Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Valency PDF
Valency PDF
Uploaded by
Leanne BonniciOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Valency PDF
Valency PDF
Uploaded by
Leanne BonniciCopyright:
Available Formats
Ms. L.
Bonnici Form 3 Chemistry
Valency
In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valence number, is a measure
of the number of bonds formed by an atom of a given element. "Valence" can
be defined as the number of valence bonds a given atom has formed, or can
form, with one or more other atoms. For most elements the number of bonds
can vary. The IUPAC definition limits valence to the maximum number of
univalent atoms that may combine with the atom, that is the maximum
number of valence bonds that is possible for the given element.
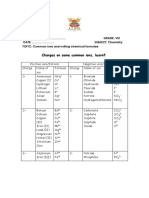
1 2 3 4
Metals Li (Lithium) Pb (Lead) Al (Aluminium) Si (Silicon)
Na (Sodium) Cu (Copper) Fe (Iron) Pb (Lead)
K (Potassium) Zn (Zinc)
Ag (Silver) Fe (Iron)
Cu (Copper) Mg (Magnesium)
Ca (Calcium)
Ba (Barium)
Non- F (Flourine) O (Oxygen) N (Nitrogen) C (Carbon)
metals Cl (Chlorine) S (Sulfur) B (Boron)
Br (Bromine)
I (Iodine)
H (Hydrogen)
-
Polyatomic OH (Hydroxide) CO32- (Carbonate) PO43-
ions (Phosphate)
–
SO42- (Sulfate)
(radicals) NO3 - (Nitrate)
NO2 (Nitrite) SO32-(Sulfite)
NH4+ (Ammonium) S2-(Sulfide)
HCO3- (Hydrogen
Carbonate)
HSO4- (Hydrogen Sulfate)
Last revised 06/08/2017
You might also like
- 1.1 Chemical FormulaeDocument14 pages1.1 Chemical FormulaeShyamal DlrNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Ions and Compounds: Bente Dos KadigmaDocument13 pagesLesson 3: Ions and Compounds: Bente Dos KadigmaAljon CatibanNo ratings yet
- Class-7 Dlalal Simplified Elements Compound and Mixtures ICSE Chemistry SolutionsDocument15 pagesClass-7 Dlalal Simplified Elements Compound and Mixtures ICSE Chemistry SolutionssrobeNo ratings yet
- ApsummerDocument5 pagesApsummerLayleeNo ratings yet
- Summer Assignment For AP Chemistry Class 2020-2021Document5 pagesSummer Assignment For AP Chemistry Class 2020-2021shelly zhangNo ratings yet
- 5.9 Polyatomic CompoundsDocument3 pages5.9 Polyatomic Compoundsmichael.delaney8541No ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and Chemical EquationsDocument11 pagesElements, Compounds and Chemical EquationsKasman Kasonde MumbaNo ratings yet
- Valency TableDocument2 pagesValency TableZarbEChishtiNo ratings yet
- Formulas & Nomenclature PDFDocument6 pagesFormulas & Nomenclature PDFYatish PantNo ratings yet
- Formulas & Nomenclature PDFDocument6 pagesFormulas & Nomenclature PDFRaven FranciscoNo ratings yet
- 10 CBSE ChemistryDocument67 pages10 CBSE ChemistryAlifiyah HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Atoms and MoleculesDocument15 pagesChapter - 3: Atoms and Moleculesuma mishra0% (1)
- Symbols and Names For Common Polyatomic IonsDocument1 pageSymbols and Names For Common Polyatomic IonsElixirNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument11 pagesChemical BondingXenia Mae FloresNo ratings yet
- CH Naming 命名學 可預習Document35 pagesCH Naming 命名學 可預習TsaiBenyanNo ratings yet
- Naming Compounds, Cations and AnionsDocument12 pagesNaming Compounds, Cations and AnionsJae DeNo ratings yet
- Polyatomic Ions, Monatomic Ions and Elements (Honors Chemistry Nomenclature/Bonding Unit)Document3 pagesPolyatomic Ions, Monatomic Ions and Elements (Honors Chemistry Nomenclature/Bonding Unit)JaharaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Nomenclature: Experiment #3Document27 pagesChemical Nomenclature: Experiment #3Ayi PunsalanNo ratings yet
- Etymology: Electrostatic Potential Nitrate Ion N ODocument7 pagesEtymology: Electrostatic Potential Nitrate Ion N ORigioGerryNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes PT 3 4Document53 pagesChemistry Notes PT 3 4Eunice Kyla MapisaNo ratings yet
- Naming CompoundsDocument3 pagesNaming Compoundswhgdrm75kmNo ratings yet
- مراجعة ساينس بالاجابات للصف الاول الاعدادي الترم الثاني 2023 مستر شريف هواريDocument33 pagesمراجعة ساينس بالاجابات للصف الاول الاعدادي الترم الثاني 2023 مستر شريف هواريhuricanes1777No ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Elements and Polyatomic IonsDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table of Elements and Polyatomic IonsRegie G. GalangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Stoichiometry - StudentDocument105 pagesChapter 1 Stoichiometry - StudentNur AlisaNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Formulas 2 1Document6 pagesSymbols and Formulas 2 1jessie katoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 StoichiometryDocument111 pagesChapter 2 StoichiometryNORMASLAILA JAAFARNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formula, Naming & Writing Compound: General Chemistry 1Document30 pagesChemical Formula, Naming & Writing Compound: General Chemistry 1Synne Mae BorneaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Atoms and MoleculesDocument15 pagesChapter - 3: Atoms and MoleculesJanahvi PawarNo ratings yet
- Language of ChemistryDocument12 pagesLanguage of ChemistryVenkatNo ratings yet
- GenChem Nomenclature Updated PDFDocument2 pagesGenChem Nomenclature Updated PDFCamille AquinoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 10 Lecture 1 (3 April)Document5 pagesChemistry Class 10 Lecture 1 (3 April)allroundersaksham304No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Atoms and MoleculesDocument34 pagesChapter 3 Atoms and MoleculesManushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Ion Reference Updated 19-20Document2 pagesIon Reference Updated 19-20waxove1775No ratings yet
- Ions and Their Common NamesDocument1 pageIons and Their Common NamesAnaya ChNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 NamingDocument108 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 NamingJolo Allexice R. PinedaNo ratings yet
- CH 3 PPT - Part 1 To PostDocument45 pagesCH 3 PPT - Part 1 To PostGrace FernandesNo ratings yet
- GCI Topics PDFDocument4 pagesGCI Topics PDFMuhammad QaisarNo ratings yet
- Ion ReferenceDocument2 pagesIon Referenceapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Element and CompoundsDocument14 pagesElement and CompoundsKehekeshan RizwanNo ratings yet
- Elements For Grade 8 2022Document15 pagesElements For Grade 8 2022ahmed amrNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Charges-Monoatomic IonsDocument20 pagesSymbols and Charges-Monoatomic Ionsjon_kasilagNo ratings yet
- AP Summer AssignmentDocument14 pagesAP Summer AssignmentNaleen EshuchiNo ratings yet
- 10 Naming and Writing Chemical CompoundsDocument42 pages10 Naming and Writing Chemical CompoundsRheden AedriannNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 EquationsDocument11 pagesLecture 1 Equationsmerabamoding11No ratings yet
- 01 Hints ChemicalNomenclatureDocument7 pages01 Hints ChemicalNomenclatureSmartsoft LibraryNo ratings yet
- Naming ReviewDocument1 pageNaming Reviewlee_magsinoNo ratings yet
- Chemical NomenclatureDocument7 pagesChemical NomenclatureKeith Lavin100% (1)
- Symbols and Charges For Monoatomic IonsDocument2 pagesSymbols and Charges For Monoatomic IonsaNo ratings yet
- Chemical NomenclatureDocument23 pagesChemical NomenclatureDương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Ms. Hanani Yazid: Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARA Perlis Branch Arau, Perlis, MalaysiaDocument74 pagesMs. Hanani Yazid: Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARA Perlis Branch Arau, Perlis, MalaysiaMuhammad Asyraaf Haqimi bin BaharinNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument2 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionsAmf Talino AhNo ratings yet
- Valency and Formulae-HandoutDocument3 pagesValency and Formulae-HandoutABHAVYA RAJNo ratings yet
- CATIONS AND ANIONS Chemistry EDITEDDocument4 pagesCATIONS AND ANIONS Chemistry EDITEDDenize Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Presentation-Matter and Its Transformation-Stage 4Document24 pagesPresentation-Matter and Its Transformation-Stage 4alanmauriciohdzNo ratings yet
- Examples of Chemical Names of CompoundsDocument2 pagesExamples of Chemical Names of CompoundsAileen A. MonaresNo ratings yet
- Common Cations, Anions, Acids, Salts.Document2 pagesCommon Cations, Anions, Acids, Salts.Jas MeeraNo ratings yet
- Naming Chemical CompoundsDocument3 pagesNaming Chemical Compoundszubair195No ratings yet
- Formula and Equations - NotesDocument5 pagesFormula and Equations - Notesshrikant19829No ratings yet
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet