Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4 Disaster Management
Uploaded by
수지0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
220 views4 pagesdisaster management
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdisaster management
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
220 views4 pagesChapter 4 Disaster Management
Uploaded by
수지disaster management
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
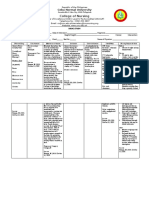
Chapter 4 (Disaster Management)
DISASTER- is a serious disruption of a community or society, It involves widespread human,
material, economic and environmental impact which exceeds the ability of the affected society to
cope up using its own resources.
Red Cross & Red crescent Society
They define disaster management as an organization and management of resources and
responsibilities for dealing with all humanitarian aspect of emergencies.
According to the UNDRO, there is an increasing number of people affected by disasters
all over the world.
5 Reasons:
1. Rapid population growth
2. Concentration of population in high-risk areas
3. Capital development
4. Man-made destruction
5. Growing poverty
Disasters: Natural
1. Earthquakes/Tsunamis
2. Landslides
3. Typhoons
4. Floods
5. Drought
6. Volcanic Eruptions
Disasters: Human-made
1. Air and water pollution
2. Industrial accidents
3. Fire
4. Civil disturbances
5. War
6. Poverty
7. Bomb threats
8. Accidents
Disasters: Categories of Severity
1. Accident
2. Emergency
3. Disaster
4. Catastrophe
Situations in the Philippines: Poverty and Marginalization
1. Malnutrition
2. Poor health
3. Inadequate basic services
4. Unemployment
Situations in the Philippines: Resource Depletion
1. Forest denudation
2. Soil erosion
3. Genetic erosion
4. Marine pollution
5. Agrochemicals
6. Air and water pollution
Situations in the Philippines: Human-made Disasters
1. Flood
2. Civil war
Situations in the Philippines: Natural Forces
1. Typhoons
2. Drought
3. Torrential rains with flooding
4. Earthquakes
5. Volcanic terrain
Assessment/Reporting on Preparedness
1. Knowledge of pre-disaster situations
2. Capability to assess
a) Medical/nutritional situation
b) Agricultural situation
c) Infrastructure situation
d) Structural stability
e) Relief operation capabilities
3. Established lines of communication
4. Established data collection points
5. Established format of reporting
6. Established confirmation/verification procedures
7. Established authority for releasing reports
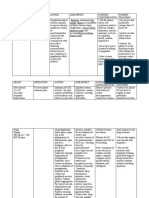
Relief Operations
1. Certain operation qualities of the key players
a) Cool and unbiased assessment
b) Swift and decisive action
c) Balanced response
d) Leadership
e) Discipline for operational reliability
f) Resource management
g) Rehabilitation already planned
h) Planning already accomplished
2. Food relief
a) General food distribution
b) Mass feeding
c) Supplementary feeding
d) Intensive or therapeutic feeding
3. Food-for-work
Rehabilitation/Construction and Emergency Preparedness
Resources need to be tapped for emergency assistance.
Plans should include rehabilitation.
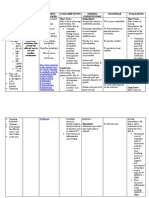
Disaster Prevention and Mitigation
Measures need to be drawn to minimize the loss and destruction of life and property.
The measures cover legislation, regulatory measures, drills and shelters.
1. Identification of areas most prone to typhoons and other calamities.
2. Display and teaching of structural improvements.
3. Preparation of educational materials.
4. Community systems.
5. Media liaison.
Disaster Preparedness
1. Principles
a) The risk must be known
b) Vulnerability must be known
c) Mitigation measures must be in place
d) Preparedness system must be ready
2. Effective warning message
a) Clear
b) Consistent
c) Convincing
d) Community-specific
e) Information on technical consequences
f) Repetitiveness
3. Land-use Planning
a) Surveys of mountainsides, riverbanks and coastal areas
b) Rational plans for urban centers
c) Identification of areas for reforestation
d) Building codes
4. Public Awareness
a) Mitigation awareness
b) Preparedness awareness
c) Emergency response awareness
You might also like
- Field Operations Guide for Disaster Assessment and ResponseFrom EverandField Operations Guide for Disaster Assessment and ResponseNo ratings yet
- NCP - Risk For Other-Directed ViolenceDocument2 pagesNCP - Risk For Other-Directed ViolenceKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- Page 17 ACUTE PAIN Related To Joint Stiffness Secondary To Aging.Document3 pagesPage 17 ACUTE PAIN Related To Joint Stiffness Secondary To Aging.Senyorita KHayeNo ratings yet
- DRUG CLASSIFICATION AND ACTIONDocument8 pagesDRUG CLASSIFICATION AND ACTIONtintinNo ratings yet
- History and Assessment & Anatomy and Physiology of BurnsDocument10 pagesHistory and Assessment & Anatomy and Physiology of BurnsRina MaeNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects and The NurseDocument50 pagesLegal Aspects and The NurseClark Lim100% (1)
- IFOSFAMIDEDocument4 pagesIFOSFAMIDEErza GenatrikaNo ratings yet
- PHINMA - UNIVERSITY OF ILOILO DRUG STUDY ON ROPIVACAINE/BUPIVACAINEDocument2 pagesPHINMA - UNIVERSITY OF ILOILO DRUG STUDY ON ROPIVACAINE/BUPIVACAINErica sebabillonesNo ratings yet
- Brunner CTEA CH 62Document6 pagesBrunner CTEA CH 62Avani PatelNo ratings yet
- PNSSDocument2 pagesPNSSBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- 005LEU11EDocument4 pages005LEU11ELiaWahyuniNo ratings yet
- Kabiven: (Amino Acids, Electrolytes, Dextrose and Lipid Injectable Emulsion), For Intravenous UseDocument24 pagesKabiven: (Amino Acids, Electrolytes, Dextrose and Lipid Injectable Emulsion), For Intravenous UseDivine Mercy De JulianNo ratings yet
- Nursing care plan for eczema patientDocument3 pagesNursing care plan for eczema patientAkira PinedaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Nursing NotesDocument4 pagesDisaster Nursing NotesChannelG100% (1)
- Disaster Management ContinuumDocument36 pagesDisaster Management ContinuumJonathan Jr GatelaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Nursing SAS Session 13Document7 pagesDisaster Nursing SAS Session 13Niceniadas CaraballeNo ratings yet
- BSN4D-SG2 DM Type2Document201 pagesBSN4D-SG2 DM Type2Charisse CaydanNo ratings yet
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome CASEDocument38 pagesStevens-Johnson Syndrome CASEChristy Rose AgrisNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk InfectionDocument1 pageNCP Risk InfectionEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Students Learn About Infectious Disease EmergenciesDocument8 pagesNursing Students Learn About Infectious Disease EmergenciesNiceniadas CaraballeNo ratings yet
- Journal DengueDocument3 pagesJournal DengueCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- PP Mecobalamin for Nerve SupplementationDocument2 pagesPP Mecobalamin for Nerve SupplementationshindyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Pain ManagementDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan for Acute Pain ManagementKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- TherablocDocument3 pagesTherablocianecunar100% (2)
- DioxelDocument1 pageDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- DS BiperidenDocument3 pagesDS BiperidenbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityShiva TorinsNo ratings yet
- LacipilDocument2 pagesLacipilianecunarNo ratings yet
- Activase for Acute Ischemic Stroke and Heart ConditionsDocument3 pagesActivase for Acute Ischemic Stroke and Heart Conditionsmharjoe pulmanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: During 8 Hours Nursing Management: (5) After 8 HoursDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: During 8 Hours Nursing Management: (5) After 8 HoursRawan KhateebNo ratings yet
- Prednisolone AcetateDocument1 pagePrednisolone AcetateAkuba AmanNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY: NCM 106 PHARMACOLOGYDocument6 pagesDRUG STUDY: NCM 106 PHARMACOLOGYKevin RosalesNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain Care PlanDocument2 pagesChest Pain Care Planapi-545292605No ratings yet
- ActemraDocument7 pagesActemraLinda KvastadNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between CKD Stage and Pulmonary Edema on Chest X-RayDocument6 pagesRelationship Between CKD Stage and Pulmonary Edema on Chest X-RayAnnisa RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Action Plan - Inadequate IncomeDocument2 pagesAction Plan - Inadequate IncomeBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- AmiodaroneDocument2 pagesAmiodaroneanindiawNo ratings yet
- Final RRLDocument4 pagesFinal RRLAnonymous 25dfWwmNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Insipidus HandoutDocument4 pagesDiabetes Insipidus HandoutllianNo ratings yet
- Example of Drug StudyDocument2 pagesExample of Drug Studydonna mae junioNo ratings yet
- DRUGSDocument5 pagesDRUGSDanica EspejoNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesAcute Pain Nursing Care PlanSiafei RabeNo ratings yet
- Citicoline Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCiticoline Drug StudyJC LumayaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Ketorolac)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Ketorolac)Andrea De RuedaNo ratings yet
- XareltoDocument2 pagesXareltoMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Bisacodyl Drug Classification, Mechanism of Action, Indication, Contraindication and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument1 pageBisacodyl Drug Classification, Mechanism of Action, Indication, Contraindication and Nursing ConsiderationsJewel GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Neuro Vital Signs Glaslow Coma ScaleDocument3 pagesNeuro Vital Signs Glaslow Coma ScaleMark PabalanNo ratings yet
- Im Case Study 04Document49 pagesIm Case Study 04Shaine BalverdeNo ratings yet
- Salazar DsDocument4 pagesSalazar DsDjayNo ratings yet
- Cefixime and Azithromycin Drug GuideDocument3 pagesCefixime and Azithromycin Drug GuideArianne Joy SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology DengueDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Denguenva226No ratings yet
- Assessing and Managing Cerebral Perfusion IssuesDocument3 pagesAssessing and Managing Cerebral Perfusion IssuesMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Suxamethonium Chloride Injection BP Product Information SummaryDocument8 pagesSuxamethonium Chloride Injection BP Product Information SummarynanaNo ratings yet
- J.Paquit NCP ECCEDocument7 pagesJ.Paquit NCP ECCEJon Gab Paquit100% (1)
- NSTP 2Document7 pagesNSTP 2Andrew SanchezNo ratings yet
- NSTP MODULE 1st Sem Updated Chapter 4Document8 pagesNSTP MODULE 1st Sem Updated Chapter 4Jhon Kenneth L. AguadoNo ratings yet
- ROTC Disaster RiskDocument7 pagesROTC Disaster RiskF Cordero, KaecelNo ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument4 pagesDisaster ManagementShaira Del MonteNo ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument25 pagesDisaster Managementpat alvarezNo ratings yet
- Tests of Controls Are Necessary If The Auditor Plans To Use The Primarily Substantive ApproachDocument3 pagesTests of Controls Are Necessary If The Auditor Plans To Use The Primarily Substantive Approach수지No ratings yet
- Gov QuizletDocument2 pagesGov Quizlet수지No ratings yet
- Gov QuizletDocument2 pagesGov Quizlet수지No ratings yet
- International Acc QuizletDocument3 pagesInternational Acc Quizlet수지No ratings yet
- Auditing QuizletDocument3 pagesAuditing Quizlet수지No ratings yet
- International Acc Quizlet No9Document2 pagesInternational Acc Quizlet No9수지No ratings yet
- International Acc QuizletDocument3 pagesInternational Acc Quizlet수지No ratings yet
- The Heavisest Emphasis of The Auditors Is On Controls Over Classes of Transactions Rather Than Account Balnaces or DisclosuresDocument3 pagesThe Heavisest Emphasis of The Auditors Is On Controls Over Classes of Transactions Rather Than Account Balnaces or Disclosures수지No ratings yet
- Service Concession Arrangement Assets RecognitionDocument3 pagesService Concession Arrangement Assets Recognition수지No ratings yet
- Understanding interest rate swaps and their impact on financial reportingDocument4 pagesUnderstanding interest rate swaps and their impact on financial reporting수지No ratings yet
- International Acc QuizletDocument2 pagesInternational Acc Quizlet수지No ratings yet
- ESSAY: Criteria for Effective State InstitutionsDocument1 pageESSAY: Criteria for Effective State Institutions수지No ratings yet
- International Acc Quizlet No8Document2 pagesInternational Acc Quizlet No8수지No ratings yet
- International Acc QuizletDocument2 pagesInternational Acc Quizlet수지No ratings yet
- International Acc Quizlet No11Document3 pagesInternational Acc Quizlet No11수지No ratings yet
- Don Quixote: Miguel de CervantesDocument1 pageDon Quixote: Miguel de CervantesAARONLEMUEL CLIDORONo ratings yet
- International Acc Quizlet No10Document3 pagesInternational Acc Quizlet No10수지No ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politics수지No ratings yet
- UNIT IV: Lesson 3 Trade and Cash Discounts - Part 1Document3 pagesUNIT IV: Lesson 3 Trade and Cash Discounts - Part 1수지100% (1)
- UNIT IV: Lesson 3 Trade and Cash Discounts - Part 2Document3 pagesUNIT IV: Lesson 3 Trade and Cash Discounts - Part 2수지No ratings yet
- Ethical Dilemmas in Marketing: An OverviewDocument55 pagesEthical Dilemmas in Marketing: An OverviewKate Hernández.No ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1617763030485 6785389949818179229Document15 pagesOrca Share Media1617763030485 6785389949818179229Cindie Jane T JaymeNo ratings yet
- The Revenue Cycle:: Sales To Cash CollectionsDocument12 pagesThe Revenue Cycle:: Sales To Cash Collections수지No ratings yet
- Actual & Appropriate TimeDocument2 pagesActual & Appropriate Time수지No ratings yet
- Survey (Fraud)Document1 pageSurvey (Fraud)수지No ratings yet
- Explanation of Icons Bar in SAP Business One 9.2Document5 pagesExplanation of Icons Bar in SAP Business One 9.2수지No ratings yet
- Ethical Dilemmas Infographics by SlidesgoDocument27 pagesEthical Dilemmas Infographics by Slidesgo수지No ratings yet
- Cordelia SlidesCarnivalDocument40 pagesCordelia SlidesCarnivalEnzo Alcívar ThomasNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accounting using SAP B1Document80 pagesFundamentals of Accounting using SAP B1수지No ratings yet
- Jessica SlidesCarnivalDocument39 pagesJessica SlidesCarnivalBianca AdelinaNo ratings yet
- Ipcc Far WG II Full ReportDocument273 pagesIpcc Far WG II Full ReportMohamed WahbyNo ratings yet
- NLC Science 8 Lesson 9Document26 pagesNLC Science 8 Lesson 9Cher JoanaNo ratings yet
- CTS-Small Wastewater Treatment SystemDocument12 pagesCTS-Small Wastewater Treatment SystemVinayNo ratings yet
- Epitome Bambowood BrochureDocument8 pagesEpitome Bambowood Brochurerajaram_brs6189No ratings yet
- Better Health and Productivity: Benefits of Green BuildingDocument18 pagesBetter Health and Productivity: Benefits of Green BuildingSakshiChugh100% (1)
- 5e Inquiry Lesson PlanDocument7 pages5e Inquiry Lesson Planapi-300681597100% (1)
- Waste Management Plant in Bangladesh (Economies)Document22 pagesWaste Management Plant in Bangladesh (Economies)Pulak09100% (3)
- Alamri Ashwaq S2019Document76 pagesAlamri Ashwaq S2019Moonlight 01No ratings yet
- Maintenance of Wheat VarietiesDocument4 pagesMaintenance of Wheat VarietiesMuhammad Boota SarwarNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Biodegradable Drought Energy-Saving Environment-Friendly Global Warming Landfill Natural Resources Toxic Chemicals Water ConsumptionDocument3 pagesAir Pollution Biodegradable Drought Energy-Saving Environment-Friendly Global Warming Landfill Natural Resources Toxic Chemicals Water ConsumptionJenny ThuNo ratings yet
- The UN Convention On Biological Diversity 1996Document40 pagesThe UN Convention On Biological Diversity 1996torrentiyNo ratings yet
- Traditional Culture and Modern CultureDocument5 pagesTraditional Culture and Modern CultureDineshNo ratings yet
- Sip (Science) (Insecticide)Document9 pagesSip (Science) (Insecticide)GabrielMichaelMalubayCapuyanNo ratings yet
- DLP - SCI9 BiodiversityDocument7 pagesDLP - SCI9 BiodiversityYolanda CarpioNo ratings yet
- 1 Horned RhinoDocument12 pages1 Horned RhinoPrachi NikhadeNo ratings yet
- Desertification ENGDocument2 pagesDesertification ENGSonya BungiacNo ratings yet
- Landscape EvolutionsDocument107 pagesLandscape EvolutionsAbhishek TatvawitNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies SyllabusDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Studies SyllabusShona ShonaNo ratings yet
- Some Animals Are More Equal Than Others Short Film Student HandoutDocument5 pagesSome Animals Are More Equal Than Others Short Film Student HandoutEVEisFunNo ratings yet
- Fungsi TanahDocument5 pagesFungsi TanahM. Ilham Tegar YunusNo ratings yet
- DISASTER MANAGEMENT OVERVIEWDocument17 pagesDISASTER MANAGEMENT OVERVIEWFusionpoint IwayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EEDocument42 pagesIntroduction To EESwapnilNo ratings yet
- Urban Freight Consolidation Centers Trends Challenges and SolutionsDocument21 pagesUrban Freight Consolidation Centers Trends Challenges and SolutionsLidia GranjaNo ratings yet
- Revision For Mid-Second Term - Grade 12: Find The Word Which Has A Different Sound in The Part UnderlinedDocument8 pagesRevision For Mid-Second Term - Grade 12: Find The Word Which Has A Different Sound in The Part UnderlinedBui My HangNo ratings yet
- Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction: Lesson 2 Exposure and VulnerabilityDocument11 pagesDisaster Readiness and Risk Reduction: Lesson 2 Exposure and VulnerabilityJem DenumNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Is Tourism Beneficial To An Environment - Should Tourism Be Banned in Order To Protect The EnvironmentDocument3 pagesWeek 8 - Is Tourism Beneficial To An Environment - Should Tourism Be Banned in Order To Protect The EnvironmentThuy LinhNo ratings yet
- Key Words-Spatial Quality, Form, Space, Functions, OrganizationsDocument3 pagesKey Words-Spatial Quality, Form, Space, Functions, OrganizationsYash SethiNo ratings yet
- Zoren Bricks T. LagmayDocument8 pagesZoren Bricks T. LagmayJulius MacaballugNo ratings yet
- Green Building Concepts and Technologies Explored at KPR InstituteDocument17 pagesGreen Building Concepts and Technologies Explored at KPR InstituteTamil Videos100% (1)
- DRRR SpeechDocument1 pageDRRR SpeechMarl SumaelNo ratings yet
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (222)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (63)
- Why Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeFrom EverandWhy Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (699)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateFrom EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1002)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- The Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanFrom EverandThe Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanNo ratings yet
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogFrom EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Last Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderFrom EverandLast Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (283)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (593)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeFrom EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (19)