Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Finding Asymptotes of A Graph of A Rational Function
Uploaded by
Yahya AliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Finding Asymptotes of A Graph of A Rational Function
Uploaded by
Yahya AliCopyright:
Available Formats
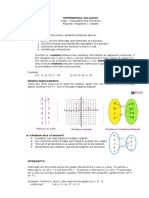
Finding asymptotes of a graph of a rational function.
An asymptote is a line that the graph of a function approaches but never touches it. There are three
types of asymptotes:
Vertical asymptotes
Horizontal asymptotes
Slant asymptotes
1. Vertical asymptotes:
To find the vertical asymptote or asymptotes of a rational function, one sets the denominator of the
rational function equal to 0 and then solves for x. the value got as x is the vertical asymptote. E.g.
Line x=5 or x=-5
2. Horizontal asymptotes:
There are different ways in finding the horizontal asymptote, this change depending on how the
degrees of the polynomials in the numerator and denominator of the function compare.
If both polynomials are the same degree, divide the coefficients of the highest degree terms.
The answer you get is the horizontal asymptote e.g. y=8 or y=-10.
If the polynomial in the numerator is a lower degree than the denominator, the x-axis (y = 0)
is the horizontal asymptote.
3. Slant asymptotes
A slant asymptote occurs when the polynomial in the numerator is of a higher degree than the
polynomial in the denominator.
To find the slant asymptote you must first divide the numerator by the denominator using either
long division or synthetic division. Then the remainder gives you the equation of the asymptote. E.g.
y=1.5x+1 (in the form of y=mx=c).
You might also like
- Lesson 3Document8 pagesLesson 3John More ClapanoNo ratings yet
- AsymptotesDocument4 pagesAsymptotesJamal MesidorNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument2 pagesDocumentAanish Raj SinhaNo ratings yet
- Intercepts, Zeroes, and AsymptotesDocument12 pagesIntercepts, Zeroes, and AsymptotesMoses Zackary TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Asymptotes Tutorial: Horizontal Vertical Slant and HolesDocument30 pagesAsymptotes Tutorial: Horizontal Vertical Slant and Holesgregory_k_sherman100% (1)
- Asymptote - WikipediaDocument50 pagesAsymptote - WikipediaAjay MahatoNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Gen MathDocument22 pagesWeek 3 Gen MathMa Joy E BarradasNo ratings yet
- Vertical Asymptotes: A Rational Function Has The FormDocument5 pagesVertical Asymptotes: A Rational Function Has The FormRaghav KumarNo ratings yet
- AsymptotesDocument17 pagesAsymptotesAsif AliNo ratings yet
- Concept 3: Review: Polynomial and Rational Function FittingDocument2 pagesConcept 3: Review: Polynomial and Rational Function Fittingvincentliu11No ratings yet
- Asymptotes, Holes, and Graphing Rational FunctionsDocument4 pagesAsymptotes, Holes, and Graphing Rational Functions1DerfulHarrehNo ratings yet
- Itech Audio PortfolioDocument1 pageItech Audio Portfolioapi-688172917No ratings yet
- GM The Domain, Range, Intercepts, ZeroesDocument35 pagesGM The Domain, Range, Intercepts, ZeroesKaizel BritosNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra IDocument43 pagesLinear Algebra IDaniel GreenNo ratings yet
- 2006 Mathematics Extension 1 NotesDocument15 pages2006 Mathematics Extension 1 NotesShahrazad8No ratings yet
- Rational FuncionDocument14 pagesRational FuncionRicardo ToledoNo ratings yet
- 14 - Rational Function - MC - Guide and LabDocument13 pages14 - Rational Function - MC - Guide and LabElsa BrounsNo ratings yet
- Rational FunctionsDocument12 pagesRational FunctionsVy TranNo ratings yet
- Graphing Rational FunctionsDocument7 pagesGraphing Rational FunctionsSam PiehlNo ratings yet
- Definition of Arithmetic Sequences and SeriesDocument18 pagesDefinition of Arithmetic Sequences and Seriesroyce59No ratings yet
- 2.6 Rational Functions Asymptotes TutorialDocument30 pages2.6 Rational Functions Asymptotes TutorialAljun Aldava BadeNo ratings yet
- Rational FunctionsDocument8 pagesRational FunctionsTannaoNo ratings yet
- Intercepts, Zeroes, and Asymptotes of Rational FunctionsDocument33 pagesIntercepts, Zeroes, and Asymptotes of Rational Functionsaiza100% (2)
- Definition of Horizontal AsymptoteDocument3 pagesDefinition of Horizontal AsymptoteSarahNo ratings yet
- Rational FunctionDocument18 pagesRational FunctionDarrel SusayaNo ratings yet
- Finding Horizontal AsymptoteDocument5 pagesFinding Horizontal Asymptoteapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Q1 W4 Part 2Document3 pagesQ1 W4 Part 2Joel HinayNo ratings yet
- Vertical AsymptoteDocument6 pagesVertical AsymptoteSarahNo ratings yet
- Maths For Econ - Econ 1003 NotesDocument18 pagesMaths For Econ - Econ 1003 NotesamandaNo ratings yet
- PC Functions RationalDocument11 pagesPC Functions RationalHector R.No ratings yet
- Horizontal and Slant AsymptotesDocument4 pagesHorizontal and Slant AsymptotesAnonymous NL4u0dtVbcNo ratings yet
- Genmath Week 2Document18 pagesGenmath Week 2Rhoda May Bermejo TrompetaNo ratings yet
- MidtermreviewprojectpptxDocument37 pagesMidtermreviewprojectpptxapi-553954607No ratings yet
- Math ReviewerDocument5 pagesMath Reviewerdanniellekaye14No ratings yet
- A Rith Me Tic: Adj. Ar Ith Met Ic (Ăr ĬthDocument4 pagesA Rith Me Tic: Adj. Ar Ith Met Ic (Ăr ĬthRahf AhmadNo ratings yet
- Finding AsymptotesDocument4 pagesFinding Asymptotesapi-140032165No ratings yet
- Asymptote SDocument4 pagesAsymptote Sbkjr2008No ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Graphing Rational FunctionsDocument40 pagesLesson 8 Graphing Rational FunctionsCarbon CopyNo ratings yet
- Common CurvesDocument9 pagesCommon CurvesTagore uNo ratings yet
- Try To Graph and Name The Following EquationsDocument46 pagesTry To Graph and Name The Following EquationsStephanie DecidaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer BSEE (Calculus)Document13 pagesReviewer BSEE (Calculus)Ronalyn ManzanoNo ratings yet
- James Math 10Document22 pagesJames Math 10Ijhalyne ValinNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionDocument2 pagesQuadratic FunctionLeeanna ElhizNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics - Q1 Week 3Document8 pagesGeneral Mathematics - Q1 Week 3Johnson BautistaNo ratings yet
- Eigenvalue Problems: Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsDocument11 pagesEigenvalue Problems: Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsWilly KwokNo ratings yet
- Equatons of Straight LineDocument7 pagesEquatons of Straight LineBilly CheungNo ratings yet
- Steps On Finding Zeroes of Rational Functions and Graphing Rational FunctionsDocument29 pagesSteps On Finding Zeroes of Rational Functions and Graphing Rational FunctionsJeric ColumbinoNo ratings yet
- Inequalities and Functions 2 - AdanteDocument11 pagesInequalities and Functions 2 - AdanteKarenNo ratings yet
- Cu 3Document39 pagesCu 3omgitsjediNo ratings yet
- Rational Functions: Rational Functions Are Quotients of Polynomial Functions. This Means ThatDocument16 pagesRational Functions: Rational Functions Are Quotients of Polynomial Functions. This Means ThatSalih AnwarNo ratings yet
- Gen. Math 11 Lesson 4Document24 pagesGen. Math 11 Lesson 4Maricon SorongonNo ratings yet
- Algebra Reference: Basic IdentitiesDocument18 pagesAlgebra Reference: Basic IdentitiesgowsikhNo ratings yet
- Eigen Values & Eigen VectorsDocument6 pagesEigen Values & Eigen Vectorsmadhuri thakkarNo ratings yet
- Anglo ReviewerDocument25 pagesAnglo ReviewerIbraham John JimenezNo ratings yet
- Square Root PropertiesDocument4 pagesSquare Root Propertiescircleteam123No ratings yet
- 16 Martie - Asimptote - Teorie + QuizDocument5 pages16 Martie - Asimptote - Teorie + Quizdm.jebeleanNo ratings yet
- Graphs of FunctionsDocument4 pagesGraphs of Functionsapi-174648067No ratings yet
- Graphing Rational FunctionsDocument25 pagesGraphing Rational FunctionsDondon Tayaban100% (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)