Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ejercicio #4
Uploaded by
Doris Arias SierraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ejercicio #4
Uploaded by
Doris Arias SierraCopyright:
Available Formats
Ejercicio 4
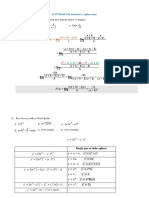
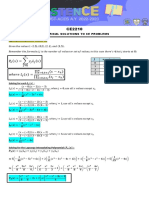
Dar la ecuación del plano que contiene a los puntos
𝐀 (𝟏, 𝟐, 𝟏); 𝐁 (𝟏, 𝟎, 𝟏); 𝐂 (𝟎, 𝟏, −𝟏)
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ y 𝐴𝐶
Formamos los vectores 𝐴𝐵 ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴𝐵 = 𝐵 − 𝐴 = (1, 0, 1) − (1, 2 ,1) = (0, −2, 0)
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴𝐶 = 𝐶 − 𝐴 = (0, 1, −1) − (1, 2, 1) = (−1, −1, −2)
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ y 𝐴𝐶
⃗ 𝑣𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 𝑛𝑜𝑟𝑚𝑎𝑙) que sea perpendicular a 𝐴𝐵
Hallamos ahora un vector (𝑁 ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
simultáneamente.
𝑖 𝑗 𝑘
⃗𝑁 = ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ −2 0 0 0 0 −2
𝐴𝐵 𝑋 𝐴𝐶 = [ 0 −2 0 ] = 𝑖 [ ]−𝑗[ ]+𝑘[ ]
−1 −2 −1 2 −1 −1
−1 −1 −2
⃗ = 𝑖[(−2 ∗ −2) − (−1 ∗ 0)] − 𝑗[(0 ∗ 2) − (−1 ∗ 0)] + 𝑘[(0 ∗ −1) − (−1 ∗ −2)]
𝑁
⃗ = 𝑖[(4) − (0)] − 𝑗[(0) − (0)] + 𝑘[(0) − (2)]
𝑁
⃗ = 4𝑖 − 0𝑗 − 2𝑘
𝑁
⃗ = 4𝑖 − 2𝑘
𝑁
Utilizamos el punto B para hallar la ecuación.
4(𝑥 − 1) − 2(𝑧 − 1) = 0
4𝑥 − 4 − 2𝑧 + 2 = 0
4𝑥 − 2𝑧 = 4 − 2
4𝑥 − 2𝑧 = 2 𝑬𝒄𝒖𝒂𝒄𝒊ó𝒏 𝒅𝒆𝒍 𝒑𝒍𝒂𝒏𝒐.
You might also like
- ACTIVIDAD VII - Unidad IV MS Algunas SolucionesDocument7 pagesACTIVIDAD VII - Unidad IV MS Algunas SolucionesMiguel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Entregable 3Document3 pagesTrabajo Entregable 3Andy Amed Rómulo CantincaNo ratings yet
- Tareas BDocument7 pagesTareas BAlexander Guaitero MojicaNo ratings yet
- Tarea N°4 EcuacionesDocument8 pagesTarea N°4 EcuacionesJhoana RamirezNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones de Cauchy-Euler - anaruthCruzaleyHdezDocument5 pagesEcuaciones de Cauchy-Euler - anaruthCruzaleyHdezAna Ruth CruzaleyNo ratings yet
- Señales DiscretasDocument7 pagesSeñales DiscretasJuan Sebastián BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de Vectores-AreaDocument12 pagesEjercicios de Vectores-AreaMiguel AnteloNo ratings yet
- Eedi U3 EaDocument15 pagesEedi U3 EaGuadalupe LòpezNo ratings yet
- Eedi U3 EaDocument15 pagesEedi U3 EaGuadalupe LòpezNo ratings yet
- Metodos para Constantes Examen Ejer 2Document10 pagesMetodos para Constantes Examen Ejer 2CURSOS MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Funciones y Relaciones Matemáticas IDocument38 pagesFunciones y Relaciones Matemáticas IRodrigo Escalante RojasNo ratings yet
- Calculo Grupo N°1Document17 pagesCalculo Grupo N°1Nicol Melany HuamanrimachiNo ratings yet
- Determinar La Solución de Las Siguientes Ecuaciones DiferencialesDocument4 pagesDeterminar La Solución de Las Siguientes Ecuaciones DiferencialesLuis David Orozco GarcíaNo ratings yet
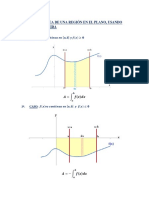
- Clase 08 Cálculo de Areas de Una Región.Document10 pagesClase 08 Cálculo de Areas de Una Región.jhon socaNo ratings yet
- Solucion Taller CuadraticasDocument11 pagesSolucion Taller CuadraticasVictor RomeroNo ratings yet
- TAREA 3-Diana MonroyDocument5 pagesTAREA 3-Diana MonroyDiana MonroyNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de Números ComplejosDocument5 pagesEjercicios de Números ComplejosMario RojasNo ratings yet
- Pembuktian Persamaan ElipsDocument14 pagesPembuktian Persamaan ElipsArif BudimanNo ratings yet
- Zestawy Maturalne: Zestaw 3Document5 pagesZestawy Maturalne: Zestaw 3m3ssi94No ratings yet
- Actividad No. 1 Taller de Estudio de Secciones Cónicas 2Document17 pagesActividad No. 1 Taller de Estudio de Secciones Cónicas 2DIANA CAROLINA TAUTIVA BARBOSANo ratings yet
- 16a Ejer IntegralesDoblesTriplesDocument22 pages16a Ejer IntegralesDoblesTriplesk1ll3rs 777No ratings yet
- Demostración de La ECUACIÓN de La ELIPSEDocument2 pagesDemostración de La ECUACIÓN de La ELIPSEDiego MoyaNo ratings yet
- (ED-G9) Grupo 5 - Practica 04Document28 pages(ED-G9) Grupo 5 - Practica 04SANDRO XAVIER CCAMA SARANo ratings yet
- Kwadratowa CDocument11 pagesKwadratowa CJulia RycerzNo ratings yet
- Expo Cálculo..Document6 pagesExpo Cálculo..Ousmane Dembélé DembouzNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio de ConvoluciónDocument1 pageEjercicio de ConvoluciónFLORA ESMERALDA MOSCOSO ARENASNo ratings yet
- PRACTICA CALIFICADA - Ecuaciones DiferencialesDocument6 pagesPRACTICA CALIFICADA - Ecuaciones DiferencialesFLORA ESMERALDA MOSCOSO ARENASNo ratings yet
- Practica Nº2 - Aux. - Calculo IDocument5 pagesPractica Nº2 - Aux. - Calculo ISilvio CubaNo ratings yet
- Pizarra Mat129 2.40 24y25-FebDocument3 pagesPizarra Mat129 2.40 24y25-FebSteven GutierrezNo ratings yet
- ZZ - Zestawy Maturalne - PR - Zestaw 2Document5 pagesZZ - Zestawy Maturalne - PR - Zestaw 2Julia KurekNo ratings yet
- Taller Final Economia InternacionalDocument3 pagesTaller Final Economia InternacionalCristian Camilo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones IIDocument3 pagesEcuaciones IIcamila soto gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Actividad 1 PDFDocument8 pagesActividad 1 PDFMartin ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Taller #2Document27 pagesTaller #2coordinador.serviciosNo ratings yet
- Analisis Numerico Eje # 3Document13 pagesAnalisis Numerico Eje # 3Jeismar TellezNo ratings yet
- Sgdo Parc de Mate III 2023 I - A1Document7 pagesSgdo Parc de Mate III 2023 I - A1WILLY BRANDT PEÑA SILVANo ratings yet
- Taller 1 Mat 1Document1 pageTaller 1 Mat 1JulianmateoNo ratings yet
- Tarea #3Document6 pagesTarea #3JORGE EDUARDO PEREZ TEMBLADORNo ratings yet
- Taller #3Document13 pagesTaller #3coordinador.serviciosNo ratings yet
- Problema 19Document2 pagesProblema 19Rodrigo David Espinoza SeminarioNo ratings yet
- Funkcje. Funkcja Liniowa: Zestaw A. Zadania PowtórzenioweDocument15 pagesFunkcje. Funkcja Liniowa: Zestaw A. Zadania Powtórzeniowem3ssi94No ratings yet
- Sistemas de Ecuaciones DiferencialesDocument11 pagesSistemas de Ecuaciones DiferencialesNatsu DragneelNo ratings yet
- Practico de Derivadas ParcialesDocument16 pagesPractico de Derivadas Parcialesyoutalktv10No ratings yet
- AtividadesDocument2 pagesAtividadesMateus VianaNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving and Mathematical Reasoning - Math For Elementary 2nd Grade by SlidesgoDocument6 pagesProblem Solving and Mathematical Reasoning - Math For Elementary 2nd Grade by SlidesgoSahira Tejada PenaNo ratings yet
- Taller de Sesión de Aprendizaje 2 Complemento de MatematicaDocument13 pagesTaller de Sesión de Aprendizaje 2 Complemento de MatematicaJoysi JuarezNo ratings yet
- Arkusz 7 PP RozwiązaniaDocument11 pagesArkusz 7 PP RozwiązaniaWiktoria SołtysikNo ratings yet
- Zestawy Maturalne: Zestaw 4Document5 pagesZestawy Maturalne: Zestaw 4m3ssi94No ratings yet
- Corrigé Ex°12 Fiche 2Document1 pageCorrigé Ex°12 Fiche 2Issa SangareNo ratings yet
- Logistyka - Gr.6 Tomasz Biały ćw.05Document10 pagesLogistyka - Gr.6 Tomasz Biały ćw.05Paulina PaolaNo ratings yet
- DERIVADAS DE FUNCIONES TRIGONOMETRICAS Nuevos Ejemplos AmpliadoDocument4 pagesDERIVADAS DE FUNCIONES TRIGONOMETRICAS Nuevos Ejemplos AmpliadoJesus G FANo ratings yet
- Lenguaje Algebraico y Pensamiento FuncionalDocument24 pagesLenguaje Algebraico y Pensamiento FuncionalWilson Marin DiazNo ratings yet
- A1b4 PDFDocument17 pagesA1b4 PDFFernando de Jesús López MazaNo ratings yet
- CE22102Document6 pagesCE22102Josephh CryptNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones Trigonometricas-1Document1 pageEcuaciones Trigonometricas-1Luz Andrea Vera SandovalNo ratings yet
- Prueba Del Segundo HemisemestreDocument7 pagesPrueba Del Segundo HemisemestreSandy NicolaldeNo ratings yet
- Taller Matematicas MIGUEL BAEZ 4LDocument4 pagesTaller Matematicas MIGUEL BAEZ 4Lparroquiaelpadremisericor2005No ratings yet
- Ejercicios de Aplicación de FuncionesDocument4 pagesEjercicios de Aplicación de FuncionesAnghela Luna Silva RodríguezNo ratings yet