Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circuit Switching Is A Switching Method in Which A Dedicated Communication Path in
Uploaded by
Kapil DoraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circuit Switching Is A Switching Method in Which A Dedicated Communication Path in
Uploaded by
Kapil DoraCopyright:
Available Formats
Circuit Switching - What is Circuit Switching?
Circuit switching is a switching method in which a dedicated communication path in
physical form between two stations within a network is established, maintained and
terminated for each communication session. It has basically three phases as circuit
establishment, data transfer and circuit disconnect.
Once the connection is established, the data transfer is transparent. The main feature of
such a connection is that it provides a fixed data rate channel and both subscribers must
operate at this rate, It is considered inefficient compared to packet switching because
channel capacity is completely dedicated for duration of connection. If there is no data
at any moment of time, channel capacity goes wasted. Moreover, setting up of
connection takes time.
Circuit switching has two types of transmissions.
Datagram transmissions - Datagram transmissions have individually addressed
frames.
Data-stream transmissions - Data-stream transmissions have a stream of data for
which address checking occurs only once. The routing in circuit switching may have
either static routing or dynamic routing. In case of static routing, this methodology uses
the same approach all the time while dynamic routing allows alternate routing
depending on traffic.
The Key Point of Circuit Switching are.
1. It is the simplest method of data communication in which a dedicated physical
connection or path is established between the sending and receiving device.
2. In circuit switched networks, a set of switches are connected by physical links. A
connection between two stations is a dedicated path made of one or more links.
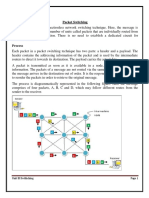
3. Figure shows a circuit switched network in which computer A, B and C are connected
to computer D, E, F and G via four switches. If these computers are to be connected with
a point-to-point connections, 12 dedicated lines are required which will incur high line
cost.
4. The four switches connecting these computers thus provide dedicated links by
reducing the line cost. Here I, II, III and IV are the circuit switches or nodes. Nodes I,
III, IV are connected to computers while II is only routing node.
5. In circuit switching the routing decision is made when path is set up across the
network. After the link has been set between the sender and receiver, the information is
forwarded continuously over the link.
6. The dedicated path established between the sender and the receiver is maintained for
entire duration of conversation.
7. This link or path is released only when data transmission between sender and
receiver is over.
8. Circuit switching takes place at the physical layer.
9. Before starting communication, the stations must make a reservation of resources to
be used during the communication. These resources can be switch buffers, switch
processing time, switch input/output ports. These resources remain dedicated during
the entire duration of data transfer.
10 Data transferred between the two stations are not packetized (i.e. in form of
packets). The data are a continuous flow sent by the source station and received by the
destination station and there may be periods of silence.
11. There is no addressing involved in data transfer. The switches route the data
based on their occupied band (FDM) or time slot (TDM). However, there is end-to-end
addressing used during set up phase.
12. In telephone systems circuit switching is used.
13. The communication in a circuit switched network takes place in three phases:
1. Circuit establishment or setup phase.
2. Data transfer phase.
3. Circuit disconnects or tears down phase.
Circuit establishment or Setup Phase
1. In circuit .switched network, before actual data transfer takes place, a dedicated circuit
or path is established between the sender and receiver.
2. For example, as shown in fig. if two communicating devices are A and D, then a
dedicated path will be set up from A to I, I to II, II to III and III to D first.
3. End-to-End addressing (i.e. source and destination address) is required for creating a
connection between two end systems.
Data Transfer Phase
1. Actual data transfer between the source and destination takes place after the dedicated
path is set up between them.
2. The data flows are continuous between sender and receiver. There may be periods of
silence in between.
3. Generally all the internal connections are duplex.
Circuit Disconnect or Teardown Phase.
When one of the parties needs to disconnect, a signal is sent to each switch to release the
resources.
Circuit Switch
1. A circuit switch is a device that creates a temporary connection between an input link
and output link.
2. A circuit switch usually has n input lines and m output lines i.e. number of input lines
and number of output lines may not be equal.
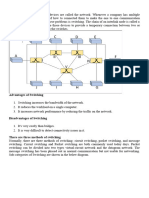
Advantages of Circuit Switching
The advantages of circuit switching are:
1. The dedicated path/circuit established between sender and receiver provides a
guaranteed data rate.
2. Once the circuit is established, data is transmitted without any delay as there is no
waiting time at each switch.
3. Since a dedicated continuous transmission path is established, the method is suitable
for long continuous transmission.
Disadvantages of Circuit Switching
The various disadvantages of circuit switching are:
1. As the connection is dedicated it cannot be used to transmit any other data even if the
channel is free.
2. It is inefficient in terms of utilization of system resources. As resources are allocated
for the entire duration of connection, these are not available to other connections.
3. Dedicated channels require more bandwidth.
4. Prior to actual data transfer, the time required to establish a physical link between the
two stations is too long.
You might also like
- SWITCHINGDocument5 pagesSWITCHINGM-soft solutionsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Switching: Delivered by Joel Anandraj.E Ap/ItDocument30 pagesLecture 7 - Switching: Delivered by Joel Anandraj.E Ap/ItjoelanandrajNo ratings yet
- Switching TechniquesDocument22 pagesSwitching Techniqueskrushitghevariya41No ratings yet
- SwitchingDocument42 pagesSwitchingparidhiagarwal129No ratings yet
- 1.7 Circuit Switching - 1.8 Packet Switching NotesDocument11 pages1.7 Circuit Switching - 1.8 Packet Switching NotesMAGESH K SEC 2020No ratings yet
- Switching Networks: Circuit, Packet & MessageDocument20 pagesSwitching Networks: Circuit, Packet & MessageShalini Kumari GuptaNo ratings yet
- Switching and Types of Switching TechniquesDocument20 pagesSwitching and Types of Switching TechniquesLena DevarajNo ratings yet
- ECE 542 - Lecture 2Document15 pagesECE 542 - Lecture 2JohnCross DavidMaryNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Network ModelDocument28 pagesUnit-3 Network Modeljaydipzinzuvadiya098No ratings yet
- Central Women's University: Assignment No: 1 Assignment On SwitchingDocument14 pagesCentral Women's University: Assignment No: 1 Assignment On SwitchingAfrina DiptiNo ratings yet
- Module-2: Switching FundamentalsDocument41 pagesModule-2: Switching FundamentalsAchin BatwaraNo ratings yet
- CN Unit IIIDocument40 pagesCN Unit IIIVIJAY KARTHICK X CSE studentNo ratings yet
- Packet Switching: Unit III SwithchingDocument5 pagesPacket Switching: Unit III Swithchinghello hiNo ratings yet
- Switching NotesDocument12 pagesSwitching Notesdivyanshu11111100% (1)
- SwitchingDocument21 pagesSwitchingJay GholapNo ratings yet
- Network / Message Switching Techniques: Unit 4Document9 pagesNetwork / Message Switching Techniques: Unit 4Rahul singh bishtNo ratings yet
- Circuit-Switched vs Packet-Switched Networks ExplainedDocument23 pagesCircuit-Switched vs Packet-Switched Networks ExplainedswethaNo ratings yet
- Switching and It's TypesDocument6 pagesSwitching and It's TypesElangovan MNo ratings yet
- 8 ways to send data across networksDocument3 pages8 ways to send data across networksSneha JainNo ratings yet
- CN UNIT-5 MaterialDocument25 pagesCN UNIT-5 MaterialAparna GattimiNo ratings yet
- Mod5 Switching PDFDocument50 pagesMod5 Switching PDFAyush kumarNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer Networks (EENG-4308)Document28 pagesData Communication and Computer Networks (EENG-4308)Bezabh Abebaw100% (1)
- Computer NetworksDocument70 pagesComputer NetworksSahil NishadNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Note 12Document7 pagesData Communication Note 12Shahariar Kabir ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and NetworkingDocument21 pagesData Communication and NetworkingH-Muhaimen Ul AzizNo ratings yet
- Network Switching ExplainedDocument7 pagesNetwork Switching ExplainedMarinette MedranoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Network Switching Character and Bit Oriented ProtocolDocument5 pagesModule 4 Network Switching Character and Bit Oriented Protocoleltn s.No ratings yet
- UNIT 3-SwitchingDocument42 pagesUNIT 3-SwitchingBeghin BoseNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1 Typical Functions:: 1.1 Communication NetworksDocument71 pages1.1.1 Typical Functions:: 1.1 Communication NetworksAjay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Concepts: Dr. Shuchita Upadhyaya Bhasin Professor Department of Computer Science & ApplicationsDocument28 pagesData Communication Concepts: Dr. Shuchita Upadhyaya Bhasin Professor Department of Computer Science & ApplicationsRaj VermaNo ratings yet
- What is the Network LayerDocument26 pagesWhat is the Network LayerDeepKiran MunjalNo ratings yet
- C1006 Chapter 6Document9 pagesC1006 Chapter 6feezy1No ratings yet
- Q1. Explain All Design Issues For Several Layers in Computer. What Is Connection Oriented and Connectionless Service?Document8 pagesQ1. Explain All Design Issues For Several Layers in Computer. What Is Connection Oriented and Connectionless Service?Shabbir KahodawalaNo ratings yet
- SwitchingDocument3 pagesSwitchingaswinNo ratings yet
- Switching Techniques ClassificationDocument4 pagesSwitching Techniques ClassificationMajid AliNo ratings yet
- Switching and Network ch33Document61 pagesSwitching and Network ch33mohammed draeyNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Packet SwitchingDocument3 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Packet SwitchingkasdaNo ratings yet
- SwitchingDocument3 pagesSwitchingSelvakrishnan SekarNo ratings yet
- Switching TechniquesDocument6 pagesSwitching TechniquesNoman M HasanNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Telecommunication Network Model and TypesDocument19 pagesLecture - Telecommunication Network Model and TypesMOHAMMED FAYEZ KHANNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document13 pagesUnit 2Nihal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit3 CNDocument11 pagesUnit3 CNthaarshine aNo ratings yet
- Unit-7: Packet SwitchingDocument21 pagesUnit-7: Packet SwitchingSubeksha PiyaNo ratings yet
- CN Module 3Document23 pagesCN Module 3Priya RanaNo ratings yet
- Data CommunicationsDocument54 pagesData CommunicationsAhmed RamadanNo ratings yet
- Switching TechnologiesDocument16 pagesSwitching TechnologiesPravallika MaddaliNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer Switching Networks ExplainedDocument42 pagesPhysical Layer Switching Networks ExplainedPalashAhujaNo ratings yet
- Week # 04: Data Communication & NetworkDocument32 pagesWeek # 04: Data Communication & NetworkSaad Ashfaq XaadNo ratings yet
- 13 Network LayerDocument32 pages13 Network Layeranushka aroraNo ratings yet
- SwitchingDocument7 pagesSwitchingkrgcegNo ratings yet
- Cs52 Computer Networks Unit Iii 9 Circuit Switching vs. Packet Switching / Packet Switched Networks - IP - ARP - RARP - DHCP - ICMPDocument33 pagesCs52 Computer Networks Unit Iii 9 Circuit Switching vs. Packet Switching / Packet Switched Networks - IP - ARP - RARP - DHCP - ICMPsamueljamespeterNo ratings yet
- 10 Circuit Packet SwitchingDocument18 pages10 Circuit Packet SwitchingAmmar salahNo ratings yet
- Data CommunicationDocument18 pagesData Communicationmukesh244No ratings yet
- SYN CH - 1 and 2Document20 pagesSYN CH - 1 and 2IG TECHNo ratings yet
- Amitava Nag: Assistant Professor Dept. of IT Academy of TechnologyDocument14 pagesAmitava Nag: Assistant Professor Dept. of IT Academy of TechnologyParomita BiswasNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication Network Topic: Switching: By: Dr. Ritesh Kumar JaiswalDocument12 pagesComputer Communication Network Topic: Switching: By: Dr. Ritesh Kumar JaiswalashwiniNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication Network Topic: Switching: By: Dr. Ritesh Kumar JaiswalDocument12 pagesComputer Communication Network Topic: Switching: By: Dr. Ritesh Kumar JaiswalashwiniNo ratings yet
- Network Communication Modes and ImpairmentsDocument44 pagesNetwork Communication Modes and Impairmentseskedar assefaNo ratings yet
- Switching TechniquesDocument14 pagesSwitching TechniquesKavya ParasharNo ratings yet
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- Addition of ArrayDocument2 pagesAddition of ArrayVaishnavi ChundiNo ratings yet
- The differences between LAN, MAN and WANDocument3 pagesThe differences between LAN, MAN and WANKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Java Programs 1Document1 pageJava Programs 1Kapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds: SolutionDocument49 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds: SolutionKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Checksum Calculation Ensures Data Packet IntegrityDocument2 pagesChecksum Calculation Ensures Data Packet IntegrityKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Once A Connection Is Obtained We Can Interact With The DatabaseDocument5 pagesOnce A Connection Is Obtained We Can Interact With The DatabaseKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- This Keyword in JavaDocument6 pagesThis Keyword in JavaKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Types of VariablesDocument1 pageTypes of VariablesKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Node Network Routes Workstation ISP Proxy Server Firewall Router Headers Packets SwitchDocument1 pageNode Network Routes Workstation ISP Proxy Server Firewall Router Headers Packets SwitchKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Lab QuestionsDocument2 pagesData Structure Lab QuestionsKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Exponent and RadicalDocument1 pageExponent and RadicalKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Lab QuestionDocument1 pageInformation Technology Lab QuestionKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- ALOHA protocol for shared communication channelsDocument6 pagesALOHA protocol for shared communication channelsKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- 2D TransformationsDocument5 pages2D TransformationsKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Checksum Calculation Ensures Data Packet IntegrityDocument2 pagesChecksum Calculation Ensures Data Packet IntegrityKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Raster and Random ScanDocument2 pagesRaster and Random ScanKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Awt Event HandlingDocument4 pagesAwt Event HandlingsornajaNo ratings yet
- Java GUI Programming TutorialDocument45 pagesJava GUI Programming TutorialKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- 2D TransformationsDocument5 pages2D TransformationsKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument8 pagesCryptographyKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Quiz Project ReportDocument27 pagesQuiz Project ReportKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Wrapper ClassesDocument10 pagesWrapper ClassesKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Object Class in JavaDocument2 pagesObject Class in JavaKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Method DispatchDocument2 pagesDynamic Method DispatchKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Awt Event HandlingDocument4 pagesAwt Event HandlingsornajaNo ratings yet
- Analog Transmission TechniquesDocument8 pagesAnalog Transmission TechniquesKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Raster and Random ScanDocument2 pagesRaster and Random ScanKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- ALOHA protocol for shared communication channelsDocument6 pagesALOHA protocol for shared communication channelsKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Type Checking in JavaDocument1 pageType Checking in JavaKapil DoraNo ratings yet
- Analytics For TwitterDocument300 pagesAnalytics For TwitterHarryRaoNo ratings yet
- JPSP 2022 191Document14 pagesJPSP 2022 191Jem VenturaNo ratings yet
- Ha - Nursing ProcessDocument81 pagesHa - Nursing ProcessPam LalaNo ratings yet
- Sentence Patterns ExplainedDocument7 pagesSentence Patterns ExplainedCharmaine DivinaNo ratings yet
- Norstar Plus Meridian Nortel PBX Manual Install Guide 4.0Document523 pagesNorstar Plus Meridian Nortel PBX Manual Install Guide 4.0pquesnel3No ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document19 pagesChapter 11THƯ LÊNo ratings yet
- 01-ATM and DSL Interface ConfigurationDocument17 pages01-ATM and DSL Interface ConfigurationDzenan CeranicNo ratings yet
- Field Study 2 Episode 5Document7 pagesField Study 2 Episode 5Jerome RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Downstream TA Execution Plan DevelopmentDocument88 pagesDownstream TA Execution Plan DevelopmentNack Abd RauofNo ratings yet
- Module 1.2Document29 pagesModule 1.2Kathleen Grace MagnoNo ratings yet
- The 21st Century Teacher As A Facilitator of LearningDocument16 pagesThe 21st Century Teacher As A Facilitator of LearningRamil F. Adubal100% (3)
- Lesson Plan - TransportationsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan - TransportationsRadivan InzmNo ratings yet
- Kurt LewinDocument3 pagesKurt LewinNguyên Nguyễn100% (2)
- Prepared By: Maimunah BT Mohd Nordin KKTM KuantanDocument21 pagesPrepared By: Maimunah BT Mohd Nordin KKTM KuantanMoon NordinNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Math Addition Without RegroupingDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Math Addition Without Regroupingapi-486190068No ratings yet
- TEAM Lesson Plan Template: StandardsDocument5 pagesTEAM Lesson Plan Template: Standardsapi-317249345No ratings yet
- CLIL Assessment Powerpoint - Compatibility ModeDocument5 pagesCLIL Assessment Powerpoint - Compatibility ModeNicoletaNicoletaNo ratings yet
- DLL-FORMAT-for-5-MAPEH 5 - Q2 - W4Document7 pagesDLL-FORMAT-for-5-MAPEH 5 - Q2 - W4KHRISTINE M. VASALLONo ratings yet
- Tesis Final B.A AbielDocument40 pagesTesis Final B.A AbielAbiel SantosNo ratings yet
- Sample MCQ-Code No. 19604-Subject-Ethics, Constitution and Media Laws-Dept of Communication & JournalismDocument6 pagesSample MCQ-Code No. 19604-Subject-Ethics, Constitution and Media Laws-Dept of Communication & JournalismMisha MrinayaNo ratings yet
- Economics Essay TopicsDocument6 pagesEconomics Essay Topicsmiwaj0pabuk2100% (2)
- E-Commerce 2017 Business. Technology. Society.: 13 EditionDocument46 pagesE-Commerce 2017 Business. Technology. Society.: 13 Editiontekendra nath100% (1)
- Chapter 22 Managing Personal Communications - Direct and Database Marketing and Personal SellingDocument17 pagesChapter 22 Managing Personal Communications - Direct and Database Marketing and Personal SellingBrian Duela100% (1)
- Improving Students' Listening Skill and Vocabulary Mastery Through Contextual Teaching and LearningDocument12 pagesImproving Students' Listening Skill and Vocabulary Mastery Through Contextual Teaching and LearningJennet SenawatiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture Society and Politics How Society Is OrganizedDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Culture Society and Politics How Society Is OrganizedSTEPHEN JAMES RONCESVALLES LIZANo ratings yet
- AF AssignmentDocument2 pagesAF AssignmentKavya PandyaNo ratings yet
- Categorical Conventions in Music Discourse Style and Genre ALLAN MOOREDocument12 pagesCategorical Conventions in Music Discourse Style and Genre ALLAN MOORELeonardo AguiarNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy - Q3 - Week 1Document7 pagesMedia and Information Literacy - Q3 - Week 1Angelo Martinez75% (4)
- Classwide Peer TutoringDocument2 pagesClasswide Peer Tutoringapi-313063092No ratings yet
- Effects of Social Media On SocietyDocument17 pagesEffects of Social Media On SocietyPooja RamNo ratings yet