Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Envi Sci Report
Uploaded by
Myra Dionela Soriano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views4 pagesEnvi sci report
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEnvi sci report
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views4 pagesEnvi Sci Report
Uploaded by
Myra Dionela SorianoEnvi sci report
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
-Fossil Fuels take so long to form, they are essentially non-renewable
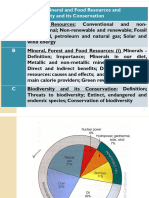
Chapter 12: Energy resources.
*Coal (solid)
Energy Sources and Uses
*Petroleum (liquid)
Being able to utilize external energy to do useful work is one of
*Natural Gas (Gas)
the most unique characteristics of human.
*Oil Shale and Tar Sands (Semisolid tars trap in rocks)
Current Energy Uses
Coal- are vast, ten times greater than conventional oil and gas resources
Fossil fuels (petroleum, natural gas, and coal)
combined.
-now provide about 86% of all commercial energy in the world.
- Comes in a variety of forms with varying chemical composition,
Renewable sources (solar, wind, geothermal and hydroelectricity)
harness and energy content.
-make up about 9.5% of our commercial power.
- Lignite- the softest of this family, is not much more concentrated
In many poorer countries, such as Haiti, Bhutan and Malawi,
than peat and has about 4,000 BTU/lb.
biomass supplies more than 90% of the energy used for heating
- Subbituminous and bituminous coal- have energy contents between
and cooking. --> (forest destruction)
8,000 and 15,000 BTU/lb and generally have 1 to 5 percent sulphur
Nuclear Power- makes up about 20% of all electric power in more-
content.
developed countries, and has the benefit of not contributing to global
- Anthracite- the hardest coal, can be 96 percent carbon and have
warming.
Energy Consumption: U.S.A. Compared to the Philippines
more than 15,000 BTU/lb.
U.S.A. Ratio Philippines Oil- is estimated to be about 4 trillion bbl (600 billion metric tons), half
Population: 302 million 3:1 89 million of which is thought to be ultimately recoverable.
(2007) - Largest supply of proven-in-place oil is in Saudi Arabia, which has 250
Energy Consumption: 17,260 77:1 223 billion bbl, about one-fourth of the total proven world reserve.
(million barrels - Like coal, petroleum often contains high sulfur levels. Because it is
of oil equivalent) highly corrosive.
Energy Per Capita: 57.2 23:1 2.5
- Oil is used primarily for transportation and heating.
(barrels of oil
equivalent per person) - Oil drilling is far less destructive to the earth’s surface than coal
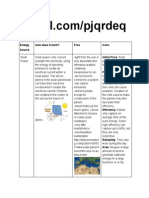
Natural Gas is our most efficient fuel. mining, but the huge amounts of oil shipped around the world and
FOSSIL FUELS- are organic chemicals created by living organisms million used as lubricants and fuels result in very serious soil and water
years ago and buried in sediments, where high pressures and pollution.
temperatures concentrated and transformed them into energy-rich Tar Sands- are composed of sand and shale particles coated with
compounds. bitumen.
- Shallow tar sands- are excavated and mixed with hot water and ENERGY CONSERVATION- one of the best ways to avoid energy
steam to extract the bitumen, then fractioned to make new products. shortages and to relieve environment and health effects of our current
Oil shales- are fine-grained sedimentary rock rich in solid organic energy technologies is simply to use less.
material called kerogen. Like tar sands, kerogen can be heated, Using energy more efficiently- much of the energy we consume is
liquefied, and pumped out like liquid crude oil. wasted.
Natural gas- is the world’s third largest commercial fuel, making up 23% -Reducing air infiltration is usually the cheapest, quickest, and most
of global energy consumption. effective way of saving energy because it is the largest source of losses
- large amounts of methane are released from coal deposits. in a typical house.
NUCLEAR POWER - one of the most direct and immediate ways that individuals can save
- In 1953 President Dwight Eisenhower announced that the US would energy is to turn off appliances.
build nuclear-powered electrical generators to provide clean, abundant Cogeneration- one of the fastest growing sources of new energy, the
energy. Technology and engineering would tame the evil genie of atomic simultaneous production of both electricity and steam or hot water in
energy and use its enormous power to do useful work. the same plant.
-nuclear power industry has been campaigning for greater acceptance, -by 1970s, cogeneration had fallen to less than 5% of our power
arguing that reactors don’t release greenhouse gases that cause global supplies, but interest in this technology is being renewed.
warming. SOLAR ENERGY
-the greatest danger in one of the complex machines is a cooling system -the sun is a giant nuclear furnace in space, constantly bathing our
failure. If the pumps fail or pipes break during operation, the nuclear planet with a free energy supply. Solar heat drives winds and the
fuel quickly overheats, and a “meltdown” can result that releases deadly hydrologic cycle.
radioactive material. -all biomass, as well as fossil fuels and our food, results from conversion
-`70% of the world’s nuclear power plants are pressurized water of light energy(photons) into chemical bond energy by photosynthetic
reactors (PWR). bacteria, algae and plants.
-one of the most difficult problems associated with nuclear power is the Passive Solar Heat- our simplest and oldest use of solar energy, using
disposal of wastes produced during mining, fuel production, and reactor natural materials or absorptive structures with no moving parts to
operation. simply gather and hold heat.
- some nuclear experts believe that monitored, retrievable storage -a built of thick-walled stone and adobe dwellings that slowly collect
would be a much better way to handle wastes. This method involves heat during the day and gradually release it at night and maintain a
holding wastes in underground mines or secure surface facilities where comfortable daytime temperature within the house, even as they
they can be watched. absorb external warmth glass-walled “sunspace,” or greenhouse in
modern time.
-Trombe wall- an interior, heating absorbing wall is an effective passive Transporting and Storing Electrical Energy
heat collector. Electrical energy is difficult and expensive to store or to transport over
Active Solar Heat- generally pump a heat-absorbing fluid medium(air, long distance, to depend on solar, wind, or other renewable energy
water, or an antifreeze solution) through a relatively small collector, sources may need many more high-voltage power lines to transport
rather than passively collecting heat in a stationary medium, such as electricity to distant markets.
masonry. Storage is a problem for photovoltaic generation as well as other
-active collectors can be located adjacent to or on top of buildings, sources of electric power.
rather than being built into the structure. Traditional lead-acid batteries- can store only moderate amounts of
-a flat, black surface sealed with a double layer of glass makes a good energy per unit mass or volume. (acid from batteries are hazardous)
solar collector. Pumped-hydro storage- involves pumping water to an elevated
High-Temperature Solar Energy reservoir at times when excess electricity is available.
-Parabolic mirrors are curved reflecting surfaces that collect light and Flywheels- are also the subject of current experimentation for energy
focus it into a concentrated point. storage.
-we haven’t had enough experience with these facilities to know how Promoting Renewable Energy
reliable the mirrors, motors, heat absorbers, and other equipment will 1. “distributional surcharges” in which a small per kilowatt-hour
be over the long run. charge is levied on all utility customers to help finance renewable
Photovoltaic Energy energy research and development,
-offers an exciting potential for capturing solar energy in a way that will 2. “renewable portfolio” standards to require power suppliers to
provide clean, versatile, renewable energy. This simple device has no obtain a minimum percentage of their energy from sustainable
moving parts and negligible maintenance costs, produces no pollution, sources, and
and has a lifetime equal to that of a conventional fossil fuel or nuclear 3. Green pricing that allows utilities to profit from conservation
power plant. programs and charge premium prices for energy from renewable
-the photovoltaic effect, which is the basis of these devices, was first sources.
observed in 1839 by French physicist Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel, who FUEL CELLS
also discovered radioactivity. -are devices that use ongoing electrochemical reactions to produce an
-one of the most promising developments in photovoltaic cell electrical current. They are very similar to batteries except that, rather
technology in recent years is the invention of amorphous silicon than recharging them with an electrical current, you add more fuel for
collectors.--> noncrystalline silicon semiconductors can be made into the chemical reaction.
lightweight, paper-thin sheets that require much less material than -all fuel cells consist of a positive electrode (the cathode) and a
conventional photovoltaic cells. They are vastly cheaper to manufacture negative electrode (the anode) separated by an electrolyte, a material
and can be made in variety of shapes and sizes. that allows the passage of charged atoms, called ions.
-fuel cells provide direct-current electricity as long as they are supplied -much of the hydropower development in recent years has been
with hydrogen and oxygen and produces no waste product except in enormous dams.
drinkable water and radiant heat.—far less pollutants. -in tropical climates, large reservoirs often suffer enormous water
BIOMASS losses.
Dung and Methane as Fuels Wind Energy
- where wood and other fuels are in short supply, people often dry and -like solar power, hydropower, wind power taps a natural physical
burn animal manure.-dung force.
-Methane gas, the main component of natural gas, is produced by -like solar power, wind power is an abundant, non-polluting
anaerobic decomposition of any moist organic material. resource, and it causes minimal environmental disruption but also
-burning methane produced from manure provides more heat than the it requires expensive storage during peak production times to
dung itself, and the sludge left over from bacterial digestion is a rich offset non-windy periods.
fertilizer, containing bacterial biomass as well as most of the nutrients -wind farms are large concentrations of wind generators
originally in the dung. producing commercial electricity.
-methane is a clean fuel that burns efficiently produced in a low- -The 1978 Public Utilities Regulatory Policies Act required utilities
technology, low-capital process from any kind of organic material: to buy power generated by small hydro, wind, cogeneration, and
livestock manure, kitchen and garden scraps, and even municipal other privately owned technologies at a fair price.
garbage and sewage. Geothermal, Tidal, and Wave Energy
Fuels from Biomass -while few places have geothermal steam, the earth’s warmth can
-Ethanol (grain alcohol) and methanol (wood alcohol) are produced by help reduce energy costs nearly everywhere. Pumping water
anaerobic digestion of plant materials with high sugar content, mainly through deeply buried pipes can extract enough heat so that a
grain and sugarcane. heat pump will operate more efficiently.
-gasohol- a mixture of gasoline and ethanol -Ocean tides and waves contain enormous amounts of energy
ENERGY FROM THE EARTH’S FORCES that can be harnessed to do useful work.
-the winds, waves, tides, ocean thermal gradients, and geothermal areas -a tidal station works like a hydropower dam, with its turbines
are renewable energy sources. spinning as the tide flows through them.
Hydropower -Ocean wave energy can easily be seen and felt on any seashore.
-falling water has been used as an energy source since ancient The energy that waves expend as millions of tons of water are
times. The invention of water turbines in the 19th century greatly picked up and hurled against the land, over and over, day after
increased the efficiency of hydropower dams. day, can far exceed the combined energy for both insolation (solar
-the total world potential for hydropower is estimated to be energy) and wind power in localized areas.
about 3 million MW.
You might also like
- Unit 6Document6 pagesUnit 6Ernie CoachNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 and 16 Enviro SciDocument4 pagesChapter 15 and 16 Enviro SciAnonymous oTtlhPNo ratings yet
- Renewable EnergyDocument35 pagesRenewable EnergyEngr Abubakar AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2 Energy Sustainability and EnvironmentDocument40 pages2 Energy Sustainability and Environmentsittieaysah02No ratings yet
- Diosdado Macapagal BLVD, Pasay, Philippines College of NursingDocument8 pagesDiosdado Macapagal BLVD, Pasay, Philippines College of NursingSkyeNo ratings yet
- Altenative Energy SourcesDocument21 pagesAltenative Energy SourceshetveedesaiNo ratings yet
- (Chemistry) Fuel and CementDocument73 pages(Chemistry) Fuel and CementAshutosh TripathyNo ratings yet
- Envi Sci ReviewerDocument10 pagesEnvi Sci Reviewerkilla WestNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument78 pagesSolar EnergySai VikasNo ratings yet
- Alternate Source For Fossil FuelDocument6 pagesAlternate Source For Fossil FuelHari Hara Sudhan KaliappanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies (U-5)Document91 pagesEnvironmental Studies (U-5)aryavats2005No ratings yet
- Ib DP Ess Unit 7 NotesDocument8 pagesIb DP Ess Unit 7 NotesAnnaya Rangkuty0% (1)
- Sources of EnergyDocument38 pagesSources of EnergyAtulya MishraNo ratings yet
- Geography Project: NAME: Aritra Dey CLASS: 10 Section: A1 Roll Number: B/206/2011 Project Topic: Energy ResourcesDocument7 pagesGeography Project: NAME: Aritra Dey CLASS: 10 Section: A1 Roll Number: B/206/2011 Project Topic: Energy ResourcesAritra DeyNo ratings yet
- ENV 107 Alternative Energy ResourcesDocument41 pagesENV 107 Alternative Energy Resourcesshaanrahman1459No ratings yet
- Energy Fuels Report 20178Document50 pagesEnergy Fuels Report 20178Mariane BraganzaNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To Energy ScienceDocument42 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Energy ScienceNishita Waghmare50% (2)
- UNIT-1 Energy Sources: Energy Source Can Be Divided Into 3-TypesDocument17 pagesUNIT-1 Energy Sources: Energy Source Can Be Divided Into 3-TypesSuprava GhoshPaulNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument16 pagesEnergy ResourcesBhaskar TiwariNo ratings yet
- Availibilty of ResourcesDocument34 pagesAvailibilty of Resourcespreeti sahuNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - M02 - L02 - WEEK 4Document5 pagesEarth Science - M02 - L02 - WEEK 4Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - M02 - L02 - L03 - WEEK 4Document9 pagesEarth Science - M02 - L02 - L03 - WEEK 4Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Energy and Environment - SEM 3 - RRGU - Part 1Document14 pagesEnergy and Environment - SEM 3 - RRGU - Part 1Simran NandiNo ratings yet
- Energy: Dr. Md. Sirajul IslamDocument35 pagesEnergy: Dr. Md. Sirajul IslamMstJahanaraKhanamNo ratings yet
- Energy Sources JustificationDocument13 pagesEnergy Sources Justificationapi-272862164No ratings yet
- Advantage and DisadvantegesDocument16 pagesAdvantage and DisadvantegesÃví MãddýNo ratings yet
- Apes Quiz Revision Unit 6Document9 pagesApes Quiz Revision Unit 61264No ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument45 pagesEnergy ResourcesLevi LeviNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Energy Resources-Conventional Energy-SBSDocument21 pagesUNIT 2 Energy Resources-Conventional Energy-SBSpranavchoubey89No ratings yet
- Class 10th Source of Energy NotesDocument12 pagesClass 10th Source of Energy NotesAnkitJugranNo ratings yet
- Final Sci 01Document3 pagesFinal Sci 01jaymel gabrielle escasinasNo ratings yet
- Sources of Energy: Chapter - 14Document9 pagesSources of Energy: Chapter - 14milind dhamaniyaNo ratings yet
- Non Renewable Resources: Presented By: Chetan Chauhan Deepak Singh Deepanshu Soni Devashish GiriDocument32 pagesNon Renewable Resources: Presented By: Chetan Chauhan Deepak Singh Deepanshu Soni Devashish GiriDeepak RajputNo ratings yet
- Renewable Non Renewable Energy Resources 110308030738 Phpapp02Document53 pagesRenewable Non Renewable Energy Resources 110308030738 Phpapp02ieykahNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument92 pagesIlovepdf MergedFiras 01No ratings yet
- Sources of EnergyDocument11 pagesSources of EnergyHVBCBMNZNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Energy Resourses and UtilizationDocument40 pagesLecture 2-Energy Resourses and UtilizationsamwelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Study MaterialDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Study MaterialNayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Oil & Gas ConsumptionDocument35 pagesOil & Gas ConsumptionSuleiman BaruniNo ratings yet
- 20bscagh065 Siddharth ChakrabortyDocument21 pages20bscagh065 Siddharth ChakrabortySiddharth ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- RenewableDocument273 pagesRenewableAjith AchuthaNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuel: " The Fuels of The Past & The Fuels For The Future "Document39 pagesFossil Fuel: " The Fuels of The Past & The Fuels For The Future "thomasNo ratings yet
- Caie A2 Level Geography 9696 Advanced Human Geography v1Document29 pagesCaie A2 Level Geography 9696 Advanced Human Geography v1j53846004No ratings yet
- Day 12-Non Conventional Energy-Final - 2021Document41 pagesDay 12-Non Conventional Energy-Final - 2021Kashish Manish JariwalaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science S-WPS OfficeDocument14 pagesEarth Science S-WPS OfficeBai Johaira BenitoNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument19 pagesElectricityAdie Alie PumpNo ratings yet
- EE 8703 - RES - Unit - 1 PDFDocument68 pagesEE 8703 - RES - Unit - 1 PDFSuryaNo ratings yet
- PIKE Renewable Energy 2014-2015Document76 pagesPIKE Renewable Energy 2014-2015AdistiNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Environmental ManagementDocument21 pagesAssignment On Environmental Managementtabz786No ratings yet
- Bahir Dar UniversityDocument37 pagesBahir Dar UniversityBirhanu GirmaNo ratings yet
- Unit VI. Fossil Fuels and Nuclear EnergyDocument70 pagesUnit VI. Fossil Fuels and Nuclear EnergyPatricia Sofia DizonNo ratings yet
- PPE Lect 1Document19 pagesPPE Lect 1A ZNo ratings yet
- Energy Source How Does It Work? Pros ConsDocument12 pagesEnergy Source How Does It Work? Pros Consapi-272560904No ratings yet
- Me 496 Renewable Energy Assignment - 1: Aben PAUL 17301270Document5 pagesMe 496 Renewable Energy Assignment - 1: Aben PAUL 17301270Chrionny AlumediNo ratings yet
- How Different Forms of Energy Are HarnessedDocument6 pagesHow Different Forms of Energy Are HarnessedMary JuntillaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument10 pagesNotesIsrael SapnuNo ratings yet
- Commercial ApplicationsDocument6 pagesCommercial ApplicationsAaryaman Rathi (Yr. 21-23)No ratings yet
- Benefits of NuclearDocument7 pagesBenefits of Nuclearapi-320457297No ratings yet
- Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources Notes PDFDocument34 pagesRenewable and Nonrenewable Resources Notes PDFMr. PoGoNo ratings yet
- SORIANO - Environmental LawDocument4 pagesSORIANO - Environmental LawMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- SORIANO FinalExamDocument5 pagesSORIANO FinalExamMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- SORIANO - Commitment StatementDocument2 pagesSORIANO - Commitment StatementMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- SORIANO Assignment#2&3Document3 pagesSORIANO Assignment#2&3Myra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- Soriano - Research FrameworkDocument9 pagesSoriano - Research FrameworkMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday: Month ofDocument4 pagesSunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday: Month ofMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- Sci Camp TarpDocument1 pageSci Camp TarpMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- Genetics Report KoDocument8 pagesGenetics Report KoMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- Envi Sci ReportDocument4 pagesEnvi Sci ReportMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- ENERGYDocument24 pagesENERGYMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- ENERGYDocument24 pagesENERGYMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- ENERGYDocument24 pagesENERGYMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 7Document7 pagesLesson Plan in Science 7Myra Dionela Soriano0% (1)
- Foundation CertDocument1 pageFoundation CertMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power Efficiency Problems PDFDocument1 pageWork Energy Power Efficiency Problems PDFMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Stress Among Grade 7 and Grade 10 Students of City High During The Academic Year 2017Document1 pageFactors Affecting Stress Among Grade 7 and Grade 10 Students of City High During The Academic Year 2017Myra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesGeothermal Power PlantJiana NasirNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 FossilfuelsDocument39 pagesChap 2 FossilfuelsNeptune SrimalNo ratings yet
- Driving Innovation For Field Gas ConditioningDocument4 pagesDriving Innovation For Field Gas ConditioningIvan RinconNo ratings yet
- Science ArticleDocument6 pagesScience ArticleThinh NgoNo ratings yet
- LPG bioLPG Infographics PDFDocument4 pagesLPG bioLPG Infographics PDFShivanand SinghNo ratings yet
- Daily Cutting Coal Pit Kgu 30 Agustus 2022Document1 pageDaily Cutting Coal Pit Kgu 30 Agustus 2022Dian Ramadhan ArifinNo ratings yet
- Financial Offers Submitted Using A Different Format May Not Be ConsideredDocument4 pagesFinancial Offers Submitted Using A Different Format May Not Be ConsideredIssa SweissNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No 2641Document44 pagesRepublic Act No 2641Mark PascoNo ratings yet
- Final Project ReportDocument15 pagesFinal Project ReportHarishNo ratings yet
- Sunket Solar ProjectDocument23 pagesSunket Solar ProjectJesse XiaNo ratings yet
- Gayan Solar Mini Grid TeaserDocument17 pagesGayan Solar Mini Grid TeaserPSL TradingNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Theory by Hih Saravanamuttoo, H. Cohen & GFC RogersDocument5 pagesGas Turbine Theory by Hih Saravanamuttoo, H. Cohen & GFC RogersNitishNo ratings yet
- ASPE Presentation Rev 5Document27 pagesASPE Presentation Rev 5janechuacruzNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel ProjectDocument38 pagesBiodiesel ProjectVaibhav KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- For KnowledgeDocument4 pagesFor KnowledgeDeepak SashidharanNo ratings yet
- A Reaction Paper About The Article 1Document1 pageA Reaction Paper About The Article 1Joemer GalmanNo ratings yet
- Study Notes CBSE Class 8th Physics Coal and Petroleum WWW - CbseportalDocument3 pagesStudy Notes CBSE Class 8th Physics Coal and Petroleum WWW - CbseportalArshad Ahmad MasoodiNo ratings yet
- Natural Liquid FuelsDocument44 pagesNatural Liquid FuelsRhyan PulmanoNo ratings yet
- MNRE's Solar Park PlansDocument1 pageMNRE's Solar Park Plansevonik123456No ratings yet
- Algae Photobioreactor GuideDocument22 pagesAlgae Photobioreactor GuidePeyman SazandehchiNo ratings yet
- SolarPower Europe Global Market Outlook For Solar 2021 2025 V3Document136 pagesSolarPower Europe Global Market Outlook For Solar 2021 2025 V3hjacaNo ratings yet
- Startup & Shutdown Procedure and Maintenance GuidelinesDocument2 pagesStartup & Shutdown Procedure and Maintenance GuidelinesKrystianNo ratings yet
- Progress Test 8 L Maturita SolutionDocument4 pagesProgress Test 8 L Maturita SolutionPre SranduNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Non Renewable ResourcesDocument40 pagesRenewable and Non Renewable ResourcesChristian John Musngi0% (1)
- Block Flow Diagram2Document6 pagesBlock Flow Diagram2eng20072007No ratings yet
- Biogas A Renewable Energy SourceDocument3 pagesBiogas A Renewable Energy Sourcejaj009No ratings yet
- Non Conventional Energy SourcesDocument1 pageNon Conventional Energy Sourcessambu11217% (12)
- Petrol 1 Trial Bill Sample EmptyDocument1 pagePetrol 1 Trial Bill Sample EmptyShubham gupta100% (1)
- Reflection Paper Elective 3Document2 pagesReflection Paper Elective 3ChaskieNo ratings yet
- Azerbaijan Renewable EnergyDocument20 pagesAzerbaijan Renewable EnergyAhmed Imtiaz RaoNo ratings yet
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (65)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (223)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeFrom EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (19)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogFrom EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- Why Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeFrom EverandWhy Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (699)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- When the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeFrom EverandWhen the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateFrom EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1002)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (593)