Professional Documents
Culture Documents
P6 Part 4
P6 Part 4
Uploaded by
Kenneth Duro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOriginal Title
P6-PART-4.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesP6 Part 4
P6 Part 4
Uploaded by
Kenneth DuroCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
SIR ISAAC NEWTON (1642-1727) The motion of an object is completely
determined by its mass and the net force acting
upon it.
F = ma
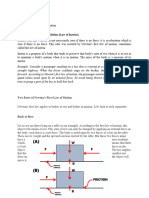
THIRD LAW OF MOTION
LAW OF ACTION AND REACTION
For every action, there is an equal and opposite
reaction.
Interacting bodies exert forces on each other.
FIRST LAW OF MOTION
LAW OF INERTIA
A body at rest or in the state of uniform motion
will remain at rest or in uniform motion, unless
acted upon by a net external force.
SECOND LAW OF MOTION
LAW OF ACCELERATION
The acceleration of an object is equal to the net
force applied to it, divided by its mass.
You might also like
- Forces and Movement (Push, Pull, Fast, Slow and More): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Physics Books EditionFrom EverandForces and Movement (Push, Pull, Fast, Slow and More): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Physics Books EditionNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument31 pagesLaws of MotionManas ThakurNo ratings yet
- Stem 305 Final Exam ReviewerDocument6 pagesStem 305 Final Exam ReviewerBeyoncé GalvezNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Module 1 - Newtons Law of MotionDocument24 pagesGrade 8 Module 1 - Newtons Law of Motionjohn charles garaldeNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion UpdatedDocument31 pagesForces and Motion UpdatedIrvin GrabosoNo ratings yet
- Force and Newton's Laws: Concise 2-Page Class 10 CBSE NotesDocument2 pagesForce and Newton's Laws: Concise 2-Page Class 10 CBSE Notesamaan 10 BNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument21 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionCharles DaquioagNo ratings yet
- Physics - Newton's Law of MotionDocument1 pagePhysics - Newton's Law of MotionMay PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Genphy1 Force Newtons Laws of MotionDocument41 pagesGenphy1 Force Newtons Laws of Motionanak nivebNo ratings yet
- Physics Research Project On Newton's Laws of Motion (3rd Law Specifically)Document9 pagesPhysics Research Project On Newton's Laws of Motion (3rd Law Specifically)Ranjitha RaviproluNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument1 pageScienceChaela ApplebyNo ratings yet
- P6-Topic 1Document5 pagesP6-Topic 1Erianne ReyesNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - Laws of MotionDocument16 pagesCHAPTER 1 - Laws of MotionmaryelNo ratings yet
- Scince 8Document2 pagesScince 8MCristina MondejarNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion Student Presentation Colorful Illustrated - 20240207 - 130732 - 0000Document18 pagesForce and Motion Student Presentation Colorful Illustrated - 20240207 - 130732 - 0000Jomar CasolNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in ScienceDocument6 pagesReviewer in ScienceBAD-E, JUSTINE ALEXIS BALBUENANo ratings yet
- Law of OnersiaDocument2 pagesLaw of Onersiaวงกลม มิ.ย.No ratings yet
- NEWTONSLAWSOFMOTIONDocument29 pagesNEWTONSLAWSOFMOTIONAngel SagreNo ratings yet
- 7th Lesson Newtons Laws of MotionDocument27 pages7th Lesson Newtons Laws of MotionMRmister123No ratings yet
- Newton's Law of MotionDocument13 pagesNewton's Law of MotionKhawaja EshaNo ratings yet
- COE 105 Chap02EquilibriumDocument11 pagesCOE 105 Chap02Equilibriumjethrocunanan04No ratings yet
- COE 105 CHAPTER 2 EquilibriumDocument11 pagesCOE 105 CHAPTER 2 EquilibriumCarrie100% (1)
- PHYSICS HANDOUT Newtons LawDocument6 pagesPHYSICS HANDOUT Newtons LawAlexander DolinNo ratings yet
- The Laws of MotionDocument15 pagesThe Laws of MotionAmar Poñado BagacinaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third Law: Action and ReactionDocument6 pagesNewton's Third Law: Action and ReactionAnuva KachruNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 MotionDocument4 pagesLecture 2 MotionAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- What Is PhysicsDocument5 pagesWhat Is PhysicswatermelonNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Feb 10, 2021Document4 pagesAdobe Scan Feb 10, 2021Filip SalekNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion Student Presentation Colorful Illustrated - 20240206 - 203710 - 0000Document16 pagesForce and Motion Student Presentation Colorful Illustrated - 20240206 - 203710 - 0000Jomar CasolNo ratings yet
- Graphic Organizer Answer Sample Shin SulDocument1 pageGraphic Organizer Answer Sample Shin Sulapi-302581865100% (2)
- Newton' S Law of MotionDocument1 pageNewton' S Law of MotionjenjenNo ratings yet
- Notes Physics Part 1Document1 pageNotes Physics Part 1Norell TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Terms 8 Grade PhysicsDocument1 pageTerms 8 Grade PhysicsНаталья ФедосикNo ratings yet
- Module 1 3 LectureDocument2 pagesModule 1 3 LectureaileenNo ratings yet
- Nkdievid 2Document10 pagesNkdievid 2nik100% (2)
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: Mark Anthony C. Burgonio, MSCDocument37 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motion: Mark Anthony C. Burgonio, MSCChristel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physics Note 1.Document6 pagesGrade 12 Physics Note 1.babaNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion Teacher Presentation Colorful IllustratedDocument15 pagesForce and Motion Teacher Presentation Colorful IllustratedAmira ElsisiNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion. Byju'sDocument135 pagesLaws of Motion. Byju'sjimmyemandeeNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Newtons Law of MotionDocument52 pagesTopic 4 Newtons Law of Motionalianapaloma77No ratings yet
- Newtons LawsDocument17 pagesNewtons LawsJennelyn Tiburcio-DascoNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument5 pagesSciencemalaitslasharmanniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document36 pagesChapter 3sigitNo ratings yet
- Newtons Third Law of MotionDocument24 pagesNewtons Third Law of MotionMARY GRACE FACULARINNo ratings yet
- Physics I: Key Concepts To Remember: Derived Physical Quantities Law of InteractionDocument2 pagesPhysics I: Key Concepts To Remember: Derived Physical Quantities Law of InteractionPrincess jashminNo ratings yet
- Statistics of Rigid BodiesDocument7 pagesStatistics of Rigid BodiesAphaedes AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Law of Motion @moazzam - GuidesDocument1 pageLaw of Motion @moazzam - GuidesMoazzamNo ratings yet
- Contact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesDocument6 pagesContact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesBethlehem CuradaNo ratings yet
- Stem BL - Gre RefugiaDocument6 pagesStem BL - Gre RefugiaMichaela RefugiaNo ratings yet
- Forces: Briefly Explained by Max de RooijDocument1 pageForces: Briefly Explained by Max de RooijMax De RooijNo ratings yet
- Physics: First Law (Law of Inertia)Document2 pagesPhysics: First Law (Law of Inertia)Kumanan CultureshockNo ratings yet
- General Physics PrefinalsDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics PrefinalssarmientojoonsunNo ratings yet
- Physics 2Document1 pagePhysics 2Willow ItchiroNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - 1st QuizDocument2 pagesScience 8 - 1st QuizRutchie LasqueNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of MotionDocument28 pagesNewton's Law of MotionJosh JavierNo ratings yet
- Physics Nmat ReviewerDocument7 pagesPhysics Nmat ReviewerLeanna DaneNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion: InertiaDocument5 pagesLaws of Motion: InertiaSubhashakti BeheraNo ratings yet
- Nivelación ProjectDocument11 pagesNivelación ProjectJAVIER EDUARDO PORTILLO IRIASNo ratings yet
- CH - 4 Laws of MotionDocument7 pagesCH - 4 Laws of MotionstudartzofficialNo ratings yet
- Hand Out DYNAMICSDocument11 pagesHand Out DYNAMICSBry RamosNo ratings yet