0% found this document useful (0 votes)
490 views9 pagesSingle Phase AC Voltage Controller With RL Load
This document describes a single phase AC voltage controller with an RL load. It discusses:
1) How AC voltage controllers use thyristors like SCRs or triacs to variably control output voltage without changing frequency through phase or on/off control.
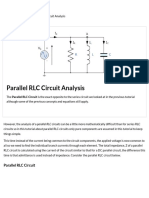
2) The circuit diagram and working, where thyristors T1 and T2 are fired at angles α and 180+α to build current through the load from 0 to 180 degrees and 180 to 360 degrees respectively.
3) A numerical example calculates the firing angle range, maximum RMS load value, maximum power and power factor, and maximum average and RMS thyristor currents for a 230V 50Hz source supplying a 3Ω resistor
Uploaded by
Sunny ModiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
490 views9 pagesSingle Phase AC Voltage Controller With RL Load
This document describes a single phase AC voltage controller with an RL load. It discusses:
1) How AC voltage controllers use thyristors like SCRs or triacs to variably control output voltage without changing frequency through phase or on/off control.
2) The circuit diagram and working, where thyristors T1 and T2 are fired at angles α and 180+α to build current through the load from 0 to 180 degrees and 180 to 360 degrees respectively.
3) A numerical example calculates the firing angle range, maximum RMS load value, maximum power and power factor, and maximum average and RMS thyristor currents for a 230V 50Hz source supplying a 3Ω resistor
Uploaded by
Sunny ModiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd