Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Engr. Mel Kenneth Mabute FIRST Semester, A.Y. 2018-2019
Engr. Mel Kenneth Mabute FIRST Semester, A.Y. 2018-2019
Uploaded by
Jayron Madrid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views13 pagesThis document contains examples and problems related to base units, unit pressures, mass density, specific weight, gravity force, specific volume, pressure gauges, manometers, surface tension, and gas properties. It includes 9 examples calculating values like mass density, specific weight, pressure differences, amounts of depression or rise in manometers, and properties of chlorine gas under given temperature and pressure conditions. The examples work through technical calculations and problems involving fluid properties, pressure measurement devices, and gas behavior.
Original Description:
Baseunits
Original Title
Baseunits
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains examples and problems related to base units, unit pressures, mass density, specific weight, gravity force, specific volume, pressure gauges, manometers, surface tension, and gas properties. It includes 9 examples calculating values like mass density, specific weight, pressure differences, amounts of depression or rise in manometers, and properties of chlorine gas under given temperature and pressure conditions. The examples work through technical calculations and problems involving fluid properties, pressure measurement devices, and gas behavior.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views13 pagesEngr. Mel Kenneth Mabute FIRST Semester, A.Y. 2018-2019
Engr. Mel Kenneth Mabute FIRST Semester, A.Y. 2018-2019
Uploaded by
Jayron MadridThis document contains examples and problems related to base units, unit pressures, mass density, specific weight, gravity force, specific volume, pressure gauges, manometers, surface tension, and gas properties. It includes 9 examples calculating values like mass density, specific weight, pressure differences, amounts of depression or rise in manometers, and properties of chlorine gas under given temperature and pressure conditions. The examples work through technical calculations and problems involving fluid properties, pressure measurement devices, and gas behavior.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Engr.
Mel Kenneth Mabute
FIRST Semester, A.Y. 2018-2019
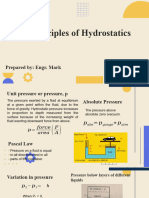
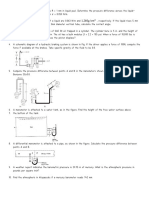
1. Base Units
2. Unit Pressures
Example HGE1.1
One slug is equivalent to how many kg?
Example HGE1.2
What is the mass density of fresh water
in slugs per cubic foot?
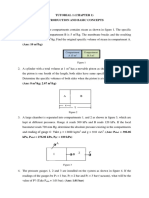
Example HGE1.3
A liquid in a 750-m3 container has a
mass of 1010 kg.
a. What is its mass density?
b. What is its specific weight
c. What is its gravity force?
d. What is its specific volume?
Example HGE1.4
The pressure gage in a given tank reads
115 mmHg. Calculate the equivalent height
of column of oil.
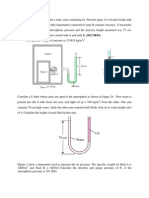
Example HGE1.5
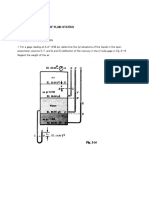
The elevation at the bottom of the tank
shown is 4.0m. Find the elevation of the
liquid surface in piezometer B. See figure
on the board.
Example HGE1.6
Determine the gage pressure at A in the
given open-type manometer.
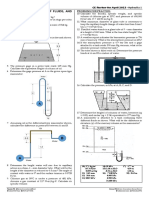
Example HGE1.7
Assuming oil in the differential-type
manometer shown at the board, calculate
the difference in pressures between A and
B.
Example HGE1.8
A 3-mm diameter tube is inserted in
mercury and later in water.
a. Assuming the tube is clean so that its
angle of contact with mercury is 140-deg
and the surface tension is 0.5140 N/m,
what is the amount of depression?
Example HGE1.8
b. Assuming the tube is clean so that its
angle of contact with water is 0-deg and the
surface tension is 0.0728 N/m, what is the
amount of rise?
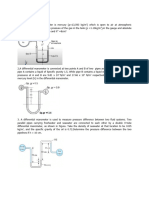
Example HGE1.9
Chlorine gas at 30-deg is under a pressure
of 481 kPa. Assume a gas constant of 117
N-m/kg-K. Calculate the following:
a. Density
b. Specific weight
c. Specific volume
Review Innovations. May 2018 CE Review
Handout: Review Innovations. 2018
You might also like
- Homeworks 1-10 PDFDocument95 pagesHomeworks 1-10 PDFWendy LinNo ratings yet
- Manometer ProblemsDocument4 pagesManometer ProblemsArjayMacasaetCaballes100% (1)
- Density Measurement Lab ReportDocument8 pagesDensity Measurement Lab ReportcrumsyNo ratings yet
- Problems FluidsDocument4 pagesProblems Fluidsabdul khalid ampuanNo ratings yet
- Fluid StaticDocument2 pagesFluid StaticAditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- CEP372 Week 6 ProblemsDocument2 pagesCEP372 Week 6 ProblemsJoshua Jay JetomoNo ratings yet
- PS 1Document8 pagesPS 1naverfallNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Lecture 2 Solutions-1Document8 pagesTutorial - Lecture 2 Solutions-1Bastián Olfos MárquezNo ratings yet
- Department of Biomedical Engineering (Aait) : Work Sheet #2Document3 pagesDepartment of Biomedical Engineering (Aait) : Work Sheet #2gfsfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Concepts Definition and Basic PrinciplesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Concepts Definition and Basic PrinciplesEyron EyronNo ratings yet
- Tarea 1 TermodinamicaDocument3 pagesTarea 1 TermodinamicaMario Gonzalez100% (1)
- Engineering Thermodynamics (Tutorial 1) PDFDocument4 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics (Tutorial 1) PDFSahil AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 ReviewerDocument6 pagesChapter2 ReviewerLJ IDANE ARANASNo ratings yet
- BLB - CH10 Ejercicios ResueltosDocument38 pagesBLB - CH10 Ejercicios ResueltosRosa Elsy Puentes LondoñoNo ratings yet
- FileDocument19 pagesFileRaymart CubidNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 (Pressure Measurements)Document2 pagesWorksheet 1 (Pressure Measurements)Jose Ruben SortoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 FluidsDocument51 pagesChapter 4 FluidsshahrulNo ratings yet
- List2 TasksDocument3 pagesList2 Taskserney03No ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument50 pagesFluid MechanicsLurking RogueNo ratings yet
- CompreDocument3 pagesCompreJohn Dominic B. EugenioNo ratings yet
- CompreDocument3 pagesCompreJohn Dominic B. EugenioNo ratings yet
- Principles of HydrostaticsDocument16 pagesPrinciples of Hydrostaticsmark galangNo ratings yet
- Applications of Bernoulli's EquationDocument11 pagesApplications of Bernoulli's Equationيوميات عبداللهNo ratings yet
- Ce140 PS 1 PDFDocument1 pageCe140 PS 1 PDFsoontobengineerNo ratings yet
- Ce140 PS 1 PDFDocument1 pageCe140 PS 1 PDFAydinAkhtarpourNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document2 pagesProblem Set 2jisnglvblNo ratings yet
- Activity 4:: Engr - Francia L. Abarientos, MEDocument2 pagesActivity 4:: Engr - Francia L. Abarientos, MEDeliadina B. QuintoNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 QDocument3 pagesChap 2 QnurudinsatharNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lectures and Tutorials 30: Abs Atm GageDocument11 pagesFluid Mechanics Lectures and Tutorials 30: Abs Atm GageAnees Kadhum AlsaadiNo ratings yet
- Hyd 1Document1 pageHyd 1Kitchen KnifeNo ratings yet
- Mecanica de FluidosDocument4 pagesMecanica de FluidosAlejandra FloresNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Fluid StaticDocument5 pagesTutorial 2 Fluid StaticAiman HakimNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics AND Pneumatics: DPG Polytechnic College Gurugram (HR)Document40 pagesHydraulics AND Pneumatics: DPG Polytechnic College Gurugram (HR)Shanu RawNo ratings yet
- FLUMECH New Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesFLUMECH New Practice ProblemsMLNDG boysNo ratings yet
- Set2ans 12Document6 pagesSet2ans 12footballtrack_21No ratings yet
- Base Units, Properties of Fluids, and Unit Pressures: CE Review For Nov 2022 - Hydraulics 1Document1 pageBase Units, Properties of Fluids, and Unit Pressures: CE Review For Nov 2022 - Hydraulics 1Jocelyn CabarlesNo ratings yet
- 2nd and 3rd WeeksDocument51 pages2nd and 3rd WeeksnaverfallNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1: Gage Vac Vac AbsDocument2 pagesThermodynamics 1: Gage Vac Vac AbsItsMeRyanCNo ratings yet
- Basic Integration Problems With Answers PDFDocument158 pagesBasic Integration Problems With Answers PDFLily Antonette AgustinNo ratings yet
- Actividad 1 Mecanica FLuidosDocument5 pagesActividad 1 Mecanica FLuidosAngel HCastNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem Sheets On FM-I Group A A. PressureDocument3 pagesPractice Problem Sheets On FM-I Group A A. PressureSWAGATAM BAZNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - HydDocument13 pagesWeek 1 - HydAsif UsmanNo ratings yet
- Sikkerarv - DK Fluids PDFDocument84 pagesSikkerarv - DK Fluids PDFJoymi Claire100% (1)
- Group 2 Chapter 2: Principle of Fluid StaticsDocument4 pagesGroup 2 Chapter 2: Principle of Fluid StaticsCharlyn FloresNo ratings yet
- Unit Practice Test: Gas Laws: Multiple ChoiceDocument8 pagesUnit Practice Test: Gas Laws: Multiple Choiceanj pianoNo ratings yet
- Pressure Distribution: GATE-2001/One MarkDocument5 pagesPressure Distribution: GATE-2001/One MarkIshu PatelNo ratings yet
- Practice Solving Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesPractice Solving Fluid MechanicsJan HernandezNo ratings yet
- FluidMechanics ActivityDocument8 pagesFluidMechanics ActivityBorja, Alexandra C.No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Powerpoint - Student VersionDocument95 pagesChapter 10 Powerpoint - Student VersionAnj LTNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document39 pagesChapter 2Brian King CrosdaleNo ratings yet
- ChE CalculationsDocument39 pagesChE Calculationsneil loNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2071 PDFDocument24 pagesTutorial 2071 PDFPrabin Acharya100% (1)
- WORK Sheet PressureDocument6 pagesWORK Sheet PressureSherazNo ratings yet
- Pressure Questions For IGCSE PhysicsDocument14 pagesPressure Questions For IGCSE PhysicsAgus SetyawanNo ratings yet
- FLUID I CH 1 Fluid Statics Tut 2 ADocument5 pagesFLUID I CH 1 Fluid Statics Tut 2 ANaser KhalidNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Concepts, Definitions, and Basic PrinciplesDocument4 pagesModule 1 Concepts, Definitions, and Basic Principlesernest quitaligNo ratings yet
- Sec - 2 Notes Part 2Document5 pagesSec - 2 Notes Part 2FatmaNo ratings yet
- Lec 4aDocument15 pagesLec 4aNust Razi0% (1)