Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Force: Definisi Satuan Untuk Force Pengonversi
Force: Definisi Satuan Untuk Force Pengonversi
Uploaded by
Danunurarifin1230 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesThe document defines various units of force used in physics and engineering. It provides the definitions and conversions for SI derived units like the newton as well as other common and obsolete units. These include kilogram-force, pound-force, kilopond, and others. All units are defined in terms of their relationship to accelerating a standard mass over distance or time based on fundamental equations of motion.
Original Description:
mek flu
Original Title
Force.docxczxcx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines various units of force used in physics and engineering. It provides the definitions and conversions for SI derived units like the newton as well as other common and obsolete units. These include kilogram-force, pound-force, kilopond, and others. All units are defined in terms of their relationship to accelerating a standard mass over distance or time based on fundamental equations of motion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesForce: Definisi Satuan Untuk Force Pengonversi
Force: Definisi Satuan Untuk Force Pengonversi
Uploaded by
Danunurarifin123The document defines various units of force used in physics and engineering. It provides the definitions and conversions for SI derived units like the newton as well as other common and obsolete units. These include kilogram-force, pound-force, kilopond, and others. All units are defined in terms of their relationship to accelerating a standard mass over distance or time based on fundamental equations of motion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Force
Pengonversi Unit Online • Pengonversi Satuan Umum
• Bantuan
Bahasa Situs
Pilih pengonversi Mengonversi satuan menggunakan Force
lain:
IDIndonesian – Bahasa pengonversi
Indonesia
Definisi satuan untuk Force pengonversi
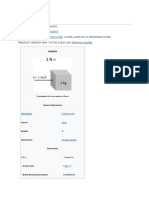
newton
A newton (N) is the SI derived unit of force. According to Newton’s second law of
motion, it is equal to the amount of force required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at
a rate of one meter per second squared. Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
exanewton
An exanewton (EN) is a decimal multiple of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
petanewton
A petanewton (PN) is a decimal multiple of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
teranewton
A teranewton (TN) is a decimal multiple of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
giganewton
A giganewton (GN) is a decimal multiple of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
meganewton
A meganewton (MN) is a decimal multiple of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
kilonewton
A kilonewton (kN) is a decimal multiple of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
hectonewton
A hectonewton (hN) is a decimal multiple of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
dekanewton
A dekanewton (daN) is a decimal multiple of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
decinewton
A decinewton (dN) is a decimal fraction of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
centinewton
A centinewton (cN) is a decimal fraction of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
millinewton
A millinewton (mN) is a decimal fraction of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
micronewton
A micronewton (μN) is a decimal fraction of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
nanonewton
A nanonewton (nN) is a decimal fraction of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
piconewton
A piconewton (pN) is a decimal fraction of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
femtonewton
A femtonewton (fN) is a decimal fraction of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
attonewton
An attonewton (aN) is a decimal fraction of the SI derived unit of force newton.
According to Newton’s second law of motion, one newton is equal to the amount of force
required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared.
Therefore, 1 N = 1 kg·m/s².
dyne
A dyne (dyn) is a unit of force specified in the centimeter-gram-second (CGS) system of
units. Equivalently, the dyne is defined as the force required to accelerate a mass of one
gram at a rate of one centimeter per second squared. One dyne is equal to 10
micronewtons.
joule/meter
A joule per meter (J/m) is a metric unit of force. In mechanics, a joule is defined as the
work done by a force of one newton acting to move an object through a distance of one
meter in the direction in which the force is applied (1 J = 1 N·m). Therefore, joule per
meter is equal to newton.
joule/centimeter
A joule per centimeter (J/cm) is a metric unit of force. In mechanics, a joule is defined
as the work done by a force of one newton acting to move an object through a distance of
one meter in the direction in which the force is applied (1 J = 1 N·m). Therefore joule per
meter is equal to newton and, correspondingly, joule per centimeter is equal to 10
millinewtons.
gram-force
A gram-force (gf) , is a gravitational metric unit of force. It is equal to the force exerted
by one gram of mass in a standard gravitational field. Therefore, one gram-force is by
definition equal to 9.80665 mN. A gram-force is a convenient unit because its value is
equal to the weight of an object with a mass of 1 g and it is easy to imagine what is, e.g., a
100 gf force.
kilogram-force
A kilogram-force (kgf), also called kilopond (kp), is a gravitational metric unit of force.
It is equal to the force exerted by one kilogram of mass in a standard gravitational field.
Therefore, one kilogram-force is by definition equal to 9.80665 N. A kilogram-force is a
convenient unit because its value is equal to the weight of an object with a mass of 1 kg
and it is easy to imagine what is, e.g., a 10 kgf force.
ton-force (short)
A short ton-force (short tf), is a gravitational US Customary and British Imperial unit of
force. It is equal to the force exerted by one short ton of mass in a standard gravitational
field. One short ton-force is approximately equal to 8.896 kN.
ton-force (long)
A long ton-force (long tf), is a gravitational US Customary and British Imperial unit of
force. It is equal to the force exerted by one short ton of mass in a standard gravitational
field. One long ton-force is approximately equal to 9.964 kN.
ton-force (metric)
A metric ton-force (tf), is a gravitational metric unit of force. It is equal to the force
exerted by one metric ton of mass in a standard gravitational field. One metric ton-force is
approximately equal to 9.80665 kN.
kip-force
A kip or kip-force, or kilopound (kip, klb, kipf) is a non-SI non-metric unit of force. It
is equal to 1,000 pounds-force and used primarily by American architects and engineers
to measure engineering loads. 1 kip = 4448.22 newtons (N) = 4.44822 kilonewtons (kN).
The name kip comes from combining two words: “kilo” and “pound”. It is also called
kilopound-force.
kilopound-force
A kilopound-force, also called kip, kip-force (kip, klb, kipf) is a non-SI non-metric
unit of force. It is equal to 1,000 pounds-force and used primarily by American architects
and engineers to measure engineering loads. 1 kip = 4448.22 newtons (N) = 4.44822
kilonewtons (kN). The name kip comes from combining two words: “kilo” and “pound”
pound-force
A pound-force (lb, lbf) is a unit of force in some systems of measurement including
English engineering units and British gravitational units. It is equal to the force exerted by
one pound of mass in a standard gravitational field. 1 pound-force ≈ 4.44822 N.
ounce-force
An ounce-force is a unit of force in some systems of measurement including English
engineering units and British gravitational units. It is equal to the force exerted by one
ounce of mass in a standard gravitational field. 1 ounce-force = 1/16 lbf ≈ 0.27801 N.
poundal
A poundal (pdl) is a unit of force in the foot-pound-second (FPS) system of units and in
the British imperial units. It is defined as the force necessary to accelerate 1 pound-mass
at a rate of 1 foot per second per second. 1 pdl ≈ 0.13825 N. 1 pdl = 1 lb·ft/s².
pound foot/second²
A pound foot per second squared (lb·ft/s²) is a unit of force in the foot-pound-second
system of units and in the British imperial units. It is defined as the force necessary to
accelerate 1 pound-mass at a rate of 1 foot per second per second. 1 lb·ft/s² ≈ 0.13825 N.
Another name of this unit is the poundal (pdl).
pond
A pond (p) , also called or gram-force (gf), is an obsolete gravitational metric unit of
force. It is equal to the force exerted by one gram of mass in a standard gravitational field.
Therefore, one pond is by definition equal to 9.80665 mN.
kilopond
A kilopond (kp), also called kilogram-force (kgf), is an obsolete gravitational metric unit
of force. It is equal to the force exerted by one kilogram of mass in a standard
gravitational field. Therefore, one kilopond is by definition equal to 9.80665 N.
You might also like
- Me 214 HW Assignment #1 Page 1 Date: 01-05-'16 Name: Sid #Document14 pagesMe 214 HW Assignment #1 Page 1 Date: 01-05-'16 Name: Sid #Muhammad Usman Saifullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Physics (Newtons' Laws)Document12 pagesConceptual Physics (Newtons' Laws)Angeline Tan0% (1)
- M3 RFPDocument16 pagesM3 RFPflimarkNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire-Benchmarking of Best HR PracticesDocument13 pagesQuestionnaire-Benchmarking of Best HR PracticesUtkalKhatiwadaNo ratings yet
- Event Sustainability Management SystemsDocument24 pagesEvent Sustainability Management SystemsIbnu HassanNo ratings yet
- Utilities Relocation ProcedureDocument8 pagesUtilities Relocation Procedureshah1980100% (1)
- PHYSICS Newtons-1st-LawDocument52 pagesPHYSICS Newtons-1st-LawLago, Azel Chin L.No ratings yet
- Module - 1Document23 pagesModule - 1Daniel EscolanoNo ratings yet
- Module - 1Document23 pagesModule - 1Daniel EscolanoNo ratings yet
- GP 1 Module 4Document91 pagesGP 1 Module 4Raymund EspinoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1Document113 pagesThermodynamics 1Lloyd MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Manual Thermo IDocument124 pagesManual Thermo IJay-ar MohammadsaidNo ratings yet
- Physics CtuDocument72 pagesPhysics CtuMarc Liam LuNo ratings yet
- Newton (Unit) : Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument3 pagesNewton (Unit) : Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchR ContinueNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second Law of Motion - Force and AccelerationDocument31 pagesNewton's Second Law of Motion - Force and AccelerationJayhia Malaga JarlegaNo ratings yet
- General Science For WbcsDocument95 pagesGeneral Science For WbcsMITHUN CHATTERJEE100% (1)
- IJSO Part-8Document1 pageIJSO Part-8SadguruNo ratings yet
- 1 Force Stress IDocument13 pages1 Force Stress Iaravind grandhiNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument26 pagesForceShinji100% (1)
- 2858 Topper 21 110 2 4 322 2541 Newton S Laws of Motion Up201508051951 1438784483 8881Document4 pages2858 Topper 21 110 2 4 322 2541 Newton S Laws of Motion Up201508051951 1438784483 8881Ilaiya Maha LakshmiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 5 - Law of Motion - .Document36 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 5 - Law of Motion - .kaushikvanshika06No ratings yet
- Kilogram Force WikipediaDocument11 pagesKilogram Force Wikipediasharik shahNo ratings yet
- Applied - Physics - Notes 1Document248 pagesApplied - Physics - Notes 1Ashutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 0 Part 1Document28 pagesModule 0 Part 1Yoo JeongyeonNo ratings yet
- TJD UnitsAnalogDocument10 pagesTJD UnitsAnalogTheodore Bouras-SoulimasNo ratings yet
- GR 12 Physics Momentum-And-Impulse (Worksheet)Document21 pagesGR 12 Physics Momentum-And-Impulse (Worksheet)AN - 12BM 795510 Harold M Brathwaite SSNo ratings yet
- 05a MASS ACCELERATION AND WEIGHTDocument2 pages05a MASS ACCELERATION AND WEIGHTMohamed ShazlyNo ratings yet
- Edited Module1 ThermoDocument18 pagesEdited Module1 ThermoAnnaliza Alcazar ApostolNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws F MaDocument12 pagesNewtons Laws F MaMaruli AmbaritaNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws GR 10Document31 pagesNewtons Laws GR 10Jonathan ThomasNo ratings yet
- Physics CHP 3 (C)Document15 pagesPhysics CHP 3 (C)Omkar PawarNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion 1Document9 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion 1grantstuartwNo ratings yet
- What Is Kpag?: Table of ContentsDocument2 pagesWhat Is Kpag?: Table of Contentsangelito bernalNo ratings yet
- Manual Thermo IDocument121 pagesManual Thermo IKevin RamiroNo ratings yet
- Manual Thermo IDocument121 pagesManual Thermo IKevin RamiroNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Forces and MotionDocument88 pagesChapter - 3: Forces and MotionAlisha QaziNo ratings yet
- Joules To KGMDocument1 pageJoules To KGMchhakula07No ratings yet
- Newtonovi ZakoniDocument68 pagesNewtonovi ZakoniGoran MaliNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument3 pagesLaws of Motionryan valerioNo ratings yet
- Force, Work, Power & Energy (1) IcseDocument62 pagesForce, Work, Power & Energy (1) IcsesachiduthNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics I PDFDocument113 pagesThermodynamics I PDFdaniceNo ratings yet
- Newton'S Law of MotionDocument44 pagesNewton'S Law of MotionRussel SalvacionNo ratings yet
- Review Topic 1Document14 pagesReview Topic 1AlteaAlNo ratings yet
- Classical MechanicsDocument5 pagesClassical MechanicsFarjana KabirNo ratings yet
- Poundal: Absolute English Units Force PDLDocument3 pagesPoundal: Absolute English Units Force PDLLeandro VargasNo ratings yet
- Ancy C Simon Physical Science Optional Register Number-13971004Document20 pagesAncy C Simon Physical Science Optional Register Number-13971004Mark Jay BongolanNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument8 pagesDynamicsLaud FumhandaNo ratings yet
- CPC - 1 Chp. Lec.Document17 pagesCPC - 1 Chp. Lec.Latu BharaliNo ratings yet
- Study Plan - Brief Activation CE2Document15 pagesStudy Plan - Brief Activation CE2Hebrew TeacherNo ratings yet
- Notes - Force and Laws of MotionDocument4 pagesNotes - Force and Laws of Motionvaniak01028No ratings yet
- 3 Chapter 2A 19062023 051232pmDocument20 pages3 Chapter 2A 19062023 051232pmAbdullah ZamirNo ratings yet
- Force Equals Mass Times AccelerationDocument1 pageForce Equals Mass Times AccelerationDen EsicNo ratings yet
- What Is ForceDocument2 pagesWhat Is ForcevickyprabaNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Laws of MotinDocument32 pagesCH 5 Laws of MotinZeel ShahNo ratings yet
- LAWS OF MOTION - NOTES Grade 11Document47 pagesLAWS OF MOTION - NOTES Grade 11Zian100% (1)
- Force: Presented By: Jignasha PatelDocument36 pagesForce: Presented By: Jignasha PatelBhargavNo ratings yet
- 1.5 ForcesDocument25 pages1.5 ForcesEbrahimNo ratings yet
- PkemDocument42 pagesPkemGarcia RaphNo ratings yet
- Dynamics - ForcesDocument10 pagesDynamics - Forces333po2024No ratings yet
- Unit-1 10Document19 pagesUnit-1 10Murugesh RNo ratings yet
- Electrical BasicSDocument77 pagesElectrical BasicSsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Momentum, Change of Momentum, Angular Momentum, Impulse: BUS 1303 BY Dr. Md. Nurul Islam SiddiqueDocument11 pagesMomentum, Change of Momentum, Angular Momentum, Impulse: BUS 1303 BY Dr. Md. Nurul Islam SiddiqueAlia AtikahNo ratings yet
- T2.2B Newton 1st - StudentDocument28 pagesT2.2B Newton 1st - StudentYiesun KimNo ratings yet
- 3 ConcreteWorksDocument19 pages3 ConcreteWorksMuhammad AgungNo ratings yet
- Air Filter Media VNF 300Document2 pagesAir Filter Media VNF 300roariza75No ratings yet
- 2012 11 Full Paper BROESDER Coatings-And-cathodic-disbondmentDocument7 pages2012 11 Full Paper BROESDER Coatings-And-cathodic-disbondmentkakrasana100% (1)
- A17EU Rev 17 FAA PDFDocument26 pagesA17EU Rev 17 FAA PDFRoger EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Tac Doc 01 2 Issue 2 Rev 0 Information Package Latest As Registered With TecsDocument17 pagesTac Doc 01 2 Issue 2 Rev 0 Information Package Latest As Registered With TecsWildan Amar ZainNo ratings yet
- QuickRide LogcatDocument123 pagesQuickRide LogcatSubhadra YNo ratings yet
- Wartung Assyst Plus 204 enDocument32 pagesWartung Assyst Plus 204 enKent Wai100% (1)
- GC 2024 05 12Document13 pagesGC 2024 05 12brionesmaricela893No ratings yet
- SDCCHDocument82 pagesSDCCHVenu MadhavNo ratings yet
- AS9120 AQMS Auditor Application User GuideDocument11 pagesAS9120 AQMS Auditor Application User GuideBenjamin GalvezNo ratings yet
- All About StylesDocument12 pagesAll About StylesMoultrie CreekNo ratings yet
- Boeing Magazine AERO - Q307Document32 pagesBoeing Magazine AERO - Q307harry_n75% (4)
- What Coolant Does & Different Types of CoolantDocument2 pagesWhat Coolant Does & Different Types of CoolantsupljinaNo ratings yet
- NEMA Frame AssignmentsDocument3 pagesNEMA Frame AssignmentsGustavo CuatzoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Object-Relational Databases: Course: Object-Oriented Database Effective Period: September 2015Document35 pagesIntroduction To Object-Relational Databases: Course: Object-Oriented Database Effective Period: September 2015Prima ApriastikaNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Test Report: Calibration Test Report - Pressure Gauge SATR-A-2002 22-Jan-18 MechDocument2 pagesSaudi Aramco Test Report: Calibration Test Report - Pressure Gauge SATR-A-2002 22-Jan-18 MechaneeshNo ratings yet
- .Platform-Independent Customizable UART Soft-CoreDocument3 pages.Platform-Independent Customizable UART Soft-CoreRanjan NayakNo ratings yet
- Packaging Dielines Booklet For DesignersDocument240 pagesPackaging Dielines Booklet For DesignersMartin CvetanovskiNo ratings yet
- SQL With TADOQueryDocument3 pagesSQL With TADOQueryMarcel ChisNo ratings yet
- Pacer WB-67 HydrantDocument6 pagesPacer WB-67 HydrantullalvasuNo ratings yet
- GeneralDocument12 pagesGeneralLokesh NarasimhaiahNo ratings yet
- Power Cable DatasheetDocument16 pagesPower Cable DatasheetYosses Sang NahkodaNo ratings yet
- Exam MtcreDocument31 pagesExam Mtcreirfanmaulana20No ratings yet
- Medidor CAudal Seametrics AG2000 - 2Document4 pagesMedidor CAudal Seametrics AG2000 - 2Marcos Aldana VillaldaNo ratings yet
- Express Me M DataDocument98 pagesExpress Me M DataMartin Miguel Parody NarvaezNo ratings yet
- U1Document85 pagesU1bhijNo ratings yet