Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Three-Dimensional or Free-Standing Sculpture
Uploaded by
Mach VargasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Three-Dimensional or Free-Standing Sculpture
Uploaded by
Mach VargasCopyright:
Available Formats
WHAT IS SCULPTURE ?
Sculpture is the art of making figures, such as human forms, animals or
geometrics that can either be standing freely or attached to a background
frame, either single or in a group. When it can stand freely, it is called
three-dimensional or free-standing sculpture.
Three-Dimensional or Free-Standing Sculpture
Relief Sculpture
Relief Sculpture is when the figure is mounted to the background, which
may either be a frame, a wall or a flat surface
High Relief Sculpture
the form is embossed or raised above the surface of the background. The
artist, however, does not show the human figure, for example, in its actual
form and dimension as the form blends with the flat background
Low Relief Sculpture
the figure is raised only a little from the background, as in the case of coins.
In some artworks, the artist cuts into the surface or carves deep into the
material until the form is incised but separated from the background
The Composition of Sculpture
Subtraction
Carved works are subtractive. Using a large block of wood or stone, the
sculptor carves out the figure or “frees” the figure from imprisonment in its
original block form to give it an artistic look
Construction
The sculptor chooses a base material such as metal, plastics, aluminum,
steel or found objects and then adds other elements to “construct” the idea
or image that he/she wants to express.
Substitution
Any material transformable from a plastic, molten or fluid state can be
molded or cast into a work of sculpture.
HISTORY TIMELINE OF SCULPTURE
1. In the recesses of caves, people begin to decorate the rock face with
an important theme in their daily lives, the bison and reindeer which
are their prey as Ice Age hunters. And sculptors carve portable images
of another predominant interest of mankind - the swelling curves of
the female form, emphasizing the fertility on which the survival of the
tribe depends.
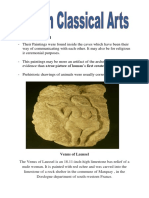
Perhaps the most famous of early sculptures is the so-called Venus of
Willendorf. Found at Willendorf in Austria, and dating from more than
25,000 years ago, she is only about four inches high. More than 100
fertility figures of this kind have been found in an area reaching from
France to southern Russia.
2. The first civilization to establish a recognizable artistic style is Egypt. This style
follows a strange but remarkably consistent convention, by which the feet,
legs and head of each human figure are shown in profile, but the torso,
shoulders, arms and eye are depicted as if from the front.
Sculpture in Egypt depicts their pharaoh often and as a commemorative
symbol of their victories
Some of the known Egyptian sculptures are the
SPHINX
ABU SIMBEL TEMPLE
SCULPTURES FOUND AT TELL ELL AMARMA
3. Greece inthe classical period makes the innovations which underlie the
mainstream western tradition in art. This is true of both painting and
sculpture.
The essential characteristic of classical Greek art is a heroic realism. Painters
and sculptors attempt to reveal the human body, in movement or repose,
exactly as it appears to the eye. The emphasis will be on people of unusual
beauty, or moments of high and noble drama.
o Charioteer of Delphi,is one of the best
known statues surviving from Ancient Greece,
and is considered one of the finest examples of
ancient bronze sculptures. The life-size
(1.8m)] statue of a chariot driver was found in
1896 at the Sanctuary of Apollo in Delphi.
o The Aphrodite of Knidos (or Cnidus) was
an Ancient Greek sculpture of the
goddess Aphrodite created
by Praxiteles of Athens around the 4th century BCE. It
is one of the first life-sized representations of the
nude female form in Greek history, displaying an
alternative idea to male heroic nudity
Romans and greeks use sculpture as public statements of victories
Sculpting is used as a means to tell the stories of victories
4. The lively traditions of Indian sculpture date back to the first Indian empire,
that of the Maurya dynasty. Sculptors begin to carve characters and scenes
from the stories of India's three interconnected religions
- Hinduism, Buddhismand to a lesser extent Jainism.
o HINDUISM - The presentation tends to
be frontal, as though the figures are
posing for the camera. From the start,
among other themes, there are
examples of Hindu art's most abiding
image - magnificent young women,
nude, full-breasted, and often in some
strikingly athletic pose (as in the famous
temples of Khajuraho, of about the 11th
century AD). Occasionally these are just female
attendants, but more often they are characters
of legend.
o BUDDHISM - The Seated Buddha from
Gandhara is an early statue of
the Buddha discovered at the site of Jamal
Garhi in ancient Gandhara in modern-
day Pakistan, that dates to the 2nd or 3rd century AD.
5. Romanesque, a word not coined until the 18th
century, is first used to describe the architecture
of western Europe from about the 9th to 12th
century. It has become applied by extension to
other arts, in particular sculpture. But the term
remains most appropriate to architecture, where
the round arches of Romanesque can easily be
seen as what the name implies - a continuation of
the Roman tradition. The capitals of columns,
carved with nothing more exotic than acanthus
leaves in the classical tradition, provide one area
in which the Romanesque sculptor lets his
imagination run wild. In abbey cloisters of the
period (and abbots are among the main patrons of
art in the Romanesque centuries) the tops of the
pillars are often alive with vivid biblical scenes or
endearingly grotesque monsters, cunningly carved
to make the most of the available shape.
6. The Gothic style, though also used in secular
buildings, is most associated with the great cathedrals
of Europe. There are certain immediately recognizable
characteristics in any Gothic cathedral.
By contrast Gothic sculptures are tall and thin,
reflecting the soaring vertical lines of the new style.
Alcoves to each side of high cathedral porches are the
favourite location for these figures
• Chartres offers the earliest surviving examples of Gothic sculpture.
1. RENNAISANCE
An important element of the Renaissance is the rediscovery of the realistic
free-standing human figure as sculpted in Greece and Rome. But the
emergence of Renaissance sculpture is not nearly as sudden a process as the
change involved in Renaissance architecture. In this era well known artisans
where born like
Donatello,
Michelangelo,
Da Vinci and many more
You might also like
- Definition of SculptureDocument6 pagesDefinition of SculptureErwin Roquid IsagaNo ratings yet
- Greek Sculpture: A Collection of 16 Pictures of Greek Marbles (Illustrated)From EverandGreek Sculpture: A Collection of 16 Pictures of Greek Marbles (Illustrated)No ratings yet
- Types of SculptureDocument16 pagesTypes of SculptureJundee L. CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Portrait - WikipediaDocument30 pagesPortrait - Wikipediakhloodwalied304No ratings yet
- Final Submission RishitaDocument5 pagesFinal Submission RishitaRishita kohliNo ratings yet
- Stone Age Art & Its CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesStone Age Art & Its CharacteristicsGuia LeeNo ratings yet
- Era in SculptureDocument7 pagesEra in SculptureAngela BofillNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greek and Roman Art HistoryDocument107 pagesAncient Greek and Roman Art HistoryMark Lorenzo TorresNo ratings yet
- History of Art Movements TimelineDocument25 pagesHistory of Art Movements TimelineLovelyn MaristelaNo ratings yet
- Art HistoryDocument27 pagesArt HistoryAbegail GolimlimNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greek Art Styles and InfluencesDocument34 pagesAncient Greek Art Styles and InfluencesKanishka Raj RathoreNo ratings yet
- Additional NotesDocument8 pagesAdditional NoteschasitydelrosarioNo ratings yet
- The Art of Europe from Prehistoric to Roman TimesDocument3 pagesThe Art of Europe from Prehistoric to Roman TimesEmpire100No ratings yet
- Additional NotesDocument5 pagesAdditional NoteschasitydelrosarioNo ratings yet
- Greek Art & Architecture AssaingmentDocument24 pagesGreek Art & Architecture Assaingmentabul kalam azadNo ratings yet
- Ge - 103 Art Appreciation Module 4Document34 pagesGe - 103 Art Appreciation Module 4Hannah Rube G. FabroneroNo ratings yet
- Greek and Roman ArtDocument101 pagesGreek and Roman ArtMark Lorenzo TorresNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Greek and Roman ArtDocument21 pagesGroup 3 Greek and Roman Artabigail arellanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper For Week 8: Download Full Document HereDocument7 pagesLesson Proper For Week 8: Download Full Document HereRalph LawrenzeNo ratings yet
- Arts Appreciation AssignmentDocument9 pagesArts Appreciation AssignmentMahnoor AkhterNo ratings yet
- Baao Community College Sculpture Development GuideDocument53 pagesBaao Community College Sculpture Development GuideEarlie WritesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - SculptureDocument94 pagesChapter 3 - SculptureKim Loyola Ronario100% (1)
- History of Painting from Pre-History to Modern EraDocument5 pagesHistory of Painting from Pre-History to Modern EraJeffrey SiyNo ratings yet
- Art History and DevelopmentDocument6 pagesArt History and DevelopmentDE CASTRO, Xyra Kate D.0% (1)
- Ancient and Classical Art TraditionsDocument80 pagesAncient and Classical Art TraditionsArwen MargalloNo ratings yet
- Sculptures From The Early AgeDocument31 pagesSculptures From The Early AgeROXANNE APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- FrankyDocument21 pagesFrankyapi-320981054No ratings yet
- The Development of Visual ArtsDocument81 pagesThe Development of Visual ArtsreijinemaebNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1-Lesson 2 (Sculptures From The Early Age)Document18 pagesUNIT 1-Lesson 2 (Sculptures From The Early Age)krizel.biantanNo ratings yet
- Ancient Art History: Paleolithic, Egyptian, and Prehistoric WorksDocument52 pagesAncient Art History: Paleolithic, Egyptian, and Prehistoric WorksSyd InformanesNo ratings yet
- Portrait History KELLYDocument4 pagesPortrait History KELLYSalome EkeNo ratings yet
- ARTSDocument25 pagesARTSdsvsf hgNo ratings yet
- Ancient Art in Greece: Corinthian OrderDocument7 pagesAncient Art in Greece: Corinthian OrderrbytesNo ratings yet
- Prehistoric Cave ArtDocument8 pagesPrehistoric Cave ArtLenard GarciaNo ratings yet
- Art App ReviewerDocument10 pagesArt App Revieweraerien ferrerNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 10 - History of Art (Pre Historic To Modern)Document4 pagesLECTURE 10 - History of Art (Pre Historic To Modern)Aeleu JoverzNo ratings yet
- Quarterone 160718122200Document63 pagesQuarterone 160718122200ivy macalaladNo ratings yet
- History of SculptureDocument58 pagesHistory of Sculpturemuslimsalifu123No ratings yet
- Roman Sculpture Mark Cartwright: Marcus Aurelius Equestrian StatueDocument10 pagesRoman Sculpture Mark Cartwright: Marcus Aurelius Equestrian StatueAncuta IlieNo ratings yet
- Garts Sample 1Document12 pagesGarts Sample 1Mary LeeNo ratings yet
- Minimalism: Minimalism Is A Popular Art Movement That Developed in Late 1950s and Early 60s. DuringDocument17 pagesMinimalism: Minimalism Is A Popular Art Movement That Developed in Late 1950s and Early 60s. Duringleslie jimenoNo ratings yet
- SculptureDocument59 pagesSculptureJulia Stefanel PerezNo ratings yet
- SculptureDocument33 pagesSculptureFlorence Keetz Abarquez AbuevaNo ratings yet
- Sculpture in Ancient TimesDocument9 pagesSculpture in Ancient TimesAnonymous ge3lqE8No ratings yet
- Timeline of Art History. (New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2000)Document8 pagesTimeline of Art History. (New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2000)Jurhidy RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Ancient to Medieval Art History Timeline and MovementsDocument10 pagesAncient to Medieval Art History Timeline and MovementsJohn DavidNo ratings yet
- Unit I Western Classical Art TraditionsDocument81 pagesUnit I Western Classical Art TraditionsRian James IcoNo ratings yet
- Final EssayDocument6 pagesFinal Essayapi-719827870No ratings yet
- Greek Civilization 2Document14 pagesGreek Civilization 2Mahnoor AkhterNo ratings yet
- Sculpture: Sculptor (Disambiguation) Sculpture (Disambiguation) Visual ArtsDocument35 pagesSculpture: Sculptor (Disambiguation) Sculpture (Disambiguation) Visual ArtsMeghan LangNo ratings yet
- ANCIENT GREEK ART PERIODSDocument9 pagesANCIENT GREEK ART PERIODSEdith DalidaNo ratings yet
- Ancient Paintings and Sculptures from Prehistoric to Gothic ErasDocument30 pagesAncient Paintings and Sculptures from Prehistoric to Gothic ErasMicoper ApolinarioNo ratings yet
- Visual ArtDocument111 pagesVisual Artglaudine andersonNo ratings yet
- History of Sculpture - Sculptor and Its WorksDocument76 pagesHistory of Sculpture - Sculptor and Its WorksMichael Jay MostolesNo ratings yet
- Egyptian ArtDocument27 pagesEgyptian ArtJobert John BatallonesNo ratings yet
- Ancient and Prehistoric Art Styles and ThemesDocument5 pagesAncient and Prehistoric Art Styles and ThemesMeghan Maureen VillacampaNo ratings yet
- Mapeh Spa Aquino g2 g9Document22 pagesMapeh Spa Aquino g2 g9ivanwaynelluvido06No ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument10 pagesArt AppreciationEllen VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- SculptureDocument62 pagesSculptureJasmine Lailani ChulipaNo ratings yet
- Ground Floor Plan Second Floor PlanDocument1 pageGround Floor Plan Second Floor PlanMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Resort floor planDocument1 pageResort floor planMach VargasNo ratings yet
- CAD-SDP Labeled - 11-9-20-VARGAS-ModelDocument1 pageCAD-SDP Labeled - 11-9-20-VARGAS-ModelMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: WC. BathDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: WC. BathMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: Clo. Toi. RaceDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: Clo. Toi. RaceMach VargasNo ratings yet
- CAD SDP 11 9 20 VARGAS ModelDocument1 pageCAD SDP 11 9 20 VARGAS ModelMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: Ent. and Ext. Ent. and ExtDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: Ent. and Ext. Ent. and ExtMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Lot Model2 PDFDocument1 pageLot Model2 PDFMach VargasNo ratings yet
- 4.1.2. Building Sapce Prgoram Space Analysis Cottage Space AnalysisDocument10 pages4.1.2. Building Sapce Prgoram Space Analysis Cottage Space AnalysisMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Lo3t ModelDocument1 pageLo3t ModelMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Econ Chapter 10 Monopoly - Monopoly BehvaiorDocument3 pagesEcon Chapter 10 Monopoly - Monopoly BehvaiorMach VargasNo ratings yet
- 12313Document1 page12313Mach VargasNo ratings yet
- 2lot Model PDFDocument1 page2lot Model PDFMach VargasNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD lot layout diagramDocument1 pageAutoCAD lot layout diagramMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Informatics 06 00002 PDFDocument43 pagesInformatics 06 00002 PDFMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Econ Chapter 10 Monopoly - Monopoly BehvaiorDocument3 pagesEcon Chapter 10 Monopoly - Monopoly BehvaiorMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Lot Model PDFDocument1 pageLot Model PDFMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Proposal For Volleyball Coaching ClinicDocument1 pageProposal For Volleyball Coaching ClinicMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Prado Real Hotel Title PDFDocument1 pagePrado Real Hotel Title PDFMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Zambales Quickstat June 2018 update of key statsDocument4 pagesZambales Quickstat June 2018 update of key statsDanica Ella PaneloNo ratings yet
- Envelope Tag and Book Tag For 2nd Defense. PDFDocument3 pagesEnvelope Tag and Book Tag For 2nd Defense. PDFMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Cities Briefing - Asian Business CouncilDocument21 pagesCities Briefing - Asian Business CouncilMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Collective Behavior Reviewer PDFDocument3 pagesCollective Behavior Reviewer PDFMach VargasNo ratings yet
- CAPSTONE CALENDAR 2nd Semester AY 2019 - 2020Document1 pageCAPSTONE CALENDAR 2nd Semester AY 2019 - 2020Mach VargasNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document5 pagesPresentation 1Mach VargasNo ratings yet
- Zambales Tourism PDFDocument4 pagesZambales Tourism PDFMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Final 1-60 PDFDocument104 pagesFinal 1-60 PDFMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Prado Real HotelDocument50 pagesPrado Real HotelMach VargasNo ratings yet
- Prado Real HotelDocument6 pagesPrado Real HotelMach VargasNo ratings yet
- ParkDocument1 pageParkMach VargasNo ratings yet
- História Do OrnamentoDocument488 pagesHistória Do Ornamentoramonvsbh100% (1)
- Gothic SculptureDocument8 pagesGothic SculpturePoleng CruzNo ratings yet
- A History of Architecture For The Studen PDFDocument604 pagesA History of Architecture For The Studen PDFarl kevin cadagNo ratings yet
- Romanesque Architecture: Formation and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesRomanesque Architecture: Formation and DevelopmentMooni BrokeNo ratings yet
- Medieval ArtDocument36 pagesMedieval ArtDama MoralloNo ratings yet
- Romanesque ArchitectureDocument15 pagesRomanesque ArchitectureRida Irfan100% (1)
- Church ArchitectureDocument22 pagesChurch ArchitectureRobin TimkangNo ratings yet
- Gothic Architecture Features and Notre Dame CathedralDocument9 pagesGothic Architecture Features and Notre Dame CathedralDivya Varghese KurumuttathuNo ratings yet
- Conques Step by Step Histoire GB 2016 2Document2 pagesConques Step by Step Histoire GB 2016 2cyn hgNo ratings yet
- Gothic ArchitectureDocument41 pagesGothic ArchitectureGilmar A. GeronNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Santa Maria NovellaDocument4 pages2.4 Santa Maria NovellaJaceNo ratings yet
- Marina MihaljeviC. Change in Byzantine ArchitectureDocument23 pagesMarina MihaljeviC. Change in Byzantine ArchitectureNikoloz NikolozishviliNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture & Ornament 1922 PDFDocument736 pagesHistory of Architecture & Ornament 1922 PDFEmile Mardacany100% (1)
- Romanesque Architecture in ItalyDocument300 pagesRomanesque Architecture in ItalyRicardo Salcido100% (1)
- Medieval Art - Painting, Sculpture, Architecture, IV To XIV Century (Art Ebook)Document520 pagesMedieval Art - Painting, Sculpture, Architecture, IV To XIV Century (Art Ebook)Marko Marusic97% (59)
- ALE HOA ReviewerDocument6 pagesALE HOA ReviewerJo-anne RiveraNo ratings yet
- Romanesque ArtDocument28 pagesRomanesque ArtVanny NaragasNo ratings yet
- Hoa2 CompilationDocument34 pagesHoa2 CompilationPatricia FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Rudolf Wittkower Art and Architecture in Italy 1600 1750Document40 pagesRudolf Wittkower Art and Architecture in Italy 1600 1750Miljan ZivaljevicNo ratings yet
- Dec. 01-06, 2020 (1) 1Document5 pagesDec. 01-06, 2020 (1) 1Renalyn Samuya JardioNo ratings yet
- History of ArchitectureDocument24 pagesHistory of ArchitectureJosh Joshua100% (1)
- Sauerländer, Willibald. "Romanesque Sculpture in Its Architectural Context"Document37 pagesSauerländer, Willibald. "Romanesque Sculpture in Its Architectural Context"AnnaNo ratings yet
- A History of Architecture For The Student, Craftsman, and Amateur (1896)Document418 pagesA History of Architecture For The Student, Craftsman, and Amateur (1896)김동훈100% (1)
- 009 009 - 2 Snezana Filipova - Patrimonium 2016Document10 pages009 009 - 2 Snezana Filipova - Patrimonium 2016Snezhana FilipovaNo ratings yet
- History of Art (5 Medieval Arts)Document97 pagesHistory of Art (5 Medieval Arts)Jay-Jay BordeosNo ratings yet
- Romansque ArchitectureDocument45 pagesRomansque ArchitectureKreya Patel100% (1)
- Italy Architectural History PresentationDocument20 pagesItaly Architectural History PresentationLujain MtawaNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture - IcaDocument81 pagesHistory of Architecture - IcaAngelo Blazado Oñedo IINo ratings yet
- Architectural styles from Early Christian to GothicDocument19 pagesArchitectural styles from Early Christian to GothicMarie Joannie Cardenas CabudsanNo ratings yet
- Mimaropa: Mindoro, Marinduque, Romblon, PalawanDocument27 pagesMimaropa: Mindoro, Marinduque, Romblon, PalawanMyla Balueta100% (3)
- Creative Abstract Watercolor: The beginner's guide to expressive and imaginative paintingFrom EverandCreative Abstract Watercolor: The beginner's guide to expressive and imaginative paintingNo ratings yet
- Jackie Shaw's Learn to Paint Flowers: A Step-by-Step Approach to Beautiful ResultsFrom EverandJackie Shaw's Learn to Paint Flowers: A Step-by-Step Approach to Beautiful ResultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Coloring Book for Adults & Grown Ups : An Easy & Quick Guide to Mastering Coloring for Stress Relieving Relaxation & Health Today!: The Stress Relieving Adult Coloring PagesFrom EverandColoring Book for Adults & Grown Ups : An Easy & Quick Guide to Mastering Coloring for Stress Relieving Relaxation & Health Today!: The Stress Relieving Adult Coloring PagesRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (12)
- Sharpie Art Workshop: Techniques & Ideas for Transforming Your WorldFrom EverandSharpie Art Workshop: Techniques & Ideas for Transforming Your WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (16)
- Layers of Meaning: Elements of Visual JournalingFrom EverandLayers of Meaning: Elements of Visual JournalingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Art Models AnaIv309: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models AnaIv309: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- CROCHET FOR BEGINNERS TO ADVANCED GUIDE: A Step-by-Step Journey from Novice to Expert in the Art of Crochet (2024)From EverandCROCHET FOR BEGINNERS TO ADVANCED GUIDE: A Step-by-Step Journey from Novice to Expert in the Art of Crochet (2024)No ratings yet
- Paint Lab: 52 Exercises Inspired by Artists, Materials, Time, Place, and MethodFrom EverandPaint Lab: 52 Exercises Inspired by Artists, Materials, Time, Place, and MethodRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Portrait Painting in Oil: 10 Step by Step Guides from Old Masters: Learn to Paint Portraits via Detailed Oil Painting DemonstrationsFrom EverandPortrait Painting in Oil: 10 Step by Step Guides from Old Masters: Learn to Paint Portraits via Detailed Oil Painting DemonstrationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Art Models Ginger040: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models Ginger040: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Celestial Watercolor: Learn to Paint the Zodiac Constellations and Seasonal Night SkiesFrom EverandCelestial Watercolor: Learn to Paint the Zodiac Constellations and Seasonal Night SkiesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Art Models AnaRebecca002: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models AnaRebecca002: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Just Draw Botanicals: Beautiful Botanical Art, Contemporary Artists, Modern MaterialsFrom EverandJust Draw Botanicals: Beautiful Botanical Art, Contemporary Artists, Modern MaterialsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Art and Technique of Sumi-e Japanese Ink Painting: Japanese Ink Painting as Taught by Ukao UchiyamaFrom EverandArt and Technique of Sumi-e Japanese Ink Painting: Japanese Ink Painting as Taught by Ukao UchiyamaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Complete Guide to Drawing & Illustration: A Practical and Inspirational Course for Artists of All AbilitiesFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Drawing & Illustration: A Practical and Inspirational Course for Artists of All AbilitiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Drawing: Flowers: Learn to Draw Step-by-StepFrom EverandDrawing: Flowers: Learn to Draw Step-by-StepRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Pottery for Beginners: Projects for Beautiful Ceramic Bowls, Mugs, Vases and MoreFrom EverandPottery for Beginners: Projects for Beautiful Ceramic Bowls, Mugs, Vases and MoreNo ratings yet
- The Everything Art Handbook: A Comprehensive Guide to More Than 100 Art Techniques and Tools of the TradeFrom EverandThe Everything Art Handbook: A Comprehensive Guide to More Than 100 Art Techniques and Tools of the TradeNo ratings yet
- Ceramics: Contemporary Artists Working in ClayFrom EverandCeramics: Contemporary Artists Working in ClayRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Zentangle 2, Expanded Workbook EditionFrom EverandZentangle 2, Expanded Workbook EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Drawing in Black & White: Creative Exercises, Art Techniques, and Explorations in Positive and Negative DesignFrom EverandDrawing in Black & White: Creative Exercises, Art Techniques, and Explorations in Positive and Negative DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Art Models SarahAnn031: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models SarahAnn031: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)
- Watercolor: Wild & Free: Paint Cute Animals and Wildlife in 12 Easy LessonsFrom EverandWatercolor: Wild & Free: Paint Cute Animals and Wildlife in 12 Easy LessonsNo ratings yet
- Art Models Becca425: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models Becca425: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)