Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8 Hydrologycram Sheet
Uploaded by
api-326958203Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8 Hydrologycram Sheet
Uploaded by
api-326958203Copyright:
Available Formats
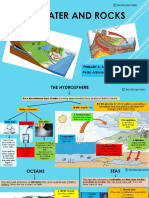
EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT: HYDROLOGY
Properties of Water Structure of the Hydrosphere Oceans
Polarity: Water is a polar molecule. This *Only 3% of the water in the world is freshwater. *The ocean is divided into three zones:
means that it has uneven charges because the That means that 97% of the water in our world is salt intertidal, neritic, and oceanic.
electrons in its covalent bond tend to move water found in the oceans, which humans cannot
around the oxygen atom more than they move drink. *The intertidal zone is the area of the
around the hydrogen atoms. beach that is sometimes covered by water
(during high tide) and sometimes in the air
(during low tide).
*The neritic zone is the area from that
slopes from the shore to the ocean floor.
*The oceanic zone is made up of the open
waters of the ocean.
*Estuaries are where salt water mixes with
Cohesion: Water molecules like to stick fresh water. They are usually protected by
together because they are polar. The negative barrier islands or reefs.
charge on one water molecule is attracted to the
positive charge on another water molecule. *The calm waters of an estuary are
generally the home to MANY different
Adhesion: Water molecules also like to stick to organisms.
other polar substances. When water sticks to *Salinity is a measure of how salty water actually is.
anything but water, its adhesion. *Benthos are organisms that live at the
bottom of the ocean.
*To get fresh water from salt water, we have to take
Surface tension: Because water molecules are the salt out. That process is called desalination.
polar and stick together, water molecules at the *Plankton are organisms that float in the
top of a body of water constantly try to stay as ocean.
*Of the freshwater, 69% of it is in ice form. 30% is
close together as possible. They pull down and groundwater (water underground), and 1% is found
to the sides, creating a layer of tension at the *Nekton are organisms that swim in the
in rivers and lakes.
top of bodies of water. ocean.
*Watersheds are an area where water collects and all
Universal solvent: Because water dissolves so *Upwelling is the movement of nutrient-rich
runs to one point, like the ocean.
many substances, we call it the universal waters from the deep ocean into shallow
solvent. A solvent does the dissolving and a areas, bringing nutrients that help
*Tributaries are small streams or rivers than run into
solute gets dissolved in a solution. organisms to thrive in upwelling areas.
larger rivers.
Density: Its how packed together molecules *Upwelling occurs when winds blow warm
*Wetlands are an area that is wet during all or part of
are. Mass/volume. Substances that are less water away from the shore. This brings
the year. They are a great habitat for animals and
dense than water will float in water, but more colder water to the surface.
absorb water to keep the earth from flooding.
dense stuff will sink.
Buoyancy: Water pushes up on everything that Groundwater
is put in it. If a substance is less dense than
water, water can push hard enough that it will *Humans get most of their drinking water from
float. If a substance is more dense than water, aquifers and rivers/lakes.
it will still sink (even though water is pushing
up!) *Groundwater is water underground thats usually
stored in layers of rock called aquifers.
Specific heat: Its the amount of energy it
takes to change the temperature of a substance. *Some rocks are permeable, so water can run
Water has a high one, which means it takes lots through them. When the water reaches an
of energy to change the temperature of water. impermeable rock formation (which wont hold
*The ocean supplies many resources to
Our bodies are made of water, so this helps water), it builds up in the permeable rock.
humans, including water (when
keep us alive. desalinated) and many different types of
*To produce water, a well has to be drilled below the
food.
water table and in a permeable rock formation.
*The oceans resources, especially the foods
that we obtain from the ocean, are not
unlimited.
*Humans use sonar to measure how deep
areas of the ocean are. Sound waves are
sent from a boat, bounce off the bottom of
the ocean, and bounce back up to the boat.
Water Quality Indicators Indicator Levels
Temperature: A healthy water system has
moderate to cool temperatures (because cool *Low dissolved oxygen=fish death poor water
water holds more dissolved oxygen). quality
Dissolved oxygen: High dissolved oxygen *High water temperature=low dissolved oxygen
levels are good. Cold water can hold more (because hot water cant hold much dissolved
dissolved oxygen that warm water can. oxygen). poor water quality
pH: Most aquatic life functions best in water at a *If there are too many nutrients in a body of water,
neutral or slightly basic (8.0-9.0) pH. the water will have high turbidity, and algal blooms
will occur. This leads to low dissolved oxygen too
Nitrates: Nitrogen-containing compounds found water quality
in fertilizers that can pollute water systems.
*pH should be between 6-9 for a healthy water
Turbidity: High turbidity (murky water) is a sign system.
of an unhealthy water system.
*pH if there are few bio-indicators present, the water
Bio-indicators: High levels of bio-indicators source cannot support life poor water quality
indicate a healthy water system. Low levels of
bio-indicators indicate a polluted water system.
Water Treatment
Pollution *Because water can be polluted and carry diseases,
its important that water be treated (or cleaned)
*Point-source pollution is pollution that comes before humans drink it.
from one identifiable place.
*Wastewater treatment plants are places that process
*Non-point-source pollution is pollution that water to remove waste and then release the water
comes from more than one identifiable place. into a lake or stream.
Its hard to pinpoint THE place its coming from.
*Point-source pollution is usually easier to stop
than non-point-source pollution because we can
point to exactly where its coming from
You might also like
- 9 STD E.M GEOGRAPHY DistinguishDocument4 pages9 STD E.M GEOGRAPHY DistinguishTamilaruviNo ratings yet
- Kegy 213Document9 pagesKegy 213PremKumarNo ratings yet
- Clearias.com-Erosion and Deposition Action of Wind and WavesDocument7 pagesClearias.com-Erosion and Deposition Action of Wind and WavesPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Earths WaterDocument13 pagesEarths WaterAna Marie Corales TabunarNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument37 pagesWater Resourceszionpedroso23No ratings yet
- Test 4 Study Page: Tides: Waves: Currents: WaterDocument2 pagesTest 4 Study Page: Tides: Waves: Currents: WaterКагел МагтгиезNo ratings yet
- Properties of Liquids and Role of WaterDocument4 pagesProperties of Liquids and Role of WaterKC MasedmanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Introduction To Marine EcologyDocument98 pagesTopic 1 - Introduction To Marine EcologykontollesportsNo ratings yet
- Kegy 212Document9 pagesKegy 212Kishan TiwariNo ratings yet
- Science reviewDocument8 pagesScience reviewmelaniesrios2007No ratings yet
- Esci Finals 1Document2 pagesEsci Finals 1Franz CalopeNo ratings yet
- Aquatic EcosystemDocument43 pagesAquatic EcosystemCarla KhyllNo ratings yet
- ADLC Science 8 - Fresh & Saltwater Systems PDFDocument38 pagesADLC Science 8 - Fresh & Saltwater Systems PDFLizaNo ratings yet
- Water On The Lifeline: Aditi Vijay, Class 7 BDocument9 pagesWater On The Lifeline: Aditi Vijay, Class 7 Bhweta173No ratings yet
- O132 CO1 Littoral. Between High and Low TidesDocument12 pagesO132 CO1 Littoral. Between High and Low TidesEunicia BascoNo ratings yet
- Erosion and Deposition Action of Wind and WavesDocument6 pagesErosion and Deposition Action of Wind and WavesELEVATED KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- AQUATIC BIOME in Earth Science (3rd Year College)Document23 pagesAQUATIC BIOME in Earth Science (3rd Year College)Aileen Mae TabileNo ratings yet
- A. Decomposers Are Responsible For The Breaking Down of Nutrients in Decaying Matters of Dead Bodies of Plants, Animals, or Other Living OrganismsDocument6 pagesA. Decomposers Are Responsible For The Breaking Down of Nutrients in Decaying Matters of Dead Bodies of Plants, Animals, or Other Living OrganismsJoenetha Ann ApariciNo ratings yet
- Hydro SphereDocument6 pagesHydro SphereMARIEL DATINGALINGNo ratings yet
- Notes - Our Changing EarthDocument2 pagesNotes - Our Changing EarthjpadmmiNo ratings yet
- Unit DDocument10 pagesUnit Dharsha vardhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen Geografi KelompokDocument16 pagesDokumen Geografi KelompokMario Pamdika Esvannado PutraNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle and RocksDocument8 pagesWater Cycle and Rocksmcarmendgj74No ratings yet
- Coastal Processes and LandformsDocument20 pagesCoastal Processes and LandformsClea Allosa JunillerNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Ecosystems Study GuideDocument7 pagesAquatic Ecosystems Study Guideapi-239136335No ratings yet
- $R75FB84Document2 pages$R75FB84muzammil sardarNo ratings yet
- Lingkungan Aquatik (Renhat-Devi)Document31 pagesLingkungan Aquatik (Renhat-Devi)Ade Nur HidayatNo ratings yet
- 5 Impending Signs of Landslides and Sinkholes Continuation... Feb. 8 2021Document23 pages5 Impending Signs of Landslides and Sinkholes Continuation... Feb. 8 2021Shiela Jean H. RescoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Aquatic Ecosystems: Neighborhood Water QualityDocument12 pagesLesson 1: Aquatic Ecosystems: Neighborhood Water QualityVainapriya RNo ratings yet
- Pacific Ocean Facts from Water in the Oceans DocumentDocument5 pagesPacific Ocean Facts from Water in the Oceans DocumentAV EDITSNo ratings yet
- Basic Environmental Engineering (Che4103) : Water and Water Quality ParametersDocument38 pagesBasic Environmental Engineering (Che4103) : Water and Water Quality ParametersNasir Ahmed YusufNo ratings yet
- Gess 205Document9 pagesGess 205balajiNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Aquatic Biome: Two Basic Regions I. Freshwater Ii. MarineDocument2 pagesScience 9 Aquatic Biome: Two Basic Regions I. Freshwater Ii. MarineJF BatucalNo ratings yet
- Oceans Water Distribution Temperature MovementsDocument5 pagesOceans Water Distribution Temperature MovementsMrityunjay KrNo ratings yet
- Properties of Ocean WaterDocument5 pagesProperties of Ocean WaterJaymeeSolomon100% (1)
- Project or AssignmentDocument5 pagesProject or AssignmentangelNo ratings yet
- Geography AssignmentDocument2 pagesGeography AssignmentVarlee KannehNo ratings yet
- OceansDocument9 pagesOceansapi-407083560No ratings yet
- Earth's Life-Supporting CharacteristicsDocument11 pagesEarth's Life-Supporting CharacteristicsZannieNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 GeologyDocument5 pagesQuiz 2 Geologyhaha xdNo ratings yet
- Earth's Water Resources in 40 CharactersDocument15 pagesEarth's Water Resources in 40 CharactersLuisNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer Finals Grade 6Document5 pagesScience Reviewer Finals Grade 6LyrMa NCNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Course Guide on Water Resources & Soil ConservationDocument19 pagesEarth Science Course Guide on Water Resources & Soil ConservationRacquel BanaoNo ratings yet
- Lakes and Reservoir: Prepared By: Muhammad Musaab 14-CE-133 Section-ADocument14 pagesLakes and Reservoir: Prepared By: Muhammad Musaab 14-CE-133 Section-AMuhammad MusaabNo ratings yet
- Soil General BackgroundDocument16 pagesSoil General Backgroundnwankwovincent61No ratings yet
- Aquatic EcosystemsDocument5 pagesAquatic Ecosystemsapi-236697820No ratings yet
- Learn About Natural Water Bodies Like Seas, Lagoons, Oceans, Glaciers & MoreDocument1 pageLearn About Natural Water Bodies Like Seas, Lagoons, Oceans, Glaciers & MoreSaadiaNo ratings yet
- Envi Sci NotesDocument10 pagesEnvi Sci NoteslamusaojudeNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Ecosystems: The Sea, Once It Casts Its Spell, Holds One in Its Net of Wonder Forever. - Jacques Ives CousteauDocument25 pagesAquatic Ecosystems: The Sea, Once It Casts Its Spell, Holds One in Its Net of Wonder Forever. - Jacques Ives CousteauAmaan SaifiNo ratings yet
- Geological Formation and Earthy EpochsDocument15 pagesGeological Formation and Earthy EpochsDexiDesireeNo ratings yet
- Group-5-Chapter-6Document12 pagesGroup-5-Chapter-6Franz PampolinaNo ratings yet
- PublicationbackpageDocument2 pagesPublicationbackpageapi-351820473No ratings yet
- Major Water Bodies AssignmentDocument3 pagesMajor Water Bodies AssignmentGarvit PahwaNo ratings yet
- $R2ZYIT1Document2 pages$R2ZYIT1muzammil sardarNo ratings yet
- Seawater Density & SalinityDocument3 pagesSeawater Density & SalinityKarthik MathivananNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HydrosphereDocument39 pagesIntroduction To HydrosphereMaster MirrorNo ratings yet
- Make Me Water - 20231204 - 213226 - 0000Document66 pagesMake Me Water - 20231204 - 213226 - 0000Amberlane LimpinNo ratings yet
- Estuarine EcologyDocument96 pagesEstuarine EcologyNayeema Ferdausy Hoque100% (1)
- Aquatic Ecosystems Study GuideDocument8 pagesAquatic Ecosystems Study Guideapi-236004181No ratings yet
- 8 EvolutioncramsheetDocument2 pages8 Evolutioncramsheetapi-326958203No ratings yet
- 8 MicrobiologycramsheetDocument2 pages8 Microbiologycramsheetapi-326958203No ratings yet
- 8 EnergycramsheetDocument1 page8 Energycramsheetapi-326958203No ratings yet
- 8 PathologycramsheetDocument2 pages8 Pathologycramsheetapi-326958203No ratings yet
- 8 EcosystemcramsheetDocument1 page8 Ecosystemcramsheetapi-326958203No ratings yet
- Eog Review ProjectDocument2 pagesEog Review Projectapi-326958203No ratings yet
- Chemistry Vocabulary SheetDocument2 pagesChemistry Vocabulary Sheetapi-326958203No ratings yet
- Chemistry Day 1Document2 pagesChemistry Day 1api-326958203No ratings yet
- 8 ChemistrycramsheetDocument2 pages8 Chemistrycramsheetapi-326958203No ratings yet
- Ecosystems Vocabulary SheetDocument2 pagesEcosystems Vocabulary Sheetapi-326958203No ratings yet
- L 3 2 Independent QuestionsDocument1 pageL 3 2 Independent Questionsapi-326958203No ratings yet
- Chemistry Day 1 Student VersionDocument40 pagesChemistry Day 1 Student Versionapi-326958203No ratings yet
- Darwins Theory of EvolutionDocument2 pagesDarwins Theory of Evolutionapi-326958203No ratings yet
- L 3 1 Individual QuestionsDocument1 pageL 3 1 Individual Questionsapi-326958203No ratings yet
- Ecosystems Day 1Document28 pagesEcosystems Day 1api-326958203No ratings yet
- Hydrology Vocabulary SheetDocument2 pagesHydrology Vocabulary Sheetapi-326958203100% (2)
- Benchmark 1 Hydrology Review Student VersionDocument4 pagesBenchmark 1 Hydrology Review Student Versionapi-326958203No ratings yet
- 8th Grade Science Syllabus 2016-2017Document5 pages8th Grade Science Syllabus 2016-2017api-326958203No ratings yet
- Review JeopardyDocument56 pagesReview Jeopardyapi-326958203No ratings yet
- Review JeopardyDocument56 pagesReview Jeopardyapi-326958203No ratings yet
- ArticalDocument2 pagesArticalRabi Krishna Budha ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Sanitation and Drainage Systems - Ancient CivilisationsDocument21 pagesSanitation and Drainage Systems - Ancient CivilisationsBrian Boby ThomasNo ratings yet
- China HidrologiaDocument19 pagesChina HidrologiaMonica Andrea DiazNo ratings yet
- Techno Water PresentationDocument13 pagesTechno Water PresentationJoe BabNo ratings yet
- FEMA Flood Zone DefinitionsDocument1 pageFEMA Flood Zone DefinitionsTodd ConiffNo ratings yet
- WRE & HYDROLOGY ER KSG G-Flix KT PDFDocument169 pagesWRE & HYDROLOGY ER KSG G-Flix KT PDFSubhajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Layout P 1Document1 pageLayout P 1CIELO OLEANo ratings yet
- Extreme Weather Conditions 1Document11 pagesExtreme Weather Conditions 1Airene PalerNo ratings yet
- Flooding Bald Hills North Flood Flag MapDocument1 pageFlooding Bald Hills North Flood Flag MapNgaire TaylorNo ratings yet
- Indian Standards in Wastewater Treatment An OverviewDocument40 pagesIndian Standards in Wastewater Treatment An Overviewkbmsaami82% (11)
- Engineering Hydrology GradeupDocument74 pagesEngineering Hydrology GradeupCaalaa MirgaaNo ratings yet
- AMRUT Co-Treatment STP DPR - Adoni PDFDocument141 pagesAMRUT Co-Treatment STP DPR - Adoni PDFAdditya ChoudhharyNo ratings yet
- Plumbing ArrangementDocument6 pagesPlumbing ArrangementNivedetha VedanayagamNo ratings yet
- Crookes History Booklets Reservoirs in CrookesDocument2 pagesCrookes History Booklets Reservoirs in Crookes焚烛No ratings yet
- CHAPTER I & II - RESEARCH - BSED-MATH 2B - New Version-1Document17 pagesCHAPTER I & II - RESEARCH - BSED-MATH 2B - New Version-1Alliah Mae CastilNo ratings yet
- CE 80 Water Resources Engineering ModuleDocument3 pagesCE 80 Water Resources Engineering ModuleKristelle V. TorrealbaNo ratings yet
- 68BDocument5 pages68BJamie Schultz100% (1)
- Marine Survey Methods for Seafloor MappingDocument27 pagesMarine Survey Methods for Seafloor MappingMikhael MangopoNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Long Crested WeirDocument61 pagesCalibration of Long Crested WeirSudharsananPRSNo ratings yet
- Insights Into Sustainable EngineeringDocument24 pagesInsights Into Sustainable Engineeringcmanning17No ratings yet
- Seminar Report On:-: Pervious ConcreteDocument13 pagesSeminar Report On:-: Pervious Concreteneeraj meenaNo ratings yet
- Flood Risk and Flood ManagementDocument10 pagesFlood Risk and Flood ManagementSugeeth 107No ratings yet
- Building drainage compliance and standard notesDocument1 pageBuilding drainage compliance and standard notesmhmdjdgmailcomNo ratings yet
- Alberti - 2010 - Maintaining Ecological Integrity and Sustaining EcDocument7 pagesAlberti - 2010 - Maintaining Ecological Integrity and Sustaining Ecma hiryeNo ratings yet
- Article THIRI CV GSD 2022Document13 pagesArticle THIRI CV GSD 2022Fouad AmraouiNo ratings yet
- USACE Hydrologic AssessmentDocument44 pagesUSACE Hydrologic AssessmentYapeng ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Establishing Lon-oy Watershed Forest ReservationDocument3 pagesEstablishing Lon-oy Watershed Forest ReservationdyameswantstohelpNo ratings yet
- Foraminifera and Its ApplicationsDocument23 pagesForaminifera and Its ApplicationsAzhar UddinNo ratings yet
- Design House Drainage System at Plot Level (Autosaved)Document16 pagesDesign House Drainage System at Plot Level (Autosaved)Om BavachkarNo ratings yet
- What Is Alum and How Does It Work?Document4 pagesWhat Is Alum and How Does It Work?David AruotuNo ratings yet