Professional Documents
Culture Documents
E Mpe A L/K B e Mpe A L/K e Mpe B
Uploaded by
Zakaria MuhammadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
E Mpe A L/K B e Mpe A L/K e Mpe B
Uploaded by
Zakaria MuhammadCopyright:
Available Formats
Performance Assessment Method of Coordinate Measuring Machines
Regarding the performance assessment method of CMM, a revision of ISO Table 1 ISO 10360 series
10360 series was issued in 2003, and was partially revised in 2009. Item ISO Standard No. Year of issue
The following describes the standard inspection method including the revised 1 Terms ISO 10360-1:2000 2002
content. 2 Length measurement* ISO 10360-2:2001 2001 PG
3 Rotary table equipped CMM ISO 10360-3:2000 2000 67
4 Scanning measurement ISO 10360-4:2000 2000
5 Single/Multi-styli measurement** ISO 10360-5:2002 2002
6 Software inspection ISO 10360-6:2001 2001
* Revised in 2009 **Revised in 2010
Maximum permissible length measurement error E0,MPE [ISO 10360-2:2009]
Using the standard CMM with specified probe, measure 5 different calibrated Length meas. error 3(Z)
Length meas. error 5 Length meas. error 4
lengths 3 times each in 7 directions within the measuring volume (as indicated
in Figure 1), making a total of 105 measurements. Length meas. error 6 Length meas. error 7
If these measurement results, including the allowance for the uncertainty of Length meas. error 2(Y)
measurement, are equal to or less than the values specified by the manufac- Z Z
turer, then it proves that the performance of the CMM meets its specification. Y Y
The result of OK/NG is required to be judged considering the uncertainties. X X
The maximum permissible error (standard value) of the test may be expressed Length meas. error 1(X)
in any of the following three forms (unit: µm). Figure 1 Measuring directions to obtain length measurement error
E 0,MPE(MPEE)= A + L/K ≦ B
A: Constant (µm) specified by the manufacturer
E 0,MPE(MPEE)= A + L/K K: Dimensionless constant specified by the manufacturer
E 0,MPE(MPEE)= B L: Measured length (mm)
B: Upper limit value (µm) specified by the manufacturer
* ISO 10360-2:2009 specifies measurement in 4 different directions as essential and recommends measurement parallel to each axis, while ISO
10360-2:2001 specified the measurement "in arbitrary 7 directions."
The following error definitions were added in ISO 10360-2:2009.
Maximum Permissible Length Measurement Error / Length Measurement Error when
Z-axis stylus offset is 150mm E150, MPE [ISO 10360-2:2009]
In addition to length measurement in 7 directions, ISO 10360-2:2009 specifies
measuring in 2 lines over the diagonal YZ or XZ plane with probe offset.
Note: The stylus offset is set at 150mm as default.
150mm
Z
Z
Y X or Y軸
X
Figure 2 Length measurement error when Z-axis stylus offset is 150mm
Maximum Permissible Limit in Repetitive Length Measurements R0, MPL [ISO 10360-2:2009]
Maximum Permissible Limit in Repetitive Length Measurements R0, MPL [ISO 10360-2:2009] 6.0
After measuring the given length 3 times, evaluate variation in measurement results. Then, 4.0
Error[µm]
calculate the repeatability range R0. 2.0
0.0 R0
-2.0
-4.0
1 2 3 Standard value
-6.0
0 200 400 600 800
Measurement length [mm]
Figure 3 Repeating range of length measurement
Maximum Permissible Rotation Axis Radial-Direction Error MPE FR,
Maximum Permissible Rotation Axis Connecting-Direction Error MPE FT, and Sphere B
Z
Maximum Permissible Rotation Axis Axial-Direction Error MPE FA [ISO 10360-3:2000] Y
hB
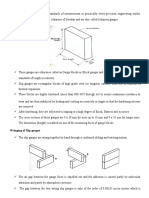
The test procedure under this standard is to place two standard spheres on the rotary table as shown in Figure 4.
r
Rotate the rotary table to a total of 15 positions including 0˚, 7 positions in the plus (+) direction, and 7 positions in the X
minus (-) direction and measure the center coordinates of the two spheres in each position. Then, add the uncertainty h
Sphere A
of the standard sphere shape to each variation (range) of radial direction elements, connecting direction elements, and hA
rotational axis direction elements of the two standard sphere center coordinates. If these calculated values are less than
the specified values, the evaluation test is passed.
Figure 4 Evaluation of a CMM with a rotary table
Quick Guide to Measurement
You might also like
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringFrom EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Meditation On God's WordDocument26 pagesMeditation On God's WordBeghin BoseNo ratings yet
- Measure Uncertainity in Torque WrenchDocument11 pagesMeasure Uncertainity in Torque WrenchAnonymous uXdS9Y7100% (2)
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisFrom EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Laser Trackers: Testing and StandardsDocument34 pagesLaser Trackers: Testing and StandardsJDNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Conducting A Systematic Literature Review ofDocument51 pagesA Guide To Conducting A Systematic Literature Review ofDarryl WallaceNo ratings yet
- Ahu & Chiller OkDocument40 pagesAhu & Chiller OkAndy DwiNo ratings yet
- DB2 UsefullcommandDocument8 pagesDB2 Usefullcommandganeshreddy_dspxNo ratings yet
- Fujifilm X-T3: Pocket Guide: Buttons, Dials, Settings, Modes, and Shooting TipsFrom EverandFujifilm X-T3: Pocket Guide: Buttons, Dials, Settings, Modes, and Shooting TipsNo ratings yet
- ISO-TC135-SC5 N0220 New Standards On Digital Industrial RadiologyDocument52 pagesISO-TC135-SC5 N0220 New Standards On Digital Industrial RadiologyHappy2021No ratings yet
- Acceptance and Re-Verification Tests For Coordinate Measuring MachinesDocument16 pagesAcceptance and Re-Verification Tests For Coordinate Measuring MachinesMohamed Khalifa100% (1)
- Din en Iso 10360-9 - 2014-04Document26 pagesDin en Iso 10360-9 - 2014-04gviola1405No ratings yet
- Iso 21670 2003 PDFDocument9 pagesIso 21670 2003 PDFGiuseppeNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second LawDocument3 pagesNewton's Second LawBHAGWAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Mitutoyo CMMDocument26 pagesMitutoyo CMMSniderNo ratings yet
- Din 862Document4 pagesDin 862068999100% (1)
- Click Here For Download: (PDF) HerDocument2 pagesClick Here For Download: (PDF) HerJerahm Flancia0% (1)
- International Standard: Metallic Materials - Brinell Hardness TestDocument8 pagesInternational Standard: Metallic Materials - Brinell Hardness TestFilipe AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Comparison ISO 10360-2 To ASME B89.4.1Document15 pagesComparison ISO 10360-2 To ASME B89.4.1Zakaria MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Lines & SurfacesDocument84 pagesMeasurement of Lines & Surfacessushil.vgiNo ratings yet
- Process Plant Layout - Becoming A Lost ArtDocument7 pagesProcess Plant Layout - Becoming A Lost ArtRajendraNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 201354 September 21, 2016Document11 pagesG.R. No. 201354 September 21, 2016Winston YutaNo ratings yet
- Mitutoyo CMM Accuracy StatementsDocument14 pagesMitutoyo CMM Accuracy StatementsAryanNo ratings yet
- Standard Incercari MecaniceDocument35 pagesStandard Incercari Mecanicenicolicescu_claudiu5152No ratings yet
- Purpose List of Machines and Equipment in Test Floor LabDocument10 pagesPurpose List of Machines and Equipment in Test Floor LabAsfand KhalidNo ratings yet
- Technology of Precision Callibration of Electro Optical Rangefinders Using Laboratory Methods and Field Test BaselineDocument13 pagesTechnology of Precision Callibration of Electro Optical Rangefinders Using Laboratory Methods and Field Test BaselineSarmad BarwaryNo ratings yet
- Proposed New Tests For Evaluating CMM PerformanceDocument6 pagesProposed New Tests For Evaluating CMM PerformanceharipachanNo ratings yet
- Index: Ex. No Name of The Experiment Page No. Cycle IDocument29 pagesIndex: Ex. No Name of The Experiment Page No. Cycle Iprakashrs295No ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Nivel de Precision Topcon AT-G-1-2-3-4-7NDocument4 pagesFicha Tecnica Nivel de Precision Topcon AT-G-1-2-3-4-7NHeris Mauricio Gonzalez LosadaNo ratings yet
- Haze Meter 3color® HM-300 SeriesDocument4 pagesHaze Meter 3color® HM-300 SeriesbugajonesNo ratings yet
- Checking The Geometrik AccuracyDocument6 pagesChecking The Geometrik AccuracyCatalyst IchsanNo ratings yet
- Calibration PDFDocument20 pagesCalibration PDFHakim HakimNo ratings yet
- IDM Lab3Document9 pagesIDM Lab3gudursrinath11No ratings yet
- Metrology and Measurements Lab Manual: V Semester Mechanical Engineering Rajalakshmi Engineering CollegeDocument30 pagesMetrology and Measurements Lab Manual: V Semester Mechanical Engineering Rajalakshmi Engineering CollegeSanju JohnNo ratings yet
- Mds Acousticork U32 enDocument4 pagesMds Acousticork U32 enahmadNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document4 pagesModule 4sathiaNo ratings yet
- Iso 5768 1998Document8 pagesIso 5768 1998Jonas FrykbergNo ratings yet
- Iso 9969 2007 Determining The Ring Stiffness ValueDocument14 pagesIso 9969 2007 Determining The Ring Stiffness ValueMICHAEL SCOTTY100% (1)
- Size (MM) Increment (MM) No. of Pieces: Total 88Document5 pagesSize (MM) Increment (MM) No. of Pieces: Total 88Omar GamalNo ratings yet
- ME2308 Lab ManualDocument28 pagesME2308 Lab Manualvenkateshyadav2116No ratings yet
- Testo 470 PDFDocument2 pagesTesto 470 PDFZankar R ParikhNo ratings yet
- Ch-25 Measurement of Lines - SurfacesDocument92 pagesCh-25 Measurement of Lines - SurfacesManojNo ratings yet
- NDT Laboratory No04 New USM36Document5 pagesNDT Laboratory No04 New USM36Miruna ClinciuNo ratings yet
- Torsion Spring Testing MachineDocument1 pageTorsion Spring Testing MachineArun MurthyNo ratings yet
- Ballscrew Selection 1.1Document25 pagesBallscrew Selection 1.1Абдельнасир АбдельрахманNo ratings yet
- Iso 09969-2016Document14 pagesIso 09969-2016phamngochaocd09aNo ratings yet
- MME-ME2308 EMM Lab ManualDocument29 pagesMME-ME2308 EMM Lab ManualRakesh Kumar100% (1)
- IDM Lab1Document5 pagesIDM Lab1gudursrinath11No ratings yet
- IsoDocument8 pagesIsochandramohanNo ratings yet
- Specification FOR External Micrometer: MarchDocument6 pagesSpecification FOR External Micrometer: MarchAnirban DasNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Metrology Lab ManualDocument29 pagesMeasurement and Metrology Lab ManualVINITNo ratings yet
- Praktikum 2 Perawatan MS - Modul 4 - ISO & Bearing - Virtual PracticumDocument8 pagesPraktikum 2 Perawatan MS - Modul 4 - ISO & Bearing - Virtual Practicumyohanes alvinNo ratings yet
- Ds Lc15dx enDocument3 pagesDs Lc15dx enradule021No ratings yet
- Sensor Fuerza Torque Spec Sheet 90M40x3 SIDocument1 pageSensor Fuerza Torque Spec Sheet 90M40x3 SISAN JUAN BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Vibrationsmessungen An Motor Und GeneratorDocument1 pageVibrationsmessungen An Motor Und GeneratorDjoko PurnomoNo ratings yet
- AN521 StepHgtRep 04304Document2 pagesAN521 StepHgtRep 04304huffingtonpost12No ratings yet
- 3179 1990 Reff2020Document6 pages3179 1990 Reff2020Anirban DasNo ratings yet
- Traceable Roughness of ProductsDocument7 pagesTraceable Roughness of ProductsSaraswantoNo ratings yet
- 50RX BrochureDocument2 pages50RX BrochureCristian ComanNo ratings yet
- Mitutoyo - Mikroskopy Pomiarowe MF I MF-U - E14003 (3) - 2015 ENDocument48 pagesMitutoyo - Mikroskopy Pomiarowe MF I MF-U - E14003 (3) - 2015 END.T.No ratings yet
- FF Met ManualDocument29 pagesFF Met ManualHitendra SinghNo ratings yet
- A301 - EN MethodDocument1 pageA301 - EN MethodAhmad ElghazolyNo ratings yet
- L22-51 Sistemas M Meril Cal MK ApprovalDocument8 pagesL22-51 Sistemas M Meril Cal MK ApprovalIsaacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Review QuestionsSouthernGurl99No ratings yet
- IC HDL Lab ManualDocument82 pagesIC HDL Lab ManualRakshitha AngelNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Division of Bohol Department of Education Region VII, Central VisayasDocument12 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Division of Bohol Department of Education Region VII, Central VisayasCecille HernandoNo ratings yet
- Impulsive Buying PDFDocument146 pagesImpulsive Buying PDFrukwavuNo ratings yet
- 280-Article Text-1201-1-10-20220426Document8 pages280-Article Text-1201-1-10-20220426Ayu Ratri PNo ratings yet
- Fraud Best PracticeDocument35 pagesFraud Best PracticeIkhwanNo ratings yet
- WhatsApp Chat With MiniSoDocument28 pagesWhatsApp Chat With MiniSoShivam KumarNo ratings yet
- La FolianotesDocument4 pagesLa Folianoteslamond4100% (1)
- Resume - General Manager - Mohit - IIM BDocument3 pagesResume - General Manager - Mohit - IIM BBrexa ManagementNo ratings yet
- Physical Education 10 WEEK 2Document10 pagesPhysical Education 10 WEEK 2Israel MarquezNo ratings yet
- JKSSB Panchayat Secretary Adfar NabiDocument3 pagesJKSSB Panchayat Secretary Adfar NabiSHEIKHXUNINo ratings yet
- Communist Party of India - WikipediaDocument104 pagesCommunist Party of India - WikipediaRameshwar ChandravanshiNo ratings yet
- Fernando Pessoa LectureDocument20 pagesFernando Pessoa LecturerodrigoaxavierNo ratings yet
- BTCTL 17Document5 pagesBTCTL 17Alvin BenaventeNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2022 - HeyJobsDocument6 pagesCase Study 2022 - HeyJobsericka.rolim8715No ratings yet
- Effect of Boron Content On Hot Ductility and Hot Cracking TIG 316L SSDocument10 pagesEffect of Boron Content On Hot Ductility and Hot Cracking TIG 316L SSafnene1No ratings yet
- Literacy Block Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLiteracy Block Lesson Planapi-286592038No ratings yet
- 07.03.09 Chest PhysiotherapyDocument10 pages07.03.09 Chest PhysiotherapyMuhammad Fuad MahfudNo ratings yet
- Lee. Building Balanced Scorecard With SWOT Analysis, and Implementing "Sun Tzu's The Art of Business Management Strategies" On QFD Methodology PDFDocument13 pagesLee. Building Balanced Scorecard With SWOT Analysis, and Implementing "Sun Tzu's The Art of Business Management Strategies" On QFD Methodology PDFSekar Ayu ParamitaNo ratings yet
- CaseDocument2 pagesCaseKimi Walia0% (2)
- Hussain Kapadawala 1Document56 pagesHussain Kapadawala 1hussainkapda7276No ratings yet
- The Cave Tab With Lyrics by Mumford and Sons Guitar TabDocument2 pagesThe Cave Tab With Lyrics by Mumford and Sons Guitar TabMassimiliano MalerbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Scheduling AlgorithmDocument42 pagesChapter 6 - Scheduling AlgorithmBinyam KebedeNo ratings yet