Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Go To Ka 3 3 - 1
Uploaded by
api-462875978Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Go To Ka 3 3 - 1
Uploaded by
api-462875978Copyright:
Available Formats
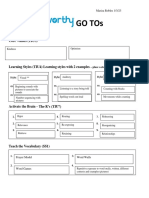
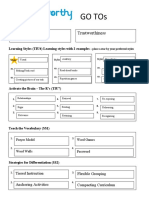
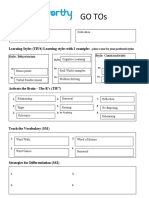
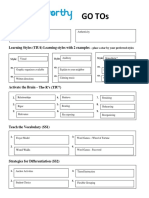
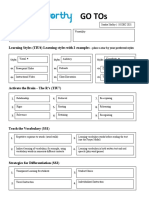
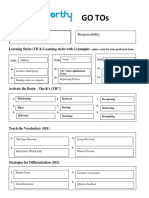
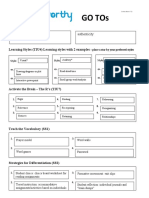
GO TOs
Core Values (TIU3)
Warmth Authenticity Hannah Mancill 5/30/19
Learning Styles (TIU4) Learning styles with 2 examples – place a star by your preferred styles
Visual* Auditory Kinesthetic
Style: Style: Style:
have student stand up and role play
ex. ask student to draw and label ex. have student watch a video ex. gas molecules (bump shoulders with
parts of a solution neighbor, wall, desk, etc.)
ex. ex. teach student cheer to help ex. ask student to answer question
assign the student reading by writing answer on white board
remember compound naming
Activate the Brain – The R’s (TIU7)
1. Relationship 4. Retrieval 7. Re-Exposing
2. Rigor 5. Routing 8. Rehearsing
3. Relevance 6. Retaining 9. Recognize
Teach the Vocabulary (SS1)
1. Frayer Model 3. Word Game (Wheel of Fortune, Password)
Personal Dictionary
2. Word Wall 4.
Strategies for Differentiation (SS1)
1.
Flexible Grouping 3. Formative Assessment
2. Respectful Tasks 4. Student Choice
Strategies for Success (SS2-7) Provide 2 examples of each
Strategies for Success (SS2-7) – Provide 2 examples of each
Example 1 Example 2
Collaborative Problem Solving Four Corners
Cooperative Grouping
Graphic Organizers Foldable Graphic Organizer SkimmingConcept Map
Advanced Organizers Analogy SkimmingConcept Map
Experimenting
Similarities / Differences Classifying
3-2-1 Summary Problem Solving Graphic
Summarizing & Notetaking
Cues & Questions 1 Minute Paper Investigating the Question (IQ) Slap Down
Game
Blooms Verbs (SS8)
Create Justify, Choose, Defend, Describe, Conclude
APPS: WeVideo Movie & Video Editor, Blogger
Evaluate Hypothesize, Arrange, Categorize, Design, Formulate
APPS: Twitter, Google Groups/Forms
Analyze Analyze, Compare, Contrast, Show, Write
APPS: WUFOO, ThingLink
Apply Use, Solve, Choose, Produce, Predict
APPS: IPEVO, Google Earth
Comprehension Explain, Give examples, Indicate, Predict, Rewrite
APPS: Airtable, Tumblr
Remember Define, Describe, Identify, Label, Order
APPS: Quizlet, Popplet
Four Questions to redirect behavior (CBM5)
What are you doing?
1.
2.What are you supposed to be doing?
3. Are you doing it?
4. What are you going to do about it?
Modifications and Accommodations (E6)
Quantity Time Level of Support
Definition Definition Definition
Adapt the number of items that the Increase the amount of personal assistance to keep
learner is expected to learn or the number
Adapt the time allotted and the student on task or to reinforce or prompt the use
of activities student will complete prior to allowed for learning, task of specific skills. Enhance adult-student relationship;
use physical space and environmental structure.
assessment for mastery. completion, or testing.
Example Example Example
Reduce the number of chemistry terms Individualize a timeline for completing a Assign peer buddies, teaching assistants, peer
a learner must learn at any one time. tutors, or cross-age tutors. Specify how to interact
task; pace learning differently (increase with the student or how to structure the
Add more practice activities or
worksheets. or decrease) for some learners. environment.
Input Difficulty Output
Definition Definition Definition
Adapt the way instruction is Adapt the skill level, problem type, Adapt how the student can
delivered to the learner. or the rules on how the learner respond to instruction.
may approach the work.
Example Example Example
Use different visual aids, enlarge text, plan more Allow the use of a calculator to figure math Instead of answering questions in writing, allow
concrete examples, provide hands-on activities,
place students in cooperative groups, pre-teach
problem, simplify task directions, or change a verbal response. Use a communication book
key concepts or terms before the lesson. rules to accommodate learner needs. for some students, or allow students to show
knowledge with hands-on materials.
Alternate Goals - Adapt the goals or outcome expectations while using the same
Participation Notes: materials. When routinely utilized, this is only for students with moderate to severe
disabilities.
Definition
For example: In a social studies lesson, expect a student to be able to locate the
Adapt the extent to which a learner colors of the states on a map, while other students learn to locate each state and
is actively involved in the task. name the capital.
Example Substitute Curriculum Sometimes called “functional curriculum” - Provide different
instruction and materials to meet a learner’s individual goals. When routinely utilized,
Ask the student to lead a group. this is only for students with moderate to severe disabilities.
Have the student watch others
perform the experiment rather For example: During a language lesson, a student is learning toileting skills with an
aide.
than performing it themselves
Suggestions for working with Students in Poverty (E12)
Provide access to computers, magazines, newspapers, and books Take time to explain the rationale for rules and
so low-income students can see and work with printed materials.
1. 4. procedures in your classroom.
Be careful about the school supplies you expect students to purchase.
2. Keep your expectations for poor students high. 5. Keep your requirements as simple as you can for all students.
3. Don’t make comments about your students’ clothes or 6. Do not require costly activities.
belongings unless they are in violation of the dress code.
Reading Strategies to Strengthen Literacy Skills (R8)
Strategy name When / how to use it Define it
nonfiction writing that encourages careful word choice,
1. Persuasive Writing N/A the development of logical arguments, and a cohesive
summary
Inferences are what we figure out based on an experience. Helping
Use individually, with small groups, or in a
2. Inferences whole class setting
students understand when information is implied, or not directly stated,
will improve their skill in drawing conclusions and making inferences.
Students read aloud to each other. When using partners, more fluent readers can be
Paired Reading Use during reading with small groups paired with less fluent readers, or children who read at the same level can be paired
to reread a story they have already read. Paired reading can be used with any book,
3. taking turns reading by sentence, paragraph, page or chapter.
Making content comprehensible for ELL students (R9)
Write at least 3 strategies / techniques that you could easily implement in your classroom for your content
1. Prepare the lesson
2. Build background
3. Make verbal communication understandable
4. Learning strategies (this one should be easy!)
5. Opportunities for interaction
6. Practice and application
7. Lesson delivery
8. Review and assess
You might also like
- Is the Answer Reasonable?, Grade 4: The Test ConnectionFrom EverandIs the Answer Reasonable?, Grade 4: The Test ConnectionNo ratings yet
- Go ToDocument4 pagesGo Toapi-513371370No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-473551229No ratings yet
- Go ToDocument4 pagesGo Toapi-519213101No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word FillableDocument4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillableapi-524477527No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1api-612529167No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-515609227No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable 11Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable 11api-510157133No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-653779848No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument5 pagesGo To Pageapi-589972069No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-481528960No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1api-607084998No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable 11Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable 11api-520915806No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To PageKeith CalhounNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-524545342No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable 11Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable 11api-588120954No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-558436275No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-660941021No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1 2Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1 2api-612739569No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-469013911No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1api-616396340No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable FinalDocument4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable Finalapi-563430348No ratings yet
- Go To Page 9Document4 pagesGo To Page 9api-510325289No ratings yet
- DT GTPDocument5 pagesDT GTPapi-557122090No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1Document5 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1api-622775702No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-555629186No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-470471721100% (1)
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-555629186No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-622195317No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1api-623358929No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word FillableDocument5 pagesGo To Page Word Fillableapi-648732384No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word FillableDocument4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillableapi-557422843No ratings yet
- Go To Page 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page 1 1api-648403099No ratings yet
- TW Go To Page CompletedDocument4 pagesTW Go To Page Completedapi-731915719No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document7 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-625414606No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1api-537777991No ratings yet
- Go To Page 9Document4 pagesGo To Page 9api-514491655No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-517815541No ratings yet
- Go To Page FinalDocument5 pagesGo To Page Finalapi-523061177No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-583972926No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-CompleteDocument4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-Completeapi-621043961No ratings yet
- Go To Page CompletedDocument4 pagesGo To Page Completedapi-516915537No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-620568882No ratings yet
- Go To Page 9Document4 pagesGo To Page 9api-512760489No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1api-522702297No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-482430210No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-559213951No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1api-647617886No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable 11Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable 11api-515746239No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-624104394No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-469053152No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-557069199No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-575280910No ratings yet
- Go To Page - 021921tribittDocument4 pagesGo To Page - 021921tribittapi-541257444No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-595895092No ratings yet
- Go To Page 9Document4 pagesGo To Page 9api-340637026No ratings yet
- Go-To PageDocument4 pagesGo-To Pageapi-538158244No ratings yet
- Core ValuesDocument4 pagesCore Valuesapi-508554958No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-CompleteDocument4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-Completeapi-601782495No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1api-616973358No ratings yet
- cbm8 Teacher Introduction Letter To ParentsDocument2 pagescbm8 Teacher Introduction Letter To Parentsapi-462875978No ratings yet
- Qualities of Effective Teachers 1 This Is UsDocument1 pageQualities of Effective Teachers 1 This Is Usapi-462875978No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Assignment TW Nuclear ChemistryDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Assignment TW Nuclear Chemistryapi-462875978No ratings yet
- cbm5 Behavioral Management PlanDocument1 pagecbm5 Behavioral Management Planapi-462875978No ratings yet
- Resume TeachingDocument1 pageResume Teachingapi-462875978No ratings yet
- Plato & AristotleDocument37 pagesPlato & Aristotlehasnain abbasNo ratings yet
- Who Am I and How I Change Personal Essay On PDFDocument1 pageWho Am I and How I Change Personal Essay On PDFShaira Mae CacNo ratings yet
- Learners Manual Grade 10 FilipinoDocument2 pagesLearners Manual Grade 10 FilipinoClethon Masalunga100% (1)
- Stages of Literature Learning in The ClassroomDocument44 pagesStages of Literature Learning in The ClassroomDanielle Akutagawa100% (1)
- Kaidah-Kaidah Fonologi: AbstracDocument19 pagesKaidah-Kaidah Fonologi: AbstracEber Felora Maru'aoNo ratings yet
- Edu 220 Cooperative Learning Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesEdu 220 Cooperative Learning Lesson Planapi-533889645No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Selection and Placement: at The End of This Lesson, You Should Be Able ToDocument6 pagesLesson 4 Selection and Placement: at The End of This Lesson, You Should Be Able ToRuby SparksNo ratings yet
- First English Panel MeetingDocument3 pagesFirst English Panel MeetingAzman JaafarNo ratings yet
- GESE Grade 1 - Lesson Plan 1 - Colours, Body and Clothing (Final)Document3 pagesGESE Grade 1 - Lesson Plan 1 - Colours, Body and Clothing (Final)Ornella Grasso100% (2)
- Designs in Clinical ResearchDocument29 pagesDesigns in Clinical ResearchAli KhanNo ratings yet
- Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS)Document12 pagesGroup Decision Support Systems (GDSS)Samuel Bassah100% (1)
- Brainstroming - EX - 7 Ui Ux Design Lab ExerciseDocument3 pagesBrainstroming - EX - 7 Ui Ux Design Lab ExercisemadhuarthickcseNo ratings yet
- Gatiawin High School: En8Rc - Ie-7 En8Vc - Ie-9 En8V - Ie-4 En8Lt - Ie-2.2Document4 pagesGatiawin High School: En8Rc - Ie-7 En8Vc - Ie-9 En8V - Ie-4 En8Lt - Ie-2.2Cristina Sarmiento JulioNo ratings yet
- Creswell 2003 Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesCreswell 2003 Literature Reviewc5swkkcn100% (2)
- How Do Krashen's Hypotheses Apply To The SL/FL Classroom?: Communicative CompetencyDocument3 pagesHow Do Krashen's Hypotheses Apply To The SL/FL Classroom?: Communicative CompetencyAwatif AuniNo ratings yet
- NCSC-16 - 3. Project ReportDocument30 pagesNCSC-16 - 3. Project ReportChaudharybana87% (15)
- Product Competency GuideDocument45 pagesProduct Competency GuideGopal MohanNo ratings yet
- Info For Parents 7 Areas of LearningDocument11 pagesInfo For Parents 7 Areas of LearningHolly Maria CassonNo ratings yet
- Lab Report RubricDocument2 pagesLab Report RubricnlolatNo ratings yet
- Cur528 Week 6 Signature Assignement Week 2 Presentation Facilitator Skills Instruction MaterialsDocument9 pagesCur528 Week 6 Signature Assignement Week 2 Presentation Facilitator Skills Instruction Materialsapi-348608704No ratings yet
- Preparation: Reading Skills Practice: Are We Losing The Art of Conversation? - ExercisesDocument3 pagesPreparation: Reading Skills Practice: Are We Losing The Art of Conversation? - ExercisesPooja BasuNo ratings yet
- Classroom ManagementDocument16 pagesClassroom ManagementPaola Siguas ChavarriaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Freuds Psychoanalytic TheoryDocument13 pagesModule 3 Freuds Psychoanalytic Theoryivan culaNo ratings yet
- Round and Flat Characters LPDocument4 pagesRound and Flat Characters LPJames Andrew PaddayumanNo ratings yet
- W W W W W: Writing StrategiesDocument59 pagesW W W W W: Writing StrategiesHenao LuciaNo ratings yet
- Classroom Assessment TechniquesDocument4 pagesClassroom Assessment TechniquesBlerim MorinaNo ratings yet
- Reflections of Feelings - RogersDocument3 pagesReflections of Feelings - RogersUyên TrươngNo ratings yet
- Impact of On-The-Job Training To Hotel and Restaurant Services Students of Higher School of The University of MakatiDocument35 pagesImpact of On-The-Job Training To Hotel and Restaurant Services Students of Higher School of The University of MakatiJed ValdezNo ratings yet
- Involving Students in AssessmentDocument7 pagesInvolving Students in AssessmentMaricris BlgtsNo ratings yet
- MECHANICS AND RUBRIC For MonologueDocument1 pageMECHANICS AND RUBRIC For MonologueLee Nico Emiliano0% (1)