Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluid Flow PDF
Fluid Flow PDF
Uploaded by
Christian Mercado PagsinohinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluid Flow PDF
Fluid Flow PDF
Uploaded by
Christian Mercado PagsinohinCopyright:
Available Formats
FLUID FLOW (MOMENTUM TRANSFER)
(Section 6, ChE Handbook) Fluid and Particle Dynamics
(Section 10, ChE Handbook) Transport and Storage of Fluids
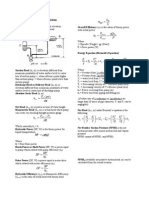
1.) Fluid Head, H
where Hf =head of the fluid inside the pipe, m (ft)
Hm=head of the fluid used in manometer, m (ft)
ρf= density of the fluid inside the pipe, kg/m3 (lb/ft3)
ρm= density of the fluid inside the pipe, kg/m3 (lb/ft3)
2.) Continuity Equation
̇ ̇
where m= mass, kg (lbm)
A=area, m2 (ft2)
v= velocity, m/s (ft/s)
3.) Overall Energy Balance
́
Used when there is temperature change
For OPEN SYSTEM
where Q= heat, [absorbed (+), released (-)], J/kg (ft-lbf/lbm)
W= Work, [done to the system (+), done by the system (-)], J/kg (ft-lbf/lbm)
Δz= z2-z1 , m, ft
gc=1kg-m/(N-s2) SI
32.2 lbm-ft/(lbf-s2) English
4.) Mechanical Energy Balance
can be used in fans, (can be assumed that gases involved in the process follows Incompressible
Theory)
Total Dynamic Head (TDH)
Shaft work delivered by the equipment (e.g. pump) to the fluid
Shaft work of the fluid
Mechanical energy delivered to the fluid
Shaft work of the equipment (e.g. pump, compressors) delivered by the fluid
applicable to + work
5.) Frictional Losses
( )
( )
Moody Chart, Fig. 6-9 (ChE Handbook)
Note:
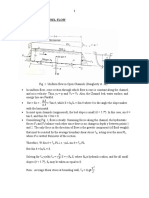
For Non-circular channels:
Hydraulic diameter - if the flow is TURBULENT
- Four times the channel cross-sectional area divided by the wetted perimeter
For annulus: –
For rectangular duct:
Hydraulic radius = ¼ DH
Equivalent diameter – if the flow is LAMINAR
For ellipse: semi-axes a and b ( ) Eq. 6-50
For rectangle: width a, height b ( ) Eq. 6-51;
K values are given in p. 6-12
For annulus { [ ]} Eq. 6-52
6.) Meters, Fm
Meters Coefficient, C Description
Orifice 0.61 Maximum losses
Venturi 0.98
Nozzle 0.95-0.99
Pitot Tube 1 M ’
velocity
Friction losses due to meters
where y-> …… 0.1 ( ) (orifice)
Eqn 10-20 (7th), 10-22 (8th) (ChE Handbook)- applicable to orifice and venturi
̇ √
Y=1 if liquids
β=d2/d1
d=diameter, m (ft)s
P= pressure, Pa
Eqn 10-7 (7th), 10-13 (8th) ChE Handbook for pitot tube
FLUID FLOW (MOMENTUM TRANSFER)
Prepared by Engr. Christian Pagsinohin
7.) Transportation of Fluids
a.) Compressors
See p. 10-39 (7th), p. 10-45 (8th) ChE Handbook
Adiabatic Process
[( ) ]
where n -> no of compression stages
k-> specific heat ratio , Table 2-199 (7th), Table 2-157 (8th) (ChE Handbook)
R -> ideal gas constant
T -> absolute temperature
Isothermal Process
Note: If not stated in the problem, assume the process is ADIABATIC.
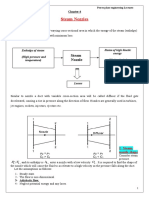
b.) Turbines
use Energy Balance
c.) Pumps
Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH)
[ ]
where Psuction=suction pressure
Po= vapor pressure
ΣF= friction losses from the initial point to the pump suction
8.) Compressible Flow
Eqn. 6-114 (ChE Handbook)
[ ]
9.) Differential flow of fluid (Unsteady-state)
where A1(h)= area of the container as a function of h
A2= area of the orifice or the hole, usually constant
v(h)= velocity of the fluid as function of h
FLUID FLOW (MOMENTUM TRANSFER)
Prepared by Engr. Christian Pagsinohin
You might also like
- TG-Op1 Enunciados v01Document53 pagesTG-Op1 Enunciados v01VlmScarletQcaritaNo ratings yet
- Cavitation CFD in A Centrifugal PumpDocument7 pagesCavitation CFD in A Centrifugal Pumpazispn99100% (1)
- Lab Report - Determining Coefficient of DischargeDocument9 pagesLab Report - Determining Coefficient of DischargeNikhil Penchalwar100% (2)
- Astm B917 - B917M-2009 - 5000Document3 pagesAstm B917 - B917M-2009 - 5000Grayson100% (1)
- Material Imprimir Taller BiogalDocument10 pagesMaterial Imprimir Taller BiogalOmar Daniel CM100% (1)
- XC100 Series Monitor XT300 Series Dehydrator User ManualDocument36 pagesXC100 Series Monitor XT300 Series Dehydrator User ManualMaria Canales OliveiraNo ratings yet
- ENPE 523 Practice MidtermDocument11 pagesENPE 523 Practice Midtermsiraj1993No ratings yet
- Hazen William's Equation: by Eng. Ahmed Ghassan & Eng. Ahmed AmmarDocument13 pagesHazen William's Equation: by Eng. Ahmed Ghassan & Eng. Ahmed AmmarvasudhaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Number: 4 A) Experiment Name: Venturimeter Experiment B) EXPERIMENTAL SETUP: Venturimeter Exp. SetupDocument4 pagesExperiment Number: 4 A) Experiment Name: Venturimeter Experiment B) EXPERIMENTAL SETUP: Venturimeter Exp. SetupNicole Ann ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Pumps and TurbinesDocument12 pagesClassification of Pumps and TurbinesKarim SayedNo ratings yet
- (Instrumentation) Measurement of Flow of FluidsDocument40 pages(Instrumentation) Measurement of Flow of FluidsLWYenNo ratings yet
- Pump and Hydraulic CalculationDocument9 pagesPump and Hydraulic CalculationHasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Oil and Gas Transport - 1987 - Developments in Petroleum ScienceDocument67 pagesChapter 8 Oil and Gas Transport - 1987 - Developments in Petroleum ScienceFalokid RaboNo ratings yet
- Nozzles and Steam TurbineDocument25 pagesNozzles and Steam TurbineAswin AravindNo ratings yet
- Title: Orificemeter AimDocument4 pagesTitle: Orificemeter AimPrashant GiriNo ratings yet
- Air Flow Velocity Measurement Using Pitot-Static Tube PDFDocument8 pagesAir Flow Velocity Measurement Using Pitot-Static Tube PDFWalid AdnanNo ratings yet
- Ground Water Lecture 2 - 1Document31 pagesGround Water Lecture 2 - 1James McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Uniform Flow in Open Channels Economical SectionsDocument16 pagesUniform Flow in Open Channels Economical Sectionscarl ingariNo ratings yet
- Operating Instruction Manual Of: Orifice and Mouthpiece ApparatusDocument9 pagesOperating Instruction Manual Of: Orifice and Mouthpiece ApparatusRavi ParikhNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectric System Models: 3.1 Preliminary ConceptsDocument51 pagesHydroelectric System Models: 3.1 Preliminary ConceptsTilahun weldcherkosNo ratings yet
- Lab. Manual Orifice MeterDocument6 pagesLab. Manual Orifice MeterSavan PatelNo ratings yet
- Ground Water Flow and Well MechanicsDocument47 pagesGround Water Flow and Well MechanicsZainab JereckoNo ratings yet
- Pump and Hydraulic CalculationDocument9 pagesPump and Hydraulic Calculationchem_taNo ratings yet
- Observations and Tabulation Table 1 Test For Single PumpDocument7 pagesObservations and Tabulation Table 1 Test For Single PumpadityaNo ratings yet
- Flow EqualizationDocument9 pagesFlow EqualizationhaymedeleonNo ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-200410-Fluid MechanicsDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-200410-Fluid Mechanicsonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Engineering Hydraulics/OPEN CHANNEL FLOWDocument37 pagesEngineering Hydraulics/OPEN CHANNEL FLOWbasher rajabNo ratings yet
- Flugel-Design Jet PumpsDocument67 pagesFlugel-Design Jet PumpsAnonymous hHWOMl4FvNo ratings yet
- 4FLUIDMAN EX4-Bernoulli ExperimentDocument9 pages4FLUIDMAN EX4-Bernoulli ExperimentSaid AlabriNo ratings yet
- GWH-PPT ch3 SumDocument41 pagesGWH-PPT ch3 SumMistireselassieNo ratings yet
- FME 432 - 532 Compressible Flow Theory 02-04-2024Document29 pagesFME 432 - 532 Compressible Flow Theory 02-04-2024Melody WachukaNo ratings yet
- ChE Lab 1 Experiment 2Document33 pagesChE Lab 1 Experiment 2Julie Anne CristalesNo ratings yet
- 5542-Article Text PDF-9300-1-10-20130718Document21 pages5542-Article Text PDF-9300-1-10-20130718zeinabNo ratings yet
- Gas DynamicsDocument17 pagesGas DynamicsAmrMashhourNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Pump Test RigDocument7 pagesReciprocating Pump Test RigPurtain MENo ratings yet
- Impo1 9Document20 pagesImpo1 9mouhcine maouhoubNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument27 pagesHeat ExchangerKashish Mehta75% (4)
- FM & HM - Manual - 2019-2020Document34 pagesFM & HM - Manual - 2019-2020madhu sudhanNo ratings yet
- A Spreadsheet Approach To Diverter Design Calculations: LouisianaDocument12 pagesA Spreadsheet Approach To Diverter Design Calculations: LouisianaMRizwanSadiq313No ratings yet
- 414CC3 - Excel Template - Prelim Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design - Si - UnitsDocument4 pages414CC3 - Excel Template - Prelim Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design - Si - Unitsvazzoleralex6884No ratings yet
- EXP1Document6 pagesEXP1Hafiz MubashirNo ratings yet
- Experiment Title: Phenomenon of Choing in A Convergent-Divergent DuctDocument26 pagesExperiment Title: Phenomenon of Choing in A Convergent-Divergent DuctjohnNo ratings yet
- Viscosity Correction Factor For Rotameter: J. WojtkowiakDocument5 pagesViscosity Correction Factor For Rotameter: J. WojtkowiakHasan RabyNo ratings yet
- Rigid conduit for fluid flow in two-phase fluid systems - MATLAB - MathWorks 中国Document6 pagesRigid conduit for fluid flow in two-phase fluid systems - MATLAB - MathWorks 中国944062528qqNo ratings yet
- Thermal Considerations in Pipe FlowsDocument11 pagesThermal Considerations in Pipe FlowsHimank JainNo ratings yet
- University of Tennessee - ChattanoogaDocument49 pagesUniversity of Tennessee - ChattanoogaMALIK ZARYABBABARNo ratings yet
- Linear MomentumDocument42 pagesLinear MomentumFady MichealNo ratings yet
- My Lecturenozle - NewDocument10 pagesMy Lecturenozle - NewSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- (Asce) 0733 9429 (2000) 126 2Document7 pages(Asce) 0733 9429 (2000) 126 2wangzhanchangNo ratings yet
- Venturi MeterDocument5 pagesVenturi MeterAzoo Moon100% (1)
- Exp 3Document9 pagesExp 3Sajib Chandra RoyNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Lecture Notes - 9Document13 pagesFluid Flow Lecture Notes - 9Lin Xian Xing100% (1)
- Fluid Dynamics and Turbomachines: Module 1: Tutorial - 01Document8 pagesFluid Dynamics and Turbomachines: Module 1: Tutorial - 01Asrar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Friction in Pipes Aim:: FM&HM LabDocument7 pagesFriction in Pipes Aim:: FM&HM Labashoku2No ratings yet
- Exercice F 7017 TDocument19 pagesExercice F 7017 TtankimsinNo ratings yet
- Impact Of Jet Test Rig AIM: ρ is the density of water (= 1000 Kg/m Q is the volumetric flow rate of fluid, mDocument4 pagesImpact Of Jet Test Rig AIM: ρ is the density of water (= 1000 Kg/m Q is the volumetric flow rate of fluid, mSuman kumar DashNo ratings yet
- 03-Lecture (August 27) - 1Document10 pages03-Lecture (August 27) - 1Goura Sundar TripathyNo ratings yet
- Saturation Pressure FoyDocument6 pagesSaturation Pressure Foyzulfan allifNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - I Experiments Index Expt. No. Name of The ExperimentDocument37 pagesFluid Mechanics - I Experiments Index Expt. No. Name of The ExperimentAnand DattNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction EngineeringDocument4 pagesChemical Reaction EngineeringChristian Mercado PagsinohinNo ratings yet
- For Overall Mass BalanceDocument6 pagesFor Overall Mass BalanceChristian Mercado PagsinohinNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument36 pagesRefrigerationChristian Mercado PagsinohinNo ratings yet
- Unit Operations IIDocument2 pagesUnit Operations IIChristian Mercado PagsinohinNo ratings yet
- Unit5 CrudeOilDesalting Exercises-2Document17 pagesUnit5 CrudeOilDesalting Exercises-2Patricia.PNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Exam PDFDocument6 pagesMachine Design Exam PDFLanz Cruzat100% (1)
- Mark LeClair - Nanospire Cavitation Jet Machining, Transmutation, Crystalline WaterDocument44 pagesMark LeClair - Nanospire Cavitation Jet Machining, Transmutation, Crystalline WatershizuyeNo ratings yet
- Esab Filler Metal Handbook 2016 - Asia Pacific PDFDocument454 pagesEsab Filler Metal Handbook 2016 - Asia Pacific PDFDr. S.No ratings yet
- Gypsum Products: Dental Materials Assis. Prof. Dr. Ibrahim AlfahdawiDocument4 pagesGypsum Products: Dental Materials Assis. Prof. Dr. Ibrahim Alfahdawiزهراء فاضل اجبير فعيلNo ratings yet
- 9.calculations Involving RadiopharmaceuticalsDocument9 pages9.calculations Involving RadiopharmaceuticalsTsegaye NigussieNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Science Chapter 3 NotesDocument12 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 3 NotesAnonymous klhru5ENo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument8 pagesGreenhouse EffectAmple CunananNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 20-Forensic-Chemistry-Serology-and-blood-stain-patterns-this-is-it-2Document16 pagesCHAPTER 20-Forensic-Chemistry-Serology-and-blood-stain-patterns-this-is-it-2BARCELON, CHRISTOPHER JAMESNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 7 - Miller Indices: Unit - IDocument23 pagesLecture - 7 - Miller Indices: Unit - IyashvantNo ratings yet
- Forever Living Product, InternationalDocument32 pagesForever Living Product, InternationalBirchand Thakur PahaadiNo ratings yet
- Consideration For Approval of ATU For Use in Trinidad and TobagoDocument5 pagesConsideration For Approval of ATU For Use in Trinidad and TobagoJeffrey James100% (1)
- The Capsugel Advantage: Pharmaceutical Industry Symposium November 7-9 PolandDocument45 pagesThe Capsugel Advantage: Pharmaceutical Industry Symposium November 7-9 PolandoanabalosacheNo ratings yet
- Abnt NBR 15514Document20 pagesAbnt NBR 15514Andre alexander dos santosNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic PropertiesDocument35 pagesThermodynamic PropertiesRajeshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- !qfpira00v5t3lot Details For Lot - Detalles de Lote 374bz-1043jfDocument2 pages!qfpira00v5t3lot Details For Lot - Detalles de Lote 374bz-1043jftrungkiensccNo ratings yet
- Moldova Slides 5Document12 pagesMoldova Slides 5Igor GîdeiNo ratings yet
- 03 120000 4800000441 Boc Civ Mat 000026 - 01Document56 pages03 120000 4800000441 Boc Civ Mat 000026 - 01Yasir Nisar SyedNo ratings yet
- Heat SettingDocument15 pagesHeat SettingnikitaNo ratings yet
- Calcipotriol+Betamethasone OintmentDocument50 pagesCalcipotriol+Betamethasone OintmentJai MurugeshNo ratings yet
- Your Gate Way To Life Science CareerDocument273 pagesYour Gate Way To Life Science Careerpatialokkumar100% (2)
- Martin Catalog PDFDocument936 pagesMartin Catalog PDFFernando MedinaNo ratings yet
- Interbond 808: Epoxy AnticorrosiveDocument4 pagesInterbond 808: Epoxy AnticorrosivedcsamaraweeraNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds and Carbohydrates I.Data and Results Compound Homogeneity ObservationsDocument11 pagesCarbonyl Compounds and Carbohydrates I.Data and Results Compound Homogeneity ObservationsKateNo ratings yet
- DLP COokery 11Document15 pagesDLP COokery 11Jeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- Link Box-1Document3 pagesLink Box-1Akram MohamedNo ratings yet