Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ho1 PDF
Ho1 PDF
Uploaded by
Hendri Hermawan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesOriginal Title
ho1.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesHo1 PDF
Ho1 PDF
Uploaded by
Hendri HermawanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
MIT, 16.
20 Fall, 2002
16.20 HANDOUT #1
Fall, 2002
Review of Design Considerations
OVERVIEW OF STRUCTURAL DESIGN PROCESS
Purpose: Assure structural integrity while minimizing cost
Structural integrity: Capability of a structure to carry out the operation for which it
was designed
Aspects to consider:
Loads
Deformations
Corrosion
Fatigue/Long life
Factors in Determining cost:
Material
Waste amount
Manufacturing
Weight
Subassembly/Assembly
Durability and maintenance
Useful life
Repair
Paul A. Lagace 2002 Handout 1-1
MIT, 16.20 Fall, 2002
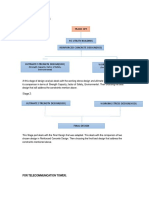
STRUCTURAL DESIGN PROCESS
1. Design restrictions/specifications
2. Determine applied loads and operating
environment to which structure is subjected
3. Layout structural arrangement, select materials,
size components
2
1
4. Determine internal stresses and deflections
5. Determine capability of structure to carry loads
(of box 2) subject to design restrictions (of box 1)
Manufacturing & Maintenance
considered throughout
SOURCES OF APPLED LOADS (and resulting stresses and strains)
Normal operative environment
Environmental effects
Isolated effects/special conditions
TERMINOLOGY
Limit load/stress/condition: maximum load/stress/condition where structure shows no
permanent deformation (operationally defined as maximum condition the structure is
expected to see under normal operation)
Ultimate load/stress/condition: maximum load/stress/condition where structure does not
fail (operationally defined as limit condition times factor of safety).
Ultimate Factor of Safety = Ultimate Condition
(design value) Limit Condition
Margin of Safety = Tested Value Design Value
(experimental reality) Design Value
Definition of failure depends on operational requirements.
Paul A. Lagace 2002 Handout 1-2
You might also like
- Design and Manufacturing Guideline For Aerospace CompositesDocument11 pagesDesign and Manufacturing Guideline For Aerospace CompositesBrice_ParmentierNo ratings yet
- Steel Design Handout Chapters 1 3Document119 pagesSteel Design Handout Chapters 1 3Hannan Sarrondo VitugNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel DesignDocument15 pagesStructural Steel DesignTonymeriNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Design of Building StructuresFrom EverandIntroduction to Design of Building StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (22)
- Steel Design Handout Chapters 1-3Document124 pagesSteel Design Handout Chapters 1-3Kevin Banez100% (1)
- POWER SYSTEM HARMONICS 2022 by Engr. Denis EstrellaDocument36 pagesPOWER SYSTEM HARMONICS 2022 by Engr. Denis EstrellaSoftCore GamerNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of Rocket Motor Cases Using Advanced FilameDocument11 pagesManufacture of Rocket Motor Cases Using Advanced FilameSumithrananthanNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Hole CleaningDocument28 pages3.3 Hole CleaningRasya RefanNo ratings yet
- ULS and SLSDocument4 pagesULS and SLSlolorek100% (8)
- Girder Design - Pull Out TestDocument15 pagesGirder Design - Pull Out TestSantosh ZunjarNo ratings yet
- Steel Structures Design and Drawing PDFDocument38 pagesSteel Structures Design and Drawing PDFShri100% (5)
- LECTURE NOTE 01 - RCC DesignDocument14 pagesLECTURE NOTE 01 - RCC DesignMohamed AbdNo ratings yet
- Virgin and Filled PTFE (Teflon) PDFDocument1 pageVirgin and Filled PTFE (Teflon) PDFAnjani PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 CapstoneDocument5 pagesChapter 2 CapstoneMæbēTh CuarterosNo ratings yet
- Steel Lecture 2 - Design Loads, ASD Vs LRFDDocument55 pagesSteel Lecture 2 - Design Loads, ASD Vs LRFDSana'a AamirNo ratings yet
- Centralloy Et 45 Micro: Material Data SheetDocument8 pagesCentralloy Et 45 Micro: Material Data SheetJorge BonillaNo ratings yet
- Soil Heave Due To Pile DrivingDocument19 pagesSoil Heave Due To Pile DrivingK. Rainer MassarschNo ratings yet
- Damage MechanismDocument10 pagesDamage MechanismAndiappan PillaiNo ratings yet
- A Study of Metal Extrusion ProcessDocument7 pagesA Study of Metal Extrusion ProcessYogesh DewangNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Design CriteriaDocument32 pagesCivil Engineering Design Criteriacall1986100% (1)
- Metric Handbook - StructureDocument50 pagesMetric Handbook - StructurexufafruitjuiceNo ratings yet
- RCD1Document24 pagesRCD1Nelle SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Intro To Steel DesignDocument9 pagesModule 1 Intro To Steel DesignAbren DaysoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Structural Design Part of Steel StructuresDocument10 pagesFundamentals of Structural Design Part of Steel StructuresJanice FernandezNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept Limit State Design Partial Factor of Safety Types of LoadingsDocument9 pagesBasic Concept Limit State Design Partial Factor of Safety Types of LoadingsRCdesign2012No ratings yet
- Advance Reinforced Concrete Design To BS 8110-1:1997: F. M. M AbdullahDocument12 pagesAdvance Reinforced Concrete Design To BS 8110-1:1997: F. M. M AbdullahMohamed AbdNo ratings yet
- W2 L2 Limit State DesignDocument28 pagesW2 L2 Limit State Design木辛耳总No ratings yet
- Pce 411 Structural Steel Design: Module 2: Philosophies of DesignDocument5 pagesPce 411 Structural Steel Design: Module 2: Philosophies of DesignJonathan LlegoNo ratings yet
- Cee 483 - 1Document26 pagesCee 483 - 1HuNo ratings yet
- Module+2 Design+LoadsDocument125 pagesModule+2 Design+LoadsfrnkbartsNo ratings yet
- Bridge Design Practice-2011Document173 pagesBridge Design Practice-2011Ahmed AllamNo ratings yet
- No. 106 IACS Guideline For Rule Development - Ship Structure No. 106Document54 pagesNo. 106 IACS Guideline For Rule Development - Ship Structure No. 106Jym GensonNo ratings yet
- TRADE OFF FlowchatfinalsDocument2 pagesTRADE OFF FlowchatfinalsJoy lauriaNo ratings yet
- ARCH 415-S&TD - M1 - T1 - W2 - Introduction For Steel and TimberDocument6 pagesARCH 415-S&TD - M1 - T1 - W2 - Introduction For Steel and TimberJomarie AfricaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2: Basic Concepts of DesignDocument18 pagesChapter - 2: Basic Concepts of DesignashenafiNo ratings yet
- Steel Structure Bolted Connections DesignDocument4 pagesSteel Structure Bolted Connections Designramu karriNo ratings yet
- Limit States Method (Cec402 Assignment of Group3a)Document50 pagesLimit States Method (Cec402 Assignment of Group3a)Kingshuk MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- RCI Chapter 2 ADocument16 pagesRCI Chapter 2 AsasaNo ratings yet
- Design of Concrete Structures IDocument102 pagesDesign of Concrete Structures IDulanga kameshNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction Reinforced Concrete StructuresDocument9 pages1.introduction Reinforced Concrete StructuresJamali AdamNo ratings yet
- Project Final Repord 2076 PDFDocument106 pagesProject Final Repord 2076 PDFPawan Kumar Karki100% (1)
- Construction Loads PDFDocument41 pagesConstruction Loads PDFcaner_kurtoglu-1No ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Structural EngineeringDocument15 pages01 Introduction To Structural EngineeringKENNETHPAUL HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Unit No 1: Reinforced Concrete IntroductionDocument29 pagesUnit No 1: Reinforced Concrete IntroductionOladimeji Ibukun IjaodolaNo ratings yet
- 202210-BDP-Chapter-1BridgeDesign Specifications-A11yDocument15 pages202210-BDP-Chapter-1BridgeDesign Specifications-A11ydvegaucentralNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structure Reinforced ConcreteDocument2 pagesTheory of Structure Reinforced ConcreteRosaline MainaNo ratings yet
- 1 Background Theory: Failure CriterionDocument51 pages1 Background Theory: Failure CriterionAntehun MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Design Overview: Unit 1Document9 pagesIntroduction and Design Overview: Unit 1sabanayagamn1991No ratings yet
- RCD1 Topic 2Document29 pagesRCD1 Topic 2calchan79No ratings yet
- How Is Working Stress Method (ASD) Different From Limit State Method (LRFD or LFD) - Assumptions, Advantages and Comparisons - CivilDigitalDocument4 pagesHow Is Working Stress Method (ASD) Different From Limit State Method (LRFD or LFD) - Assumptions, Advantages and Comparisons - CivilDigitalStacy JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Lect 7-9 - B.tech V Sem (Civil) Cs-I Ce 15103 - 2022 - LSMDocument37 pagesLect 7-9 - B.tech V Sem (Civil) Cs-I Ce 15103 - 2022 - LSMSandeep MishraNo ratings yet
- Performance Based DesignDocument8 pagesPerformance Based Designigunz245200No ratings yet
- NSCP Chapter 2 Summary FinalDocument2 pagesNSCP Chapter 2 Summary FinalshienellajacildoNo ratings yet
- Shallow Founda1ons: OutlineDocument65 pagesShallow Founda1ons: OutlineCharles Warren GoNo ratings yet
- Unit No 1: Reinforced Concrete IntroductionDocument29 pagesUnit No 1: Reinforced Concrete IntroductionAbdur Rasheed RasheedNo ratings yet
- Concrete Notes 2011-6Document68 pagesConcrete Notes 2011-6Kaveesh NCDNo ratings yet
- Technical Note: Aefac - Tn01Document9 pagesTechnical Note: Aefac - Tn01Anonymous YW5mvpNo ratings yet
- AE228-222-Lec 5 - Materials 1 PDFDocument8 pagesAE228-222-Lec 5 - Materials 1 PDFjjNo ratings yet
- On Drift Limits Associated With Different Damage Levels: June 2004Document13 pagesOn Drift Limits Associated With Different Damage Levels: June 2004RaviKanthSrivastavNo ratings yet
- Chap-1 (Design Philosophy-Structure) FinalDocument19 pagesChap-1 (Design Philosophy-Structure) FinalAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- 054 1 541 Mechanics and Design of ConcreDocument7 pages054 1 541 Mechanics and Design of Concreengsamim.walizadaNo ratings yet
- SCI P252 SecureDocument114 pagesSCI P252 SecureDan CiucuNo ratings yet
- The Basic Principles of Limit State Design MethodDocument57 pagesThe Basic Principles of Limit State Design MethoddavidNo ratings yet
- Design Codes and Safety ProvisionsDocument23 pagesDesign Codes and Safety ProvisionsAhmad Faraz JuttNo ratings yet
- CE71 Module 2 2ND SEM 2022Document13 pagesCE71 Module 2 2ND SEM 2022Orland Son FactorNo ratings yet
- CSE30310 Lecture 2Document51 pagesCSE30310 Lecture 2sze yin wongNo ratings yet
- 1) Size Dependent Analysis of Wave Propagation in Functionally Graded CompositeDocument24 pages1) Size Dependent Analysis of Wave Propagation in Functionally Graded CompositeHamid M SedighiNo ratings yet
- E4 - Marcet Boiler - NewDocument7 pagesE4 - Marcet Boiler - NewSalahuddin NorazmiNo ratings yet
- Crastin Rynite PDFDocument60 pagesCrastin Rynite PDFkfaravNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes For Properties of Bulk MatterDocument20 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Notes For Properties of Bulk MatterAyush Kumar100% (1)
- Btech Ce 3 Sem Fluid Mechanics Rce303 2019Document3 pagesBtech Ce 3 Sem Fluid Mechanics Rce303 2019shivchauhan0507No ratings yet
- CIVE 302 - Lab 1 - Tensile Testing of Steel PDFDocument9 pagesCIVE 302 - Lab 1 - Tensile Testing of Steel PDFAhmadAliAKbarPhambraNo ratings yet
- TD-esc-02-De-En-12-004 Rev001 Introduction of DUSPOL Analogue Voltage TesterDocument2 pagesTD-esc-02-De-En-12-004 Rev001 Introduction of DUSPOL Analogue Voltage TesterFelipe SilvaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Introduction To SemiconductorDocument32 pagesTopic 1 Introduction To SemiconductoridasyarmilaNo ratings yet
- 731504Document2 pages731504Sanket PatelNo ratings yet
- Concept Strengthening Sheet CSS 03 Based On AIATS 03 CF+OYM PhysicsDocument7 pagesConcept Strengthening Sheet CSS 03 Based On AIATS 03 CF+OYM PhysicsJIDNESH BHERENo ratings yet
- User Guide Sika Carbodur TR55Eurocode2 EnglishDocument52 pagesUser Guide Sika Carbodur TR55Eurocode2 EnglishMihaiNo ratings yet
- Material Report 2 ToughnessDocument7 pagesMaterial Report 2 ToughnessPiyal MendisNo ratings yet
- KT Transducers P ENDocument4 pagesKT Transducers P ENHemant PatilNo ratings yet
- SFB 2Document1 pageSFB 2Gelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Final Revision 3Document151 pagesFinal Revision 3KairosNo ratings yet
- Kapci 615 Adplast Plastic PrimerDocument2 pagesKapci 615 Adplast Plastic Primermena ashrafNo ratings yet
- Guo YueleiDocument65 pagesGuo YueleiABDULAJEESNo ratings yet
- Tribology: Important Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesTribology: Important Questions and AnswersTHRISHAN SINGH R LNo ratings yet
- Aao 2 Clinical OpticDocument4 pagesAao 2 Clinical Opticria mutiaraNo ratings yet
- CZ 132Document1 pageCZ 132Taner DemirelNo ratings yet
- Column AnalysisDocument8 pagesColumn AnalysisRashi GoelNo ratings yet
- Effect of y Ashes On The Mechanical Performance of Hemp Modified MortarDocument7 pagesEffect of y Ashes On The Mechanical Performance of Hemp Modified MortarJean AbelaNo ratings yet