Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nanorobotics in Medicine: How Tiny Robots Could Revolutionize Heart Surgery
Uploaded by
StevenSteven0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
246 views51 pagesThis document discusses nanorobotics and its applications in medicine. It begins by defining robots, robotics, nanotechnology and nanorobotics. It then describes different types of nanorobots and how they are made. The document outlines several potential medical applications of nanorobots such as for targeted drug delivery, diagnosis and treatment of diseases like diabetes. Finally, it provides a detailed example of how a hypothetical nanorobot could be used to perform minimally invasive heart bypass surgery.
Original Description:
Ya
Original Title
02 Nanorobotics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses nanorobotics and its applications in medicine. It begins by defining robots, robotics, nanotechnology and nanorobotics. It then describes different types of nanorobots and how they are made. The document outlines several potential medical applications of nanorobots such as for targeted drug delivery, diagnosis and treatment of diseases like diabetes. Finally, it provides a detailed example of how a hypothetical nanorobot could be used to perform minimally invasive heart bypass surgery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
246 views51 pagesNanorobotics in Medicine: How Tiny Robots Could Revolutionize Heart Surgery
Uploaded by
StevenStevenThis document discusses nanorobotics and its applications in medicine. It begins by defining robots, robotics, nanotechnology and nanorobotics. It then describes different types of nanorobots and how they are made. The document outlines several potential medical applications of nanorobots such as for targeted drug delivery, diagnosis and treatment of diseases like diabetes. Finally, it provides a detailed example of how a hypothetical nanorobot could be used to perform minimally invasive heart bypass surgery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 51
NANOROBOTICS
AND ITS APPLICATION IN MEDICINE
CONTENTS:
Introduction to Robots
Robotics
Nanotechnology
Nanorobotics
Nanorobots
Types of making Nanorobots
Applications
ROBOTS:
It is a mechanical or virtual artificial agent usually an
electromechanical machine that is guided by computer
program or electronic circuitry.
Examples: ASIMO , TOPIO, Nanorobots, Swarm robots
and Industrial robots.
Types:
1. Mobile robots 2. Rolling robots
3. Walking robots 4.Stationary robots
5. Autonomous robots 6. Beam robots
7. Virtual robots 8. Remote control robots
ROBOTICS:
It deals with design, construction, operation and
application of robots and computer systems for their
control, sensory feedback and information processing.
These technologies deal with automated machines that can
take place of humans in hazardous or manufacturing
processes.
Today, robotics is rapidly growing field, as we continue to
research, design, and build new robots that serve various
practical purpose.
NANOTECHNOLOGY:
It is the manipulation of matter on an atomic and
molecular scale.
It works with materials, devices and other structures
with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100
nanometers.
With a variety of potential applications,
nanotechnology is a key technology for the future.
NANOROBOTICS:
It is the emerging technology field creating machines or robots whose
components are at or close to the scale of a nanometer (10-9 meters).
Nanorobotics refers to the nanotechnology engineering discipline of
designing and building nanorobots, with devices ranging in size from 0.1–
10 micrometers and constructed of nanoscale or molecular components.
Other names: nanobots, nanoids, nanites, nano-machines, nanomites
NANOROBOTS:
One of the most advanced forms of nano-medicine is
nanorobots. Nanorobots are microscopic devices measured
on the scale of nanometers.
Fig: A design of nanorobot
with sensors, molecular
sorting rotors and fins
SENSORS:
A sensor (also called detector) is a converter that measures
a physical quantity and converts it into a signal which can be read
by an observer or by an (mostly electronic) instrument.
Molecular sorting rotor:
A class of nanomechanical device capable of selectively binding
(or releasing) molecules from/ to solution, and of transporting
these bound molecules against significant concentration gradients.
Fins:
A fin is a surface used for stability and/or to produce lift and
thrust or to steer while traveling in water, air, or other fluid media.
TYPES OF MAKING NANOROBOTS:
1. Nubots
2. Bacteria based
3. Biochip
4. Surface Bound system
5. Positional Nano Assembly
6. Virus based
7. Open Nanotechnology
APPLICATIONS:
Atomic force microscope
Nano macro/microscale robots
Nanomachines
Toxicity detectors
Single molecule car
Nubots
Medicine
Dentistry
Diagnosis and treatment of Diabetes
INTRODUCTION TO HEART BYPASS SURGERY:
• It reroutes the blood supply around clogged arteries to improve
blood flow and oxygen to the heart.
• It involves an incision in the middle of the chest and separation
of the breastbone and detouring ,the breastbone is joined using
wire and the incision sewed.
Side effects of normal heart bypass surgery:
1.loss of appetite, constipation
2.swelling in the area from which the segment of
blood vessel was removed
3.fatigue,mood swings, feelings of depression,
difficulty sleeping
4.muscle pain or tightness in the shoulders and upper
back
PROPERTIES OF NANOROBOT USED:
It has 2 spaces-interior and exterior
An electric motor is attached for it’s propagation inside
the circulatory system in the blood vessels
The microprocessor, artery thermometer, camera, rotating
needle are incorporated
The microprocessor based control unit is used to control
the overall operations of nanorobot
Radioactive material is used as a part of exterior surface,
which helps to nanorobot at any period of time
Magnetic switch is used to provide to switch on and off
nanorobot at any point of time
Introduction of nanorobot into human
body:
The nanorobot gets access into the
body through a large diameter artery
so that it may be without being
too destructive in the first place.
Fig. The robot swims through the arteries
and using a pair of tail appendages
Driving of nanorobot to the site of plaque:
•Long range sensors are used to allow
the machine to navigate to the site of
the plaque closely enough so that the
use of short range sensors is practical
•These are used during actual
operations, to allow the device to
distinguish between healthy and
unwanted tissue
•Long-range sensor-Radioactive dye
•Short-range sensors-Arterial
thermometer Fig: Nanorobot detecting
the site of plaque
•Device for monitoring the whole
operation-TV camera
Source of power and means of recovery:
• The nuclear power is carried onboard to supply required
amount of energy for the operation of the device
• After the nanorobot has removed the plaque, and its function is
over, it has to be removed from the body. This can be made
possible by guiding the nanorobot to anchor a blood vessel that
is easily accessible from outside, and perform a small surgical
operation to remove it.
Fig. Removal of nanorobot
From the body
CONCLUSION:
NANOROBOTICS is one of the emerging fields in technology and
robotics.
Nanorobotics is the technology of creating machines or robots at or
close to the scale of a nanometer (10-9 meters).
More specifically, nanorobotics refers to the still largely theoretical
nanotechnology engineering discipline of designing and building
nanorobots.
Nanorobots (nanobots or nanoids) are typically devices constructed of
nanoscale or molecular components.
REFERENCES:
1. Nocks, Lisa (2007). The robot : the life story of a technology. Westport, CT: Greenwood
Publishing Group
2. Nanorobot “International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences”.
[Online] Available: http://www.ijpbs.net/51.pdf
3. "What Nanobots Are Made Out Of." How Nanorobots Are Made.
[Online] Available: http://nanogloss.com/nanobots/how-nanorobots-are-made/
4. (2011,April 12). H.Wang. "Basic Properties of Diamond." Diamond Blade Select.
[Online] Available: http://www.diamondbladeselect.com/knowledge/basic-properties-of-
diamond/
5. (2012, February 22). J. Malone."Advanced Nanobots Deliver Targeted Drugs." COSMOS.
[Online]Available:http://www.cosmosmagazine.com/news/5321/dna-nanobots-deliver-
targetted-drugs
6. (2009, January 7). "Nanorobots to Fight Cancer, Diagnose Disease - Health - CBC
News." CBC.ca - Canadian News Sports Entertainment Kids Docs Radio TV.
[Online]Available:http://www.cbc.ca/news/health/story/2009/01/07/nanomedicine.html
7. S. Hede and N. Huilgol.(2006) ""Nano": The New Nemesis of Cancer ." Journal of Cancer
Research and Therapeutics: Free Full Text Articles from JCRT, India.
[Online]Available:http://www.cancerjournal.net/article.asp?issn=0973-
1482;year=2006;volume=2;issue=4;spage=186;epage=195;aulast=Hede
Thank You!!
You might also like
- Submitted By: Neha Bothra Roll No.: 22Document60 pagesSubmitted By: Neha Bothra Roll No.: 22NehaNo ratings yet
- Nano RoboticsDocument11 pagesNano RoboticsNishanth Madhavan0% (1)
- Nanorobots in Heart SurgeryDocument41 pagesNanorobots in Heart SurgerySushma Dasari0% (1)
- Nanorobots for Medical TreatmentDocument21 pagesNanorobots for Medical TreatmentSantosh Kumar PrasadNo ratings yet
- A Report On NanorobotsDocument14 pagesA Report On NanorobotsMd AliujjamanNo ratings yet
- Nanorobots: Applications and Future in Medical ScienceDocument5 pagesNanorobots: Applications and Future in Medical ScienceMạc Đăng QuangNo ratings yet
- Nanobots Revolutionizing HealthcareDocument42 pagesNanobots Revolutionizing HealthcareAnkit Jain67% (3)
- Design of NANOROBOT in Human BodyDocument12 pagesDesign of NANOROBOT in Human BodyAbin Varkey VargheseNo ratings yet
- NanoRobotics DOCUMENTDocument16 pagesNanoRobotics DOCUMENTAnirudh D DyagaNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR REPORT On NANOROBOT in Human BodyDocument12 pagesSEMINAR REPORT On NANOROBOT in Human BodyPadmarajPopNo ratings yet
- Nanorobotics PDFDocument21 pagesNanorobotics PDFXtremeInfosoftAlwar100% (2)
- Nano RoboticsDocument30 pagesNano RoboticsAnshumanMishraNo ratings yet
- Nanorobotics: The Future of Medical SciencesDocument21 pagesNanorobotics: The Future of Medical Sciencesvinamra m singh100% (1)
- Nano RobotDocument23 pagesNano RobotAnbazhagan Selvanathan100% (1)
- A Seminar Report Nano RoboticsDocument16 pagesA Seminar Report Nano RoboticsShaiksha Syed100% (1)
- NanoroboticsDocument12 pagesNanoroboticsebrohusaini100% (1)
- Nanobots PPT Main SvuDocument18 pagesNanobots PPT Main SvukirubaNo ratings yet
- Nano RoboticsDocument25 pagesNano Roboticsharsha chittiNo ratings yet
- Nanorobotics: Soumyadeep SinhaDocument25 pagesNanorobotics: Soumyadeep SinhaMayukh SinhaNo ratings yet
- Nano RoboticsDocument34 pagesNano Roboticssonam angdue0% (1)
- Fractal Robots Seminar ReportDocument29 pagesFractal Robots Seminar ReportSindhura ReddyNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Nanotechnology Seminar ReportDocument13 pagesIntroduction to Nanotechnology Seminar Reportyogesh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecular Computing: C C C CDocument11 pagesBio Molecular Computing: C C C CSpandana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology: The Next Very Big (Small) ThingDocument36 pagesNanotechnology: The Next Very Big (Small) ThingSukanya ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Nanorobotics and Their ApplicationsDocument25 pagesIntroduction to Nanorobotics and Their ApplicationsSharifa RahamadullahNo ratings yet
- Lab-On-A-Chip, Microfluidics and Interfacial ElectrokineticsDocument6 pagesLab-On-A-Chip, Microfluidics and Interfacial ElectrokineticsAditya RaghunandanNo ratings yet
- Infrared Plastic Solar CellDocument19 pagesInfrared Plastic Solar CellAjay Mv100% (2)
- Application of Nano Robots in MedicineDocument28 pagesApplication of Nano Robots in MedicineShilpa Verma100% (1)
- VTU Seminar Report on Using Nanotech to Detect and Treat CancerDocument17 pagesVTU Seminar Report on Using Nanotech to Detect and Treat CancerRitesh Zaveri100% (1)
- Nano Report PDFDocument32 pagesNano Report PDFAkshita BhargavNo ratings yet
- NANOELECTRONICS 1 (2) Seminar ReportDocument31 pagesNANOELECTRONICS 1 (2) Seminar ReportPramod RoyNo ratings yet
- Brain Machine InterfaceDocument26 pagesBrain Machine InterfaceMettu Balanandu100% (3)
- X MAXDocument20 pagesX MAXGirish Chougule100% (1)
- NanotechnologyDocument17 pagesNanotechnologyPuneet KumarNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in Biomedical ApplicationsDocument17 pagesNanotechnology in Biomedical ApplicationsAbhiroop KumarNo ratings yet
- Nano Robots and Application in MedicalDocument21 pagesNano Robots and Application in MedicalInzamam Ul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Nanorobotics: By: A.Chandrika Bhargavi 2451-15-735-169Document23 pagesNanorobotics: By: A.Chandrika Bhargavi 2451-15-735-169chandrikaNo ratings yet
- KallDocument20 pagesKallBharatha LalithNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Report Nano RoboticsDocument16 pagesA Seminar Report Nano Roboticsnature loverNo ratings yet
- Nanorobots in Heart Surgery: BY YUVARAJ.S (Third Year ECE) SHAJAHAN.P (Third Year ECE)Document12 pagesNanorobots in Heart Surgery: BY YUVARAJ.S (Third Year ECE) SHAJAHAN.P (Third Year ECE)Cherman BabuNo ratings yet
- Nanorobots To Perform SurgeryDocument16 pagesNanorobots To Perform SurgeryglangstiehNo ratings yet
- Nanorobotics: Nithya .M Roll No:16Document20 pagesNanorobotics: Nithya .M Roll No:16Nithya MothangaNo ratings yet
- WELCOMEDocument13 pagesWELCOMEfelicia.wNo ratings yet
- Nano - Robotics: Linux GroupDocument43 pagesNano - Robotics: Linux Grouptata14789296No ratings yet
- Respirocytes: Artificial Red Blood Cells Using NanorobotsDocument14 pagesRespirocytes: Artificial Red Blood Cells Using NanorobotsDivya DiviNo ratings yet
- JETIR1809611Document7 pagesJETIR1809611Sujatha MadhuNo ratings yet
- Nano RoboticsDocument4 pagesNano RoboticsVinay Partap SinghNo ratings yet
- Nano 2Document1 pageNano 2api-3761679No ratings yet
- Nano RobotsDocument11 pagesNano RobotsAfraa AnwarNo ratings yet
- Title Page: Term Paper of Nanotechnology Roll No. Re4005b34 Registration No.11008677Document16 pagesTitle Page: Term Paper of Nanotechnology Roll No. Re4005b34 Registration No.11008677Saime IlltutmishNo ratings yet
- NANOROBOTICSRAJDocument6 pagesNANOROBOTICSRAJRajashekar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Nanorobots in Heart SurgeryDocument14 pagesNanorobots in Heart SurgeryFawaz Bin AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in Robotics: An Intermediate PresentationDocument13 pagesNanotechnology in Robotics: An Intermediate PresentationmiyokofongNo ratings yet
- Nano RobotsDocument32 pagesNano Robotsajaygill5785No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitled廖翊辰No ratings yet
- Jurnal Nanobot 3Document9 pagesJurnal Nanobot 3Hasya HafiyanNo ratings yet
- Nano BotsDocument31 pagesNano Botspradeepagarwal62No ratings yet
- RoboticsDocument3 pagesRoboticsstardinesNo ratings yet
- Navy ADocument17 pagesNavy AKarthik GudavarthiNo ratings yet
- Nanorobots in Heart SurgeryDocument15 pagesNanorobots in Heart Surgeryhafizsyed67% (3)
- DifusiDocument23 pagesDifusiStevenStevenNo ratings yet
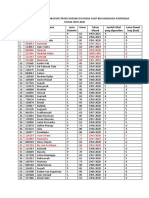
- Daftar Nama Pasien Di Rumah Sakit BhayangkaraDocument2 pagesDaftar Nama Pasien Di Rumah Sakit BhayangkaraStevenStevenNo ratings yet
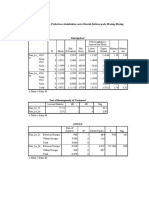
- Uji One Way Anova, Perbedaan Antioksidan Antar Bentuk Sediaan Pada Masing-Masing Suhu Suhu Suhu 40 DescriptivesDocument8 pagesUji One Way Anova, Perbedaan Antioksidan Antar Bentuk Sediaan Pada Masing-Masing Suhu Suhu Suhu 40 DescriptivesStevenStevenNo ratings yet
- Lampiran 1 Perbedaan Kadar Antara Suhu Ruang Dengan Suhu 40 Pada Masing-Masing Bentuk Sediaan Dan HariDocument31 pagesLampiran 1 Perbedaan Kadar Antara Suhu Ruang Dengan Suhu 40 Pada Masing-Masing Bentuk Sediaan Dan HariStevenStevenNo ratings yet
- Debby QDocument1 pageDebby QStevenStevenNo ratings yet
- Nanorobotics in Medicine: How Tiny Robots Could Revolutionize Heart SurgeryDocument51 pagesNanorobotics in Medicine: How Tiny Robots Could Revolutionize Heart SurgeryStevenStevenNo ratings yet
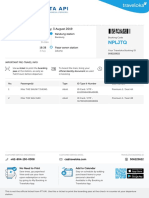
- NPLJTQ: E-Ticket (Departure Train)Document2 pagesNPLJTQ: E-Ticket (Departure Train)StevenStevenNo ratings yet
- Structural and Functional Significance of NiosomeDocument17 pagesStructural and Functional Significance of NiosomeStevenStevenNo ratings yet
- JURNAL UntanDocument5 pagesJURNAL UntanStevenStevenNo ratings yet
- CCID 90781 Phosphatidylcholine Liposomes As Carriers To Improve Topical 121715Document9 pagesCCID 90781 Phosphatidylcholine Liposomes As Carriers To Improve Topical 121715StevenStevenNo ratings yet
- Vsia Ip AssetsDocument56 pagesVsia Ip AssetsAbelGuilherminoNo ratings yet
- DQFAQsDocument8 pagesDQFAQsBhagyashree kawaleNo ratings yet
- Report On MinesDocument7 pagesReport On MinesYhaneNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 The Rise of Instrumental Music - 141-152Document8 pagesCHAPTER 8 The Rise of Instrumental Music - 141-152Aleksandre Roderick-LorenzNo ratings yet
- Methanol from Syngas Plant DesignDocument13 pagesMethanol from Syngas Plant DesignKhalidMadaniNo ratings yet
- EPS: Electric Power Steering Components & ModesDocument9 pagesEPS: Electric Power Steering Components & ModesTilahun Worku100% (1)
- CH 2 Financial Analysis Technoques PresentationDocument44 pagesCH 2 Financial Analysis Technoques PresentationHamza AsifNo ratings yet
- ZEOLITEDocument13 pagesZEOLITEShubham Yele100% (1)
- Laptops and Desktop-MAY PRICE 2011Document8 pagesLaptops and Desktop-MAY PRICE 2011Innocent StrangerNo ratings yet
- HER201 Flex Tiles Set 01 - VehiclesDocument3 pagesHER201 Flex Tiles Set 01 - VehiclesDouglas Mears100% (2)
- E44 - Wet Cooling Tower: InstructionsDocument3 pagesE44 - Wet Cooling Tower: InstructionsMarc AnmellaNo ratings yet
- Business Result 2e Writing Advanced 1 SBDocument1 pageBusiness Result 2e Writing Advanced 1 SBPressCall Academy100% (1)
- Daniel Fast Recipes A Couple CooksDocument12 pagesDaniel Fast Recipes A Couple CooksmariamNo ratings yet
- LAC Intraregional IRF GuideDocument81 pagesLAC Intraregional IRF GuideMario Cortez EscárateNo ratings yet
- BA Mckesson Interview 2Document3 pagesBA Mckesson Interview 2Vikram hostNo ratings yet
- Silent Spring: What's InsideDocument22 pagesSilent Spring: What's InsideDelina TedrosNo ratings yet
- 6.4 Qualitative Quantitative AnalysisDocument6 pages6.4 Qualitative Quantitative AnalysisAndrea PagsuguironNo ratings yet
- Shri Mata Vaishno Devi Shrine Board - Welcome To Online ServicesjjDocument2 pagesShri Mata Vaishno Devi Shrine Board - Welcome To Online Servicesjjeternal diagnosticsNo ratings yet
- Detecting Voltage Differences Between Two Points With A Phase ComparatorDocument1 pageDetecting Voltage Differences Between Two Points With A Phase ComparatorContract 42154No ratings yet
- Calculating production costs and selling pricesDocument2 pagesCalculating production costs and selling pricesMitch BelmonteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. COST IDocument8 pagesChapter 2. COST IyebegashetNo ratings yet
- D 3 Econo SPP 2110 1 eDocument123 pagesD 3 Econo SPP 2110 1 eMargarida MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Dh76 Auto HemaDocument271 pagesDh76 Auto HemaJoshua NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Analog ElectronicsDocument90 pagesAnalog ElectronicsBikashDeyNo ratings yet
- Biografia Buerkli-ZieglerDocument7 pagesBiografia Buerkli-ZieglerJesús Ángel Ortiz OrdazNo ratings yet
- Surface Modification of Titanium Orthodontic ImplaDocument30 pagesSurface Modification of Titanium Orthodontic ImplaMary SmileNo ratings yet
- Biology of Tooth MovementDocument22 pagesBiology of Tooth MovementsakshiNo ratings yet
- 5 BFU 07406 Assessment of Credit ApplicationsDocument109 pages5 BFU 07406 Assessment of Credit ApplicationsDeogratias MsigalaNo ratings yet
- Lec # 10 Earthing and GroundingDocument68 pagesLec # 10 Earthing and GroundingSaddam jatt786No ratings yet
- Labview ProgrammingDocument20 pagesLabview ProgrammingJames WoodNo ratings yet