Professional Documents
Culture Documents
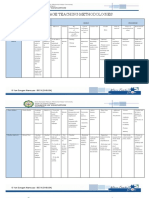
Topic 13 PDF
Uploaded by
ManuelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 13 PDF
Uploaded by
ManuelCopyright:
Available Formats
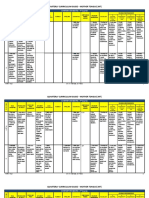
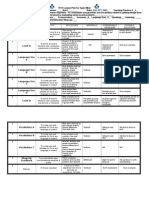
-O. Com.
B- Literature C - Explanation
-RW A- Increase of communication
Useful literary texts -Grammar inductively
-V. Bilingual Words Lists, dict. studies, F.Gouin, language in a context
Easy To apply - A. C- Think in F.L
memorization Language needs -Translation avoided Form-meaning
-T - A- Memorize endless 3.1: THE DIRECT METHOD -Teacher own plan Correct pronunciation
Grammar Deductively -Speech, listening No natural learning
Boring experience
-Mother tongue-Reference,explanation Native or high level speakers
-Textbooks Mother tongue explanation
3-MODERN APPROACHES 3.2: THE ORAL APPROACH
Rules, conjugations,
translation, sentences
Oral skills Speaking and oral forms 1
1840s-1940s
Items in sentences, drills and accuracy Language in a context
No grammatical explanations Not able to use language real communication
R. D. 126/2014: O.S. F Ecclectic Approach A-British Structuralism No mother tongue
2-THE TRADITIONAL Textbooks and visual aids
APPROACH: THE GRAMMAR
Approach Chance TRANSLATION METHOD
Method 1-The USA Army Programmes
B-Oral skills goal, 1
Technique 3.3: THE AUDIOLINGUAL METHOD 2-Structural Approaches
Struture-based: phonology, morphology, sintax
Proliferation 1-INTRODUCCIN 3- Behaviourism
Langauge by imitation and repetition, dialogues and drills
Real situations A.
Goal- orientated communicative activity 13: EVOLUTION AND HISTORY OF LANGUAGE TEACHING: No translation, grammatical explanations, mother tongue
Prabhu, finding
Language from beginning FROM GRAMMAR TRANSLATION TILL MODERN DAY A.
solution a natural
4.4.- TBL APPROACHES No translation, grammatical explanations, mother tongue
acquisition
Conversational fluency
Methodology: 4-CURRENT APPROACHES 1 Oral skills
1-Pre-task phase Very mechanica
1970S, active role 4.3.-LCA
2-The task-cycle phase:task itself,the 4.2 HUMANISTIC APPROACHES Patterns no realising
planning,the report 4.1-THE COMMUNICATIVE APPROACH Unable language real communication
3-Thelanguage-focus phase
S. take charge their own learning B) Natural
Teacher helper, not teach directly Approach Pupilspersonality and positive 1970s
Meaning and c.c feelings
Training for Personal assessment C: real world, l.active role, work
E) Suggestopedia independently, t. facilitate c. and Chomsky: language no imitation and repetition, innate
problem-solving Learning strategies
Krashen: underlying and creative abilities. Halliday, Hymes, Austin,
L.more aware Language awareness childrenautonomy.
principles.Acquisition and A)TPR
Fluency> A Lozanov: decoration, Not suitable, grammar of the language functional -communicative potential
learning. Input. Affective filter
L.lack abilities to furniture, voice (Non- language
direct Take on more responsability conscious influence)
Dificculty matching learning Asher: adultscommands C.C. Meter Ley
O.C
group needs Associated Items meaningful context. Pairs and group work
Types of help Meaning no form
L-R.Speech Imperative
Rel.atm, m.c,groups, Richard: understandig and oral Reduce stress
Widdowson: The essential emotional factors proeficiency Translation students need
5-CONCLUSION
is that there are no Acq. Long time, language
universal solutions not to acquisition Functional syllabus, meaning and
Fluency >Accuracy. Errors normal, trial and error
C) The Silent Way use of structures:
D) CLL Grammar expl. benefit
6- BIBLIOGRAPHY Curran Discover and create no repeating
Cognitive- affective abilities: Whole Physical objects
Gattegno:Teachers
7- WEBSITES person learning Silence concentration
Whisper- translation- messages silent Materials:games, realia, c.act.
Self-awareness
Lack of syllabus- objectives unclear
You might also like
- Caparing TableDocument4 pagesCaparing TableNgọc HồNo ratings yet
- Acp English Class 4Document10 pagesAcp English Class 4Chinmayee MishraNo ratings yet
- Fall Semesters Spring Semester S1 S2Document2 pagesFall Semesters Spring Semester S1 S2Omar EzzaouaNo ratings yet
- Language Teaching MethodologiesDocument10 pagesLanguage Teaching MethodologiesG-yan Dungan MamuyacNo ratings yet
- CM - English 9Document7 pagesCM - English 9Yuri IssangNo ratings yet
- Year 1 English phonics lessonDocument2 pagesYear 1 English phonics lessonatiqahNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map 7 2019 2020Document9 pagesCurriculum Map 7 2019 2020Junna Gariando BalolotNo ratings yet
- Curriculum MapDocument2 pagesCurriculum MapKrishna Berbano Pama CerbasNo ratings yet
- English 9 CMDocument3 pagesEnglish 9 CMJohn Mark PascoNo ratings yet
- 01.bahasa Inggris MaritimDocument143 pages01.bahasa Inggris Maritimhermundus100% (3)
- 9 Learning PlanDocument6 pages9 Learning PlanOlive AsuncionNo ratings yet
- SD Phonetics PronunciationDocument7 pagesSD Phonetics PronunciationElena IzvoreanNo ratings yet
- English Language Scheme of Work FORM 3 2018Document16 pagesEnglish Language Scheme of Work FORM 3 2018Ct Sabaya SaadNo ratings yet
- English 9Document4 pagesEnglish 9Glenn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Progetto To Teach in EuropeDocument6 pagesProgetto To Teach in Europenaee19800No ratings yet
- SD PronunciationDocument10 pagesSD PronunciationElena IzvoreanNo ratings yet
- Annual Planning 2 Ms by Desert RoseDocument4 pagesAnnual Planning 2 Ms by Desert Roseyaniss adamNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map ENGlish7 Q1Document4 pagesCurriculum Map ENGlish7 Q1Normina Leah FelizardoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Curriculum MapDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Curriculum MapJzaninna SolNo ratings yet
- Updated - WEEK 3Document40 pagesUpdated - WEEK 3Nguyễn Đan NhiNo ratings yet
- Straightforward 2ed Level 2B Mapping Trinity GESE Grade 6Document3 pagesStraightforward 2ed Level 2B Mapping Trinity GESE Grade 6Aliyah LoriyanoNo ratings yet
- Lý Thuyết Dịch Theories Final TestDocument23 pagesLý Thuyết Dịch Theories Final TestPhan Thùy TrangNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument3 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayEvan Maagad LutchaNo ratings yet
- Edeng 110Document12 pagesEdeng 110Junel MamucudNo ratings yet
- English 7 Quarter 1Document6 pagesEnglish 7 Quarter 1Rhose Ann LaguraNo ratings yet
- Sta. Cruz Institute English 9 Curriculum MapDocument6 pagesSta. Cruz Institute English 9 Curriculum Maprichardsamrano100% (2)
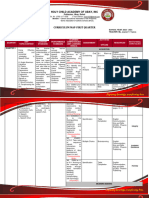
- Surigao Diocesan School System: Course Outline in English 9Document8 pagesSurigao Diocesan School System: Course Outline in English 9Aizelle Salibay OinalNo ratings yet
- Mind Map of GTM Characteristics GTM, Is A Method of Teaching Foreign LanguageDocument3 pagesMind Map of GTM Characteristics GTM, Is A Method of Teaching Foreign LanguageZAKI FURQAANNo ratings yet
- Course Guide EL 100Document4 pagesCourse Guide EL 100Joevannie AceraNo ratings yet
- SUBJECT: English QUARTER: First Grade Level: 9 TOPIC: What Keeps Life Flowing?Document6 pagesSUBJECT: English QUARTER: First Grade Level: 9 TOPIC: What Keeps Life Flowing?Abigail GumabayNo ratings yet
- Bikol MTB-MLE CompetenciesDocument30 pagesBikol MTB-MLE CompetenciesAices Jasmin Melgar BongaoNo ratings yet
- ELS-100-IDP FinallllDocument4 pagesELS-100-IDP FinallllVenus BravoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 4CDocument21 pagesSyllabus 4CKY DoanNo ratings yet
- Quarterly Curriculum Guide - Mother Tongue (MT) : Content Standard - 1 QuarterDocument30 pagesQuarterly Curriculum Guide - Mother Tongue (MT) : Content Standard - 1 QuarterAices Jasmin Melgar BongaoNo ratings yet
- Row A.: /S/ (S), /æ/ (A), /T/ (T), /P/ (P)Document19 pagesRow A.: /S/ (S), /æ/ (A), /T/ (T), /P/ (P)Arksheta MagendranNo ratings yet
- Action Plan ReadingDocument4 pagesAction Plan ReadingRHODALYN REYESNo ratings yet
- Concept Map..Document1 pageConcept Map..Josel Gigante CaraballeNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map for English 9Document6 pagesCurriculum Map for English 9Yuri Issang83% (6)
- Daily Lesson Plan: Lesson Is Postponed Due To: Choose An ItemDocument1 pageDaily Lesson Plan: Lesson Is Postponed Due To: Choose An ItemRajan UthirapathyNo ratings yet
- 5daily Lesson Plan: Personal GuidanceDocument2 pages5daily Lesson Plan: Personal GuidanceMarini MudinNo ratings yet
- SACC - G7Q1 - Curriculum MapDocument7 pagesSACC - G7Q1 - Curriculum MapSir Rannie EspantoNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: Row A.: /S/ (S), /æ/ (A), /T/ (T), /P/ (P)Document3 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: Row A.: /S/ (S), /æ/ (A), /T/ (T), /P/ (P)Syikin NorizanNo ratings yet
- RPT Bahasa Inggeris PeralihanDocument1 pageRPT Bahasa Inggeris PeralihanManjit DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- RPT Bahasa Inggeris PeralihanDocument1 pageRPT Bahasa Inggeris PeralihanZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 2 - Q1 - W1Document4 pagesDLL - English 2 - Q1 - W1Evelyn DEL ROSARIONo ratings yet
- Rica 3Document20 pagesRica 3johannasannNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: SubjectDocument1 pageDaily Lesson Plan: SubjectNur Laili Hj AliNo ratings yet
- Phonics (Transition Week) Week 1 - Week 4: English Language Year 1: Scheme of Work For PhonicsDocument6 pagesPhonics (Transition Week) Week 1 - Week 4: English Language Year 1: Scheme of Work For PhonicsKalaiarasi RajandranNo ratings yet
- dzexams-docs-4am-906142Document4 pagesdzexams-docs-4am-906142droidvoodooNo ratings yet
- Eng9 DLL Week1Document6 pagesEng9 DLL Week1JollyGay Tautoan LadoresNo ratings yet
- Specific Competences and Content in English Language LearningDocument16 pagesSpecific Competences and Content in English Language LearningAlina MNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 2 - Q1 - W2Document3 pagesDLL - English 2 - Q1 - W2Chris Loidz Ganado100% (1)
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: I. ObjectiveDocument3 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: I. ObjectiveK. AraquinNo ratings yet
- ENG Grade 3 DLL, Q3 Week 3Document3 pagesENG Grade 3 DLL, Q3 Week 3johnmorts2014100% (1)
- The Origins of Language Curriculum Development: Grammar Translation Method (1800-1900)Document1 pageThe Origins of Language Curriculum Development: Grammar Translation Method (1800-1900)To'am SalehNo ratings yet
- 1.-Poetic Vehicule 2. - Typology: 2.1. - SongsDocument1 page1.-Poetic Vehicule 2. - Typology: 2.1. - SongsMARÍA PÉREZ RICONo ratings yet
- Language Arts Activity Cards for School and Home, Grade 1From EverandLanguage Arts Activity Cards for School and Home, Grade 1No ratings yet
- Manding-English Dictionary: Maninka, Bamana Vol. 1.From EverandManding-English Dictionary: Maninka, Bamana Vol. 1.Rating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (3)
- Lesson Plan Bahasa Inggris SMK Kelas 3Document5 pagesLesson Plan Bahasa Inggris SMK Kelas 3fluthfi100% (1)
- HomeworkifyDocument2 pagesHomeworkifyFindMyAIToolNo ratings yet
- Active View of ReadingDocument20 pagesActive View of ReadingiefabiandiazNo ratings yet
- Commas Made SimpleDocument2 pagesCommas Made SimpleJean Rafenski Reynolds100% (3)
- Etp 87 PDFDocument68 pagesEtp 87 PDFtonyNo ratings yet
- A Practical Dictionary of Chinese Medicine PDFDocument14 pagesA Practical Dictionary of Chinese Medicine PDFVeronicaOntiveros100% (1)
- Barbara Johnsons Critical Difference A RDocument4 pagesBarbara Johnsons Critical Difference A Roliviu petrescuNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercises For Pre-UnitDocument7 pagesPractice Exercises For Pre-UnitAmbar CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Critical Reading ExercisesDocument23 pagesCritical Reading Exercisesztmmc100% (3)
- (Continuum Literary Studies.) Azari, Ehsanullah - Lacan, Jacques-Lacan and The Destiny of Literature - Desire, Jouissance and The Sinthome in Shakespeare, Donne, Joyce and Ashbery-Continuum (2008)Document216 pages(Continuum Literary Studies.) Azari, Ehsanullah - Lacan, Jacques-Lacan and The Destiny of Literature - Desire, Jouissance and The Sinthome in Shakespeare, Donne, Joyce and Ashbery-Continuum (2008)panamorado50% (2)
- Note-taking Strategies and MethodsDocument5 pagesNote-taking Strategies and Methodsgladen shelley billonesNo ratings yet
- Real Time Face Detection and Tracking Using Opencv: Mamata S.KalasDocument4 pagesReal Time Face Detection and Tracking Using Opencv: Mamata S.KalasClevin CkNo ratings yet
- The Language of Coaching - Nick WinkelmanDocument551 pagesThe Language of Coaching - Nick WinkelmanDiego D ToledoNo ratings yet
- Traditional Assessment ReportDocument33 pagesTraditional Assessment ReportJyra Mae Taganas50% (2)
- RCI - Book On LD PDFDocument49 pagesRCI - Book On LD PDFNikhil Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Waqar EssayDocument2 pagesWaqar Essayshabbirjamali0% (1)
- Individual Performance Commitment and Review Form (Ipcrf) For Teacher I-IiiDocument26 pagesIndividual Performance Commitment and Review Form (Ipcrf) For Teacher I-IiiQv QvNo ratings yet
- Journal of The History of Ideas Volume 48 Issue 2 1987 (Doi 10.2307/2709557) Richter, Melvin - Begriffsgeschichte and The History of IdeasDocument18 pagesJournal of The History of Ideas Volume 48 Issue 2 1987 (Doi 10.2307/2709557) Richter, Melvin - Begriffsgeschichte and The History of IdeasJuan Serey AguileraNo ratings yet
- Comparing Decimals 4th Grade LessonDocument5 pagesComparing Decimals 4th Grade Lessonapi-455810519No ratings yet
- Kgmy Sample ReportDocument18 pagesKgmy Sample ReportAyesha AhmadNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research PaperDocument8 pagesQualitative Research Paperapi-351294211No ratings yet
- Key Issues in ESP Curriculum DesignDocument3 pagesKey Issues in ESP Curriculum Designintan melati100% (3)
- Level 1, Module 3 Hot Spot Extra Reading PDFDocument3 pagesLevel 1, Module 3 Hot Spot Extra Reading PDFNgan HoangNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Employee Job Satisfaction at Ethio TelecomDocument25 pagesFactors Affecting Employee Job Satisfaction at Ethio Telecomdenekew lesemiNo ratings yet
- AEF3e Level 2 TG PCM Grammar 7BDocument1 pageAEF3e Level 2 TG PCM Grammar 7Bbhernard100% (1)
- 1 My First Perceptron With Python Eric Joel Barragan Gonzalez (WWW - Ebook DL - Com)Document96 pages1 My First Perceptron With Python Eric Joel Barragan Gonzalez (WWW - Ebook DL - Com)Sahib QafarsoyNo ratings yet
- CREATIVE NON FICTION (Lecture # 8) - Building Dramatic SentencesDocument8 pagesCREATIVE NON FICTION (Lecture # 8) - Building Dramatic SentencesNelson E. MendozaNo ratings yet
- PananaliksikDocument12 pagesPananaliksikIrah SolanoNo ratings yet
- Theories of LearningDocument112 pagesTheories of LearningPalak50% (2)
- Open Mind Lesson Plan 1Document2 pagesOpen Mind Lesson Plan 1api-240251617No ratings yet