Test
c) SAND
Q. = N/50*A.
Base Resistance Formulae:
a) CLAYQb, =
N*Ab where Ab = base area of pile
b) SILT
2. 5iN*Ab
c) SAND Qb,
4N*Ab
Design Analysis
Adopt DB/4 since worst case and assume.height of fill = 2.0m Try R.C. Pile of size B" x B"
Shaft Resistance
For depth 0 - 2.0m b. F. F. L. : FILL
For depth 2 - 5.0m ; CLAY ; assume N = 13
take Cu = 82.0 kN/m2 (Terzaghi)
adopt
= 1.0 (Tomlinson)
= 0.4 (McClalland)
= 0.7
Q = 0.7*82.0*4*B*3.0
39.37*9.81
= 1.783B tonnes
For depth 5 - 9.0m : SAND ; assume N = 7
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 71
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Q. = 7*4*B*4.0*3.281
50* 12
= 0.612B tonnes
For depth 9 - 11.0m: SILT ; assume N = 6
Q. = 6*4*B*2.0*3.281
60*12
= 0.219B tonnes
For depth 11 - 18.0m: CLAY ; assume N = 13
take = 82.0 kN/m2 a. = 0. 65
= 3.864B tonnes
Q = 0.65*82.0*4*B*7.0
39.37*9.81
Q
= 6.478B tonnes
Base Resistance
At depth 21.Om b.F.F.L. take N = 13 and since proportion of SAND is quite high (> 30%) adopt
Qb = 2.0*N*Ab (i.e. between CLAY & SILT).
Qb = 2.0*13*B*B = 0.130B2
144
Ultimate Resistance Qa
If B = 12 inches;
= Qp + Qb
= G.478B-+ 0.180B2
Q, = 77.7 + 26.0 = 103.7 tonnes
Take overall Factor of Safety = 2.0
Allowable Resistance Q11, = 103.7/2.0 = 51.8 tonnes (say 52.0)
To allow for erratic nature of underlying soil and also as per para 3.0 of report allow for '15%
increase.
Hence adopt 12" x 12" R.C.Piles @ 21.0m with Q~,s = 450.0 kH/pile
Although the bulk of the carrying capacity of pile is mainly frictional set might be achieved before
depth design.
Hence set readings to be taken during driving and if set not achieve drive to design depth.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 72
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Pile Design Report
Page 73
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Lampiran `B'
Shallow Foundation Design For Pre-School Block (1-Storey)
Proposed F.F.L. = 26.0m; Cut = 4.5 to 5.0m
Column Load
128.OkN (22 numbers); 167.OkN (23 numbers)
Deep Boring DB/14-(R.L. = 30.74m)
At depth 1.Om b. F. F. L. take N *= 9 ( lower bound) and at this depth soil is COHESIVE (silty
CLAY),
Try pad footing of size B (m) x L -(m) @ depth 1.0m b.F.F.L.
From NAVFAC DM-7.2;
q*No*(1+0.08/L) + (D
where c = undrained cohesion
Na = bearing capacity factor
D = depth of footing
below original grd. level.
= bulk density of soil
Take c = 55.0 kn/m2. Assume 0 = 0 and (=18..0 kN/m3
Consider case when ground water table is 1.0m b.F.F.L.
Therefore for square footing, B/L = 1, and for 0 = 0, Na = 5.53
55.0*5.53*1.3 + 18.0*5.74
= 395.4 + 103.3
= 498.7 kN/mz
Adopt Factor of Safety = 3.0
q~ " = 498.7/3.0 = 166.2 kN/mx (say 166.0)
If ignoring depth contribution i.e. XD,
q"lro = 395.4 kN/mz
Applying same F.o.S.; gall = 131.8 kN/mz
Therefore adopt square footing with gall = 94.0 kN/mo (2000 p.s.f.) 0 1.0m b.F.F.L. (i.e. to follow
standard drawing).
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 74
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
Lampiran C
( )dlm. PKR.RPM.
85/ 173/GO5/03
30hb. Jun. 1989
Pengarah,
Cawangan Kerja Pendidikan,
Ibu Pejabat JKR,
Jalan Sultan Salahuddin,
50582 KUALA LUMPUR.(u.p: Ir. Lam Yok Lon)
Tuan,
Perkara : CadanganMaktab Perguruan Sri Pinang, Bukit Mertajam, Pulau Pinang.
Merujuk perkara di atas dengan segala hormatnya disampaikan keputusan penyiasatan tapak dan
syor-syor asas untuk tindakan tuan selanjutnya.
2.0
Selaras dengan penguatkuasaan surat pekeliling KPKR 2/88, sistem cerucuk alternatif oleh
pentender boleh diterima.
3.0
Dimaklumkan juga bahawa seperti perbincangan yang telah diadakan dengan pegawai tuan
Ir. Lam Yok Lon pada 15/06/1989, pusat ini bersetuju bahawa kos anggaran asas bagi pro
jek ini ditambah lebih kurang 15% atas sebab desakan untuk melaksanakan projek ini
secepat mungkin. Pertambahan ini adalah untuk menyesuaikan perkara yang mungkin be
rlaku semasa pembinaan atas langkah-langkah yang dibuat semasa perancangan untuk
menyingkatkan tempoh masa perancangan dan rekabentuk seperti berikut:a)
Penyiasatan tapak telah dilakukan secara 'appointed - contractor' dan dengan ini kos
kontrak tidak boleh melebihi $50,000.00. Ini telah menghadkan skop penyiasatan
tapak yang perlu dijalankan.
b)
Lokasi-lokasi bangunan telah diubah daripada lokasi cadangan asal yang mengaki
batkan ada beberapa bangunan tidak terdapat ujian gerekan dalam dijalankan.
c)
Ketidak seragaman keadaan tanah bawahan ditapak projek ini yang mana masalah
(a) telah menyulitkan lagi keadaan ini. 4.0 Perlu dimaklumkan bahawa pusat ini
mendapati bahawa tidak terdapat apa-apa sistem perparitan yang telah disediakan
bagi projek ini. pleh yang demikian pihak tuan perlulah mengkaji akan hal ini dan
membuat pengesyoran yang sewajarnya.
Sekian, harap maklum
'BERKHIDMAT UNTUK HEGARA'
'CINTAILAH BAHASA KITA'
Saya yang menurut perintah,
( IR. NEON CHENG AIK )
Penolong Pengarah Kanan (Pusat Penyelidikan) b.p. Pengarah,
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 75
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Institut Latihan & Penyelidikan JKR, Jalan Serdang,43000 KAJANG, Selangor DarulEhsan.
Projek :
Cadangan Maktab Perguruan Sri Pinang,
Bukit Mertajam, Pulau Pinang.
1.0
Tujuan
Laporan ini adalah bertujuan untuk menyampaikan keputusan penyiasatan tapak dan syorsyor asas yang sesuai bagi projek di atas.
2.0
Skop Projek
Perlaksanaan projek ini akan melibatkan pembinaan blok-blok bangunan seperti yang tert
era di dalam lukisan pelan tatatur BKP 187/89/1 (PRE) A dan penyediaan tapak akan
melibatkan kerja-kerja pemotongan sedalam di antara 0.0 hingga b.Om dan penimbusan di
antara 0.0 hingga 5.0m.
3.0
Skop Kerja Penyiasatan
Dalam menialankan kerja-kerja penyiasatan, sebanyak 30 bil. ujian gerekan dalam, 85 bil.
ujian proba Mackintosh dan bil. ujian gerimit tangan telah dijalankan dan lot:asi-lokasi
ujian-ujian ini adalah berdasarkan kepada lukisan tatatur asal BKP 187/89/1(PRE). Kerjakerja penyiasatan tapat: ini telah dijalankan oleh Sekata Bina Sdn. Bhd. Disamping ujianujian di tapak, ujian-ujian makmal juga telah diIakukan ke atas contoh-contoh tanah yang
diperolehi bagi mengetahui jenis dan sifat-sifat tanah yang terdapat di tapak.
4.0
Syor-syor Asas
Keupayaan galas
yg. Dibenarkan
(kN/cerucuk)
Beban Ujian
(kN/cerucuk)
305 x 305
@ 21.0
450.0
900.0
Keupayaan
tanggung yg.
Dibenarkan
(kN/m 2)
-
"
305 x 305
@ 18.0
"
"
Penapak
Konkrit
Tetulang
95.0(2000 psf)
@ 1.5m b.F.L.
(JKR probes >
40 blows/foot).
(A)
"
"
(B)
"
71.0 (1500 psf)
@ 1.5m b.o.g.l.
(JKR probes >
40 blows/foot).
"
71.0 (1500 psf)
@ 1.5m b.F.L.
(JKR probes >
30 blows/foot) .
Jenis
Bangunan
Jenis
Asas
Saiz &
Panjang
Cerucuk
Konkrit
Tetulang
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 76
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
(A)
Cerucuk
Kayu
Berubat
152 x 152
@ 9.0
100.0
200.0
(B)
Penapak
Konkrit
Tetulang
71.0 (1500 psf)
@ 1.5m b.F.L.
(JKR probes >
30 blows/foot).
"
71.0 (1500 psf)
@ 1.5m b.o.g.l.
(JKR probes >
40 blows/foot).
Cerucuk
Konkrit
Tetulang
305 x 305
@ 18.0
500.0
1000.0
"
"
"
"
Penapak
Konkrit
Tetulang
Cerucuk
Konkrit
Tetulang
305 x 305
@ 15.0
430.0
860.0
71.0 (1500 psf)
@ 1.5m b.o.g.l.
(JKR probes >
40 blows/foot).
-
Penapak
Konkrit
Tetulang
Cerucuk
Konkrit
Tetulang
254 x 254
@ 6.0
160.0
320.0
95.0 (2000 psf)
@ 1.5m b.F.L.
(JKR probes >
40 blows/foot).
-
"
305 x 305
@ 15.0
500.0
1000.0
Penapak
Konkrit
Tetulang
95.0 (2000 psf)
@ 1.5m b.F.L.
(JKR probes >
40 blows/foot).
"
"
"
"
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 77
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
U1
U2
(A)
Cerucuk
Konkrit
Tetulang
381 x 381
@ 18.0
650.0
1300.0
(C)
"
381 x 381
@ 18.0
650.0
1300.0
atau
"
305 x 305
@ 18.0
450.0
900.0
(B)
Penapak
Konkrit
Tetulang
95.0 (2000 psf)
@ 1.5m b.o.g.l.
(JKR probes >
50 blows/foot).
(A)
"
95.0 (2000 psf)
@ 1.5m b.F.L.
(JKR probes >
40 blows/foot).
(B)
Cerucuk
Konkrit
Tetulang
381 x 381
@ 15.0
650.0
1300.0
atau
"
305 x 305
@ 18.0
381 x 381
450.0
900.0
650.0
1300.0
305 x 305
450.0
900.0
254 x 254
@ 15.0
300.0
600.0
"
atau
atau
"
381 x 381
@ 18.0
900.0
1800.0
Penapak
Konkrit
Tetulang
95.0 (2000 psf)
@ 1.5m b.F.L.
(JKR probes >
40 blows/foot).
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 78
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
Syor-syor asas adalah seperti berikut:Nota:
i) Cerucuk Konkrit Tetulang
a) Daya tanggung beban kebanyakan cerucuk-cerucuF: yang direkabentuk adalah dari
separa geseran badan dan separ.a tanggung huiung dan keupayaan galas yang disy
orkan adalah berdasarkan kekuatan tanah dalam lingi:ungan batasan rendah serta
menggunakan faktor keselamatan 2.0.
b) Sekurang-Wrangnya 5 bilangan cerucuk permulaan perlu ditanam bagi setiap bangu
nan yang dicadangi;an yang memerlukan asas cerucuk dan 1 bilangan cerucuk ini
perlu dijalankan ujian beban (ini bermakna bahawa sekurang-kurangnya satu ujian
beban dibuat bagi setiap bangunan yang melibatkan asas cerucuF:). Ujian beban ini
boleh dijalankan selepas 3 minggu cerucuk-cerucuk berkenaan ditanam.
ii) Penapak Konkrit Tetulang
a) Fenapak-penapak E:onkrit hendaklah ditanam ke paras dalaman yang telah ditetap
kan di dalam jadual di atas (b. F. L. - below formation, atau b.o.g.l. - below original
ground level), dan lobang-lobang asas yang dikorek hendaklah jangan dibiarkan ter
dedah terlalu lama. Kerja-kerja 'concrete sdreeding' dan konkriting hendaklah
dilakukan secepat mungkin selepas penggalian lobang asas.
b) Walaubagaimanapun ujian pengesahan proba-proba JKR perlu dijalankan terlebih
dahulu bagi setiap kedudukan tiang bangunan-bangunan yang-dicadangkan bagi
memastikan hentaman proba-proba ini tidak kurang dari apa yang dicatitkan di dal
am jadual di atas dari dasar lobang asas kebawah dan ujian-ujian ini hendaklah dibu
at sebelum kerja-kerja pergorekkan lobang-lobang asas.
iii)
Cerucuk Kayu Berubat
a) Daya tanggung cerucuk yang direkabentuh adalah separa geseran badan dan sep
ara tanggung hujung dan faktor keselamatan yang digunakan di dalam perkiraan
adalah 2.0 serta menggunakan kekuatan tanah- dalam lingkungan batasan rendah.
b) Cerucuk hendaklah ditanam sehingga mencapai set yang sesuai dan ini dijangka
akan ditemui di paras dalaman lebih dari 6.0m.
c) Cerucuk !:ayu KEMFAS Berubat yang diluluskan oleh SIRIM hendaklah digu
nakan dan perlu mematuhi keperluan-keperluan yang terkandung di dalam surat
pekeliling KF*:R 7/1984.
d) Sekurang-kurangnya 3 bil. cerucuk permulaan perlu ditanam terlebih dahulu dan
2 bil. cerucuk ini hendaklah dijalankan ujian beban. Ujian beban ini boleh
dilakukan selepas 3 minggu cerucuk-cerucul: berkenaan ditanam.
5.0
Syor-syor Tambahan
a)
Kerja-kerja penimbusan dan pemotongan hendaklah dijalankan pada perinakat
permu laan kerja-kerja pembinaan dan tanah yang ditimbus hendaklah di dalam
lapisan tidak melebihi 300mm dan setiap lapisan dipadat ke tahap 95% mengikut
Piawaian Kepadatan British dengan penentuan JKR.
b)
Bagi bangunan-bangunan di mana lantai-lantai tingkat bawah akan diletakkan di atas
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 79
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Pile Design Report
tanah timbus melebihi 2.50m kegunaan lantai gantung adalah diperakukan, dan
untuk bangunan-bangunan lain yang mana lantai-lantai tingkat bawah akan
dilekakan di atas tanah timbus tidak melebihi 2.50m lantai-lantai ini hendaklah
diperkuatakan dengan 2 lapisan BRC dan sambungan bebas disediakan di anatara
lanatai dan rasuk/dinding bangunan.
c)
Penyediaan penyambung bagi setiap jarak 6.0m adalah wajar bagi lantai-lantai
apron kesemua bangunan yang dicadangkan dan mana-mana lantai apron yang akan
diletakkan di atas timbus melebihi -1.0m lantai apron ini perlu dipisahkan daripada
tiang/rasuk/dinding bangunan dengan bitumen.
d)
Bagi blok-blok bangunan di mana pusat ini telah mengesyorkan lebih dari satu saiz
cerucuk, pihak tuan . bolehlah memilih mana-mana saiz.yang didapati lebih
ekonomik tetapi HANYA SATU SAIZ CERUCUK DIBENARKAN bagi satu ban
gunan.
e)
Pusat ini juga mengesyorkan agar. kecuraman cerun-cerun yang akan didirikan tidak
melebihi IM: 1(H) bagi cerun-cerun potong (cut slopes) dan, IM: 1.5(H) bagi cerungerun timbud (filled slopes).
6.0
Hal-hal Lain
Satu set rekod penanaman cerucuk-cerucuk yang diuji berserta dengan keputusan ujianujian bebannya hendaklah dikemukakan kepada pusat ini untuk tujuan dokumentasi.
7.0
Penutup
Dikemukakan syor-syor dan ulasan pusat ini untuk tindakan tuan selanjutnya.
Pusat Penyelidikan,Institut Latihan & Penyelidikan JKR.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 80
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Lampiran 'E'
Settlement Estimation of Fill
From classification results underlying soil is of the COHESIVE type with a fair proportion of
sandy materials. It is most probable that the fill material to be used would be obtained from the
cut-areas. Hence for settlement analysis it is assume that the fill material is of the cohesive type.
In the estimation of soil settlement it is assume that the - original underlying soil where the fill
would be place experience negligible settlement and whatever settlement that would occur is solely from consolidation of the fill under its own weight. It is also assume that the fill is uncompacted
since it is most common now that the control exercised in placing fill and compaction has frequently been insufficient to ensure an adequate and uniform support for structures immediately
after placement.
Hence for estimation of settlement of fill, fig. 1.0 below would be used.
From fig. 1.0 graph 5, cohesive material would settle around 11% of its thickness.
Suppose that construction period is 2 years and construction of ground floor would be carried out
after a period of 1.5 years after placement of fill..
Take case where height of fill = 2.50m
Therefore settlement of fill = 0.11 x 2.50 = .275m
Settlement (': of height of fill) = 0.08 x. 2.50 = 0.200m after period of 1.5 yrs.
Hence remaining settlement after = 0.275 - 0.200 = 0.075m period of 1.5 yrs.
Therefore for those buildings placed on fill ground of height >> 2.50m suspended floor is recommended and for the others . place on fill < 2.50m independent floor with 2 layers of BRC.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 81
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Projek :
Pakej :
SM. Kebangsaan Sungai Besar,Sabak Bernam, Selangor.
KBSM.
1.0. Tujuan.
Lapuran ini adalah bertujuan untuk menyampaikan keputusan penyiasatan tapak dan syor
asas yang sesuai bagi.projek diatas.
2.0. Skop Kerja
Perlaksanaan projek ini akan melibatkan pembinaan 1 Blok, 2 Tingkat (6BD,) bangunan
sekolah seperti yang tertera didalam pelan tatatur JKR/SB:765/81A. Aras tanah sediada
adalah merupakan cadangan aras formasi tapakbina ini,dan tidak-melibatkan sebarang
penambunan.
3.0. Skop Kerja Penyiasatan Tapak
Sebanyak 8 bilangan ujian proba JKR telah dijalankan oleh JKR Sabak Bernam, dan-2
bilangan ujian gerekan dalam telah dijalankan oleh Unit Makmal dilokasi-lokasi yang
bertanda didalam pelan tatatur.
4.0. Syor-syor Asas
Berdasarkan kira-kira rekabentuk, syor asas adalah seperti berikut:Jenis Asas
Cerucuk Konkrit
Tetulang
4.1.
4.2.
4.3.
Saiz Asas
(mm)
Panjang Asas
(mm)
254 x 254
30.0
Keupayaan galas
Beban
yg. Dibenarkan
Ujian
(kN/cerucuk)
300
600
Daya tanggung beban cerucuk konkrit tetulang yang direkabentuk adalah
kebanyakannya dari geseran badang, Perkiraan adalah menggunakan kekuatan tanah
di dalam lingkungan batasan rendah. Ini bermakna hanya 1 cerucuk sahaja diper
lukan bagi setiap tiang.
Bacaan set tidaklah perlu semasa penanaman cerucuk, dan cerucuk bolihlah
ditanamkan diparas dalaman 30.0m.
Sekurang-kurangnya 6 (enam) bilangan cerucuk permulaan hendaklah ditanam dan 1
(satu) bilangan cerucuk yang berdekatan dengan.lokasi ujian gerekan dalam hendak
lah dijalankan ujian.beban selepas 4 (empat) minggu cerucuk. berkenaan ditanam.
5.0. Syor-syor Tambahan
Bagi mengelakkan keretakan lantai apron unit ini berpend.apat penyed.iaan penyambung
bagi setiap jarak 6.Om adalah wajar. Lantai apron juga perlulah dipisahkan daripada dind
ing dan tiang bangunan supaya pergerakan berlainan sekiranya berlaku akan tersekat.
6.0. Hal-hal Lain
Satu set rekod penanaman cerucuk-cerucuk berserta dengan' keputusan ujian-ujian beban
nya hendaklah dikemukakan kepada unit ini bagi tujuan kaiian lanjut dan rekod.
7.0. Penutup.
Dikemukakan syor-syor dan ulasan unit ini untuk tindakan tuan selanjutnya.
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 82
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
DATAS OBTAINED FORM : EN. BAHARUDIN LOKMAN JKR(O) S B
PROJEK : SMK SUNGAI BESAR
DAERAH : SABAK BERNAM
NEGERI : SELANGOR
1. HISTORY OF SITES
*
Any Cut / Fill ?
NO
- If theres fill when ?
- What is the depth of fill?
*
Is there a slope ?
NO
- How far from the proposed building ?
- What is the height of the slope ?
2.
HISTORY OF EXISTING NEARBY BUILDINGS
*
What is the type of foundation ?
If Pile - What Type ?
- What Size ?
If Pad - What Depth ?
PILE
RC
305 x 305
-
- What Bearing Capacity ?
*
When Constructed ?
80s
How is the present conditions ?
OK
- Any apron / floor cracks ?
SIGN OF
- Other sign of distress ?
CRACKS
How far is the nearest building ?
30
3. SOIL CONDITIONS
* What type of soils ?
* What is the water level ?
SOFT CLAY
HIGH
HBB /hbb
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 83
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Pile Design Report
Page 84
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
UNIT MAKMAL
NO. HELAI 1
KIRA KIRA REKABENTUK
REKABENTUK OLEH .
CAWANGAN REKABENTUK DAN PENYELIDIKAN IBU PEJABAT, JKR.
NO. FAIL ...
PROJEK : SMK SUNGAI BESAR.
DAERAH : SABAK BERNAM.
PAKEJ
: KBSM
TARIKH 4.10.89
RUJUKAN
KIRA KIRA
CATATAN
Lukisan
1. Blok / 2 tct. (GBD) sekolah
RL : 29.54
JKR/SB: 765/81A
FL : 30.00
Column Loadings(T)
Lukisan
Frame
Front
Back
F1
20
18
F2
29
25
F3
25
21
Datas &
Assumptions
MAX 29T
No fitting included
Level
Geological
Section
SPT
(m)
(ft)
(N)
v/s
12
40
Cu
kN/m
x
2
v/s
(0.03)
v.soft
v/s 25
to
(0.23)
Cu
Stiff
1.0
0.9
Silty
Clay
Qu = Qs + Qb
Clay: Qs = As x Cu Qb = Ab 9 Cb
Sand : Qs = ASN
50
Qb = Ab 4 N
Qa = Qu
f.o.s.
E96
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 85
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
UNIT MAKMAL
NO. HELAI 2..
KIRA KIRA REKABENTUK
REKABENTUK OLEH ..
CAWANGAN REKABENTUK DAN PENYELIDIKAN IBU PEJABAT, JKR.
PROJEK : SMK SUNGAI BESAR.
DAERAH : SABAK BERNAM.
PAKEJ
: KBSM
NO. FAIL ....
TARIKH 4.10.89.
RUJUKAN
KIRA KIRA
CATATAN
Try RC Piles
Level
(m)
(ft)
30
100
BXB
Qs
Qb
Qa
Qa
(in)
(T)
(T)
(T)
(T)
61 B
3.5 B 2
10 x 10
51
2.4
35
27
12 x 12
61
3.5
42
32
15 x 15
76
5.5
53
41
67B
40B2
10 x 10
56
28
47
42
12 x 12
67
40
58
54
15 x 15
84
63
77
74
Remarks
* quite close
Cost comperison
F2
F1
F3
F2
F3
F3
F2
F3
F3
F3
F1
Frames
Front
Back
Col
F1
F2
F3
12
E96
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 86
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
UNIT MAKMAL
NO. HELAI 3...
KIRA KIRA REKABENTUK
REKABENTUK OLEH ..
CAWANGAN REKABENTUK DAN PENYELIDIKAN IBU PEJABAT, JKR.
PROJEK : SMK SUNGAI BESAR.
DAERAH : SABAK BERNAM.
PAKEJ
: KBSM
RUJUKAN
Frames
NO. FAIL ....
TARIKH 4.10.89.
KIRA KIRA
Column
CATATAN
No of Piles
10 x 10 @
30T(30m)
12 x 12 @
30T(30m)
15 x 15 @
30T(30m)
at 100
at 100
at 100
Total
22
22
22
Rate
$0.32/m 2
$0.30/m 2
$0.28/m 2
Per m
Per m
Per m
Materials
$960/-
$1296/-
$1890/-
10%
96/-
129.6/-
189/-
Total Cost
$23,232/-
$31,363/-
$45738/-
Loads(T)
F1
20
18
F2
29
25
F3
25
21
Recommended
R.C. Piles
Size : 10 x 10 (254 x 254)
Length : 1 00 (30m)
Qa : 30T/Pile (300kN Pile)
f.o.s. : 1.5 skin 3.0 bearing
Pile is of mainly friction
E96
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Page 87
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Project :
SM.KEB.SUNGAI BESAR, SABAK BERNAM, SELANGOR.
BD
SC
BDS
SCS
Bangunan
:
2 tingkat
Jenis (BD/SC/BDS/SCS)
: BD
Pile dim.
:
254 mm sq. piles
Length
:
30 m
W.Load
:
30 Tonnes
No. of
Frames
F1
2
///////////////////////////////
F2
3
///////////////////////////////
F3
6
///////////////////////// //////
Frames
Column
Position
Front
Back
Front
Back
Front
Back
Column
Load
20.0
18.0
29.0
25.0
25.0
21.0
=
=
=
=
Piles/
Column
1
1
1
1
1
1
TOTAL :
$35.20 /m. length
Cost :
Bilik Da
Makmal S
Bilik D
Makmal
Piles Reqd.
2
2
3
3
6
6
22
$23,232.00
ALTERNATIVELY : -
Pile dim.
Length
W.Load
:
:
:
305 mm sq. piles
30 m
45 Tonnes
No. of
Frames
F1
2
///////////////////////////////
F2
3
///////////////////////////////
F3
6
///////////////////////////////
Frames
Column
Position
Front
Back
Front
Back
Front
Back
Column
Load
20.0
18.0
29.0
25.0
25.0
21.0
Piles/
Column
1
1
1
1
1
1
TOTAL :
$47.52 /m. length
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Cost :
Piles Reqd.
2
2
3
3
6
6
22
$31,363.20
Page 88
Pile Design Report
FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY
Project :
SM.KEB.SUNGAI BESAR, SABAK BERNAM, SELANGOR.
BD
SC
BDS
SCS
Bangunan
:
2 tingkat
Jenis (BD/SC/BDS/SCS)
: BD
Pile dim.
:
381 mm sq. piles
Length
:
30 m
W.Load
:
30 Tonnes
No. of
Frames
F1
2
///////////////////////////////
F2
3
///////////////////////////////
F3
6
///////////////////////// //////
Frames
Column
Position
Front
Back
Front
Back
Front
Back
Column
Load
20.0
18.0
29.0
25.0
25.0
21.0
=
=
=
=
Piles/
Column
1
1
1
1
1
1
TOTAL :
$69.30 /m. length
Cost :
Bilik Da
Makmal S
Bilik D
Makmal
Piles Reqd.
2
2
3
3
6
6
22
$45,738.00
ALTERNATIVELY : -
Pile dim.
Length
W.Load
:
:
:
305 mm sq. piles
30 m
45 Tonnes
No. of
Frames
F1
2
///////////////////////////////
F2
3
///////////////////////////////
F3
6
///////////////////////////////
Frames
Column
Position
Front
Back
Front
Back
Front
Back
Column
Load
20.0
18.0
29.0
25.0
25.0
21.0
Piles/
Column
1
1
1
1
1
1
TOTAL :
$47.52 /m. length
Cawangan Jalan, Ibu Pejabat JKR, K.L
Cost :
Piles Reqd.
2
2
3
3
6
6
22
$31,363.20
Page 89
You might also like
- Liquid Retaining Reinforced Concrete Section To BS 8007& BS 8110Document1 pageLiquid Retaining Reinforced Concrete Section To BS 8007& BS 8110James LaurentNo ratings yet
- Elements of Mechanical Engineering by V. K. ManglikDocument616 pagesElements of Mechanical Engineering by V. K. ManglikHariprasad_vp100% (1)
- Foundation Design ReportDocument5 pagesFoundation Design ReportShashankSinghNo ratings yet
- Junjin CSM JET-8 No Crawler Drill Drfter Part Number Part Name Q'ty Unit Price Remarks JD-800 JET-8Document32 pagesJunjin CSM JET-8 No Crawler Drill Drfter Part Number Part Name Q'ty Unit Price Remarks JD-800 JET-8AlbertoReymundo100% (1)
- Uk Calibration StandardDocument29 pagesUk Calibration Standardgahsoon100% (1)
- Micro PileDocument8 pagesMicro PileJennifer Pearson100% (3)
- Pile Set Calculation (Hiley's Formula)Document8 pagesPile Set Calculation (Hiley's Formula)khewzyNo ratings yet
- MS of Mackintosh Probe & GuidelineDocument3 pagesMS of Mackintosh Probe & GuidelineAdam Lim100% (1)
- Catalogo de Peças 318D2Document472 pagesCatalogo de Peças 318D2norte hidraulicaNo ratings yet
- EXEDY Friction Technics Catalog Summer 2013webDocument74 pagesEXEDY Friction Technics Catalog Summer 2013webrobertoperez525No ratings yet
- A Robust Structural Stress Method For Fatigue Analysis of Offshore Marine StructuresDocument7 pagesA Robust Structural Stress Method For Fatigue Analysis of Offshore Marine StructuresXianjun Pei100% (1)
- Interpretation of Laboratory and Field Test Results For DesignDocument113 pagesInterpretation of Laboratory and Field Test Results For DesignKhairul Azmil75% (4)
- Method of Statement For Micropile 01Document7 pagesMethod of Statement For Micropile 01NedyHortetlNo ratings yet
- SUBMIT (Rev1.0) MicroPileCalculationSheet GTL5Document37 pagesSUBMIT (Rev1.0) MicroPileCalculationSheet GTL5Suneel MatchalaNo ratings yet
- Native Data Sheet Asme b73.1Document4 pagesNative Data Sheet Asme b73.1Akhmad Faruq Alhikami100% (1)
- Set Calculation For Hammer Driven Piles Using Modofoed HILLEY's FormulaDocument2 pagesSet Calculation For Hammer Driven Piles Using Modofoed HILLEY's Formulaqoci5ko89% (9)
- Coba JembatanDocument28 pagesCoba JembatanAbdi Septia PutraNo ratings yet
- GEO GEOGUIDE 7 - Guide To Soil Nail Design and Construction (2008)Document100 pagesGEO GEOGUIDE 7 - Guide To Soil Nail Design and Construction (2008)aescarameiaNo ratings yet
- RC BeamDocument36 pagesRC BeamMuhamad Amirul Md. RazdiNo ratings yet
- Tread - Riser StaircaseDocument3 pagesTread - Riser StaircasemeenuNo ratings yet
- Pile Group:: Piling Works For Bukit Batok N4C18 To C21 468A Pile Ecentricity Calculation G22Document2 pagesPile Group:: Piling Works For Bukit Batok N4C18 To C21 468A Pile Ecentricity Calculation G22lattmdy100% (3)
- Basic Guidelines On Pedestrian FacilitiesDocument14 pagesBasic Guidelines On Pedestrian FacilitiesgahsoonNo ratings yet
- Initial Load Test Pile-Calc (450 MM) Rev0Document2 pagesInitial Load Test Pile-Calc (450 MM) Rev0sathishNo ratings yet
- 1200 CFM or 2000 Cu - MTR Per HR Air Compressor (Datasheet)Document3 pages1200 CFM or 2000 Cu - MTR Per HR Air Compressor (Datasheet)kyawswarpmNo ratings yet
- 9.design of JIB Crane Supporting StructuresDocument14 pages9.design of JIB Crane Supporting Structuresepe civilNo ratings yet
- Micro Pile MSDocument91 pagesMicro Pile MSYam BalaoingNo ratings yet
- Project: Proposed Development of 242 Units of 27 Storeys Condominium (Phase 1A-Rc3)Document8 pagesProject: Proposed Development of 242 Units of 27 Storeys Condominium (Phase 1A-Rc3)pakbilal1100% (1)
- Pile Design Cal - Rev-1Document9 pagesPile Design Cal - Rev-1Nitin SakpalNo ratings yet
- Micro Pile Design and ConstructionDocument28 pagesMicro Pile Design and ConstructionMelissa SammyNo ratings yet
- Slope Design Guidelines From JKRDocument37 pagesSlope Design Guidelines From JKRHoo Yen How86% (7)
- Trench Wall Design - IS456-2000Document7 pagesTrench Wall Design - IS456-2000Nitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Micropile Design 6Y22Document2 pagesMicropile Design 6Y22riefsaldy75% (4)
- Geotechnical Design Guidelines: Jabatan Kerja Raya MalaysiaDocument90 pagesGeotechnical Design Guidelines: Jabatan Kerja Raya MalaysiaChen Fook YewNo ratings yet
- Piled Foundation Design & ConstructionDocument248 pagesPiled Foundation Design & Constructionmarcob74100% (1)
- Micropile Design ReportDocument9 pagesMicropile Design ReportAlsonChinNo ratings yet
- Deep FoundationDocument148 pagesDeep Foundationfarahazura100% (1)
- Beam DesignDocument14 pagesBeam DesignAbinash MandalNo ratings yet
- Raft 2Document17 pagesRaft 2Kushan Dhanushka NanayakkaraNo ratings yet
- Micro PileDocument7 pagesMicro PileWanZainuriadiNo ratings yet
- Section 10 Piling Works PDFDocument31 pagesSection 10 Piling Works PDFLeanna Abdul Wahab75% (4)
- An 11001 Diaphragm WallDocument20 pagesAn 11001 Diaphragm Wallgahsoon100% (4)
- Prefabricated Vertical Drains For: Soil ConsolidationDocument14 pagesPrefabricated Vertical Drains For: Soil ConsolidationFerry Yudha Mangiwa100% (1)
- Hydraulic Mining Shovel 6040AC: 08. Attachment Functions - FSDocument20 pagesHydraulic Mining Shovel 6040AC: 08. Attachment Functions - FShector50% (2)
- JKR Geotechnical SpecificationDocument9 pagesJKR Geotechnical SpecificationSousei No Keroberos100% (1)
- SlopeDesignGuidelines JKRDocument37 pagesSlopeDesignGuidelines JKRtanchuanngan100% (9)
- 200 Limestones of Jurong Formation Engineering ExperienceDocument9 pages200 Limestones of Jurong Formation Engineering ExperiencegahsoonNo ratings yet
- API 5L Pipe SpecificationDocument23 pagesAPI 5L Pipe SpecificationGalo AyalaNo ratings yet
- Deviated Piles ReportDocument10 pagesDeviated Piles Reportirmreza68No ratings yet
- Built Up Section Design SheetDocument12 pagesBuilt Up Section Design SheetBikal BastakotiNo ratings yet
- Application of Prefabricated Vertical Drain in Soil ImprovementDocument6 pagesApplication of Prefabricated Vertical Drain in Soil ImprovementUrsula Dina PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Pile EccentricityDocument8 pagesPile EccentricitySiongyung KongNo ratings yet
- 1 (85) - ARAHAN TEKNIK Barrier & Guard RailDocument20 pages1 (85) - ARAHAN TEKNIK Barrier & Guard RailAllen Neoh100% (2)
- Eccentric Check For 12 Piles GroupDocument2 pagesEccentric Check For 12 Piles GroupAlsonChinNo ratings yet
- MS SheetDocument2 pagesMS SheetAdam Lim100% (1)
- Soil Nail - GNP - GoodDocument19 pagesSoil Nail - GNP - GoodgahsoonNo ratings yet
- Middle Wall (All Intermediate Walls)Document3 pagesMiddle Wall (All Intermediate Walls)epe civilNo ratings yet
- N (Flow/Ft.) Consistency Cqu Uncomfined Compressive JKR Probe 2 Strength (Qu) Flows/Ft. PSF (Ton/Sq - FT.) kN/m2Document8 pagesN (Flow/Ft.) Consistency Cqu Uncomfined Compressive JKR Probe 2 Strength (Qu) Flows/Ft. PSF (Ton/Sq - FT.) kN/m2عصام السامرائيNo ratings yet
- RC DesignDocument72 pagesRC DesigngahsoonNo ratings yet
- Edoc - Pub - JKR Design Micropilepdf PDFDocument89 pagesEdoc - Pub - JKR Design Micropilepdf PDFmatt n100% (1)
- JKR-Arahan Teknik Road DesignDocument28 pagesJKR-Arahan Teknik Road DesignJeebers Crrebers100% (4)
- Spectrum Techno Consultants Pvt. LTD.: V EffDocument3 pagesSpectrum Techno Consultants Pvt. LTD.: V EffParshva ShahNo ratings yet
- Example of Asaoka's MethodDocument1 pageExample of Asaoka's MethodSingDollar100% (1)
- JKR Presentation (15-3-2017) PDFDocument288 pagesJKR Presentation (15-3-2017) PDFWall Panel100% (2)
- Calculation Sheet: Perunding Nusajasa SDN BHDDocument7 pagesCalculation Sheet: Perunding Nusajasa SDN BHDSarahLukakuNo ratings yet
- ESTEEM - Note & TutorialDocument34 pagesESTEEM - Note & TutorialNur Hazimah89% (19)
- Micropile CalculationDocument2 pagesMicropile CalculationMocha YaZid Rahim Ozil67% (3)
- JKR Design CriteriaDocument5 pagesJKR Design CriteriaAnonymous 6vZfB9pfza100% (2)
- JKR 20401Document8 pagesJKR 20401dinu69inNo ratings yet
- RCC Design of Toe-Slab: Input DataDocument2 pagesRCC Design of Toe-Slab: Input DataAnkitaNo ratings yet
- Design Parameter PositionDocument38 pagesDesign Parameter PositionLenielle AmatosaNo ratings yet
- RCC Design of Heel-Slab: Input DataDocument2 pagesRCC Design of Heel-Slab: Input DataAnkitaNo ratings yet
- Design of Cantilever Slab As Per Is 456 2000Document2 pagesDesign of Cantilever Slab As Per Is 456 2000airtelNo ratings yet
- 3) Backwash Water TroughDocument11 pages3) Backwash Water TroughLagnajit DasNo ratings yet
- 1 - SPLICE-WPB 700X300X204.5 - DraftDocument7 pages1 - SPLICE-WPB 700X300X204.5 - DraftAvishek DeyNo ratings yet
- Oneway SlabDocument2 pagesOneway SlabEric Pajuelas EstabayaNo ratings yet
- Pole CalcDocument11 pagesPole CalcMia SaquingNo ratings yet
- Site Concreting Record: Date: RI NoDocument1 pageSite Concreting Record: Date: RI NogahsoonNo ratings yet
- Rebar SplicingDocument12 pagesRebar SplicinggahsoonNo ratings yet
- Perspec Prime (M) Sdn. Bhd. Electrified Double Track Project Between Rawang and Ipoh. Reinforced Inspection FormDocument1 pagePerspec Prime (M) Sdn. Bhd. Electrified Double Track Project Between Rawang and Ipoh. Reinforced Inspection FormgahsoonNo ratings yet
- Dip Forms 019Document2 pagesDip Forms 019gahsoonNo ratings yet
- Electrified Double Track Project Between Rawang and Ipoh: Zone / Package: Chainage/StructureDocument2 pagesElectrified Double Track Project Between Rawang and Ipoh: Zone / Package: Chainage/StructuregahsoonNo ratings yet
- Perspec Prime (M) Sdn. Bhd. Electrified Double Tracking Between Rawang and Ipoh Daily Earthwork Production RecordDocument1 pagePerspec Prime (M) Sdn. Bhd. Electrified Double Tracking Between Rawang and Ipoh Daily Earthwork Production RecordgahsoonNo ratings yet
- Qi GongDocument83 pagesQi GonggahsoonNo ratings yet
- Electrified Double Track Project Between Rawang and Ipoh: Offset: Tested byDocument1 pageElectrified Double Track Project Between Rawang and Ipoh: Offset: Tested bygahsoonNo ratings yet
- Encardio CatalogDocument36 pagesEncardio CataloggahsoonNo ratings yet
- Swing - Anchor English Catalog (042407)Document22 pagesSwing - Anchor English Catalog (042407)gahsoonNo ratings yet
- Site Investigation by Ir - Dr.gua See SewDocument66 pagesSite Investigation by Ir - Dr.gua See SewGoh Ching SoonNo ratings yet
- Steel SpringFlexCoupling BackDocument2 pagesSteel SpringFlexCoupling BackLasse HansenNo ratings yet
- The Large Mass Method in Direct Transient and Direct Frequency ResponseDocument3 pagesThe Large Mass Method in Direct Transient and Direct Frequency ResponsenetkasiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid-Structure Interaction Analysis of A Peristaltic PumpDocument4 pagesFluid-Structure Interaction Analysis of A Peristaltic PumpSheikh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- 4530 Spec SheetDocument2 pages4530 Spec SheetLye YpNo ratings yet
- Impact of Swirl Fluctuations On The Flame Response of A Perfectly Premixed Swirl BurnerDocument7 pagesImpact of Swirl Fluctuations On The Flame Response of A Perfectly Premixed Swirl BurnerbelindaNo ratings yet
- ME 41 SyllabusDocument1 pageME 41 SyllabusElisha TanNo ratings yet
- Perkins Engine 1106C-E60TAG4 SERIES SPARE PARTSDocument2 pagesPerkins Engine 1106C-E60TAG4 SERIES SPARE PARTSIbrahim YunusNo ratings yet
- JP - Im CB Us PDFDocument77 pagesJP - Im CB Us PDFMhs EngineerNo ratings yet
- Indoor Water Cooled Condensing Units 1/2 Through 40 HP: RW SeriesDocument8 pagesIndoor Water Cooled Condensing Units 1/2 Through 40 HP: RW SeriesDaniel CastroNo ratings yet
- Characterization of The Material Properties of Two FR4 Printed Circuit Board LaminatesDocument40 pagesCharacterization of The Material Properties of Two FR4 Printed Circuit Board Laminatesعثمان أمنيسيNo ratings yet
- Bharathi Connection Design (22.5 X 56)Document22 pagesBharathi Connection Design (22.5 X 56)Chandrasekhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Component Maintenance Manual For External Design Wheels & BrakesDocument84 pagesComponent Maintenance Manual For External Design Wheels & BrakesAntonio OrtizNo ratings yet
- CVDocument11 pagesCVLaharish KakarlaNo ratings yet
- WWW - Superiorelectric.in: Making MachinesDocument52 pagesWWW - Superiorelectric.in: Making MachinesPinali Mahendradas MistryNo ratings yet
- Iso 898 2紧固件的机械性能.第2部分有规定的检验载荷值的螺母.粗牙螺纹Document19 pagesIso 898 2紧固件的机械性能.第2部分有规定的检验载荷值的螺母.粗牙螺纹Pamela Saavedra MoyaNo ratings yet
- 110 T Bucyrus Erie Truck Cranes Spec C8c4aaDocument4 pages110 T Bucyrus Erie Truck Cranes Spec C8c4aaRothsby Hoyos GomezNo ratings yet
- Tex-417-A, Unit Weight, Yield, and Air Content (Gravimetric) of ConcreteDocument9 pagesTex-417-A, Unit Weight, Yield, and Air Content (Gravimetric) of ConcreteJoe A. CagasNo ratings yet
- HySpan 6500 CatalogDocument16 pagesHySpan 6500 CatalogdragasaniNo ratings yet
- LandisDocument23 pagesLandisGustavo Brea MalavéNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Majdi JerbiDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Majdi JerbiMajdi JerbiNo ratings yet
- PIM130B1 - Daihatsu DT Series Archived JUN PDFDocument5 pagesPIM130B1 - Daihatsu DT Series Archived JUN PDFAnonymous XGsiY6rNo ratings yet