Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C. Pollutants (Paper Making) : Titanium Dioxide, Dyes, Optical Brightening Agents)
Uploaded by
Lywell TanedoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C. Pollutants (Paper Making) : Titanium Dioxide, Dyes, Optical Brightening Agents)
Uploaded by
Lywell TanedoCopyright:
Available Formats
C.
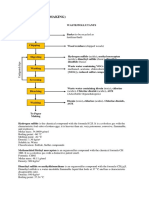
POLLUTANTS (PAPER MAKING)
PROCESS WASTE/POLLUTANTS
REFINING
CHEMICAL Waste water (contains Calcium Carbonate,
ADDITION Titanium dioxide, Dyes, Optical brightening
agents)
CLEANING
FORMING & Waste water (contains Calcium Carbonate,
DEWATERING Titanium dioxide, Dyes, Optical brightening
agents)
DRYING
COATING Minimal Pigments (such as clay,
chalk, talcum), BOD, acetone
CALENDARING
WINDING
Reject papers to be cut into
CUTTING small pieces and sold in
lower price
FINAL Reject papers to be cut
OPERATIONS into small pieces and sold
in lower price
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the formula CaCO3. It is a common substance found in
rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite (most notably as limestone), and is the main component of
shells of marine organisms, snails, pearls, and egg shells. Calcium carbonate is the active ingredient in
agricultural lime, and is created when calcium ions in hard water react with carbonate ions creating lime
scale. It is commonly used medicinally as a calcium supplement or as an antacid, but excessive
consumption can be hazardous.
Chemical formula: CaCO3
Molar mass: 100.0869 g/mol
Appearance: Fine white powder; chalky taste
Odor: odorless
Density: 2.711 g/cm3 (calcite), 2.83 g/cm3 (aragonite)
Melting point: 1,339 C (2,442 F; 1,612 K) (calcite), 825 C (1517 F; 1,098 K) (aragonite) [1]
Boiling point: decomposes
Solubility in water: 0.013 g/L (25 C)[2][3]
Titanium dioxide, (Chemical Compound) also known as titanium oxide or titania, is the naturally
occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO 2. When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white,
Pigment White 6, or CI 77891.
Formula: TiO2
Molar mass: 79.866 g/mol
Melting point: 1,843 C
Density: 4.23 g/cm
Boiling point: 2,972 C
IUPAC ID: Titanium dioxide, Titanium (IV) oxide
Optical brighteners are additives that paper manufacturers put into paper in order to help a paper look
"whiter." They are also called optical brightening agents (OBA), or sometimes "artificial whiteners."
Optical brighteners, optical brightening agents (OBAs), fluorescent brightening agents (FBAs) or
fluorescent whitening agents (FWAs) are chemical compounds that absorb light in the ultraviolet and
violet region (usually 340-370 nm) of the electromagnetic spectrum, and re-emit light in the blue region
(typically 420-470 nm) by fluorescence. Fluorescent emission is a short-lived period of light emission by
a fluorophore, unlike phosphorescence, which is long-lived. These additives are often used to enhance the
appearance of color of fabric and paper, causing a "whitening" effect; they make intrinsically
yellow/orange materials look less so, by compensating the deficit in blue and purple light reflected by the
material, with the blue and purple optical emission of the fluorophore.
A dye is a colored substance that has an affinity to the substrate to which it is being applied. The dye is
generally applied in an aqueous solution, and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on
the fiber.
You might also like
- FullBookofProceedingsSBMC2021 23 26Document1 pageFullBookofProceedingsSBMC2021 23 26nadun shameeraNo ratings yet
- Calcium carbonate paper whiteningDocument5 pagesCalcium carbonate paper whiteningLywell TanedoNo ratings yet
- List of Chemicals Used in Pulp and Paper MakingDocument5 pagesList of Chemicals Used in Pulp and Paper MakingVeena Kohli67% (3)
- Reactions_of_Main_Group_Elements_with_CarbonatesDocument4 pagesReactions_of_Main_Group_Elements_with_CarbonatesAurenio RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Factsheet Liquid Chlorine PDFDocument2 pagesFactsheet Liquid Chlorine PDFHarish TiwariNo ratings yet
- Alkali Metals and Their PropertiesDocument3 pagesAlkali Metals and Their PropertiesJhalak ChandraNo ratings yet
- Study On Dye Industry Wastewater Treatment Process by Alum and Natural CharcoalDocument5 pagesStudy On Dye Industry Wastewater Treatment Process by Alum and Natural CharcoalInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Watch Water® Initiative: Carbonblock - Titansorb 3 (Ts3)Document4 pagesWatch Water® Initiative: Carbonblock - Titansorb 3 (Ts3)Mehmet GülenerNo ratings yet
- Genchem 1 NOTESDocument14 pagesGenchem 1 NOTESGwend MemoracionNo ratings yet
- Akzo Nobel's Duomeen TDO: PointDocument1 pageAkzo Nobel's Duomeen TDO: PointさいとはちこNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Potassium Carbonate From Banana Plant (Musa Balbisiana)Document17 pagesIsolation of Potassium Carbonate From Banana Plant (Musa Balbisiana)zawNo ratings yet
- TITANIUM DIOXIDE Chemical and Technical AssessmentDocument8 pagesTITANIUM DIOXIDE Chemical and Technical AssessmentDi Stovall100% (1)
- Process Selection v7Document90 pagesProcess Selection v7VaanNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of Titanium DioxideDocument52 pagesManufacture of Titanium DioxideJayraj Dayma100% (1)
- RCF's New 100 MTPD Concentrated Nitric Acid PlantDocument27 pagesRCF's New 100 MTPD Concentrated Nitric Acid PlantMayur KhirodeNo ratings yet
- FullOzoneReport AclarusDocument32 pagesFullOzoneReport AclarusAdam FendrychNo ratings yet
- Sodium Carbonate - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesSodium Carbonate - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediad_richard_dNo ratings yet
- Sodium Percarbonate PDFDocument16 pagesSodium Percarbonate PDFillpraydo2No ratings yet
- Water Technology Requirements and ParametersDocument12 pagesWater Technology Requirements and ParametersKARTHI KRISHNANo ratings yet
- Recycling Colored Broke for High Bright Paper ManufacturingDocument7 pagesRecycling Colored Broke for High Bright Paper ManufacturingK S RAJESHNo ratings yet
- Water - OfficialDocument62 pagesWater - OfficialPushp BahukhandiNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet TexanolDocument4 pagesTechnical Data Sheet TexanolRICHARD ODINDONo ratings yet
- °C °C (Calcite), 825°C (Aragonite)Document2 pages°C °C (Calcite), 825°C (Aragonite)api-343258776No ratings yet
- Summary of Bsc. Thesis ReportDocument2 pagesSummary of Bsc. Thesis ReportGidiano De GiovannaNo ratings yet
- Pulp and Paper Mill Waste: Ajay Kumar Verma 2010PCH 116 Sanjay Verma 2010PCH 102Document15 pagesPulp and Paper Mill Waste: Ajay Kumar Verma 2010PCH 116 Sanjay Verma 2010PCH 102jefferson atienzaNo ratings yet
- DM PlantDocument30 pagesDM Plantapi-19775783No ratings yet
- Design of Water Treatment PlantDocument15 pagesDesign of Water Treatment PlantYousef ZamNo ratings yet
- Pollutants Pulp FinalDocument3 pagesPollutants Pulp FinalLywell TanedoNo ratings yet
- Sodium bicarbonate: versatile chemical raising agent and disinfectantDocument63 pagesSodium bicarbonate: versatile chemical raising agent and disinfectantSridhar RaparthiNo ratings yet
- Pulp and Paper IndustryDocument34 pagesPulp and Paper IndustryjantskieNo ratings yet
- Chemical FormulasDocument7 pagesChemical FormulasKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Key Considerations for Frac Flowback Water TreatmentDocument43 pagesKey Considerations for Frac Flowback Water TreatmentSong MunNo ratings yet
- Calcium (Ca) : CompoundsDocument7 pagesCalcium (Ca) : CompoundsTrisno AfandiNo ratings yet
- El Ac SL 01Document4 pagesEl Ac SL 01Pablo SalvatierraNo ratings yet
- Specialty ChemicalsDocument30 pagesSpecialty ChemicalsucheNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document70 pagesModule 1Xavier HunterNo ratings yet
- What Is Activated CarbonDocument6 pagesWhat Is Activated CarbonAustroCarbonNo ratings yet
- Chem Unit 1Document34 pagesChem Unit 1Ismaeel ShamsiNo ratings yet
- Unit Operations and Processes Week3Document41 pagesUnit Operations and Processes Week3Tugce ZorluNo ratings yet
- ETP Technical Hand Book - Chemical Treatment System1 PDFDocument42 pagesETP Technical Hand Book - Chemical Treatment System1 PDFmasud.imtiaz3290100% (1)
- Acuro Organics Limited PDFDocument25 pagesAcuro Organics Limited PDFphewphewphew200No ratings yet
- Comprehensive Review of Current Endodontic SealersDocument18 pagesComprehensive Review of Current Endodontic SealerskarishmaNo ratings yet
- Imwaru (Industrial and Mining Water Research Unit) Imwaru (Industrial and Mining Water Research Unit)Document15 pagesImwaru (Industrial and Mining Water Research Unit) Imwaru (Industrial and Mining Water Research Unit)sirbhimselfNo ratings yet
- Common Names and Formulas of Important Chemical CompoundsDocument7 pagesCommon Names and Formulas of Important Chemical Compoundsayush singhNo ratings yet
- Black CoringDocument8 pagesBlack CoringawadallaNo ratings yet
- Phar ChemDocument4 pagesPhar ChemChelsea100% (1)
- Match TreatmentDocument2 pagesMatch TreatmentErik WeeksNo ratings yet
- 274894.Lanak-Offshore Drilling and Environmental ProtectionDocument11 pages274894.Lanak-Offshore Drilling and Environmental ProtectionflowealthNo ratings yet
- n01522624w - Design Project (Repaired)Document68 pagesn01522624w - Design Project (Repaired)kudaNo ratings yet
- Unit - I: Water TechnologyDocument69 pagesUnit - I: Water TechnologyAkshaya MotamarriNo ratings yet
- Chemical Names, Formulas & UsesDocument7 pagesChemical Names, Formulas & Useskrishankant sharmaNo ratings yet
- Group 1ADocument4 pagesGroup 1AAna Eunice Mahilum LintagNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment EssentialsDocument24 pagesWater Treatment EssentialsNagaraju BasaNo ratings yet
- Elastomers SBR PDFDocument4 pagesElastomers SBR PDFGuoxiang ChungNo ratings yet
- Unit 4water Tech. PPT Aktu ChemistryDocument77 pagesUnit 4water Tech. PPT Aktu ChemistryVAISHNAVI SINGHNo ratings yet
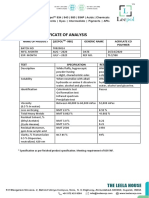
- Acrylate Polymer Certificate of AnalysisDocument1 pageAcrylate Polymer Certificate of Analysisjuan felixNo ratings yet
- Pollutants Pulp FinalDocument3 pagesPollutants Pulp FinalLywell TanedoNo ratings yet
- The Bottom Chord of A Warren Roof Truss As Shown in The Figure Below Is To Be DesignedDocument2 pagesThe Bottom Chord of A Warren Roof Truss As Shown in The Figure Below Is To Be DesignedLywell TanedoNo ratings yet
- Tarlac State University College of Engineering: Engr. Leonides A. TatuDocument1 pageTarlac State University College of Engineering: Engr. Leonides A. TatuLywell TanedoNo ratings yet
- Pollutants Pulp FinalDocument3 pagesPollutants Pulp FinalLywell TanedoNo ratings yet
- Net Pyrradiometer Definitions - Defined TermDocument2 pagesNet Pyrradiometer Definitions - Defined TermLywell TanedoNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document3 pagesBook 1Lywell TanedoNo ratings yet
- Pyranometer - WikipediaDocument6 pagesPyranometer - WikipediaLywell TanedoNo ratings yet
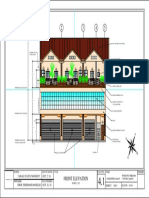
- ElevationDocument1 pageElevationLywell TanedoNo ratings yet
- Ethers and Epoxides: by Shintanovita SariDocument47 pagesEthers and Epoxides: by Shintanovita SariShinta Novita SariNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data SheetDocument5 pagesMaterial Safety Data SheetFiqua Nurul Rafiqua SimsNo ratings yet
- Comparision of GasketsDocument3 pagesComparision of Gasketsanwer_quadriNo ratings yet
- Phenates (Alkyl Phenate Sulfides) : Product Stewardship SummaryDocument4 pagesPhenates (Alkyl Phenate Sulfides) : Product Stewardship SummaryPayal MinochaNo ratings yet
- Ig 100Document16 pagesIg 100Rhoderic Radomes JrNo ratings yet
- CIP/CIL/CIC Selection Guide for Gold Mining ProcessesDocument8 pagesCIP/CIL/CIC Selection Guide for Gold Mining ProcessesChristy Alexandra Solano Gavelán0% (1)
- To What Extent Does Initial Shelf Life Affect Potency of Antacids?Document26 pagesTo What Extent Does Initial Shelf Life Affect Potency of Antacids?Joson ThomasNo ratings yet
- Plastic Fuel Alka ZadgaonkarDocument60 pagesPlastic Fuel Alka Zadgaonkarprashanth2812No ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Chemosphere 2017 10 139Document86 pages10 1016@j Chemosphere 2017 10 139Aldehir AldehirNo ratings yet
- 15W40 MECHA TOOL Hoja Tecnica PDFDocument2 pages15W40 MECHA TOOL Hoja Tecnica PDFramsi17No ratings yet
- PJSIR Series A: Physical Sciences Vol. 56, No. 1, January-February, 2013Document15 pagesPJSIR Series A: Physical Sciences Vol. 56, No. 1, January-February, 2013Syed Umair AnwerNo ratings yet
- Unit 12 - Organic Compound Containing Nitrogen Type - Match The FollowingDocument8 pagesUnit 12 - Organic Compound Containing Nitrogen Type - Match The FollowingJay VermaNo ratings yet
- Simple & Fractional Distillation ExperimentsDocument7 pagesSimple & Fractional Distillation ExperimentsPreeti Gunthey DiwanNo ratings yet
- Composite AssignmentDocument4 pagesComposite AssignmentAmna QureshiNo ratings yet
- Determination of Sodium Bisulfite Content by Iodometric MethodDocument3 pagesDetermination of Sodium Bisulfite Content by Iodometric MethodM. ade Dwi MaesandiNo ratings yet
- Impact of Cement Industries Dust On Selective Green Plantsa Case Study in Ariyalur Industrial ZoneDocument7 pagesImpact of Cement Industries Dust On Selective Green Plantsa Case Study in Ariyalur Industrial ZonekrankeneraNo ratings yet
- 8ch0 02 Que 20220528Document28 pages8ch0 02 Que 20220528Nisidini JasingheNo ratings yet
- GunkDocument9 pagesGunkFaizal JamalNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry Rvision Notes TOPIC 7: Chemical Reactions Rates of ReactionDocument7 pagesIgcse Chemistry Rvision Notes TOPIC 7: Chemical Reactions Rates of ReactionAli RizwanNo ratings yet
- Crystal pH Guide: Common & Uncommon CrystalsDocument4 pagesCrystal pH Guide: Common & Uncommon CrystalsyholicNo ratings yet
- Apm Tubes Catalogue PDFDocument28 pagesApm Tubes Catalogue PDFMayank AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Natural Nonwoven Materials Made from Leaf and Stem FibresDocument21 pagesNatural Nonwoven Materials Made from Leaf and Stem FibresRuchira WijesenaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Short Report (Preparation of Benzoic Acid)Document2 pagesChemistry Lab Short Report (Preparation of Benzoic Acid)Matthew Chu100% (2)
- Textile Wastewater TreatmentDocument21 pagesTextile Wastewater TreatmentRonak JoshiNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Previous Years' Questions SolvedDocument9 pagesHaloalkanes And Haloarenes Previous Years' Questions SolvedAkshat GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document6 pagesLesson 2NguyễnHoàiNamNo ratings yet
- Kamalkant Chem For All BBSR 1Document4 pagesKamalkant Chem For All BBSR 1kamalkantmbbsNo ratings yet
- 6 ReportDocument31 pages6 ReportAbhi Butani100% (1)
- Chapter 4-Solid Solution Equilibrium Phase Diagram PDFDocument38 pagesChapter 4-Solid Solution Equilibrium Phase Diagram PDFMohd Azizi50% (2)
- In The Name of ALLAH, The Most Gracious, The Most Merciful: A Threat To EnvironmentDocument24 pagesIn The Name of ALLAH, The Most Gracious, The Most Merciful: A Threat To EnvironmentMoeed KhanNo ratings yet