Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AHA Example For Scaffolding PDF
Uploaded by
karunaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AHA Example For Scaffolding PDF
Uploaded by
karunaCopyright:
Available Formats
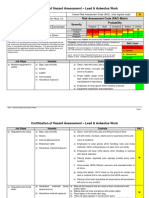
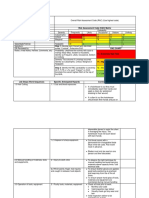
Activity Hazard Analysis (AHA)
Activity/Work Task: Scaffolding Erection Overall Risk Assessment Code (RAC) (Use highest code) M
Project Location: 1010 W. Snow Blind Street, Ft. Nowhere, Alaska Risk Assessment Code (RAC) Matrix
Contract Number: W921CM-09-M0001 Probability
Severity
Date Prepared: Frequent Likely Occasional Seldom Unlikely
Catastrophic E E H H M
Prepared by (Name/Title): Someone Else, SO Specialist
Critical E H H M L
Marginal H M M L L
Reviewed by (Name/Title): Super Safetyman/SOH Manager
Negligible M L L L L
Notes: (Field Notes, Review Comments, etc.)
Step 1: Review each Hazard with identified safety Controls and determine RAC (See above)
Crane set-up and use are on a separate AHA. Probability is the likelihood to cause an incident, near miss, or accident and
identified as: Frequent, Likely, Occasional, Seldom or Unlikely. RAC Chart
Severity is the outcome/degree if an incident, near miss, or accident did E = Extremely High Risk
occur and identified as: Catastrophic, Critical, Marginal, or Negligible H = High Risk
Step 2: Identify the RAC (Probability/Severity) as E, H, M, or L for each M = Moderate Risk
Hazard on AHA. Annotate the overall highest RAC at the top of AHA. L = Low Risk
Job Steps Hazards Controls RAC
General Safety Requirements all Steps Exposure to Cold or Hot Weather Minimum Personal Protective Equipment Dress: L
Long Pants
Dehydration Shirts with Sleeves
Hardhat
**Add additional potential hazards Safety Shoes (Steel/Composite Toe Preferred)
for general on site safety Safety Glasses (Potential Eye Hazard Areas)
requirements. **
Weather:
The above hazards are not all
inclusive and the Site Safety and Wear appropriate clothing for hot or cold weather.
Health Officer including the Quality (List specific clothing or refer to Company quick sheet, SOPs,
Assurance Representative (QAR) plan, etc. for specific details)
shall review the AHAs Sun block
Lip balm
Dehydration:
Drink at least liter of water an hour.
Refer to Company quick sheet, SOPs, plan, etc. for specific
details on heat stress signs and symptoms.
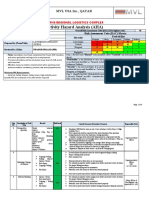
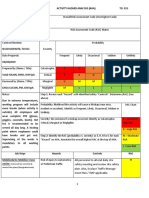
Job Steps Hazards Controls RAC
1.. Set-Up 1. Back Strain from uploading or 1a. Utilize proper lifting techniques.
moving scaffold components. 1b. Size up load before lifting.
1c. Ask for help when lifting heavy items more than 50 lbs. L
2. Lacerations on hands 2. Wear leather gloves.
3. Scaffold failure due to damaged 3a. INSPECT all scaffolding components defects or damage such as L
scaffolding components. cracks, excessive rust, metal fatigue, unauthorized repairs, bent tubing
or frame, etc. L
Frames
Tubing
Base Plates
Locking Pins
Access Ladder
Planking (Wood or Metal)
Cross Braces
3b. REMOVE damaged or defective scaffold components immediately.
3c. Attach tag or label DO NOT USE on scaffold component.
4. Struck by mechanized equipment. 4a. ALWAYS maintain eye contact with operator of equipment.
4b. NEVER stand behind (Blind Spots) equipment.
**See above Notes box** 4c. NEVER stand near unloading or moving of scaffold components. M
4d. ONLY qualified operators shall operate equipment.
5a. Secure loads from displacement with ropes, cables, chains, etc.
5. Loss of load. before movement.
5b. Ensure load to be lifted is secured, balanced, etc.
5c. Keep hands, fingers, or other body parts away from pinch points. M
6. Stuck by suspended loads or 6a. NEVER stand underneath suspended loads.
material. 6b. Use taglines to control loads when elevated.
7a. Check above for overhead power lines. L
7. Electrical Shock 7b. NEVER erect scaffolding within 10 ft (3 m) of overhead power lines.
Refer to EM 385-1-1, Table 11-1 for Minimum Clearance from
Energized Overhead Electrical Lines M
7c. NEVER string or hang temporary power cords, wires, etc. on metal
scaffolding. Consult with Safety Officer.
8a. Inspect ground conditions (level and firm).
8b. Stable base is necessary for proper scaffold assembly.
8. Scaffold failure due to improper 8c. Scaffold shall be tied into structure when the scaffold height
set-up M
exceeds four times the minimum scaffold base dimension.
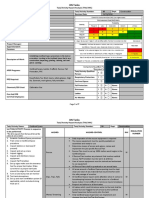
Job Steps Hazards Controls RAC
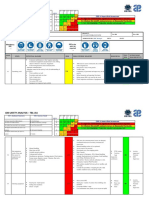
2. Assembly of Scaffolding 1 Fall from Elevated Heights
1a. 100 percent fall protection required during assembly. M
1b. Personnel shall not be exposed to unprotected sides or falls greater
than 6 ft (1.8 m).
1c. Scaffolding shall not exceed 14 inches (35.5 cm) from the planking
to the face of the building or structure.
1d. Scaffolding more than 14 inches (35.5 cm) from the planking to the
face of the building or structure shall be guardrails and/or the use of
personal fall protection.
1e. Personnel shall be tied off to a vertical lifeline with a rope grab
during assembly of scaffolding.
1f. Vertical lifeline shall be secured to an anchor point of at least 5,000
lbs (2,267.9 kg) per individual.
Develop a site specific Fall Protection Plan IAW EM 385-1-1, para
21.C.01 and refer to EM 385-1-1, Section 21.
2a. See diagram below and refer EM 385-1-1, Section 22 for specific M
2. Scaffold Failure
requirements (i.e., toe boards, guard rails, safe access, etc.)
2b. Scaffolding shall be assembled on mud sills and base plates.
2c. Mud sills shall be at least 2 times the size of the base plates to
disperse total weight of scaffolding.
2d. Scaffolding shall be plumb and level.
2e. Working levels shall be fully decked and/or planked.
2f. Planking shall extend over the end supports not less than 6 in (30.4
cm),
2g. Planking shall be secured, supported, or braced to prevent
excessive spring or deflection and secured to prevent loosening,
tipping, or displacement. Use of tie wire, cleats, etc. are options.
2h. Planking shall overlapped at least 12 inches (30.4 cm) or secured
from movement.
2i. Scaffold shall be capable of supporting without failure at least 4
times the maximum anticipated loads.
2j. Scaffolding shall be all required cross, horizontal, or diagonal braces
to secure vertical members laterally.
2k. Scaffolding shall be rigid.
3. Back Strain
3a. Utilize proper lifting techniques.
3b. Size up load before lifting.
L
3c. Ask for help when lifting heavy items more than 50 lbs.
4. Wear leather gloves. L
4. Lacerations on hands
Job Steps Hazards Controls RAC
2. Assembly of Scaffolding M
(Diagram)
3. Use of Scaffolding 1. Scaffold Failure 1a. DO NOT overload more than 4 times the maximum load rating.
1b. DO NOT attached hoists or other material lifting devices without M
Safety Officer approval.
1c. Scaffolding shall be tied into building whenever height of the scaffold
exceeds 4 times the minimal base. Refer to EM 385-1-1, para 22.B.09
for additional guidance.
1d. Scaffold usage shall cease during high winds or severe inclement
weather conditions.
2. Falls from Heights 2a. Guardrails shall be used as primary fall protection. Guard rails shall M
installed IAW EM 385-1-1, para 21.B.02.
2b. Securing of personal fall protection devices to scaffolding is
prohibited.
2c. Personnel shall have fall protection whenever above 6 ft (1.8 m).
2d. Climbing of braces or cross bracing is prohibited.
2e. Safe access (ladder) shall be provided.
2f. Personnel shall not stand on mid rails.
2g. Ladders shall extend at least 3 ft (0.9 m) past the work area.
3. Walking surfaces on and around scaffolding shall be clear of debris. L
3. Slips, Trips, or Fall
Job Steps Hazards Controls RAC
3. Use of Scaffolding M
The scaffold checklist is not all inclusive of the safety requirements for the
assembly, use, and disassembly of scaffolding. Competent Person onsite for
work platform safety shall review EM 385-1-1 Safety and Health Requirements
Manual, Host Nation safety laws, contract specifications, manufacture
specifications, etc. as additional guidance or information for work platform
safety.
4. Disassembling of Scaffolding 1 Fall from Elevated Heights 1a. 100 percent fall protection required during disassembly.
1b. Personnel shall not be exposed to unprotected sides or falls greater
M
than 6 ft (1.8 m).
1c. Personnel shall be tied off to a vertical lifeline with a rope grab
during assembly of scaffolding.
1d. Vertical lifeline shall be secured to an anchor point of at least 5,000
lbs (2,267.9 kg) per individual.
Develop a site specific Fall Protection Plan IAW EM 385-1-1, para
21.C.01 and refer to EM 385-1-1, Section 21.
Job Steps Hazards Controls RAC
4. Disassembling of Scaffolding 2. Back Strain 2a. Utilize proper lifting techniques. L
2b. Size up load before lifting.
2c. Ask for help when lifting heavy items more than 50 lbs.
3. Lacerations on hands 3. Wear leather gloves. L
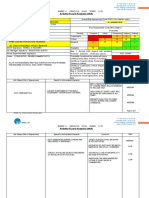
Training Requirements/Competent or
Equipment to be Used Inspection Requirements
Qualified Personnel name(s)
Scaffold components Competent/Qualified Personnel: Inspect scaffold components prior to use
Hammers
Mud sills Mr. Someone Else CP/Scaffolding Inspect scaffold daily (Use Checklist)
Full body harness Mr. Supersafety Man QP/First Aid and CPR
Lanyard Mr. Work Man QP/First Aid and CPR Inspect level and plumb of scaffoldings during erection and
Lifeline Mr. Fall Safety CP/Fall Protection daily when in use.
Fall protection anchor points Mr. Shocker Cord QP/Electrical
Float Mr. Lift Boom QP/Crane Operator Daily Housekeeping of work areas and scaffolding
Crane
Electric Hand Tools (Battery type) Training Requirements: Inspect PPE to include fall protection harnesses and
Portable Generator lanyards prior to use.
5 Ma GFCIs Scaffold Assembly
Power Cords Fall Protection Inspect fall protection anchor points.
Ladders Inspection of Work Platforms
First Aid Kit Heat or Cold Hazards Inspect crane IAW manufacture instructions.
Daily/Monthly safety toolbox meetings
Inspect power cord sets prior to use.
Inspect temporary power panel box, circuit breakers,
grounding, etc. at least monthly.
Inspect first aid kit at least monthly.
Daily site safety inspections by SSHO and CQC.
You might also like
- Activity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Overall Risk Assessment Code (RAC) (Use Highest Code)Document9 pagesActivity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Overall Risk Assessment Code (RAC) (Use Highest Code)Anthony Macatangay50% (2)
- Activity Hazard Analysis Safety ReviewDocument7 pagesActivity Hazard Analysis Safety ReviewKCV Coretech100% (1)
- AHA Ductbank InstallationDocument5 pagesAHA Ductbank InstallationYug DobariyaNo ratings yet
- AHA Temp Power - 03.03.2020 - RemarksDocument3 pagesAHA Temp Power - 03.03.2020 - RemarksJerry Word100% (1)
- AHA-003, ExcavationDocument5 pagesAHA-003, ExcavationBuddhika100% (2)
- Activity Hazard Analysis for MobilizationDocument14 pagesActivity Hazard Analysis for MobilizationAnthony Macatangay100% (2)
- AHA Excavation and Backfill 030922-BDocument3 pagesAHA Excavation and Backfill 030922-BYug Dobariya67% (3)
- DN Tanks: Step1: Review Each "Hazard" With Identified Safety "Controls" and Determine RAC (See Above)Document6 pagesDN Tanks: Step1: Review Each "Hazard" With Identified Safety "Controls" and Determine RAC (See Above)JojolasNo ratings yet
- (En) Roof Repair Works 2019-03-14Document8 pages(En) Roof Repair Works 2019-03-14Anthony MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Electrical Conduit InstallationDocument10 pagesElectrical Conduit InstallationYahya YusufzayNo ratings yet
- 9 - Aerial Lifts and Scissor Lifts THA-AHADocument5 pages9 - Aerial Lifts and Scissor Lifts THA-AHAJojolas100% (2)
- ADA Ramp Installation 061322-BDocument11 pagesADA Ramp Installation 061322-BYug Dobariya0% (1)
- AHA - Lead and Asbestos WorkDocument3 pagesAHA - Lead and Asbestos Workdg6xkzxsc9No ratings yet
- AHA - Working On Slope RoofDocument2 pagesAHA - Working On Slope RoofTopsun EnergyNo ratings yet
- P-985-SH-AHA-003. AHA For Outage Lock Our Tag OutDocument3 pagesP-985-SH-AHA-003. AHA For Outage Lock Our Tag OutPatrick Bibila NdansiNo ratings yet
- Activity Hazard Analysis (AHA) for Tiling WorksDocument6 pagesActivity Hazard Analysis (AHA) for Tiling WorksAnthony MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Repair Concrete PDFDocument3 pagesRepair Concrete PDFJaycee PagadorNo ratings yet
- Cement Stucco (Exterior Application)Document3 pagesCement Stucco (Exterior Application)Alvene TagocNo ratings yet
- Activity Hazard AnalysisDocument7 pagesActivity Hazard AnalysisAnthony MacatangayNo ratings yet
- P-985-SH-AHA-008, AHA For Demolision WorksDocument4 pagesP-985-SH-AHA-008, AHA For Demolision WorksPatrick Bibila NdansiNo ratings yet
- AHA Roofing SystemDocument8 pagesAHA Roofing SystemLawrence adeleke Omisakin100% (1)
- Crane-Hydra-deployment For Lifting-Lowering-Risk AssessmentDocument4 pagesCrane-Hydra-deployment For Lifting-Lowering-Risk AssessmentAhmed El-sherpiniNo ratings yet
- AHA-007, Concrete PouringDocument4 pagesAHA-007, Concrete PouringBuddhikaNo ratings yet
- AHA Example For ScaffoldingDocument7 pagesAHA Example For ScaffoldingVepxvia NadiradzeNo ratings yet
- X.9.1.a - Light Framed Steel Framing AHA - AnswerDocument7 pagesX.9.1.a - Light Framed Steel Framing AHA - AnswerBunyamin SelimogluNo ratings yet
- 18 - Confined Space THA-AHADocument7 pages18 - Confined Space THA-AHAJojolas50% (2)
- Aha Crane Lifting InspectionDocument2 pagesAha Crane Lifting InspectionTakiNo ratings yet
- AHA-009, Construction & Removing FormsDocument4 pagesAHA-009, Construction & Removing FormsBuddhikaNo ratings yet
- L Risk Assessment Code (RAC) MatrixDocument6 pagesL Risk Assessment Code (RAC) MatrixMario Marasigan50% (2)
- Activity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Risk Assessment Code (RAC) Matrix Severity ProbabilityDocument6 pagesActivity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Risk Assessment Code (RAC) Matrix Severity ProbabilityJaycee PagadorNo ratings yet
- DN Tanks Construction Mobilization THADocument5 pagesDN Tanks Construction Mobilization THAJojolas0% (1)
- Activity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Risk Assessment Code (RAC) Matrix Severity ProbabilityDocument14 pagesActivity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Risk Assessment Code (RAC) Matrix Severity ProbabilityThomas100% (4)
- Activity Hazards Analysis (AHA) : Severity ProbabilityDocument8 pagesActivity Hazards Analysis (AHA) : Severity ProbabilitySAsaNo ratings yet
- JHA - Ladders TemplateDocument3 pagesJHA - Ladders TemplateShannon Williams100% (1)
- P-985-SH-AHA-005, AHA For Earthwork (General Excavation)Document5 pagesP-985-SH-AHA-005, AHA For Earthwork (General Excavation)Patrick Bibila Ndansi75% (4)
- F5B-BMJV-0001-AHA-HSE 00 AHA For Precast Storm Drain and Subdrain Uty.Document13 pagesF5B-BMJV-0001-AHA-HSE 00 AHA For Precast Storm Drain and Subdrain Uty.Taiwo Oshin100% (1)
- Activity Hazard AnalysisDocument4 pagesActivity Hazard AnalysisGerrard Singh100% (1)
- RC Pipes Installation SafetyDocument15 pagesRC Pipes Installation SafetyTaiwo Oshin100% (1)
- AhaDocument6 pagesAhaCarlits MacallaNo ratings yet
- Scaffold Erection and Dismantling AHADocument2 pagesScaffold Erection and Dismantling AHACherrycherry Betonio0% (1)
- All Personnel To Attend Daily Site Safety Meeting and Review Site Safety Plan. Also, in Place Traffic Manage-Ment Plan / TMP ApplicableDocument6 pagesAll Personnel To Attend Daily Site Safety Meeting and Review Site Safety Plan. Also, in Place Traffic Manage-Ment Plan / TMP ApplicablecrnkarlosNo ratings yet
- F5B-BMJV-0001-AHA-HSE 00 AHA For Foul Sewer - Manhole ConstructionDocument11 pagesF5B-BMJV-0001-AHA-HSE 00 AHA For Foul Sewer - Manhole ConstructionTaiwo OshinNo ratings yet
- JSA For MobilizationDocument3 pagesJSA For MobilizationHossain amjad Hossain100% (1)
- JSA For Road BarrierDocument3 pagesJSA For Road BarrierMohammed MinhajNo ratings yet
- Job Activity Hazard Effect Control Measures: Project in ChargeDocument3 pagesJob Activity Hazard Effect Control Measures: Project in Chargeperquino oasanNo ratings yet
- JSA For Removal of Broken Bolts and Installation of Switch Pannel On Compressor at Process AraeDocument4 pagesJSA For Removal of Broken Bolts and Installation of Switch Pannel On Compressor at Process AraeMohammed MinhajNo ratings yet
- King Faisal Air Academy Carpentry JSADocument1 pageKing Faisal Air Academy Carpentry JSAnabeelNo ratings yet
- Activity Hazard Analysis FinalDocument23 pagesActivity Hazard Analysis FinalPedro PereiraNo ratings yet
- JSA Format Erection of Column 903-C-02,03Document5 pagesJSA Format Erection of Column 903-C-02,03sakthi venkat100% (1)
- 004-JSA Manual WeldingDocument6 pages004-JSA Manual WeldingMoaatazz NouisriNo ratings yet
- De-Com - For Existing 8 12 Inch - Pipeline - TRA1Document6 pagesDe-Com - For Existing 8 12 Inch - Pipeline - TRA1Darius DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Tower Crane Dismantling JSA HSE ProfessionalsDocument2 pagesTower Crane Dismantling JSA HSE ProfessionalsnabeelNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis for Pipeline LoadingDocument8 pagesJob Safety Analysis for Pipeline LoadingMoaatazz NouisriNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Manual Backfiling Usin Hand Roller CompactorDocument5 pagesJsa For Manual Backfiling Usin Hand Roller CompactorAbdus SamadNo ratings yet
- JSA Confined Sapce EntryDocument1 pageJSA Confined Sapce EntryprasongNo ratings yet
- Activity Hazard Analysis - Scaffolding ErectionDocument6 pagesActivity Hazard Analysis - Scaffolding Erectionnoty boyNo ratings yet
- Activity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Risk Assessment Code (RAC) Matrix Severity ProbabilityDocument6 pagesActivity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Risk Assessment Code (RAC) Matrix Severity ProbabilityAnthony MacatangayNo ratings yet
- JSA Demolition and DisposalDocument7 pagesJSA Demolition and Disposalm4l4ysia60% (5)
- Activity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Risk Assessment Code (RAC) Matrix Severity ProbabilityDocument2 pagesActivity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Risk Assessment Code (RAC) Matrix Severity ProbabilityYug DobariyaNo ratings yet
- Pipe Blocks & Sumps THADocument6 pagesPipe Blocks & Sumps THAJojolasNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Steam Trap03022017Document4 pagesDatasheet Steam Trap03022017Abu SuraisyNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD BegineersDocument82 pagesAutoCAD BegineerskarunaNo ratings yet
- C1BxaOC0 IS PDFDocument92 pagesC1BxaOC0 IS PDFSrinivas ReddyNo ratings yet
- SIF CalculationDocument8 pagesSIF CalculationkarunaNo ratings yet
- Trunnion CalculationDocument92 pagesTrunnion CalculationkarunaNo ratings yet
- Pipe Supports DesignDocument29 pagesPipe Supports DesignkarunaNo ratings yet
- CPWD Speci Civil 2009 Vol1Document544 pagesCPWD Speci Civil 2009 Vol1supriyo.podder100% (2)
- Mit Standard Building Specs enDocument373 pagesMit Standard Building Specs enmarioLhrNo ratings yet
- Autocad ShortcutsDocument13 pagesAutocad ShortcutsKriscel CaraanNo ratings yet
- Design Practise Piping Support SystemDocument46 pagesDesign Practise Piping Support Systemryncsc100% (6)
- Gs 2017Document540 pagesGs 2017CHANNo ratings yet
- Ball Float Steam TrapsDocument22 pagesBall Float Steam TrapskarunaNo ratings yet
- Application of CuNi Alloy for Seawater ServiceDocument14 pagesApplication of CuNi Alloy for Seawater ServicekarunaNo ratings yet
- Model Code of Safe Practice: 2nd EditionDocument166 pagesModel Code of Safe Practice: 2nd EditionkarunaNo ratings yet
- 22 61 13 Compressed-Air Piping For Lab-HealthCare FacilitiesDocument16 pages22 61 13 Compressed-Air Piping For Lab-HealthCare FacilitiesKaruna KaranNo ratings yet
- Enquiry Specification Civil Stru Consultancy Part 1Document33 pagesEnquiry Specification Civil Stru Consultancy Part 1Aditia C PurnomoNo ratings yet
- FW Vertical SDocument3 pagesFW Vertical SkarunaNo ratings yet
- BS en 12056 5 2000Document22 pagesBS en 12056 5 2000Vino Ratheesh50% (2)
- Nominal Pipe Sizes: Pipe Dimensions, Imperial / Metric Pipe ChartDocument5 pagesNominal Pipe Sizes: Pipe Dimensions, Imperial / Metric Pipe CharthappywhewmiNo ratings yet
- Check List For Piping GADDocument3 pagesCheck List For Piping GADkaruna100% (2)
- Aci Code ListDocument9 pagesAci Code ListkarunaNo ratings yet
- VTDocument12 pagesVTSlobodan AnticNo ratings yet
- 1055 Attachment 9 - QP GRP Piping SpecifiDocument8 pages1055 Attachment 9 - QP GRP Piping SpecifikarunaNo ratings yet
- VTDocument12 pagesVTSlobodan AnticNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual: 1 Approved For Public Release Distribution Is UnlimitedDocument1 pageTechnical Manual: 1 Approved For Public Release Distribution Is UnlimitedFahad SailorNo ratings yet
- 09 Div. 11 Equipment PDFDocument10 pages09 Div. 11 Equipment PDFkarunaNo ratings yet
- Check List For Equipment Layout (Design)Document5 pagesCheck List For Equipment Layout (Design)karunaNo ratings yet
- VTDocument12 pagesVTSlobodan AnticNo ratings yet
- 7.fuels and FurnacesDocument2 pages7.fuels and FurnaceskarunaNo ratings yet
- GSR39Document63 pagesGSR39Panchdev KumarNo ratings yet