Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Def of Timber Roofs: Wall Plate
Def of Timber Roofs: Wall Plate
Uploaded by
KrutiGDesaiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Def of Timber Roofs: Wall Plate
Def of Timber Roofs: Wall Plate
Uploaded by
KrutiGDesaiCopyright:
Available Formats
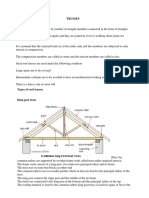
Def of timber roofs:
Wall plate:
Usually 100 x 50 mm softwood timbers are fixed to the top of load bearing walls to distribute
loads and provide fixings for roof timbers.
Ceiling joist:
These are timbers which provide a support for fixing ceiling finishes and act as a collar to
prevent rafters spreading.
Common rafters:
These are inclined timbers fixed between wall plate and ridge which transmit live and dead
loads to wall plate.
Ridge:
The ridge is a horizontal board set on edge to which the rafters are attached (not required on
trussed rafters).
Hip Rafter:
A hip rafter is a rafter running from the wall plate to the ridge which forms the external angle of
the sloping side of a roof.
Purlin:
This is a horizontal roof member supporting the rafters and usually at right angles to these. This
enables small section timbers to be used for the rafters.
Hangers :
These are timbers hanging from the purlins to the mceiling joist to give additional support to
binders.
Fascia :
A board fixed vertically to rafter ends, which provide an additional fixing for gutters.
Soffit:
A horizontal board fixed to the underside of rafter outside the building.
Bargeboard:
Verge or gable board.
Eaves:
The lower part of the roof, which usually includes the end of
the rafter, ceiling joist, soffit, fascia and gutter.
Dormer:
A vertical window coming through a sloping roof.
Valley:
This is the name for the intersection between two sloping surfaces, forming an internal angle (
the opposite to a hip).
You might also like
- Roof and Roof CoveringDocument101 pagesRoof and Roof CoveringMahipal Singh Rao78% (9)
- Carpentry TheoryDocument8 pagesCarpentry Theoryapi-272982037No ratings yet
- Framing With RoofsDocument5 pagesFraming With Roofsgreenelephant150No ratings yet
- Gujarat University: Bachelor of Architecture Outline For All Semesters (Batch 2015 Onwards)Document12 pagesGujarat University: Bachelor of Architecture Outline For All Semesters (Batch 2015 Onwards)KrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- Terms Used in RoofDocument2 pagesTerms Used in Roofrahul_5587_265238786No ratings yet
- Glossary of Roof Construction TerminologyDocument3 pagesGlossary of Roof Construction TerminologySwapnil JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Log Building TermsDocument5 pagesGlossary of Log Building TermsGoalkeeping- peyman pourmohammadiNo ratings yet
- Roofing Terminology: S&K Roofing, Siding and Windows Aims To Be Your Roofing Resource in MD & VADocument2 pagesRoofing Terminology: S&K Roofing, Siding and Windows Aims To Be Your Roofing Resource in MD & VAOnuoha ChiemezieNo ratings yet
- Aint Ichael'S Ollege of Aguna: Learning Packet No. 40 PARTS OF A FRAMED HOUSE Performance StandardsDocument6 pagesAint Ichael'S Ollege of Aguna: Learning Packet No. 40 PARTS OF A FRAMED HOUSE Performance StandardsGlenn Fortades SalandananNo ratings yet
- House Framing & StructureDocument4 pagesHouse Framing & StructureTotulRedus Ro100% (1)
- Lecture 7Document40 pagesLecture 7Ekala Xuhalx100% (2)
- Lesson 3 - FrameworksOfABuildingDocument17 pagesLesson 3 - FrameworksOfABuildingROMNICK HANDAYANNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse: Where To Place The GreenhouseDocument6 pagesGreenhouse: Where To Place The GreenhouseOlin StejNo ratings yet
- Types of RoofDocument37 pagesTypes of RoofBRAIN OF AN ARCHITECT100% (1)
- Building TechnologyDocument4 pagesBuilding TechnologyDanica LuarezNo ratings yet
- Timber Frame TermsDocument2 pagesTimber Frame TermsMark Kenneth P. OntejoNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument16 pagesAssignmentJersey Mae PerlasNo ratings yet
- Architectural TerminologyDocument25 pagesArchitectural Terminologyk kNo ratings yet
- Deck-Speak: A Glossary of Deck Construction TermsDocument2 pagesDeck-Speak: A Glossary of Deck Construction Termsloween john seloterioNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 - RoofDocument24 pagesTopic 10 - RoofNURULFARHANA DAUDNo ratings yet
- Types of RaftersDocument34 pagesTypes of RaftersJeriza AquinoNo ratings yet
- Wood Structural SystemsDocument54 pagesWood Structural SystemsRene BermudezNo ratings yet
- Carpentry TermsDocument4 pagesCarpentry TermsSameh SamehNo ratings yet
- Acc Spring 2012Document4 pagesAcc Spring 2012ramona_acosta_1No ratings yet
- Wooden TrussesDocument24 pagesWooden TrussesKanak YadavNo ratings yet
- The Basic Components of A Roof TrussDocument3 pagesThe Basic Components of A Roof TrussDaphne Ann Athena DacibarNo ratings yet
- Truss ManualDocument10 pagesTruss ManualRiyaz SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Post & Beam Glulam Hand HewnDocument2 pagesPost & Beam Glulam Hand HewnMark Kenneth P. OntejoNo ratings yet
- Rar 803: Architectural Structures Module-1 Analysis and Design of Roof Trusses (Steel) PART-1Document6 pagesRar 803: Architectural Structures Module-1 Analysis and Design of Roof Trusses (Steel) PART-1AshutoshNo ratings yet
- Type of RoofsDocument13 pagesType of Roofsparth massandNo ratings yet
- Elements. in Prefabricated StructuresDocument35 pagesElements. in Prefabricated StructuresJoyson Silva PNo ratings yet
- Variations On Wood Light Frame ConstructionDocument10 pagesVariations On Wood Light Frame ConstructionPenuel G. BantogNo ratings yet
- Classification of Beams AccordingDocument6 pagesClassification of Beams AccordingTarique AhmedNo ratings yet
- Wood ConstructionDocument28 pagesWood ConstructionEzra GarciaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ct111Document6 pagesReviewer ct111HahahahaendndmdNo ratings yet
- REPORTINGDocument14 pagesREPORTINGxishiyanNo ratings yet
- Roofs: Module-3Document29 pagesRoofs: Module-3Alex100% (1)
- Timber Floors-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesTimber Floors-WPS OfficeMusa MichaelNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument9 pagesPresentationSohanNo ratings yet
- RoofsDocument18 pagesRoofsshingkeongNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1Element of BuildingDocument381 pagesUNIT-1Element of BuildingdevpratapNo ratings yet
- Wood ColumnDocument21 pagesWood ColumnJels G STNo ratings yet
- Trusses DetailsDocument10 pagesTrusses DetailsShubhan RathourNo ratings yet
- The Basic Components of A Roof TrussDocument2 pagesThe Basic Components of A Roof TrussMridupaban DuttaNo ratings yet
- Stairs PDFDocument8 pagesStairs PDFVIGNESH ANo ratings yet
- Flat Slab1Document21 pagesFlat Slab1BGSSAP 2017No ratings yet
- CarpentryDocument44 pagesCarpentryMelwin MakalintalNo ratings yet
- Architecture TermsDocument3 pagesArchitecture TermsJoy RedolosaNo ratings yet
- VocabularyDocument1 pageVocabularyBashir HaiderNo ratings yet
- RoofsDocument45 pagesRoofsWhiskey /No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Wood Properties, Species and GradesDocument13 pagesChapter 1: Wood Properties, Species and Gradesiris coleenNo ratings yet
- Bldg. Tech WoodDocument1 pageBldg. Tech WoodFatima Shar-ina Alih AradaisNo ratings yet
- Roof Truss Buying GuideDocument4 pagesRoof Truss Buying GuidejayarNo ratings yet
- Flat Slab: Advanced RCC RoofsDocument21 pagesFlat Slab: Advanced RCC RoofsIMRAN KHANNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - 1 Week Oct 17 - 22Document43 pagesLecture 3 - 1 Week Oct 17 - 22Luis GalvezNo ratings yet
- Trusses PDFDocument2 pagesTrusses PDFRahul TomarNo ratings yet
- BC DoorsDocument11 pagesBC DoorsYachika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lamps and Lampshade Making - Including the Pedestal Table Lamp, Pendant Ceiling Light, Bracket Wall Fixture, Portable Floor Lamp, and Fifty Lamps and ShadesFrom EverandLamps and Lampshade Making - Including the Pedestal Table Lamp, Pendant Ceiling Light, Bracket Wall Fixture, Portable Floor Lamp, and Fifty Lamps and ShadesNo ratings yet
- 1971 PopDocument146 pages1971 PopKrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- Kheda 2016-17Document85 pagesKheda 2016-17KrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- Kheda - DHDR - August 2015Document149 pagesKheda - DHDR - August 2015KrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- 2416 Part A DCHB KhedaDocument488 pages2416 Part A DCHB KhedaKrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- Dang PDFDocument27 pagesDang PDFKrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- CLASS I-100000 and Above PopulationDocument941 pagesCLASS I-100000 and Above PopulationKrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- BUILDING CONSTRUCTION McKay (V-2)Document143 pagesBUILDING CONSTRUCTION McKay (V-2)KrutiGDesai100% (1)
- A Study of Rural To Urban Migration in IndiaDocument10 pagesA Study of Rural To Urban Migration in IndiaKrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- 1971 KheDocument327 pages1971 KheKrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- IMP TABLE 1 April - 2013 - 1366122989 - 113f4 - 11Document3 pagesIMP TABLE 1 April - 2013 - 1366122989 - 113f4 - 11KrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- Internal Migration in India: Integrating Migration With Development and Urbanization PoliciesDocument5 pagesInternal Migration in India: Integrating Migration With Development and Urbanization PoliciesKrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- Bharat Dangar - Case Study On Vishwamitri RiverDocument42 pagesBharat Dangar - Case Study On Vishwamitri RiverKrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- BUILDING CONSTRUCTION McKay (V-3)Document175 pagesBUILDING CONSTRUCTION McKay (V-3)KrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- Reasons Behind Using Mud As A Building MaterialDocument11 pagesReasons Behind Using Mud As A Building MaterialKrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- BUILDING CONSTRUCTION McKay (V-1)Document172 pagesBUILDING CONSTRUCTION McKay (V-1)KrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- Brick: History of BricksDocument11 pagesBrick: History of BricksKrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- 2011 D05 00 ProvDocument126 pages2011 D05 00 ProvKrutiGDesaiNo ratings yet
- Inner City HousingDocument25 pagesInner City HousingKrutiGDesai0% (1)