Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 5: Bearing: 5.1 Definition
Uploaded by
Kesava DassOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 5: Bearing: 5.1 Definition
Uploaded by
Kesava DassCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT 5: BEARING
5.1 DEFINITION
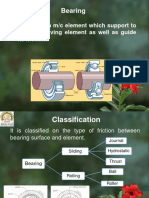
As a support/supporting parts which allows relative motion between two parts.
5.2 FUNCTIONS
There are three main functions;
a) Reduce friction
b) Carry load
c) Guide for moving parts
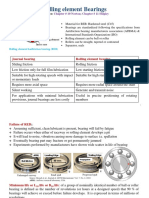
5.3 TYPES OF BEARINGS
i. Ball bearing
ii. Roller bearing
iii. Needle bearing
iv. Tapered bearing
v. Spherical bearing
vi. Thrust bearing
vii. Fluid/hydrostatic bearing
5.4 ROLLER ELEMENTS
5.5 BEARING COMPONENTS
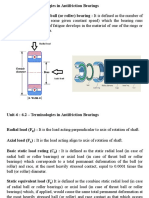
5.6 DYNAMIC LOAD CARRYING CAPACITY
Definition: radial load (radial bearing) or thrust load (thrust bearing) that can be carried for
a minimum life of one millions revolutions.
Life of bearing;
a) Individual ball bearing: the number of revolutions (or hours of service at some given
constant speed) which the bearing runs before the first evidence of fatigue crack in
ball or races.
b) Group of bearing: the number of revolutions that 90% of the bearings will
complete/exceed before the first evidence of fatigue crack
There are many terms used for this rating life;
a) Minimum life
b) Catalogue life
c) L10 life
d) B10 life
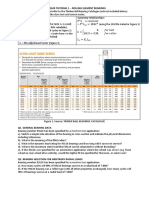
Bearing life, L10 = ( )³
Where;
L10 = rating life (in million revolutions)
C = dynamic load capacity (N)
p = 3 for ball bearings
p= for roller bearings
Bearing rating life (hours), L10 =
Where;
L10 h = Bearing rating life (hours)
n = rotational speed (rpm)
5.7 EQUIVALENT BEARING LOAD
Definition: constant radial load (radial bearing) or trust load (thrust bearing) which if applied
to the bearing would give same life as that which the bearing will attain under actual
condition of forces.
P = XVFr + YFa
Where;
P=equivalent dynamic load (N)
Fr = radial load (N)
Fa = axial load (N)
V= race rotation factor
X and Y = radial and thrust factor (given by manufacturer)
5.8 Axial, radial and combined load
Exercise (design of machine elements)
You might also like
- CoughDocument47 pagesCoughKesava Dass100% (1)
- BearingDocument18 pagesBearingBudhaditya Goswami89% (45)
- Bearing SelectionDocument6 pagesBearing SelectiondaryonoNo ratings yet
- How Unbalance Affects Bearing LifeDocument8 pagesHow Unbalance Affects Bearing Lifeagrocel_bhv5591No ratings yet
- Bearing Design PDFDocument48 pagesBearing Design PDFNon Etabas GadnatamNo ratings yet
- Slewing BearingDocument15 pagesSlewing BearingVenkatesh Kumar100% (1)
- High Speed Off-Road Vehicles: Suspensions, Tracks, Wheels and DynamicsFrom EverandHigh Speed Off-Road Vehicles: Suspensions, Tracks, Wheels and DynamicsNo ratings yet
- Bearing CalculationDocument10 pagesBearing CalculationAniket SankpalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Plant Location, Plant Layout and Line Balancing (Betul)Document40 pagesChapter 2 - Plant Location, Plant Layout and Line Balancing (Betul)Kesava Dass50% (2)
- Calculate Bearing Life (Timken)Document8 pagesCalculate Bearing Life (Timken)jacksonholland8335100% (2)
- Bearing SelectionDocument6 pagesBearing SelectionKenneth ChawNo ratings yet
- BAOLI Forklift KBG15-20 Operator's ManualDocument95 pagesBAOLI Forklift KBG15-20 Operator's ManualSARAMQR100% (1)
- Vibration Versus Bearing Life HandoutDocument11 pagesVibration Versus Bearing Life Handoutscribdtaker12345No ratings yet
- PreloadDocument3 pagesPreloadvenky364No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Maintenance Organization (Full Chapter) New PDFDocument71 pagesChapter 1 - Maintenance Organization (Full Chapter) New PDFAnastazry Faidzli100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Maintenance Organization (Full Chapter) New PDFDocument71 pagesChapter 1 - Maintenance Organization (Full Chapter) New PDFAnastazry Faidzli100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Maintenance Organization (Full Chapter) New PDFDocument71 pagesChapter 1 - Maintenance Organization (Full Chapter) New PDFAnastazry Faidzli100% (1)
- Introduction To Antifriction BearingsDocument39 pagesIntroduction To Antifriction BearingsTalha AhmadNo ratings yet
- Dte - Rolling Contact BearingsDocument32 pagesDte - Rolling Contact Bearingspotnuru Jaivanth100% (1)
- Maintenance Planning and SchedulingDocument43 pagesMaintenance Planning and SchedulingKesava DassNo ratings yet
- Design of BearingsDocument21 pagesDesign of BearingsJehan DhanushkeNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Design of Antifriction BearingsDocument19 pagesUnit 6 - Design of Antifriction BearingsKunal Ahiwale100% (1)
- Rolling Element BearingDocument7 pagesRolling Element BearingkrishNo ratings yet
- Bearing NoteDocument21 pagesBearing NoteShahir IsmailNo ratings yet
- 5 BearingDocument13 pages5 Bearingarbazkhan13218980No ratings yet
- Bearing Life Calculation - Bearing Loads & Speeds - American Roller BearingDocument7 pagesBearing Life Calculation - Bearing Loads & Speeds - American Roller BearingNNOUBAIHNo ratings yet
- Rolling Contact BearingDocument44 pagesRolling Contact BearingMuhammad Waleed Khan 940-FET/BSME/F20No ratings yet
- Machine Elements SummaryDocument10 pagesMachine Elements SummaryCengiz KöseoğluNo ratings yet
- Rolling-Contact BearingsDocument9 pagesRolling-Contact Bearingskats2404No ratings yet
- Rolling Element Bearings Childs2014Document53 pagesRolling Element Bearings Childs2014joshuaNo ratings yet
- Rating Life of BearingsDocument5 pagesRating Life of BearingsSh.nasirpurNo ratings yet
- Rolling Contact Bearings (UNIT 4) PDFDocument17 pagesRolling Contact Bearings (UNIT 4) PDFJaiPrakashNo ratings yet
- Conventional BearingDocument8 pagesConventional BearingWaqasNo ratings yet
- DOME 15 Recap Text 1 PDFDocument4 pagesDOME 15 Recap Text 1 PDFAditya Varma YalamanchiliNo ratings yet
- Rolling Contact Bearings: Dodi MulyadiDocument43 pagesRolling Contact Bearings: Dodi MulyadiManojKumar MNo ratings yet
- Inno2020 - T4 - Rolling-Contact BearingsDocument9 pagesInno2020 - T4 - Rolling-Contact BearingsGhostNo ratings yet
- University of Hail: BearingsDocument37 pagesUniversity of Hail: BearingsSHADES 4 ALLNo ratings yet
- Anti-Friction Bearings For Agricultural Machines Specifications and ApplicationsDocument15 pagesAnti-Friction Bearings For Agricultural Machines Specifications and ApplicationsFarouk PagsNo ratings yet
- Ball Bearing FundamentalsDocument44 pagesBall Bearing Fundamentalssing_rNo ratings yet
- EMD 6.2-3 Antifriction BearingsDocument5 pagesEMD 6.2-3 Antifriction Bearingsomkar digamabar sonone100% (1)
- Rolling Element Bearing SlidesDocument39 pagesRolling Element Bearing SlidesVELMURUGAN MNo ratings yet
- Rolling BearingDocument39 pagesRolling BearingashaNo ratings yet
- IBC Ball Screw Support BearingsDocument36 pagesIBC Ball Screw Support Bearingsfar23663No ratings yet
- Teoria de RodamientosDocument10 pagesTeoria de RodamientosHarol Wladimir Mamani TotoraNo ratings yet
- Machine Element Design MEC 331 Machine Element Design MEC 331Document30 pagesMachine Element Design MEC 331 Machine Element Design MEC 331Aqil AzadNo ratings yet
- Te 2019 DTSDocument6 pagesTe 2019 DTSVishalNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 2Document7 pagesLecture Notes 2Edwin kinyuaNo ratings yet
- Life Calculation of Rolling Element BearingsDocument23 pagesLife Calculation of Rolling Element BearingsMamdouh ElhanafyNo ratings yet
- CH 11: Rolling-Contact Bearings: Bearing TypesDocument9 pagesCH 11: Rolling-Contact Bearings: Bearing TypesBhuwaneshwar DahalNo ratings yet
- III Rolling Contact BearingsDocument32 pagesIII Rolling Contact BearingsRodrigo SousaNo ratings yet
- Informative Annex 3 - L10 BRG Selec Aftr Spring 04 SOMEDocument4 pagesInformative Annex 3 - L10 BRG Selec Aftr Spring 04 SOMEKRUNALNo ratings yet
- E204 S02 Exr DFTDocument8 pagesE204 S02 Exr DFTKantharaj Chinnappa100% (1)
- Miet 2420 Tutorial 01 - Rolling Element BearingsDocument2 pagesMiet 2420 Tutorial 01 - Rolling Element BearingsIsaac MahlabNo ratings yet
- Paes 309Document15 pagesPaes 309Jemina Jean Dorado SensanoNo ratings yet
- TDocument33 pagesTTheodoros AtheridisNo ratings yet
- Rolling Contact BearingDocument12 pagesRolling Contact Bearingاحمد عبدالهادي ربيع سعيدNo ratings yet
- Ball Bearings PDFDocument24 pagesBall Bearings PDFSamiullah AtaNo ratings yet
- Me 301 Chapter 11Document19 pagesMe 301 Chapter 11Melissa RokaNo ratings yet
- 7.1.theory Questions and Answers: 1) What Is A Bearing? State The Functions of A BearingDocument12 pages7.1.theory Questions and Answers: 1) What Is A Bearing? State The Functions of A BearingKunal ShindeNo ratings yet
- 7a-Design of Rolling BearingsDocument33 pages7a-Design of Rolling BearingsSOUBHIK ROYNo ratings yet
- E1226Document5 pagesE1226LLNo ratings yet
- Calculating Idler L10 LifeDocument9 pagesCalculating Idler L10 LifeJSweda100% (1)
- Introduction To PneumaticDocument19 pagesIntroduction To PneumaticKesava DassNo ratings yet
- Corrective MaintenanceDocument9 pagesCorrective MaintenanceKesava DassNo ratings yet
- Irjet V5i4884 PDFDocument4 pagesIrjet V5i4884 PDFSrikanth ThangellaNo ratings yet
- Corrective MaintenanceDocument9 pagesCorrective MaintenanceKesava DassNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 How To Write An ProposalDocument39 pagesChapter 1 How To Write An ProposalKesava DassNo ratings yet
- EDM Wire Cut ReportDocument12 pagesEDM Wire Cut ReportAidilNo ratings yet
- Report TemplateDocument36 pagesReport TemplateKesava DassNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Report Writing Tips: OMG Center For Collaborative LearningDocument3 pagesAnalysis and Report Writing Tips: OMG Center For Collaborative LearningKesava DassNo ratings yet
- Cover Eoc 1 DJJ 2022Document3 pagesCover Eoc 1 DJJ 2022Kesava DassNo ratings yet
- Edema in ChildDocument16 pagesEdema in ChildKesava DassNo ratings yet
- Partial FractionDocument9 pagesPartial FractionarnoldNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: Moment of Forces: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment 3: Moment of Forces: ObjectiveKesava DassNo ratings yet
- E-Notes 1 - Algebraic ExpressionsDocument13 pagesE-Notes 1 - Algebraic ExpressionsKesava DassNo ratings yet
- Turning Effect of Forces3233Document25 pagesTurning Effect of Forces3233Kesava DassNo ratings yet
- E-Notes 7 - Vector Cross ProductDocument4 pagesE-Notes 7 - Vector Cross ProductKesava DassNo ratings yet
- Partial FractionDocument9 pagesPartial FractionarnoldNo ratings yet
- E-Notes 1 - Algebraic ExpressionsDocument13 pagesE-Notes 1 - Algebraic ExpressionsKesava DassNo ratings yet
- E-Notes 1 - Algebraic ExpressionsDocument13 pagesE-Notes 1 - Algebraic ExpressionsKesava DassNo ratings yet
- E-Notes 1 - Algebraic ExpressionsDocument13 pagesE-Notes 1 - Algebraic ExpressionsKesava DassNo ratings yet
- Quadratic - Equations Review - 20-50 PDFDocument12 pagesQuadratic - Equations Review - 20-50 PDFAndré Rafael NasserNo ratings yet