Professional Documents
Culture Documents
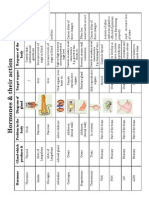
Gland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical Nature
Gland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical Nature
Uploaded by
Usha Stanyer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pageshormone chart
Original Title
32538440 Hormones Chart
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenthormone chart
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesGland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical Nature
Gland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical Nature
Uploaded by
Usha Stanyerhormone chart
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Gland Hormone Target tissue Principle Chemical
actions nature
Hypothalam Releasing hormones Adenohypophys Activate peptides
us is release of
adenohypop
hysial
hormones
Hypothalam Inhibiting hormones Adenohypophys Inhibit Peptides(e
us is release of xcept
adenohypop prolactin-
hysial inhibiting
hormones factor,
whichis
dopamine
Neurohypop Antidiuretic hormone kidneys Conserves Peptide (9
hysis (ADH) water by amino
stimulating acids)
its
reabsorption
from urine
Neurohypop Oxytocin 1) Uterus 1)stimulates Peptide (9
hysis 2) Mammar contraction amino
y glands 2)stimulates acids)
milk ejection
Adenohypop Adrenocorticotropic Adrenal cortex Stimulates Peptide (39
hysis hormone (ACTH) secretion of amino
adrenal acids)
cortical
hormones
such as
cortisol
Adenohypop Melanocyte- skin Stimulates Peptide(tw
hysis stimulating hormone color change o forms;13
(MSH) in reptiles amino
and acids and
amphibians; 22 amino
various acids)
functions in
mammals
Adenohypop Growth hormone (GH) Many organs Stimulates Protein
hysis growth by
promoting
bone growth,
protein
synthesis,
and fat
breakdown
Adenohypop Prolactin (PRL) Mammary Stimulates protein
hysis glands milk
production
Adenohypop Thyroid –stimulating Thyroid gland Stimulates glycoprotei
hysis hormone (TSH) thyroxine n
secretion
Adenohypop Luteinizing hormone gonads Stimulates glycoprotei
hysis (LH) ovulation n
and corpus
luteum
formation in
females;
stimulates
secretion of
testosterone
in males
Adenohypop Follicle-stimulating gonads Stimulates glycoprotei
hysis hormone (FSH) spermatogen n
esis in
males;
stimulates
development
of ovarian
follicles in
females
Thyroid Thyroid hormones Most cells Stimulates Amino acid
gland (thyroxine and metabolic derivative
triiodothyronine) rate; (iodinated)
essential to
normal
growth and
development
Thyroid Calcitonin bones Inhibits loss Peptide (32
gland of calcium amino
from bone acids)
Parathyroid Parathyroid hormone Bones, kidneys, Raises blood Peptide (34
glands digestive tract calcium level amino
by acids)
stimulating
bone
breakdown;
stimulates
calcium
reabsorption
to kidneys;
activates
vitamin D
Adrenal Epinephrine(adrenalin Smooth muscle, Initiates Amino acid
medulla e) and cardiac muscle, stress derivatives
norepinephrine(noradr blood vessels responses;
enaline) raises heart
rate, blood
pressure,
metabolic
rate; dilates
blood
vessels;
mobilize fat;
raises blood
glucose level
Adrenal Glucocorticoids(ex: Many organs Adaptation steroid
cortex cortisol) to long-term
stress; raises
blood
glucose
level;
mobilizes fat
Adrenal Mineralocorticoids(ex: Kidney tubules Maintains steroid
cortex aldosterone) proper
balance of
Na+ and K+
excretion
Pancreas Insulin Liver, skeletal Lowers blood Peptide (51
muscles, glucose amino
adipose tissue level; acids)
stimulates
glycogen,
fat, protein
synthesis
Pancreas Glucagon Liver, adipose Raises blood Peptide (29
tissue glucose amino
level; acids)
stimulates
breakdown
of glycogen
in liver
Ovary Estradiol 1)general 1-stimulates steroid
2) female development
Reproductive of female
structures secondary
sex
characteristi
cs
2-stimulates
growth of
sex organs
at puberty
and monthly
preparation
of uterus for
pregnancy
Ovary Progesterone 1)uterus 1)completes steroid
2)mammary preparation
glands for
pregnancy
2)stimulates
development
Testis Testosterone 1)many organs 1)stimulates steroid
2)male development
reproductive of secondary
structures sex
characteristi
cs in males
and growth
spurt at
puberty
2)stimulates
development
of sex
organs;
stimulates
spermatogen
esis
Pineal gland Melatonin Gonads, brain. Regulates Amino acid
Pigment cells biological derivative
rhythms
You might also like
- The Phoenix Protocol Dry Fasting For Rapid Healing and Radical Life Extension (August Dunning) (Z-Library)Document124 pagesThe Phoenix Protocol Dry Fasting For Rapid Healing and Radical Life Extension (August Dunning) (Z-Library)amitlkoyogaNo ratings yet
- List of Hormones - Hypersecretion and HyposecretionDocument11 pagesList of Hormones - Hypersecretion and HyposecretionAngeli Jean Koreen Corpuz88% (48)
- Mark Klimek Full Nclex ReviewerDocument30 pagesMark Klimek Full Nclex ReviewerAlex BellNo ratings yet
- Hormone Summary ChartDocument1 pageHormone Summary ChartVDiesel990% (2)
- Where Hormone Is Produced Hormone Secreted Chemical Class Target Cell Location Hormone FunctionDocument3 pagesWhere Hormone Is Produced Hormone Secreted Chemical Class Target Cell Location Hormone FunctionRNStudent1100% (1)
- Endocrine ReviewDocument9 pagesEndocrine ReviewSpencer ThomasNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument5 pagesEndocrine DisordersBilly Ray VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument1 pageHormonesTang Tiong Min 郑中铭100% (1)
- Hormones TableDocument84 pagesHormones TableSaajid AmraNo ratings yet
- Steroids HormonesDocument15 pagesSteroids HormonesZain Ul Abdin Mughal100% (1)
- The Endocrine System Study Guide 101 PDFDocument17 pagesThe Endocrine System Study Guide 101 PDFStephanie Kate PelenioNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument38 pagesFunctional Anatomy and PhysiologyNawalNo ratings yet
- Reproductive HormonesDocument43 pagesReproductive HormonesMunchkin Celina100% (1)
- Blood and LymphaticDocument4 pagesBlood and LymphaticCKNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument144 pagesEndocrineaartiNo ratings yet
- Blood Test and Normal RangeDocument40 pagesBlood Test and Normal Rangeethirukumaran0% (1)
- (HISTOLOGY) Endocrine SystemDocument11 pages(HISTOLOGY) Endocrine Systemwipi112No ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandsDocument18 pagesAdrenal GlandsNitesh BhuraNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action of HormonesDocument33 pagesMechanism of Action of HormonesMehwishNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System (Lab Notes) Pineal Gland:: MelatoninDocument4 pagesEndocrine System (Lab Notes) Pineal Gland:: MelatoninHazel Mae Tapia100% (1)
- Male and Female Sex HormonesDocument20 pagesMale and Female Sex HormonesJose Fernando Gregana ElpaNo ratings yet
- Actions of Thyroid Hormone: Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Assistant Professor MBBS, MphilDocument41 pagesActions of Thyroid Hormone: Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Assistant Professor MBBS, MphilJyoti ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument58 pagesEndocrine SystemRochelle Jade Docejo IINo ratings yet
- What Does The Endocrine System Do?Document10 pagesWhat Does The Endocrine System Do?hadiqa azizNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development TheoriesDocument8 pagesGrowth and Development TheoriesNiwerg SecoNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of Coffee's Effects On Liver EnzymesDocument5 pagesA Critical Review of Coffee's Effects On Liver EnzymesMihai DragomirNo ratings yet
- Hormones & Hormones AntagonistsDocument27 pagesHormones & Hormones AntagonistsVarsha Shende KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesRespiratory System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBDNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument101 pagesThe Endocrine SystemLeônidas ZazelisNo ratings yet
- Thiamine DeficiencyDocument11 pagesThiamine DeficiencyLotje MulderNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Presented By, MD Nasir Uddin Mahmood, Product Executive, Opsonin Pharma LimitedDocument24 pagesThe Endocrine System: Presented By, MD Nasir Uddin Mahmood, Product Executive, Opsonin Pharma LimitedMd Nasir Uddin Mahmood100% (2)
- Female Sex HormonesDocument30 pagesFemale Sex HormonesMagdy El-GammalNo ratings yet
- Male Hypogonadism: EAU Guidelines OnDocument34 pagesMale Hypogonadism: EAU Guidelines OnAyu sri WidianiNo ratings yet
- Exam 19 Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesExam 19 Endocrine SystemPurwa RaneNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument23 pagesEndocrine System NoteslacyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology I - Lecture Notes - IntroductionDocument51 pagesAnatomy and Physiology I - Lecture Notes - IntroductionNgoc TranNo ratings yet
- Corticosteroids 2 of 2Document33 pagesCorticosteroids 2 of 2VLDsNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Workbook 2015Document8 pagesEndocrine System Workbook 2015api-298277560100% (1)
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument41 pagesIntroduction To ImmunologyFYMNo ratings yet
- Atlas Purdue Univ - 1Document27 pagesAtlas Purdue Univ - 1Felipe Andres Montecinos RojasNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOLOGY BOARD EXAM AnswersDocument13 pagesPHYSIOLOGY BOARD EXAM AnswerschristinejoanNo ratings yet
- Secondary Amenorrhea Testing AlgorithmDocument1 pageSecondary Amenorrhea Testing AlgorithmpolygoneNo ratings yet
- Recommendations To Maintain Immune Health in Athletes Walsh 2018Document13 pagesRecommendations To Maintain Immune Health in Athletes Walsh 2018Felipe Ricardo Garavito PeñaNo ratings yet
- List of Physiology PracticalsDocument2 pagesList of Physiology PracticalsSeerat Ul irfanNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Role of Negative Feedback Mechanism in Thyroid ProductionDocument4 pagesDiscuss The Role of Negative Feedback Mechanism in Thyroid ProductionCLNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 2017Document28 pagesEndocrine System 2017cyber sec100% (1)
- Lab Report Assistant Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesLab Report Assistant Endocrine SystemJohn Louis AguilaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal CrisisDocument27 pagesAdrenal CrisissayednourNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of PelvisDocument40 pagesAnatomy of PelvisGovGeet100% (1)
- Cholesterol, Bile SaltsDocument94 pagesCholesterol, Bile SaltsMax Annani-akollorNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders 1234399857677955 1Document130 pagesEndocrine Disorders 1234399857677955 1api-19824701No ratings yet
- Hormones and Endocrine SystemsDocument26 pagesHormones and Endocrine SystemsNikko Adhitama100% (4)
- Biological Treatments in PsychiatryDocument56 pagesBiological Treatments in PsychiatryNurul AfzaNo ratings yet
- Pathology Lecture SeriesDocument168 pagesPathology Lecture SeriesButch DumdumNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDump Acc 2100% (1)
- CH 18 Endo F 2017Document152 pagesCH 18 Endo F 2017Julia100% (1)
- Biochemistry of HormoneDocument58 pagesBiochemistry of HormoneHaamim Sya'bani0% (1)
- Adrenal GlandDocument21 pagesAdrenal GlandMustafa KhandgawiNo ratings yet
- Chris Masterjohn Book DemoDocument15 pagesChris Masterjohn Book Demojijibiji24100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParDocument64 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParYackson Frank100% (1)
- Common Vertebrate HormonesDocument6 pagesCommon Vertebrate Hormonesjourey08No ratings yet
- Lecture - 8 EndocrineDocument4 pagesLecture - 8 EndocrineBafrin ShaqlawaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System 2Document7 pagesDigestive System 2SlaheddineNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal 3Document30 pagesResearch Proposal 3nickos navajaNo ratings yet
- Animal NutritionDocument32 pagesAnimal NutritionPalabana UniversityNo ratings yet
- BCH 307-LipoproteinsDocument3 pagesBCH 307-LipoproteinsIsabel WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Inv. Virtual Conference Ryzodeg-16 JAN 2021 - Final - OKDocument4 pagesInv. Virtual Conference Ryzodeg-16 JAN 2021 - Final - OKmelyekaNo ratings yet
- 2.the Nursing Role in Reproductive and Sexual HealthDocument70 pages2.the Nursing Role in Reproductive and Sexual HealthAngel Gabriel FornillosNo ratings yet
- A Two-Step Hormone-Signalling Mechanism That Drives Physical ActivityDocument2 pagesA Two-Step Hormone-Signalling Mechanism That Drives Physical ActivitycfibanezNo ratings yet
- Circadian RhythmsDocument66 pagesCircadian RhythmsGraemeNo ratings yet
- A-Z Diseases List For NEET PG PDFDocument10 pagesA-Z Diseases List For NEET PG PDFSubhajitPaulNo ratings yet
- File 59 - OralDocument6 pagesFile 59 - Oralbijen upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Gout and HyperuricemiaDocument41 pagesGout and HyperuricemiaMA 09No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument19 pagesMale Reproductive SystemAli JafriNo ratings yet
- NandraloneDocument24 pagesNandraloneGabriel NguyenNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa Case StudyDocument59 pagesPlacenta Previa Case Studyjuel_navarro88% (33)
- MAGNESIUM MetabolismDocument10 pagesMAGNESIUM MetabolismAlvi MuldaniNo ratings yet
- Galactosemia by SlidesgoDocument24 pagesGalactosemia by SlidesgoCherie ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Fight Cancer With A Ketogenic DietDocument168 pagesFight Cancer With A Ketogenic Dietoub67% (3)
- Vyska MaxDocument16 pagesVyska MaxJan DušekNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Symptom HackerDocument18 pagesThyroid Symptom HackerozergyalmoNo ratings yet
- Some Imp DataDocument3 pagesSome Imp DataAfshan AyemanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine SystemSheinny Rodriguez100% (1)
- Diabetes in School Powerpoint PresentationDocument16 pagesDiabetes in School Powerpoint Presentationmaria sarojiniNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood GasDocument12 pagesArterial Blood Gasعزالدين الزوقريNo ratings yet
- QP Code: 1075: Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, KarnatakaDocument5 pagesQP Code: 1075: Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, KarnatakaDyan Dixith DcNo ratings yet
- Neck Lump Examination: OSCE ChecklistDocument2 pagesNeck Lump Examination: OSCE ChecklistNur Farhana Athirah Azhari100% (4)
- Group 2 Culture TechniqueDocument38 pagesGroup 2 Culture TechniqueBartazal dawaganNo ratings yet
- MRCP Part 1Document38 pagesMRCP Part 1走过一些路No ratings yet
- Male Inf Overview and Causeleaver2016Document6 pagesMale Inf Overview and Causeleaver2016annisa habibulloh100% (1)