Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circulatory System Notes
Circulatory System Notes
Uploaded by
Justyna Lee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageThe circulatory system is divided into three main areas: pulmonary circulation, coronary circulation, and systemic circulation. It transports oxygen, glucose, heat, hormones, and aids in defense by fighting infection. The circulatory system removes waste from cells like carbon dioxide and urea. It is composed of the heart, which pumps blood continuously through a network of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Blood is the fluid that fills the circulatory system. The heart has four chambers - left and right ventricles and left and right atria - and pumps oxygenated blood to the body and deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Original Description:
Biology class notes on the circulatory system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe circulatory system is divided into three main areas: pulmonary circulation, coronary circulation, and systemic circulation. It transports oxygen, glucose, heat, hormones, and aids in defense by fighting infection. The circulatory system removes waste from cells like carbon dioxide and urea. It is composed of the heart, which pumps blood continuously through a network of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Blood is the fluid that fills the circulatory system. The heart has four chambers - left and right ventricles and left and right atria - and pumps oxygenated blood to the body and deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageCirculatory System Notes
Circulatory System Notes
Uploaded by
Justyna LeeThe circulatory system is divided into three main areas: pulmonary circulation, coronary circulation, and systemic circulation. It transports oxygen, glucose, heat, hormones, and aids in defense by fighting infection. The circulatory system removes waste from cells like carbon dioxide and urea. It is composed of the heart, which pumps blood continuously through a network of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Blood is the fluid that fills the circulatory system. The heart has four chambers - left and right ventricles and left and right atria - and pumps oxygenated blood to the body and deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
The Circulatory System
Divided into three main areas
1.) Pulmonary circulation (blood to and from the lungs)
2.) Coronary circulation (blood that services the heart muscle itself)
3.) Systemic circulation (the rest of the system’s processes).
Functions of the Circulatory System
1.) Transport materials needed by cells
Oxygen (* To carry OXYGEN to all the cells in the body)
Glucose (* To carry FOOD to all the cells in the body)
2.) Remove waste materials from cells
Carbon dioxide
Urea
3.) To distribute HEAT around the body
4.) To form a part of the DEFENCE the body has against microbes. Fight infection
(immunity)
5.) To REPAIR itself and prevent blood loss by clotting
6.) To aid in recognition of foreign material
7.) To carry hormones to target areas
Components of the Circulatory System
The Pump (heart)
continuously circulates blood
Network of tubes
Arteries-‐ blood away from heart
Veins-‐ blood back to the heart
Capillaries – allow exchange of materials with cells
Blood
Fluid that fills the circulatory system
The Heart
The human heart has four chambers
Left and right ventricle
Left and right atrium
The left side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the body while the right side of
the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs where oxygen can be absorbed by
the hemoglobin carrying red blood cells
You might also like
- Human Body Systems Study GuideDocument1 pageHuman Body Systems Study Guideapi-323141584No ratings yet
- Notes (Transport System in Humans)Document10 pagesNotes (Transport System in Humans)Hazrin ShahNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Study GuideDocument1 pageHuman Body Systems Study Guideapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Blood Circulation and Transport: 2.1 The Transport System in HumansDocument7 pagesChapter 2: Blood Circulation and Transport: 2.1 The Transport System in HumansChloe LianNo ratings yet
- BIO 103 Circulation, Respiration, Excretion L12 Fall, 2018Document29 pagesBIO 103 Circulation, Respiration, Excretion L12 Fall, 2018Demi RoseNo ratings yet
- Science 9 PointersDocument3 pagesScience 9 PointersPhilpNil8000No ratings yet
- Circulation, Respiration & Excretion: at A GlanceDocument29 pagesCirculation, Respiration & Excretion: at A GlanceHasan Mahmud Maruf 1621513630No ratings yet
- What Are The Circulatory System Parts?Document5 pagesWhat Are The Circulatory System Parts?Quốc Thái TrươngNo ratings yet
- BIOMEDIC SCIENCES (Kardiovaskular)Document2 pagesBIOMEDIC SCIENCES (Kardiovaskular)Yusuf Rifaldi lawiraNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument33 pagesCirculatory SystemMarco DadoNo ratings yet
- Genzoo Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesGenzoo Circulatory SystemAbram TicmanNo ratings yet
- Biology 3Document2 pagesBiology 3Shammy AbadNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument44 pagesCirculatory SystemAdonai Jireh Dionne BaliteNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals 1Document6 pagesTransport in Animals 1makah2711No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesCirculatory SystemMaria Theresa DemeterioNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - Kd13Document63 pagesCardiovascular System - Kd13Alyssa Curry BroderickNo ratings yet
- Unit5-Circulatory and Excretor. BGCDocument31 pagesUnit5-Circulatory and Excretor. BGCDébora Rodríguez MonteroNo ratings yet
- 9 Transport in AnimalsDocument14 pages9 Transport in AnimalsFathmath JameelNo ratings yet
- Chapter: 3 Effects of Exercise On Human Body.: Topic: 4 Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesChapter: 3 Effects of Exercise On Human Body.: Topic: 4 Circulatory Systemdaneal hustleNo ratings yet
- Importance of A Transport System in Some Multicellular OrganismsDocument46 pagesImportance of A Transport System in Some Multicellular OrganismsDanny ChewNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesCirculatory SystemRatiram LilhareNo ratings yet
- Animal Organ SystemDocument139 pagesAnimal Organ SystemMilyn Mae PalganNo ratings yet
- Sistem Peredaran Darah ResumeDocument10 pagesSistem Peredaran Darah Resumeilham ramNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System - ReviewerDocument9 pagesCirculatory System - ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Nutrients and Waste Transport SystemDocument22 pagesNutrients and Waste Transport SystemItsPotatoQueen MaeNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Transport in Animals Biology NotesDocument27 pagesUnit 9 Transport in Animals Biology NotespearlcraftsalotNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Sir Jayr TaroyDocument30 pagesCirculatory System: Sir Jayr TaroyDelfin Jr UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory SystemMarnel DincolNo ratings yet
- Major Parts of The Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesMajor Parts of The Circulatory SystemRicaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesCardiovascular Systemyousaf Murad khurramNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesCirculatory SystemKhawar HussainNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Study GuideDocument1 pageHuman Body Systems Study Guideapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Review Transport System TaylorDocument5 pagesReview Transport System TaylorPaola MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Unit 1: Module 1Document29 pagesCirculatory System: Unit 1: Module 1Michael Escriba100% (1)
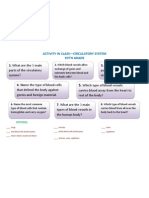
- 1 3. The Human Hearts: Activity in Class-Circulatory System Fifth GradeDocument1 page1 3. The Human Hearts: Activity in Class-Circulatory System Fifth GrademargemunozNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Summary - The Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesGrade 7 Science Summary - The Circulatory SystemNadine Salah El-DinNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument51 pagesUntitledMuhammad FadhilNo ratings yet
- Transport of Materials in The Respiratory and CirculatoryDocument16 pagesTransport of Materials in The Respiratory and CirculatoryPaul Marwen FernandezNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology Chapter 1 TransportDocument12 pagesForm 5 Biology Chapter 1 TransportMohdAmerAhmadNo ratings yet
- 2C1 Circulatory SystemsDocument17 pages2C1 Circulatory SystemsAsmaNo ratings yet
- Vascular SystemDocument20 pagesVascular SystemHama HamidNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument85 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemsxoxkakidoxoxNo ratings yet
- CirculatoryDocument9 pagesCirculatoryJason Vinluan Carinan100% (1)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCardiovascular SystemNatalie Odette Zárate BeristainNo ratings yet
- 5129 Combined Science - Biology SectionDocument11 pages5129 Combined Science - Biology SectionKhairunnisaaHAriffinNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation and TransportDocument23 pagesBlood Circulation and TransportcikzafirahNo ratings yet
- Transport SystemDocument14 pagesTransport SystemAkiela JohnsonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesCirculatory System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- The Transport System in Human Is Called Circulatory System: - Heart, - Blood Vessel - BloodDocument12 pagesThe Transport System in Human Is Called Circulatory System: - Heart, - Blood Vessel - BloodNurulAmniNo ratings yet
- Anaphy CardioDocument10 pagesAnaphy Cardiojonel lorenzoNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation and AnswersDocument2 pagesBlood Circulation and AnswersAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory Systemsyrine mendozaNo ratings yet
- Animal Circulatory SystemDocument14 pagesAnimal Circulatory System'Immey Ssi MoyNo ratings yet
- Animal TransportDocument20 pagesAnimal TransportFeranmi AkinboboyeNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Rot. 5johnDocument2 pagesAnaPhy Rot. 5johnJohn Emmanuel RevilNo ratings yet
- Animal Transport SystemDocument61 pagesAnimal Transport Systemtrixielejarso0306No ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet