Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Uploaded by
Chaudary Hassan AliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Uploaded by
Chaudary Hassan AliCopyright:
Available Formats
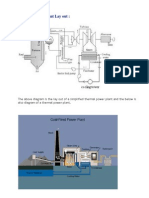
SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER
A Shell and tube heat exchanger is a class of heat exchanger. It is the most common type of heat
exchanger in oil refineries and other large chemical processes. As its name implies, this type of
heat exchanger consists of a shell (a large vessel) with a bundle of tubes inside it.
Theory and application
Two fluids, of different starting temperatures, flow through the heat exchanger. One flows
through the tubes (the tube side) and the other flows outside the tubes but inside the shell (the
shell side). Heat is transferred from one fluid to the other through the tube walls, either from tube
side to shell side or vice versa. The fluids can be either liquids or gases on either the shell or the
tube side. In order to transfer heat efficiently, a largeheat transfer area should be used, so there
are many tubes. In this way, waste heat can be put to use. This is a great way to conserve energy.
Heat exchangers with only one phase (liquid or gas) on each side can be called one-phase or
single-phase heat exchangers. Two-phase heat exchangers can be used to heat a liquid to boil it
into a gas (vapor), sometimes called boilers, or cool a vapor to condense it into a liquid (called
condensers), with the phase change usually occurring on the shell side. Boilers in steam engine
locomotives are typically large, usually cylindrically-shaped shell-and-tube heat exchangers. In
large power plants with steam-driven turbines, shell-and-tube (see Condenser (steam turbine) )
condensers are used to condense the exhaust steam exiting the turbine into condensate water
which can be recycled back to be turned into steam, possibly into a shell-and-tube type boiler.
Shell and tube heat exchanger design
There can be many variations on the shell and tube design. Typically, the ends of each tube are
connected toplenums (sometimes called water boxes) through holes in tubesheets. The tubes may
be straight or bent in the shape of a U, called U-tubes.
In nuclear power plants with pressurized water reactors, large heat exchangers called steam
generators are two-phase, shell-and-tube heat exchangers which typically have U-tubes. They are
used to boil water recycled from a steam turbine condenser into steam to drive the turbine to
produce power. Most shell-and-tube heat exchangers are either 1, 2, or 4 pass designs on the tube
side. This refers to the number of times the fluid in the tubes passes through the fluid in the shell.
In a single pass heat exchanger, the fluid goes in one end of each tube and out the other.
You might also like
- Designn of Heat ExchangerDocument53 pagesDesignn of Heat ExchangerBalu BalireddiNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger.Document10 pagesHeat Exchanger.RajarajeswariNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Project Report: Heat ExchangerDocument10 pagesEngineering Drawing Project Report: Heat ExchangerDhanis ParamaguruNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Lecture NotesDocument19 pagesHeat Exchanger Lecture NotesM J Rhoades88% (8)
- Csa N285 - 2-99 PDFDocument33 pagesCsa N285 - 2-99 PDFMiguel BazalduaNo ratings yet
- 1-Classification of Heat Exchangers & Selection CriteriaDocument56 pages1-Classification of Heat Exchangers & Selection CriteriaShahid_Rao786100% (1)
- Heat and Heat ExchangerDocument20 pagesHeat and Heat ExchangerDamisha DamishaNo ratings yet
- EHV AC Transmission - UnlockedDocument522 pagesEHV AC Transmission - UnlockedSakhidad mohammadiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 8 Heat ExchangerDocument26 pagesExperiment No. 8 Heat ExchangerAli Requiso Mahmud100% (1)
- Double Pipe Heat ExchangersDocument36 pagesDouble Pipe Heat Exchangersshreyasnil50% (2)
- Asme Stress Linearization and Classification - A Discussion Based On A Case StudyDocument12 pagesAsme Stress Linearization and Classification - A Discussion Based On A Case Studysagar1503No ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument17 pagesHeat ExchangerMedariTrinadh100% (2)
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger: Research TitleDocument10 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchanger: Research TitleDimas SatriaNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers V1 16-10-2019Document72 pagesHeat Exchangers V1 16-10-2019Bal krishna srivastava100% (1)
- Heat Exchanger Important DocumentDocument126 pagesHeat Exchanger Important DocumentUsamaAli100% (1)
- Heat ExchangerDocument58 pagesHeat ExchangercanyourunNo ratings yet
- Design and Experimental Analysis of Spiral Tube Heat ExchangerDocument6 pagesDesign and Experimental Analysis of Spiral Tube Heat ExchangergpcshfNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Shell N TubeDocument21 pagesLab Report Shell N Tuberidzuwan rahimi100% (6)
- Mechanical Design of Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument69 pagesMechanical Design of Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerFazil HassanNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument4 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchangerru4angelNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger: Wall ThicknessDocument10 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchanger: Wall ThicknessZeke KazamiNo ratings yet
- Perancangan Proses: Heat ExchangerDocument42 pagesPerancangan Proses: Heat ExchangerIiZz SangPemimpi SpNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument10 pagesHeat Exchangerizadbakhsh2010No ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger - WikipediaDocument5 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchanger - Wikipediabinok19No ratings yet
- Parallel - Counter Flow Heat ExchangerDocument12 pagesParallel - Counter Flow Heat Exchangerjr gajelesNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument30 pagesShell and Tube Heat ExchangerMurphy MofeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering: Govt - Polytechnic Mankenda (Agra)Document47 pagesChemical Engineering: Govt - Polytechnic Mankenda (Agra)Shekhar YaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument24 pagesProjectSantosh Kumar HottaNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangersDocument8 pagesHeat Exchangerskats2404No ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument5 pagesHeat ExchangerMurtaza NaeemNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger TypesDocument7 pagesHeat Exchanger TypesMarwan ShamsNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument11 pagesHeat ExchangerHuda ShahNo ratings yet
- Types of Heat Exchangers - Classification of Heat ExchangersDocument3 pagesTypes of Heat Exchangers - Classification of Heat ExchangersMuhammet Ahmet SarıkayaNo ratings yet
- Test of A Tubular CondenserDocument9 pagesTest of A Tubular CondenserDevin Bea0% (1)
- Heat ExchangersDocument3 pagesHeat Exchangersdanena88No ratings yet
- Classification & Types of BoilerDocument13 pagesClassification & Types of BoilerGnana Subramanian Arumugam100% (1)
- Heat Transfer Coefficient U That Accounts For The Contribution of All These Effects On Heat TransferDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer Coefficient U That Accounts For The Contribution of All These Effects On Heat TransferIvon MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger IntroductionDocument8 pagesHeat Exchanger Introductionalan_yaobin8409No ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Layout and OperationDocument8 pagesThermal Power Plant Layout and OperationRAJENDRA TELVEKARNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, ShibpurDocument15 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, ShibpurSuraj Kumar0% (1)
- Heat Exchangers Simple OverviewDocument20 pagesHeat Exchangers Simple OverviewAdhrith JhaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument6 pagesProjectShuvam RayNo ratings yet
- What Are The Types of Heat ExchangersDocument9 pagesWhat Are The Types of Heat Exchangersjr gajelesNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Lay OutDocument8 pagesThermal Power Plant Lay OutSaheli ChoudhuriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Heat ExchangerDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Heat ExchangernsfvhsfNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers: VMA Global CollegeDocument16 pagesHeat Exchangers: VMA Global CollegeButch VirayNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer & ExchangersDocument19 pagesHeat Transfer & ExchangersSanadNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument29 pagesHeat Exchangerrodel rentaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Diagram of A Plate and Frame Heat Exchanger02Document9 pagesConceptual Diagram of A Plate and Frame Heat Exchanger02sai thesisNo ratings yet
- 5 5-HeatexchangerDocument10 pages5 5-HeatexchangerMohamed Rafeek GhaniNo ratings yet
- CITATION Gar091 /L 1033Document4 pagesCITATION Gar091 /L 1033Salina ShaffieNo ratings yet
- Types of Heat Exchangers Shell and Tube, Plate TypeDocument4 pagesTypes of Heat Exchangers Shell and Tube, Plate TypeMohammedBujairNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument9 pagesHeat ExchangerChrissa Villaflores GanitNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument7 pagesHeat ExchangerLloyd Abadilla100% (1)
- Cement Agriculture Soil Steaming: Liquid GasDocument5 pagesCement Agriculture Soil Steaming: Liquid GasKim Mervin Llamado NisayNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument14 pagesHeat ExchangerM Y78uNo ratings yet
- Case Study Power Plant 2Document11 pagesCase Study Power Plant 2qasdinabatrisyia28No ratings yet
- Regenerative Heat ExchangerDocument4 pagesRegenerative Heat ExchangerSalehAfadlehNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Research Background: Heat Exchanger FCB40302Document68 pages1.1 Research Background: Heat Exchanger FCB40302ImranMustaffaNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument1 pageShell and Tube Heat ExchangerSagar PatilNo ratings yet
- of HXEDocument31 pagesof HXEetayhailuNo ratings yet
- Introduction Heat ExchangerDocument11 pagesIntroduction Heat ExchangerLorna AhlaamiNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- GE6251-Basic Civil and Mechanical EngineeringDocument10 pagesGE6251-Basic Civil and Mechanical EngineeringpceautohodNo ratings yet
- Final FYP ProposalDocument8 pagesFinal FYP ProposalWaseem AhmadNo ratings yet
- European Energy Markets Observatory-18th Edition-Full ReportDocument108 pagesEuropean Energy Markets Observatory-18th Edition-Full ReportpatpereiradasilvaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Power SectorDocument19 pagesPresentation On Power Sectorsonamsingla30No ratings yet
- Folio Fizik RadioactivityDocument16 pagesFolio Fizik RadioactivityMohammad AmirulNo ratings yet
- Ayub and YahyaDocument11 pagesAyub and YahyaRida FatimaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics Jan 2012 P2Document16 pagesCSEC Physics Jan 2012 P2Clendon Donai0% (1)
- The Russian Invasion of Ukraine 2Document5 pagesThe Russian Invasion of Ukraine 2908fa23b5bNo ratings yet
- Relays and TimersDocument133 pagesRelays and Timerskarstegg100% (1)
- Reactor siZIngDocument4 pagesReactor siZIngdannie3No ratings yet
- SkyFence Brochure 2018121c PDFDocument12 pagesSkyFence Brochure 2018121c PDFAnkitNo ratings yet
- Economics of Power Generation Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Preparation For Competition Exams PDF - Preparation For Engineering PDFDocument14 pagesEconomics of Power Generation Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Preparation For Competition Exams PDF - Preparation For Engineering PDFER Mukesh ThakurNo ratings yet
- List of Largest Power Stations in The United StatesDocument14 pagesList of Largest Power Stations in The United Statesoem chhunNo ratings yet
- Physic ThermalDocument4 pagesPhysic ThermalVi Tran YenNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report at Atomic Power Station, RawatbhataDocument40 pagesSummer Training Report at Atomic Power Station, RawatbhataKrishan Pal Sila100% (2)
- English For Mechanical Engineering. Student's BookDocument103 pagesEnglish For Mechanical Engineering. Student's BookVlad BortaNo ratings yet
- Bryan Erler - ASMEDocument35 pagesBryan Erler - ASMErodrigoperezsimoneNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2: CHAPTER 2. Basic Concepts of Water Francis TurbineDocument20 pagesChapter - 2: CHAPTER 2. Basic Concepts of Water Francis TurbineAdarsh Kumar ManwalNo ratings yet
- Nuclear (Atomic) Power Plant: Mr.B.RameshDocument31 pagesNuclear (Atomic) Power Plant: Mr.B.RameshDr. B. Ramesh0% (1)
- GALL ReportDocument867 pagesGALL ReportYanka IlarionovaNo ratings yet
- Final Draft PDocument41 pagesFinal Draft Pvrushabh shelkarNo ratings yet
- Modern Power Station Practice: ObjectiveDocument19 pagesModern Power Station Practice: ObjectiveWawan darmawanNo ratings yet
- Why Is Nuclear Power A Necessary EvilDocument6 pagesWhy Is Nuclear Power A Necessary Evilddkl678100% (1)
- Yaskawa Manuals 275Document31 pagesYaskawa Manuals 275speedtunningNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Sodium Cooled Fast Breeder ReactorsDocument31 pages1.1 Sodium Cooled Fast Breeder ReactorspviveknaiduNo ratings yet