Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Switchgear and Protection Lab Index Sr. No. Name of Experiment No
Switchgear and Protection Lab Index Sr. No. Name of Experiment No
Uploaded by
bals123456Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- QAQC Electrical Inspection: A Beginner's GuideFrom EverandQAQC Electrical Inspection: A Beginner's GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Tneb Hand Testing BookDocument405 pagesTneb Hand Testing BookNarinder Rawat100% (14)
- Tneb Hand Testing BookDocument405 pagesTneb Hand Testing BookNarinder Rawat100% (14)
- Commissioning Numerical RelaysDocument24 pagesCommissioning Numerical RelaysVHMANOHARNo ratings yet
- P633 Test Tools Farhad Rev 01Document5 pagesP633 Test Tools Farhad Rev 01Neelakandan MasilamaniNo ratings yet
- Line Distance Protection IED REL 670Document47 pagesLine Distance Protection IED REL 670kass_ecs100% (1)
- CKP Notes Vol 2 VERSION 2Document116 pagesCKP Notes Vol 2 VERSION 2Sivasankar AkcNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance Test PDFDocument2 pagesInsulation Resistance Test PDFusman haroonNo ratings yet
- Differential Relay With Adaptation During Saturation PeriodDocument6 pagesDifferential Relay With Adaptation During Saturation Periodasim saeedNo ratings yet
- DCRP QuestionsDocument1 pageDCRP QuestionsSiva NandhamNo ratings yet
- PWR Sys Fund Relay ApplicationsDocument231 pagesPWR Sys Fund Relay ApplicationsJohn BihagNo ratings yet
- DCRP AskedDocument3 pagesDCRP AskedSiva NandhamNo ratings yet
- Relays Makes Test ProcedureDocument25 pagesRelays Makes Test ProcedureRa HulNo ratings yet
- Transformer Stability TestsDocument5 pagesTransformer Stability Testsardianto hamonanganNo ratings yet
- Siemens Relay 7rw600Document20 pagesSiemens Relay 7rw600rajinipre-1No ratings yet
- Alfanar Co.: Respon Sibilities Legend CSDDocument5 pagesAlfanar Co.: Respon Sibilities Legend CSDjayabalNo ratings yet
- 25ref RelayDocument8 pages25ref Relaysikander843562No ratings yet
- SA2003-000019 A en Trip Circuit Supervision With RXMB 1 Auxiliary RelayDocument1 pageSA2003-000019 A en Trip Circuit Supervision With RXMB 1 Auxiliary RelayErmin FazlicNo ratings yet
- Impedance MeasurementDocument2 pagesImpedance MeasurementAhsan KaziNo ratings yet
- N6166 E05 F871 TR Diff Relay 7UT613Document6 pagesN6166 E05 F871 TR Diff Relay 7UT613মোঃ মহসিনNo ratings yet
- Phase Angle Shift Compensation For Differential Protection-One Solution To Cover All Types of TransformersDocument6 pagesPhase Angle Shift Compensation For Differential Protection-One Solution To Cover All Types of TransformersDante FilhoNo ratings yet
- CT Operated Thermal Over Load Relay Current Setting CalculationDocument5 pagesCT Operated Thermal Over Load Relay Current Setting CalculationMas Kahfi100% (1)
- TP TPD Pfs TPC QP 12Document29 pagesTP TPD Pfs TPC QP 12erbvp22No ratings yet
- Siemens 7sd5Document18 pagesSiemens 7sd5BalajiNo ratings yet
- 26 Relay Testing Techniques, Requirements, Considerations MDocument8 pages26 Relay Testing Techniques, Requirements, Considerations Mgagan0312No ratings yet
- Tan Delta Test For Power TransformersDocument9 pagesTan Delta Test For Power TransformersSreenivasanNo ratings yet
- ISA Introduction To The Test of Protection RelaysDocument23 pagesISA Introduction To The Test of Protection RelaysCata CatalinNo ratings yet
- 7sd52 7sd62 ConfigurationDocument14 pages7sd52 7sd62 ConfigurationWilber LucasNo ratings yet
- Transformer Differential RelayDocument12 pagesTransformer Differential Relaysandyarajagopalan321No ratings yet
- Bus Bar Differential Protection Relay Test ProcedureDocument1 pageBus Bar Differential Protection Relay Test Procedurem khNo ratings yet
- HT Capacitor Bank and Reactor Test and CommissioningDocument2 pagesHT Capacitor Bank and Reactor Test and CommissioningAodman4u0% (1)
- 7SA522 - Distance & DEF Relay-ADocument30 pages7SA522 - Distance & DEF Relay-Am khNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Abdul Fareh Khan 2k19Document5 pagesMuhammad Abdul Fareh Khan 2k19Fareh KhanNo ratings yet
- Functional Test of Thermal Overload ProtectionDocument1 pageFunctional Test of Thermal Overload ProtectionMihai BancuNo ratings yet
- Lab 06-Differential Bus Bar ProtectionDocument6 pagesLab 06-Differential Bus Bar ProtectionAliza SharifNo ratings yet
- What Is The Best Protective Relay Test-Set - Valence Electrical Training ServicesDocument12 pagesWhat Is The Best Protective Relay Test-Set - Valence Electrical Training ServicesanuragpugaliaNo ratings yet
- MPD 600 Article The Importance of PD Testing On Power Transformers ENUDocument8 pagesMPD 600 Article The Importance of PD Testing On Power Transformers ENUDeepen SharmaNo ratings yet
- Enerzio Product Catalog 2019-2020 New PDFDocument16 pagesEnerzio Product Catalog 2019-2020 New PDFHarvinder Singh HarryNo ratings yet
- AREVA MVAP22 Voltage Balance RelayDocument22 pagesAREVA MVAP22 Voltage Balance Relayadeelzafar100No ratings yet
- Transformer EssentialsDocument86 pagesTransformer EssentialsSalma EL HadiNo ratings yet
- SWGR Feeder - Functional TestDocument13 pagesSWGR Feeder - Functional TestChheng KimhokNo ratings yet
- ABB REL670 V1.B A32 Template Manual ENU TU3.00 V1.000 PDFDocument17 pagesABB REL670 V1.B A32 Template Manual ENU TU3.00 V1.000 PDFWafa Imene BouhaddaNo ratings yet
- F2000 Instruments Relay Test PlanDocument4 pagesF2000 Instruments Relay Test Planyand_carlosNo ratings yet
- Volt::Ch: Voltech Engineers Pvt. LTDDocument32 pagesVolt::Ch: Voltech Engineers Pvt. LTDstalin63100% (1)
- 182.testing With MZTU-34 Relay-GenPro PDFDocument7 pages182.testing With MZTU-34 Relay-GenPro PDFAnonymous nPR5nm8XMNo ratings yet
- Schneider Protection RelayDocument8 pagesSchneider Protection Relayeugene oneillNo ratings yet
- Numerical RelayDocument9 pagesNumerical Relayc_chootiaNo ratings yet
- Differential ProtectionDocument8 pagesDifferential Protectionchandra_shekhar2221941No ratings yet
- Testing of Modern Bus Protection SystemsDocument7 pagesTesting of Modern Bus Protection Systemss_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Testing Directional Overcurrent Relays From Valence PDFDocument9 pagesTesting Directional Overcurrent Relays From Valence PDFnaran19794735No ratings yet
- Ici-C&C/Seupptcl/A - S (Sup.) /2011-12/001: Tested by WitnessedDocument7 pagesIci-C&C/Seupptcl/A - S (Sup.) /2011-12/001: Tested by WitnessedkamarajkanNo ratings yet
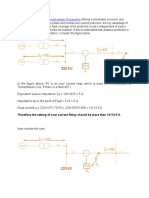
- Non-Unit System of Protection: Therefore The Setting of Over Current Relay Should Be More Than 14113.5 ADocument6 pagesNon-Unit System of Protection: Therefore The Setting of Over Current Relay Should Be More Than 14113.5 AyethweNo ratings yet
- Protective Relaying Testing ST6Document6 pagesProtective Relaying Testing ST6Darwin MesaNo ratings yet
- 2.u#1 11KV Switchgear Testing Book-2 PDFDocument219 pages2.u#1 11KV Switchgear Testing Book-2 PDFSabyasachi PatraNo ratings yet
- DCRP Written Test QuestionsDocument1 pageDCRP Written Test QuestionsSiva NandhamNo ratings yet
- Automatic Distance Relay PDFDocument4 pagesAutomatic Distance Relay PDFOmar Chayña VelásquezNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - 19Document32 pagesLecture Notes - 19Bhaskar1411No ratings yet
- Electrical Power-2 Lab ManualDocument6 pagesElectrical Power-2 Lab ManualAditya SanjeevNo ratings yet
- Ps Lab ManualDocument132 pagesPs Lab ManualRamkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Power System Laboratory Experiment - 2023-24Document51 pagesPower System Laboratory Experiment - 2023-24Manas Ranjan MishraNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument7 pagesLab Manualdurgesh choudharyNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EE852Document20 pagesLab Manual EE852Uzair Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- SRReport 1476479550735 PDFDocument1 pageSRReport 1476479550735 PDFLawrence AlexNo ratings yet
- VSJ Samayapuram BrochureDocument2 pagesVSJ Samayapuram BrochureLawrence AlexNo ratings yet
- Relay Testing ProcedureDocument144 pagesRelay Testing ProcedureLawrence Alex100% (1)
- Relay Testing ProcedureDocument144 pagesRelay Testing ProcedureLawrence Alex100% (1)
- Relay Testing Procedure PDFDocument50 pagesRelay Testing Procedure PDFLawrence Alex100% (2)
- Relay Testing Procedure PDFDocument50 pagesRelay Testing Procedure PDFLawrence Alex100% (2)
- User Manual - Payroll Service PDFDocument4 pagesUser Manual - Payroll Service PDFJaya LawrenceNo ratings yet
- User Manual - Payroll Service PDFDocument4 pagesUser Manual - Payroll Service PDFJaya LawrenceNo ratings yet
- English For Children PDFDocument39 pagesEnglish For Children PDFJaya LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Resume: PersonalDocument2 pagesResume: PersonalLawrence AlexNo ratings yet
Switchgear and Protection Lab Index Sr. No. Name of Experiment No
Switchgear and Protection Lab Index Sr. No. Name of Experiment No
Uploaded by
bals123456Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Switchgear and Protection Lab Index Sr. No. Name of Experiment No
Switchgear and Protection Lab Index Sr. No. Name of Experiment No
Uploaded by
bals123456Copyright:
Available Formats
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
G. H. RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGG.
VIII SEMESTER B.E.
SWITCHGEAR AND PROTECTION LAB
INDEX
Sr. Name of Experiment Page
No. No.
1 TO STUDY THE OPERATION OF DEFINITE TIME 2
OVERCURRENT RELAY.
2 TO PLOT THE CHARACTERISTICS OF SINGLE POLE OVER 5
CURRENT OR EARTH FAULT USING STATIC I.D.M.T.
RELAYS
3 TO STUDY THE OPERATION OF STATIC OVER VOLTAGE 8
RELAY
4 TO PLOT THE CHRACTERISTICS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC 10
IDMT RELAY (MODEL NO.ICM-21NP)
5 TO STUDY THE OPERATION OF STATIC DEFINITE TIME 13
REVERSE POWER RELAY (MODEL APDR-21)
6 A) TO STUDY THE MAGNETISATION CHARACTERISTICS 16
OF C.T.
B) TO STUDY THE PROBLEM ASSOCIATED WITH C.T.
MAGNETISATION.
7 TO PLOT THE CHARACTERISTICS OF FUSE WIRE 18
8 TO STUDY DIRECTIONAL OVER CURRENT RELAY ( ACDR 20
11 HPD)
9 TO STUDY AND PLOT THE CHARACTERISTICS OF 23
IMPEDANCE RELAY ( ABB-RAKZB
10 TO STUDY TRANSFORMER DIFFERENTIAL PROTECTION 26
11 TO STUDY UNRESTRICTED EARTH FAULT RELAYS. 28
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 1
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
EXPERIMENT NO.1
AIM: - TO STUDY THE OPERATION OF DEFINITE TIME
OVERCURRENT RELAY.
APPARATUS: -
1) Timer
2) Static definite O/C relay (Model ACTU 32 P)
3) Auxiliary D.C. supply = 110V
4) 1 phase variac =230V, 4A
5) Ammeter AC (0-5A) and (0-1/2 A)
6) Rheostat (100 ohm, 5Amp)
7) Experiment Kit
8) Connecting wires
CIRCUIT DIAGRANM:
(0-5A) OFF
36 OHM, 8.5A
ON
A
START 230V
STOP 1-PH
TIMER SUPPLY
1PH 5
230V 3
50 HZ
SUPPLY
6 4
11 110V 12
+ DC -
THEORY:
1. Principle and operation of static definite time over current relay, time
current charact. equation.
2. Block diagram of static over current relay.
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 2
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
PROCEDURE: -
1) Connect the ckt as shown in fig procedure is done & time is noted.
2) Set current and time setting of relays as per requirement
3) Connect Auxiliary D.C. Supply (110) to pin 11 & 12 of relay and pin no.
3&4 to the time interval meter.
4) Switch on the D.C. supply & make sure that relay is on Glowing of LED
on the front panel of the relay.
5) Switch on power supply from dimmer as well as to time interval meter.
6) Adjust the current setting of the relay.
7) Adjust the time setting of relay.
8) Now by making DPDT switch on, increase the value of current by
dimmer stat up to the point at which the relay trip. Trip can be observed
by glowing of trip LED on front panel of relay.
9) Switch is made off and relay is reset.
10) Now Switch is made on & time interval meter reading is noted.
11) For the same current setting , time setting is changed & same procedure
is repeated until all the time setting are covered.
12) Again current setting is changed & same PROCEDURE IS REPEATED.
OBSERVATION TABLE: -
Sr. Relay set time Set phase trip Timer Set phase tri[p Timer
No. in sec =100% time =180 % time
Ammeter Ammeter
reading reading
1.
2.
3.
4.
CHARACTERISTICS TABLE: -
Current setting = , Pick up current =
Sr. No. Fault current (A) PSM Timer Timer Timer
time, for time, for time, for
TMS = TMS = TMS =
1
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 3
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
2
.
.
.
10
RESULT & CONCLUSION: -
The operation of definite time O/C relay is studied in this experiment. The
reading is obtained for various time settings as well as current setting. It was
found that for various time delay observed for peak up values of current is
same.
Viva Question
1 Application of DTOC relay.
2 Draw back of DTOC relay
3 Importance of DC supply
4 Detail of other O/C relays
5 Use of timer
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 4
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
EXPERIMENT NO.2
AIM: -
TO PLOT THE CHARACTERISTICS OF SINGLE POLE OVER
CURRENT OR EARTH FAULT USING STATIC I.D.M.T. RELAYS
APPARATUS: -
1) Timer
2) IDMT relay (Model APR-11 P)
3) Auxiliary D.C. supplies = 110V
4) 1 phase Dimmer stat = 230V, 10A
6) Ammeter AC (0-15A)
7) Rheostat (38 ohm, 8.5 Amp)
8) Experiment Kit
9) Connecting wires
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
(0-15A) OFF
36 OHM, 8.5A ON
A
START 230
TIMER 1-P
STOP SUPP
1PH 5
230V 3
50 HZ
SUPPLY
6 4
11 110V 12
+ DC -
THEORY: -
1. Define PSM, TSM.
2. Equation of time current characteristics.
3. Principle & Operation of static IDMT Relay with block diagram
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 5
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
PROCEDURE: -
1) Make the connection as shown in fig.
2) Set current and time setting of relays as per requirement
3) Set phase trip to 50% and set phase time at X1 with phase TMS
at maximum position.
4) Switch on variac and check power ON indication provided on
relay front panel.
5) Very dimmer state with fault current of 1A,relayb will trip after
certain time delay.
6) Switch OFF dimmer state without disrobing its position and
change the position of DPT switch. Also reset time.
7) Switch ON dimmer state change the position of switch and
measure the relay time from timer.
8) Reap eat same procedure for varying a different fault current.
9) Repeat this procedure consider different set phase time (TMS)
OPERATION: -
With supply on load are continuously monitored Electronic comparator checks this
value with set value (N) of phase & earth fault trip, which can be adjusted on front
plate. Pick up response is (1.1 N) IDMT timing is applicable to over current above
2N as per chosen curve. Time setting multiplier for actual tripping time delay. TMS
is adjusted by 11-position switch & with variable preset pot. These pots adjusted
time for intermediate values indicated on TMS switch. Tripping cause is indicated
by LED lamp (OC/EF). When over current trips the circuit relay NO contact
changes to NC when relay trips indicating LED to NC when relay trip indicating
LED to NC when relay trips indicating LED to NC when relay trip indicating
LED flag will remain ON till manually reset.
OBSERVATION
1 CHARACTERISTICS TABLE: - current setting =, Phase TMS
Sr. Fault current PSM Timer time for Timer time for Timer time for
No. (A) TSM = TSM= TSM=
1
2
.
.
10
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 6
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
RESULT:
For lower values of current the time current characteristics are inverse and for
higher value of current, time observed is constant.
Viva Question
1 Application of IDMT relay.
2 Draw back of IDMT relay
3 Importance of DC supply
4 Detail of other Inverse type of relays
5 Importance of static relays
6 Why IDMT relay suitable for protection of long length of LV/MV TL.
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 7
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
EXPERIMENT NO.3
AIM: - TO STUDY THE OPERATION OF STATIC OVER VOLTAGE
RELAY
APPARATUS: -
1) Static over voltage relay (Model No.: -ASOV)
2) Auxiliary D.C. supplies 110V
3) Time interval meter
4) Single pole variac 230V, 4A
5) Voltmeter (0-300V) AC
6) Rheostat (400 ohm, 1.7 Amp)
7) Connecting wires
8) Experiment Kit
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:-
OFF
300 OHM,1.7A
ON
T
I
START M
STOP E
9
R
1-PH (0-300V)
230V, 3
50HZ,
v
SUPPLY 10 4
110V
11 DC 12
STATIC OVER VOLTAGE RELAY + -
THEORY: -
1. Principle and operation of static over voltage relay.
2. Application of static over voltage relay.
PROCEDURE:-
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 8
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
1) Connect the ckt as shown in fig procedure is done & time is
noted.
2) Set current and time setting of relays as per requirement
3) Connect Auxiliary D.C. Supply (110) to pin 11 & 12 of relay and
pin no. 3&4 to the time interval meter.
4) Switch on the D.C. supply & make sure that relay is on Glowing
of LED on the front panel of the relay.
5) Switch on power supply from dimmer as well as to time interval
meter.
6) Adjust the voltage setting of the relay.
7) Adjust the time setting of relay.
8) Now by making DPDT switch on, increase the value of voltage
by dimmer stat up to the point at which the relay trip. Trip can be
observed by glowing of trip LED on front panel of relay.
9) Switch is made off and relay is reset.
10) Now Switch is made on & time interval meter reading is noted.
11) For the same voltage setting , time setting is changed & same
procedure is repeated until all the time setting are covered.
12) Again voltage setting is changed & same PROCEDURE IS
REPEATED.
OBSERVATION TABLE: -
Sr. Time Knob Set Timer Set Timer Set Timer
No. Position in Voltage time Voltage time Voltage time
seconds. 105%= 130%= 155%=
1
2
.
.
10
RESULT: The static over-voltage relay is studied.
Viva Question
1 Application of over and under voltage relay.
2 Draw back of electromagnetic as compare to static relays relay
3 Importance of DC supply
4 Range of under voltage relay
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 9
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
EXPERIMENT NO.4
AIM: - TO PLOT THE CHRACTERISTICS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC
IDMT RELAY (MODEL NO.ICM-21NP)
APPARATUS: -
1) Timer
2) IDMT relay (MODEL NO.ICM-21NP))
3) Auxiliary D.C. supplies = 110V
4) 1 phase Dimmer stat = 230V, 10A
5) Ammeter AC (0-15A)
6) Rheostat (38 ohm, 8.5 Amp)
7) Experiment Kit
8) Connecting wires
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM :
OFF
(38 ohm,8.5A)
ON
A
START
(0-10A) 230V
T
230V S I 1-PH
1 5 T 50HZ
50HZ, M
O E SUPPLY
1-PH 6 P R
SUPPLY
2
+3 110V -4
DC
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 10
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
THEORY: -
1) Construction and operation of Induction disc/ watt-metric type
electromagnetic Relays.
2) Time current characteristics equation
3) Derivation of torque produced.
PROCEDURE: -
1) Make the connection as shown in the circuit diagram.
2) Select current setting (set phase trip) less than 100%, keeping
phase TMS at maximum position.
3) Select any time setting.
4) Switch on variac and check power ON indication provided on
relay front panel.
5) Vary dimmer stat and observe current value till Pick-Up will
show Red indication when current value exceeds set phase trip
position.
6) Switch OFF dimmer stat without disturbing its position with the
help of DPT switch. Also reset time.
7) Measure the relay time from timer by switching on DPT switch.
8) Now increase the fault current and note down timer time after
switching OFF and DPT switch every time with same time
setting.
9) Repeat same procedure for different time setting keeping current
setting same.
OBSERVATION TABLE OR CHARACTERISTICS TABLE: -
Sr. Fault current (A) PSM Timer time For Timer time Timer time
No. TSM = For TSM= For TSM=
1
2
.
.
.
10
RESULT:
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 11
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
For lower values of current the time current characteristics are inverse and for
higher value for current observed times are constant.
Viva Question
1 Pickup, PSM and TSM
2 Draw back of IDMT relay
3 Derivation of Torque equation in detail
4 Detail of other Inverse type of relays
5 Why IDMT relay suitable for protection of long length of LV/MV TL.
6 Reset time and trip time
7 Why characteristics is plotted between PSM and operating time?
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 12
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
EXPERIMENT NO.5
AIM: - TO STUDY THE OPERATION OF STATIC DEFINITE TIME
REVERSE POWER RELAY (MODEL APDR-21)
APPARATUS: -
1) Timer
2) Static definite time reverse power relay (Model APDR 21)
3) Auxiliary D.C. supply = 110V
4) 3 phase variac =440V, 50 Hz, 8A
5) 1 phase variac =230V, 4A
6) Ammeter AC (0-1A) AC
7) Rheostat (300 ohm, 1.7Amp)
8) Phase shifting transformer
9) Voltmeter (0-300V) AC
10) Experiment Kit
11) Connecting wires
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM :
(0-2A)
R
CT
P 7 8
H
A
3 PH R R
440V S
AC E
SUPPLY R
S
H E
L
I A
Y F Y
T START
I
N (0-300V)
Y
G
V 11
T
T 3
R 1 PH
I
A S M 1 PH
VARIAC
N T 230V,
B 270V, PT E
F 4A O 50HZ, AC
O P R SUPPLY
R
B M
E
R 12 4
N N N
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 13
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
THEORY:
1. Describe the operating principle, constructional feature and area
of application of reverse power relay.
2. Draw simplified block diagram of static reverse power O/C relay.
OPERATION: -
Solid static state voltage and current sensing circuits measure the
instantaneous voltage and current value in scales down format .The algorithmic
circuit does the multiplication of the derived data. The output of this circuit remains
positive as the moment when power reversal occurs, output of the circuits changes
again. It is noted as pick up point and thus indicated by pick up LED. This also
triggers the internal timer cit. This timer is adjustable by 11 positive switches. It has
very high repeat accuracy. (Better than class 17) After the end of set timing and if
power conduction are still reverse.
PROCEDURE: -
1) Make the connection as shown in fig.
2) Set current and time setting of relays as per requirement
3) Switch on supply to 3phase dimmerstate and also D.C. supply to
relay.
4) By vaaarying 3 phase dimmerstate adjust the value of current .
5) Now keeping current at this val;ue constant change the angle of
phase shifting tranfofmer gradually.
6) Observe the tripping zone of reverse power relay.
7) The relay will trip at certain angle of phase shifting transformer note
down the angle and reset the relay.
8) Again increase the angle and observe tripping of relay.
9) Plot the tripping region of reverse power relay on the graph paper.
OBSERVATION TABLE: -
Sr. No. Phase angle Trip response
1 0
2 30
3 60
- -
- -
- -
- Till 360
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 14
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
Sr.No. Time setting in sec Trip time in sec
1 0
2 1
3 -
4 -
Till 10
RESULT:
The operation of definite time reverse power relay is studied and triggering zone is
plotted in the graph paper.
Viva Question
1 Application of Reverse power relay
2 Types of relays used and its setting for protection of ring main feeders
3 Comparison of other directional relays and reverse power relays
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 15
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
EXPERIMENT NO: - 06
A) TO STUDY THE MAGNETISATION CHARACTERISTICS OF
C.T.
B) TO STUDY THE PROBLEM ASSOCIATED WITH C.T.
MAGNETISATION.
APPARATUS:-
1) Current transformer ( CT ) 5/1 Amp
2) Ammeter :- ( 0-10 A)
3) Multimeter
4) Rheostat ( 38 ohm , 1.7 amp )
5) 1 phase Dimmerstate.
THEORY:-
Plot the excitation curve and explain
(i) From origin to ankle point
(ii) From ankle pt. to knee
(iii) Knee region
(iv) Saturation region
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM :
(O-1A)
300ohm,1.7A
A
230V
50HZ, (0-75V) O.
1PH, V
OR C.
SUPPLY MULTIMETER
1:5 A
CURRENT
TRANSFORMER
PROCEDURE:-
(1) Make connections as shown
(2) Current is increased by 1 phase shown
(3) A certain value of current , measure voltage from
multimeter
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 16
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
(4) Again increase the value of current and note down voltage.
(5) Similar procedure is done and current is increased till the
saturation of C.T.
(6) Draw graph of current Vs voltage.
CONCLUSION :-
Magnetization curve of C.T. is studied. Ankle point, knee
point and saturation is observed.
Viva Question
1 Difference between protective CTs and measuring CTS
2 Why CT get saturate in differential protective scheme during external fault
3 Use of CTs in protection of any equipment
4 No. of CTs require for protection of transformer and generator and their
connection.
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 17
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
EXPERIMENT NO :- 07
AIM :- To plot the characteristics of Fuse wire
APPARATUS- 1) Fuse wire
2) Ammeter AC (0-10 A)
3) Stop watch
4) 1 ph Dimmerstat 230V, 10 A
5) Loading Rheostat
6) Rheostat (38 Ohm, 8.5 A)
7) Experimental Kit
8) Connecting Wires
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:-
(0-15A)
38 ohm,8.5A FUSE
A
1PH
230V L
50HZ, O
A
SUPPLY D
DIMMERSTATE
1PH
230V,8A
THEORY: - 1) Detail theory and operation of fuses
2) Characteristics of Fuse
3) Types of Fuses
PROCEDURE: -
1) Make the connections as shown in Fig.
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 18
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
2) Switch on the supply and keep the full load in the on
position. Adjust the current to certain value with the
help of dimmerstat
3) Stop watch is stopped when the fuse element is blown
which is indicated by decreasing of current in
ammeter to zero. Note down the time of stop watch.
4) Again after changing the fuse element increase the
current to certain value and repeat above procedure .
OBSERVATION:
Sr.No Current ( Amp) Time (Sec)
1
.
.
5
RESULT AND CONCLUSION :-
The characteristics of fuse wire is studied in this experiment
and
is found to be inverse type ,and is plotted on graph paper .
Viva Question
1 Application of fuse wire
2 comparisons of fuse and circuit breaker
3 Types of fuses and their application
4 types of fuse require for protection of transformer, generator and induction
motor
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 19
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
EXPERIEMNT NO:- 08
AIM :- TO STUDY DIRECTIONAL OVER CURRENT RELAY ( ACDR 11
HPD)
APPARATUS :-
1) ASHIDA make single pole directional O/C relay ACDR 11 HPD
2) Phase shifting transformer
3) Dimmerstat ( 3 phase , 440 volt, 50 Hz )
4) Ammeter (0-1 Amp)
5) Rheostate ( 300 ohm , 1.7 Amp)
6) Dimmerstat ( 1 phase , 230 volt, 4 Amp)
7) DC Power Supply ( 110 Volt )
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
110V
(0-2A) + DC -
1000ohm,1.2A
A
R
3-PH
440V 15
16
R R
50 HZ
AC 3-PH
SUPPLY SHIFTING
11
TRANSFO
Y RMER 7
CT PT
Y
B
12
8
B
N 3 4
N
TIMER
TO TRIP
CIRCUIT
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 20
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
THEORY : -
1. Directional O/C relay
2. Directional relay connection
OPERATION-
Load current is continuously monitored and compared to set value
and polarized with voltage for direction sensing. As soon as the current exceeds the
set value and it is operating direction then N value (Time set value) is calculated
and then the delay time count is started , two types of curves 10 times ( N=10 )
current 3.0 sec . Delay and 1.3 sec delay can be provided. At the end of the time
count if the current still exceeds the set value TRIP is exceeded. All the monitored
current value is available at the front D is skeets for external recording .
If the direction is reverse then the TRIP execution is
(represented) restrained high fault setting is also provided (2N. 20 N) IF the
current value exceeds the HF set value instant trip (i.e. 100 msec.) is executed, by
passing the directional restraint.
PROCEDURE:-
1) Make the connections as shown in the fig.
2) Apply the voltage across the P.T of relay
3) The pick up current through the relay coil.
4) Set current and time setting of relays as per requirement
5) Switch on the supply.
6) Find out the operating region and non-operating region of
relay by changing angle using the phase shifting transformer.
7) Adjust the current to such a value, which is more than plug
setting.
8) Change the shifter angle such that relay operates in that
region.
OBSERRVATION TABLE :
Sr. Phase angle MTS = MAX torque setting
No.
45 degree 60 Degree 9th Line
1 0
2 30
3 60
4 90
5 120
6 150
7 180
8 -150 degree till
9 0 degree
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 21
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
RESULT:- The static directional relay is studied and graph for different
maximum torque setting is drawn.
Viva Question
1 Application of Directional over current relay
2 Derivation of max. torque angle in directional O/C relay
3 Protection of ring main feeders
4 300, 600and 900 connection in directional relays
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 22
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
EXPERIMENT NO : 09
AIM :- TO STUDY AND PLOT THE CHARACTERISTICS OF
IMPEDANCE RELAY ( ABB-RAKZB)
APPARATUS :-
1) 3 Phase AC Autotransformer
2) Voltmeter (0-150 V)
3) Ammeter(0- 2 Amp)
4) Rheostat ( 300 ohm , 1.7 Amp)
5) 3 Phase Impedance Relay
6) Phase shifting Transformer
7) 1 Phase Variac / DIMMERSTAT
8) Auxiliary DC Supply
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM :
+ -
1 18
3 PH Ru
440V 3PH IMPEDANCE
50 HZ, DIMMERSTAT O/P V (0-75V) RELAY
Su
AC
SUPPLY
Tu
S1 S1
(0-2A)
1000 ohm,1.7A
R
3 PH R PHASE
440V SHIFTING
50 HZ, Y TRANSFORMER O/P
AC B
SUPPLY N
N
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 23
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
THEORY :
1) Explain Unit and non unit protection with examples
2) Explain characteristics of different distances relay on R-X diagram
3) Explain static impedance relay with amplitude and phase comparator.
4) Advantages of static relay over electromechanical relay.
PROCEDURE :
1) Make the connections as shown in the circuit diagram.
2) Keep the rheostat in the middle position.
3) Switch on the supply to the phase shifter and also the DC supply.
4) Now reduce the voltage of the autotransformer, note the voltages at
which the relay operates.
5) Change the position of phase shifter & repeat the steps 4,5,6.
6) After taking no of readings change the value of current and repeat
the above steps.
7) Note down the pickup impedance value of the relay.
8) Plot the operating and non-operating region of relay on R-X plane.
NOTE :- The output voltage of phase shifter is set at 110V and the voltage
output from the auto transformer is also 100 V maximum
permissible value .
OBSERVATION TABLE:
For A=20, B=6, Ia= 01 Amp
Sr No. Phase Angle( ) Voltage ( V)
1) 0 degree
2) 30 degree
3) 60 degree
4) 90 degree
5) 120 degree
6) 150 degree
7) :
8) :
9) 360 degree
10) 0 degree
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 24
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
Same table for A =40, B= 8, Ia =0.5 Amp
Sr. I (Amp) Voltage (V) volts
/ No.
1 0.1
2 0.2
3 0.3
4 0.4
5 0.5
6 0.6
7 0.7
8 0.8
9 0.9
10 1.0
RESULT :-
The relay operates for any value of the radius less than the radius of
the circle, hence the operating region of the relay inside the
circle.
Viva Questions:
1 Torque equation of Reactance and mho relay with their characteristics.
2 Effect of arc resistance in distance relay
3 Selection of distance relay.
4 Effect of power swing in distance relay
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 25
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
EXPERIMENT NO : 10
AIM :- TO STUDY TRANSFORMER DIFFERENTIAL PROTECTION
APPARATUS :-
1) Static Differential Relay (Model No. ACDF 31 HA)
2) 1 Ph Dimmerstat 230V, 10 A
3) 2 CT (10/ 5A and 20/5A)
4) Ammeter AC (0- 15 A) 3 No.
5) Ammeter AC (0- 5 A) 2 No.
6) Rheostat (38 ohm, 8.5 A)
7) Loading Rheostat
8) Multimeter
9) 1 ph Transformer 230/115 V, 50 Hz, 1 KVA
10) Connecting wires
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM :
(0-15A)
38ohm, 8.5A
A
(0-20A) (0-15A)
A M M A
L
L
(0-5A) L
O
1PH
230
A A
D
(0-5A) A
50 HZ
A.C.
SUPP
LY
27
28
+15 - 16
110V DC
THEORY: -
1. Differential protection theory
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 26
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
2. 1ph and 3 ph Transformer differential protection scheme
3. Difference between Transformer and generator Differential
protection.
PROCEDURE: -
1) Make circuit connection as shown in ckt. Diagram.
2) Open the parallel path of secondary transformer containg rheostat with
ammeter. Transformer is connected now at full load condition.
3) With the help of dimmerstat, give some supply voltage to primary side
of transformer and observe its current. Make sure secondary current is
varying in proportion to turn ratio. And current through secondary side
of two CTs are zero.
4) Now connect the parallel path of secondary transformer by touching
wire to the secondary terminal of transformer and observe the current
through secondary side of two CTs. There is a difference of two CTs
currents and at this condition differential relay will trip.
5) Note down values of these currents through secondary side of two CTs
6) Plot the characteristics between summation and difference of these two
currents.
OBSERVATION
Sr. Secondary Secondary Restraining Operating
No. current of CT= current of CT= Torque= Torque=
i1(A) i2(A) (i1(A) + i2(A))/2 i1(A) - i2(A)
1
2
.
5
RESULT- Transformer differential relay is studied. The characteristics between
restraining and operating torque are straight line.
Viva question:
1 Why ratio of two Cts is different?
2 Circuit connection of 3 phase Y transformer
3 Explain biased differential relay
4 Types of fault occur in transformer
5 No. of CTs require and their connection for protection of 3 phase
transformer
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 27
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
EXPERIMENT NO : 11
AIM- To study unrestricted earth fault relays.
APPARATUS- 1) Static IDMT earth fault relays ( Model No. APR 41 )
2) Rheostat ( 100 ohm, 5 A).3 Nos.
3) Ammeter AC ( 0- 5A).3 Nos.
4) Ammeter AC ( 0- 1A)
5) Experimental kit
6) Aux. DC supply- 110 V DC
7) Timer
8) 3 ph Dimmerstat
9) Connecting wires
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
(0-5A)
R 3
P A
H
3 - PH
AC 100ohm,5A
D (0-5A)
I
Y A
M
M
SUPPLY 100ohm,5A 100ohm,5A
E
440V, R
50 HZ (0-5A)
B S
T A
A
N T
I/P O/P
ON OFF
T
3 I
STOP M START
E
4 R
1 ph
supply
110V DC
11 12
+ -
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 28
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
THEORY- 1) Unrestricted and restricted earth fault relays with ckt
connection
2) Their application.
PROCEDURE- 1) Connect the circuit as shown in figure.
2) Set current and time setting of relays as per requirement
2) Give 3 ph. Supply to stat connected rheostat (load)
3) balance the load by making all three phase currents equal
in magnitude.
4) Create a fault by short circuiting some of the winding of a
single phase load.
5) Note down fault current and take corresponding time for
tripping relay by resetting relay and timer by switching
off without disturbing dimmerstat position.
6) Repeat same procedure with different fault current and
plot characteristics between PSM and operating
time
OBSERVATION TABLE: Relay current Setting -
TMS -
Sr. No. Fault Current (A) Timer time( Sec)
RESULT: The unrestricted earth fault relay is studied
Viva question:
1 Application of earth fault relay.
2 Importance of high impedance connected between neutral to ground
3 Difference between setting of earth fault and phase fault relays
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 29
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VIIIth SEM B.E.
G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR 30
You might also like
- QAQC Electrical Inspection: A Beginner's GuideFrom EverandQAQC Electrical Inspection: A Beginner's GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Tneb Hand Testing BookDocument405 pagesTneb Hand Testing BookNarinder Rawat100% (14)
- Tneb Hand Testing BookDocument405 pagesTneb Hand Testing BookNarinder Rawat100% (14)
- Commissioning Numerical RelaysDocument24 pagesCommissioning Numerical RelaysVHMANOHARNo ratings yet
- P633 Test Tools Farhad Rev 01Document5 pagesP633 Test Tools Farhad Rev 01Neelakandan MasilamaniNo ratings yet
- Line Distance Protection IED REL 670Document47 pagesLine Distance Protection IED REL 670kass_ecs100% (1)
- CKP Notes Vol 2 VERSION 2Document116 pagesCKP Notes Vol 2 VERSION 2Sivasankar AkcNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance Test PDFDocument2 pagesInsulation Resistance Test PDFusman haroonNo ratings yet
- Differential Relay With Adaptation During Saturation PeriodDocument6 pagesDifferential Relay With Adaptation During Saturation Periodasim saeedNo ratings yet
- DCRP QuestionsDocument1 pageDCRP QuestionsSiva NandhamNo ratings yet
- PWR Sys Fund Relay ApplicationsDocument231 pagesPWR Sys Fund Relay ApplicationsJohn BihagNo ratings yet
- DCRP AskedDocument3 pagesDCRP AskedSiva NandhamNo ratings yet
- Relays Makes Test ProcedureDocument25 pagesRelays Makes Test ProcedureRa HulNo ratings yet
- Transformer Stability TestsDocument5 pagesTransformer Stability Testsardianto hamonanganNo ratings yet
- Siemens Relay 7rw600Document20 pagesSiemens Relay 7rw600rajinipre-1No ratings yet
- Alfanar Co.: Respon Sibilities Legend CSDDocument5 pagesAlfanar Co.: Respon Sibilities Legend CSDjayabalNo ratings yet
- 25ref RelayDocument8 pages25ref Relaysikander843562No ratings yet
- SA2003-000019 A en Trip Circuit Supervision With RXMB 1 Auxiliary RelayDocument1 pageSA2003-000019 A en Trip Circuit Supervision With RXMB 1 Auxiliary RelayErmin FazlicNo ratings yet
- Impedance MeasurementDocument2 pagesImpedance MeasurementAhsan KaziNo ratings yet
- N6166 E05 F871 TR Diff Relay 7UT613Document6 pagesN6166 E05 F871 TR Diff Relay 7UT613মোঃ মহসিনNo ratings yet
- Phase Angle Shift Compensation For Differential Protection-One Solution To Cover All Types of TransformersDocument6 pagesPhase Angle Shift Compensation For Differential Protection-One Solution To Cover All Types of TransformersDante FilhoNo ratings yet
- CT Operated Thermal Over Load Relay Current Setting CalculationDocument5 pagesCT Operated Thermal Over Load Relay Current Setting CalculationMas Kahfi100% (1)
- TP TPD Pfs TPC QP 12Document29 pagesTP TPD Pfs TPC QP 12erbvp22No ratings yet
- Siemens 7sd5Document18 pagesSiemens 7sd5BalajiNo ratings yet
- 26 Relay Testing Techniques, Requirements, Considerations MDocument8 pages26 Relay Testing Techniques, Requirements, Considerations Mgagan0312No ratings yet
- Tan Delta Test For Power TransformersDocument9 pagesTan Delta Test For Power TransformersSreenivasanNo ratings yet
- ISA Introduction To The Test of Protection RelaysDocument23 pagesISA Introduction To The Test of Protection RelaysCata CatalinNo ratings yet
- 7sd52 7sd62 ConfigurationDocument14 pages7sd52 7sd62 ConfigurationWilber LucasNo ratings yet
- Transformer Differential RelayDocument12 pagesTransformer Differential Relaysandyarajagopalan321No ratings yet
- Bus Bar Differential Protection Relay Test ProcedureDocument1 pageBus Bar Differential Protection Relay Test Procedurem khNo ratings yet
- HT Capacitor Bank and Reactor Test and CommissioningDocument2 pagesHT Capacitor Bank and Reactor Test and CommissioningAodman4u0% (1)
- 7SA522 - Distance & DEF Relay-ADocument30 pages7SA522 - Distance & DEF Relay-Am khNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Abdul Fareh Khan 2k19Document5 pagesMuhammad Abdul Fareh Khan 2k19Fareh KhanNo ratings yet
- Functional Test of Thermal Overload ProtectionDocument1 pageFunctional Test of Thermal Overload ProtectionMihai BancuNo ratings yet
- Lab 06-Differential Bus Bar ProtectionDocument6 pagesLab 06-Differential Bus Bar ProtectionAliza SharifNo ratings yet
- What Is The Best Protective Relay Test-Set - Valence Electrical Training ServicesDocument12 pagesWhat Is The Best Protective Relay Test-Set - Valence Electrical Training ServicesanuragpugaliaNo ratings yet
- MPD 600 Article The Importance of PD Testing On Power Transformers ENUDocument8 pagesMPD 600 Article The Importance of PD Testing On Power Transformers ENUDeepen SharmaNo ratings yet
- Enerzio Product Catalog 2019-2020 New PDFDocument16 pagesEnerzio Product Catalog 2019-2020 New PDFHarvinder Singh HarryNo ratings yet
- AREVA MVAP22 Voltage Balance RelayDocument22 pagesAREVA MVAP22 Voltage Balance Relayadeelzafar100No ratings yet
- Transformer EssentialsDocument86 pagesTransformer EssentialsSalma EL HadiNo ratings yet
- SWGR Feeder - Functional TestDocument13 pagesSWGR Feeder - Functional TestChheng KimhokNo ratings yet
- ABB REL670 V1.B A32 Template Manual ENU TU3.00 V1.000 PDFDocument17 pagesABB REL670 V1.B A32 Template Manual ENU TU3.00 V1.000 PDFWafa Imene BouhaddaNo ratings yet
- F2000 Instruments Relay Test PlanDocument4 pagesF2000 Instruments Relay Test Planyand_carlosNo ratings yet
- Volt::Ch: Voltech Engineers Pvt. LTDDocument32 pagesVolt::Ch: Voltech Engineers Pvt. LTDstalin63100% (1)
- 182.testing With MZTU-34 Relay-GenPro PDFDocument7 pages182.testing With MZTU-34 Relay-GenPro PDFAnonymous nPR5nm8XMNo ratings yet
- Schneider Protection RelayDocument8 pagesSchneider Protection Relayeugene oneillNo ratings yet
- Numerical RelayDocument9 pagesNumerical Relayc_chootiaNo ratings yet
- Differential ProtectionDocument8 pagesDifferential Protectionchandra_shekhar2221941No ratings yet
- Testing of Modern Bus Protection SystemsDocument7 pagesTesting of Modern Bus Protection Systemss_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Testing Directional Overcurrent Relays From Valence PDFDocument9 pagesTesting Directional Overcurrent Relays From Valence PDFnaran19794735No ratings yet
- Ici-C&C/Seupptcl/A - S (Sup.) /2011-12/001: Tested by WitnessedDocument7 pagesIci-C&C/Seupptcl/A - S (Sup.) /2011-12/001: Tested by WitnessedkamarajkanNo ratings yet
- Non-Unit System of Protection: Therefore The Setting of Over Current Relay Should Be More Than 14113.5 ADocument6 pagesNon-Unit System of Protection: Therefore The Setting of Over Current Relay Should Be More Than 14113.5 AyethweNo ratings yet
- Protective Relaying Testing ST6Document6 pagesProtective Relaying Testing ST6Darwin MesaNo ratings yet
- 2.u#1 11KV Switchgear Testing Book-2 PDFDocument219 pages2.u#1 11KV Switchgear Testing Book-2 PDFSabyasachi PatraNo ratings yet
- DCRP Written Test QuestionsDocument1 pageDCRP Written Test QuestionsSiva NandhamNo ratings yet
- Automatic Distance Relay PDFDocument4 pagesAutomatic Distance Relay PDFOmar Chayña VelásquezNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - 19Document32 pagesLecture Notes - 19Bhaskar1411No ratings yet
- Electrical Power-2 Lab ManualDocument6 pagesElectrical Power-2 Lab ManualAditya SanjeevNo ratings yet
- Ps Lab ManualDocument132 pagesPs Lab ManualRamkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Power System Laboratory Experiment - 2023-24Document51 pagesPower System Laboratory Experiment - 2023-24Manas Ranjan MishraNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument7 pagesLab Manualdurgesh choudharyNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EE852Document20 pagesLab Manual EE852Uzair Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- SRReport 1476479550735 PDFDocument1 pageSRReport 1476479550735 PDFLawrence AlexNo ratings yet
- VSJ Samayapuram BrochureDocument2 pagesVSJ Samayapuram BrochureLawrence AlexNo ratings yet
- Relay Testing ProcedureDocument144 pagesRelay Testing ProcedureLawrence Alex100% (1)
- Relay Testing ProcedureDocument144 pagesRelay Testing ProcedureLawrence Alex100% (1)
- Relay Testing Procedure PDFDocument50 pagesRelay Testing Procedure PDFLawrence Alex100% (2)
- Relay Testing Procedure PDFDocument50 pagesRelay Testing Procedure PDFLawrence Alex100% (2)
- User Manual - Payroll Service PDFDocument4 pagesUser Manual - Payroll Service PDFJaya LawrenceNo ratings yet
- User Manual - Payroll Service PDFDocument4 pagesUser Manual - Payroll Service PDFJaya LawrenceNo ratings yet
- English For Children PDFDocument39 pagesEnglish For Children PDFJaya LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Resume: PersonalDocument2 pagesResume: PersonalLawrence AlexNo ratings yet