Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Development Goals (SDG) 3. Good Health and Well-Being
Uploaded by
Alexandra Alyannah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views7 pagesA reviewer for an exam
Original Title
SDG Reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA reviewer for an exam
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views7 pagesDevelopment Goals (SDG) 3. Good Health and Well-Being
Uploaded by
Alexandra AlyannahA reviewer for an exam
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
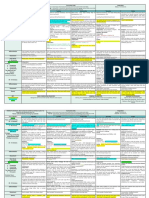
• SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT 3.
GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-
GOALS (SDG) BEING
• Also known as the Global Goals Commitment to end the epidemics of
• Adopted by all United Nations Member AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and other
States in 2015 as a universal call to action communicable diseases
to end poverty, protect the planet and (through prevention and treatment,
ensure that all people enjoy peace and education, immunization campaigns, and
prosperity by 2030. sexual and reproductive healthcare).
• UNIVERSALITY Achieve universal health coverage, and
provide access to safe and affordable
• The goal of the SDG is applied to every
medicines and vaccines for all
nation and every sector.
Supporting research and development for
• This includes; Cities, Business, Schools,
medication.
Organizations (all are challenged to act).
• INTEGRATION 4. QUALITY EDUCATION
• The goals are all inter-connected in a Ensure inclusive and equitably quality
system. education
• SDG cannot aim to achieve one goal, it Promote lifelong learning opportunities
must achieve them all. for all
• TRANSFORMATION Build and upgrade education facilities to
• Recognized that achieving these goals promote effective learning environment
involves making very big fundamental Substantially expand globally the number
changes in how we live on Earth. of scholarships available to developing
1. NO POVERTY countries
Eradicating poverty in all its forms Increase the number of qualified teachers
(involves targeting the most vulnerable).
Increasing access to basic resources and 5. GENDER EQUALITY
services. Achieve gender equality
Supporting communities affected by Empower all women and girls
conflict and climate-related disasters. Adopt and strengthen the policies and
enforceable legislation for the promotion
2. ZERO HUNGER of gender equality
Make sure all people – especially 6. CLEAN WATER AND
children – have access to sufficient and SANITATION
nutritious food all year round. Ensure availability and sustainable
Promoting sustainable agricultural management of water and sanitation for
practices: supporting small scale farmers all.
and allowing equal access to land, Improve water quality by reducing
technology and markets. pollution.
International cooperation to ensure Implement integrated water resources
investment in infrastructure and management at all levels.
technology to improve agricultural Protect and restore water-related
productivity ecosystems.
Support and strengthen the participation
of local communities in improving water
and sanitation management.
Adopt policies such as fiscal, wages and
7. AFFORDABLE AND CLEAN social protection policies.
ENERGY Facilitate orderly, safe, regular and
Ensure access to affordable, reliable, responsible migration and mobility of
sustainable and modern energy for all people.
Enhance international cooperation
Expand infrastructure and upgrade 11. SUSTAINABLE CITIES AND
technology for supplying modern and COMMUNITIES
sustainable energy services Make cities and human settlements
inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable
8. DECENT WORK AND Engineering geology to deliver safe and
ECONOMIC GROWTH adequate infrastructure
Promote sustained, inclusive and Mitigating against dangerous climate
sustainable economic growth. change
Full and productive employment and Protecting areas of geoheritage and
decent work for all. geotourism for the use of future
Protect labor rights and promote safe and generations
secure working environments for all Effective understanding and management
workers. of hydrogeology and contaminant
Devise and implement policies to geology
promote sustainable tourism, local
culture and products to create jobs. 12. RESPONSIBLE CONSUMPTION
AND PRODUCTION
9. INDUSTRY, INNOVATION AND Ensure sustainable consumption and
INFRASTRUCTURE production patterns.
Build resilient infrastructure Achieve environmentally sound
Promote inclusive and sustainable management of chemicals and all wastes.
industrialization and foster innovation Encourage companies to adopt
Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and sustainable practices.
resilient infrastructure Promote public procurement practices
Increase the access of small-scale accordance with national policies and
industries priorities.
Enhance scientific research
Upgrade technological capabilities of 13. CLIMATE ACTION
industrial sectors Take urgent action to combat climate
Support domestic technology change and its impact
development, research and innovation Protect the planet
Significantly
information
increase
and
access to
communication Developing technology for
technology carbon capture and storage
options
10. REDUCED INEQUALITIES
Reduce inequality within and among
Developing alternative source of
energy
countries.
Empower and promote the social,
economic and political inclusions of all.
Exploring for and extracting the
mineral resources needed for
electric vehicle batteries, wind
turbines and fuel cell technology
Understanding and remediating
contamination of our water
resources
14. LIFE BELOW WATER
Conserve and sustainably used the
oceans, seas and marine resources for
sustainable development.
Increase economic benefits to small
island developing states.
Increase scientific knowledge, develop
research capacity.
Implement international law as reflected
in UNCLOS.
15. LIFE ON LAND
Protect, restore and promote sustainable
use of terrestrial ecosystems.
Sustainably manage forests.
Combat desertification.
Halt and reverse land degradation.
Stop biodiversity loss.
16. PEACE, JUSTICE AND STRONG
INSTITUTIONS
Promote peaceful and inclusive societies
for sustainable development.
Provide access to justice for all.
Build effective, accountable and
inclusive institutions at all levels.
17. PARTNERSHIPS FOR THE
GOALS
Strengthen the means of implementation
Revitalize the global partnerships for
sustainable development
DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE AND The Galleon Trade have accounted in the
TECHNOLOGY (DOST) Philippine colonial economy.
• The executive department of the Filipinos were able to study in Europe
Philippine Government responsible for who were probably influenced by the
the coordination of science and rapid development of scientific
technology-related projects in the ideals (Age of Enlightenment).
Philippines. American Period and Post-Commonwealth
• Formulate policies and projects in the era
fields of science and technology in • The Bureau of Government Laboratories
support of national development. was established on July 1, 1901 (focused
• DOST ATTACHED AGENCIES on studies on tropical diseases).
• Science was inclined towards agriculture,
HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE OF SCIENCE
food processing, medicine and
EDUCATION pharmacy.
• Pre-Spanish period • The National Science Development
• Spanish Colonial period Board was established under the Science
• American period and Post- Act of 1958 under President Carlos P.
Commonwealth era Garcia.
• Marcos era and Martial law
• Fifth Republic Marcos Era and Martial Law
• 1973 Philippine Constitution, Article XV,
Pre-Spanish Period Section 9 (1) - declared that the
• Natives of the Philippines practice "advancement of science and technology
Science and Technology such as; shall have priority in the national
Medicinal and therapeutic properties of development.
plants (via extraction of herbs). • Directed the Department of Education to
Already had alphabet, numbering revitalize the science courses in public
system, measuring system. high schools.
Engaged in farming, shipbuilding, mining • Conducted seminars for public and
and weaving. private high school and college science
Spanish Colonial Period teachers, training programs and
Introduced formal education and scholarships for graduate and
founded scientific institution. undergraduate science scholars, and
Parish schools were established – have workshops on fisheries and
taught religion, reading, writing, oceanography.
arithmetic and music. • Emphasized that the upgrading of
Sanitation and more advanced methods science curricula and teaching
of agriculture. equipment is crucial to the science
Established colleges and universities in development program.
the archipelago (UST)
The study of medicine was given priority. • The modernization of the Philippine
Contributed to the field of engineering Coconut Research Institute for the
by constructing government buildings, coconut industry.
churches, roads, bridges and forts.
• Established the Philippine Textile autonomous member within the
Research Institute. University of the Philippines System to
• Philippine Atomic Energy Commission of improve the internal organization and
the NSDB explored the uses of atomic unity of leadership within its units
energy for economic development (Executive Order No. 519, s. 1979).
(sends scholar abroad). • Created the National Committee on
• Reform sectors in Education that Geological Sciences to advise
includes research and development government and private entities on
schools, technical institutes, science matters concerning development in
education centers, and agricultural geological sciences. (Executive Order No.
colleges and vocational high schools. 625, s. 1980)
• Created the National Grains Authority to • Granted salary increases to the people
provide for the development of the rice with teaching positions in the Philippine
and corn industry for the economy of the Science High School due to their
country. necessity in the advancement of national
• Established the Philippine Council for science (Executive Order No. 810, s.
Agricultural Research to support the 1982).
progressive development of agriculture, • Enacted a law on the completion of the
forestry, and fisheries. National Agriculture and Life Sciences
• Support for the promotion of scientific Research Complex at the University of
research and invention with Presidential the Philippines at Los Baños (Executive
Decree No. 49, s. 1972 (protection of Order No. 840, s. 1982).
intellectual property for the creator or • Established the Mindanao and Visayas
publisher of the work). campuses of the Philippine Science High
• Establish PAGASA under the Department School to encourage careers in science
of National Defense to provide and technology and to be more
environmental protection and to utilize accessible to the talented students in the
scientific knowledge to ensure the safety Mindanao and Visayas areas (Executive
of the people (Presidential Decree No. Order No. 1090, s. 1986).
78, s. 1972) Fifth Republic
• Created the Philippine National Oil President Corazon C. Aquino
Company to promote industrial and • Department of Science and Technology
economic development through replaces the National Science and
effective and efficient use of energy Technology Authority.
sources (Presidential Decree No. 334, s. • Philippine Inventors Incentive Act
1973). (Executive Order No.128 abolished R.A.
• Enacted a law under Presidential Decree No. 3859) - gave assistance to Filipino
No. 1003-A, s. 1976 to establish the inventors through giving financial aid,
National Academy of Science and patent application assistance, legal
Technology (composed of scientists with assistance, and to help inventors market
"innovative achievement in the basic and their products domestically and abroad.
applied sciences). • Science for the Masses Program (R.A.
• Constituted the Health Sciences Center 6655 or the Free Public Secondary
created by R.A. No. 5163 as an Education Act of 1988) - aimed at
scientific and technological literacy • Electronic Commerce Act of 2000
among Filipinos. (Republic Act No. 8792) - outlaws
• Science and Technology Master computer hacking and provides
Plan - aimed at the modernization of the opportunities for new businesses
production sector, upgrading research emerging from the Internet-driven New
activities, and development of Economy.
infrastructure for science and President Gloria M. Arroyo
technological purposes. • R.A. 9367 or the "Biofuels" act -
President Fidel V. Ramos promotes the development and usage of
• Doctors to the Barrio Program - . Health biofuels throughout the country.
care services were promoted through • Republic Act 10601 - covers research,
local programs. development, and extension (RDE),
• Magna Carta for Science and Technology promotion, distribution, supply,
Personnel (Republic Act No. 8439) - give assembling, manufacturing, regulation,
incentives and rewards for people who use, operation, maintenance and project
have been influential in the field of S&T. implementation of agricultural and
• National Program for Gifted Filipino fisheries machinery and equipment.
Children in Science and Technology - law GUIDING PRINCIPLES OF SCIENCE
creating a nationwide system of high CURRICULUM FRAMEWORK (Science
schools specializing in the field of science Education Institute SEI-DOST, 2011)
and engineering. • Science is for everyone.
Science and Technology Agenda for • Science is both content and process.
National Development (STAND) • School science should emphasize depth
Exporting winners identified by the DTI rather breadth, coherence rather than
Domestic needs identified by the fragmentation, and use of evidence in
President's Council for Countryside constructing explanation.
Development • School science should be relevant and
Support industries useful.
Coconut industry development. • School science should nurture interest in
Magna Carta for Science and Technology learning.
Personnel (Republic Act No. 8439) • School science should demonstrate a
Science and Technology Scholarship Law commitment to the development of a
of 1994 (Republic Act No. 7687) culture of science.
Inventors and Inventions Incentives Act • School science should promote the
(Republic Act No. 7459) strong link between science and
The Intellectual Property Code of the technology including indigenous
Philippines (Republic Act No. 8293) technology.
President Joseph E. Estrada • School science should recognize that
• Philippine Clean Air Act of 1999 (Republic science and technology reflect,
Act No. 8749) - designed to protect and influence, and shape our culture.
preserve the environment and ensure
the sustainable development of its
natural resources.
• Aims for eudaimonia as the ultimate
good.
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY AND
HUMAN FLOURISHING
Every discovery, innovation, and success
contributes to our pool of human
knowledge.
Human perpetual need to locate himself in
the world by finding proofs to trace
evolution
Elicits our idea of self – importance.
Technology is a human activity we excel in
a result of achieving science.
Good is inherently related to the truth.
You might also like
- Indigenous Methods of ResearchDocument2 pagesIndigenous Methods of ResearchRoland Aparece100% (1)
- Sustainable FutureDocument38 pagesSustainable Futureapi-198803582No ratings yet
- Topic 2 Art and Science in PedagogyDocument24 pagesTopic 2 Art and Science in PedagogyHanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - A Geographer's World: Section Notes VideoDocument28 pagesChapter 1 - A Geographer's World: Section Notes VideoBrian Jay GimanNo ratings yet
- ELPS and The 5E Model of InstructionDocument5 pagesELPS and The 5E Model of InstructionManisha BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Reading Comprehension:: Preparing For Passage ReadingDocument57 pagesScaffolding Reading Comprehension:: Preparing For Passage ReadingMohamed NagibNo ratings yet
- Area Formulas for Polygons and CirclesDocument7 pagesArea Formulas for Polygons and CirclesRojan MathewNo ratings yet
- History Assignment Year 10Document5 pagesHistory Assignment Year 10Calista ChengNo ratings yet
- Physical GeoDocument36 pagesPhysical GeoLalaine Marie BianzonNo ratings yet
- Story of Philemon and BaucisDocument4 pagesStory of Philemon and BaucisKen PalamosNo ratings yet
- Significance of ICT in Teaching and LearningDocument16 pagesSignificance of ICT in Teaching and LearningMark Levin HamacNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Week 8Document13 pagesGrade 6 Week 8Ric Jay TuliaoNo ratings yet
- SocialEconPolitical City of EmberDocument7 pagesSocialEconPolitical City of Emberneesin800% (1)
- 0522852505Document304 pages0522852505Oleksandra GaidaiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Exam Slides (Simplified)Document380 pagesChemistry Exam Slides (Simplified)nayef aNo ratings yet
- Edo Japan ExamDocument7 pagesEdo Japan Examapi-223862816No ratings yet
- Motivational Teaching Part 3Document29 pagesMotivational Teaching Part 3Gyuris VencelNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Prelim Geog 2018 BookletDocument28 pagesYear 11 Prelim Geog 2018 BookletJC ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Biology - Sustainable EcosystemsDocument4 pagesGrade 9 Biology - Sustainable EcosystemsAdrian WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Social - Physical Geography of Canada Unit PlanDocument42 pagesSocial - Physical Geography of Canada Unit Planapi-336712848No ratings yet
- Worksheet No. 3Document3 pagesWorksheet No. 3Adriane TingzonNo ratings yet
- In Text Citing APA Exercise 1Document2 pagesIn Text Citing APA Exercise 1Hpesoj SemlapNo ratings yet
- The Bell Bandit Discussion GuideDocument6 pagesThe Bell Bandit Discussion GuideHoughton Mifflin HarcourtNo ratings yet
- 02 - Unit 1 (Pages 1-158)Document158 pages02 - Unit 1 (Pages 1-158)Micaela DavisNo ratings yet
- Three Language FormulaDocument32 pagesThree Language Formulasanjiv kumarNo ratings yet
- Timeline of Human Evolution: 1 Taxonomy of Homo SapiensDocument6 pagesTimeline of Human Evolution: 1 Taxonomy of Homo SapiensAndino Gonthäler100% (1)
- Power Point Character Development in Novels Source UnknownDocument20 pagesPower Point Character Development in Novels Source Unknownapi-254162777No ratings yet
- Humanities Unit - Migration in AustraliaDocument2 pagesHumanities Unit - Migration in Australiaapi-326046634No ratings yet
- Population PyramidsDocument19 pagesPopulation Pyramidsapi-261914272100% (1)
- 12.1 LET 4, U3C12L2 Text, (p398-406)Document9 pages12.1 LET 4, U3C12L2 Text, (p398-406)Dela Cruz,Ruffa L.No ratings yet
- A Resource Guide For Middle School Teachers: Dr. Maya AngelouDocument21 pagesA Resource Guide For Middle School Teachers: Dr. Maya Angelouinput714No ratings yet
- Math Graphic Organizer Guide PDFDocument25 pagesMath Graphic Organizer Guide PDFPsic. Ó. Bernardo Duarte B.100% (1)
- AP Human Geography Course DescriptionDocument30 pagesAP Human Geography Course DescriptionKatie BanksNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Our World PDFDocument56 pagesMathematics in Our World PDFNicks SNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Geography Preliminary NotesDocument23 pagesYear 11 Geography Preliminary NotesBlakeTamb100% (2)
- Literacy Plan Template - Week OneDocument2 pagesLiteracy Plan Template - Week Oneapi-431984665No ratings yet
- RU Lesson Plan Format TemplateDocument2 pagesRU Lesson Plan Format TemplateCourtney WattsNo ratings yet
- Metalanguage List 1Document8 pagesMetalanguage List 1Katherine Momo ShenNo ratings yet
- Mae Jemison Biography Sample PaperDocument1 pageMae Jemison Biography Sample PaperBian HardiyantoNo ratings yet
- Environment: The Science Behind The Stories, Chapter 2 OutlineDocument5 pagesEnvironment: The Science Behind The Stories, Chapter 2 Outlineevapanda123No ratings yet
- What Is Instructional IntelligenceDocument4 pagesWhat Is Instructional Intelligenceapi-257322149No ratings yet
- Looking For AlibrandiDocument1 pageLooking For AlibrandiambaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Teaching Geography and Other DisciplinesDocument54 pagesModule 4 - Teaching Geography and Other DisciplinesMacky AguilarNo ratings yet
- Skillbuilder: Skills For Learning Geography Latitude, Longitude, and LocationDocument15 pagesSkillbuilder: Skills For Learning Geography Latitude, Longitude, and LocationEmmaHMF RomeroNo ratings yet
- 2008 Arts Education Assessment Framework: National Assessment Governing BoardDocument128 pages2008 Arts Education Assessment Framework: National Assessment Governing BoardSra L SantiagoNo ratings yet
- PSHS RESEARCH Learning Resource Package 2016-07-04 PDFDocument53 pagesPSHS RESEARCH Learning Resource Package 2016-07-04 PDFElegant PhantomNo ratings yet
- Beowulf and Its Historical BackgroundDocument28 pagesBeowulf and Its Historical BackgroundJude CastilloNo ratings yet
- Turmeric's Health Benefits and ApplicationsDocument83 pagesTurmeric's Health Benefits and ApplicationsAnonymous sq1oS1xH82100% (2)
- MYP 4 Exam Syllabus May 2022Document13 pagesMYP 4 Exam Syllabus May 2022LEO 1No ratings yet
- Course Syllabus: College: Program: EducationDocument7 pagesCourse Syllabus: College: Program: EducationGel Obenza BunedNo ratings yet
- Pronoun Reference ExercisesDocument5 pagesPronoun Reference Exerciseskazi anisNo ratings yet
- 880 The Middle Ages Introduction To The Middle AgesDocument5 pages880 The Middle Ages Introduction To The Middle AgesAnonymous 5SSgNRbNo ratings yet
- Create Stem-and-Leaf Plots (39Document12 pagesCreate Stem-and-Leaf Plots (39DavidNo ratings yet
- Expressing and Developing Ideas Interacting With Others Responding To LiteratureDocument10 pagesExpressing and Developing Ideas Interacting With Others Responding To Literatureapi-558855172No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Geography Rivision Note June 17,2020Document3 pagesGrade 10 Geography Rivision Note June 17,2020id st100% (1)
- nstw2019 Souvenir ProgramDocument41 pagesnstw2019 Souvenir ProgramRowena Cristina GuevaraNo ratings yet
- SDG For StudentsDocument90 pagesSDG For Studentsandrem101198No ratings yet
- PratheebaDocument26 pagesPratheebaPratheebaNo ratings yet
- MDG and SDGDocument15 pagesMDG and SDGKyla Claire ManubaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument36 pagesSustainable DevelopmentSH IRoNo ratings yet
- De La Salle Health Sciences InstituteDocument58 pagesDe La Salle Health Sciences InstituteAlexandra AlyannahNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument6 pagesPhilosophyAlexandra AlyannahNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument6 pagesPhilosophyAlexandra AlyannahNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument36 pagesPPTAlexandra Alyannah75% (4)
- Development Goals (SDG) 3. Good Health and Well-BeingDocument7 pagesDevelopment Goals (SDG) 3. Good Health and Well-BeingAlexandra AlyannahNo ratings yet
- Adolescence Canadian 1st Edition McMahan Test Bank 1Document13 pagesAdolescence Canadian 1st Edition McMahan Test Bank 1michael100% (30)
- Business Law SyllabusDocument11 pagesBusiness Law SyllabusTriệu Vy DươngNo ratings yet
- Effect of Advertisement On Coca ColaDocument10 pagesEffect of Advertisement On Coca ColaAnkur SheelNo ratings yet
- Psychosynthesis Quarterly March 2013Document34 pagesPsychosynthesis Quarterly March 2013CuriousOneTooNo ratings yet
- Universities - University Grants CommissionDocument3 pagesUniversities - University Grants Commissionvinod latkeNo ratings yet
- Thesis Editing ServiceDocument11 pagesThesis Editing ServiceukeditingNo ratings yet
- Northern Ireland Curriculum PrimaryDocument114 pagesNorthern Ireland Curriculum PrimaryttrbNo ratings yet
- Are Children OppressedDocument8 pagesAre Children Oppressedlaura simpsonNo ratings yet
- Ogl 350 Module 1 TBW Assignment 2Document6 pagesOgl 350 Module 1 TBW Assignment 2api-670788105No ratings yet
- Big Data & Hadoop - Course CurriculumDocument6 pagesBig Data & Hadoop - Course CurriculummanishNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Discussion 1Document2 pagesWeek 4 Discussion 1api-528651903No ratings yet
- Lefebvre and SpaceDocument15 pagesLefebvre and SpaceZainab CheemaNo ratings yet
- Faculty Profile: 1. Work ExperienceDocument4 pagesFaculty Profile: 1. Work ExperienceMohana UMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3Document53 pagesChapter 1-3ainavargasNo ratings yet
- Diversity Questionnaire ResultsDocument15 pagesDiversity Questionnaire ResultsAnonymous QE45TVC9e3No ratings yet
- Objectives of Teaching English at The Intermediate and Degree LevelDocument11 pagesObjectives of Teaching English at The Intermediate and Degree LevelAisha RahatNo ratings yet
- Fejokwu, JenniferDocument2 pagesFejokwu, Jennifernia fejokwuNo ratings yet
- 30 S. 2017Document7 pages30 S. 2017MaryroseNo ratings yet
- 2023 6 24 SIF TanauanDocument2 pages2023 6 24 SIF TanauanAbegail BathanNo ratings yet
- Project in Human Resource ManagementDocument26 pagesProject in Human Resource ManagementLouise Kevin C. BelenNo ratings yet
- STRATEGIC CONCEPTS by Dr. J. Robert ClintonDocument212 pagesSTRATEGIC CONCEPTS by Dr. J. Robert Clintontamiman100% (5)
- Unveiling The Failures: A Critical Analysis of Modern EducationDocument61 pagesUnveiling The Failures: A Critical Analysis of Modern Educationarkayodyafebrianto100% (1)
- Bedjaoui Cardiff Article For PublicationDocument8 pagesBedjaoui Cardiff Article For PublicationLina LilyNo ratings yet
- 36uf BVIEER Admission BrochureDocument37 pages36uf BVIEER Admission BrochurePawanNo ratings yet
- From Farm To Table: Tri-City TimesDocument24 pagesFrom Farm To Table: Tri-City TimesWoodsNo ratings yet
- EAC School of Nursing Midterm Exam Focuses on Community Health Nursing ProcessDocument3 pagesEAC School of Nursing Midterm Exam Focuses on Community Health Nursing Processkyle otedaNo ratings yet
- Dissertation The Female Nudes Relationship With Feminist Art and Criticism 1Document69 pagesDissertation The Female Nudes Relationship With Feminist Art and Criticism 1Mia ManaloNo ratings yet
- Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesCourse SyllabusEonart SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Elementary Teacher Resume ObjectiveDocument1 pageElementary Teacher Resume ObjectiveDolores Mayuga PanchoNo ratings yet
- Nursery Rhyme Readers Humpty Dumpty 054526720XDocument14 pagesNursery Rhyme Readers Humpty Dumpty 054526720XamyloumNo ratings yet