Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group Study Transmission Lines Answer Key
Uploaded by
Benjhon S. Elarcosa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views6 pagesOriginal Title
337307271-GROUP-STUDY-TRANSMISSION-LINES-ANSWER-KEY-docx.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views6 pagesGroup Study Transmission Lines Answer Key
Uploaded by
Benjhon S. ElarcosaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
GROUP STUDY - TRANSMISSION LINES
1. Transmission media are usually categorized as
a. Fixed or unfixed c. guided or unguided
b. Determinate or indeterminate d. metallic or non-metallic
2. Both twisted pair cable and coaxial cable transmit data in the form of
a. Light b. electric current c. induction d. heat
3. It is the input impedance of a transmission line either infinitely long or terminated in a pure
resistance equal to the line impedance.
a. Characteristic impedance c. source impedance
b. Load impedance d. Iterative Impedance
4. The characteristic impedance of a transmission line does not depend on its
a. Length b. conductor spacing c. conductor diameter d. dielectric constant
5. How many 600kHz waves can be on a 5 mile transmission line simultaneously?
a. 16.13 b. 18 c. 20.25 d. 15.25
6. The transmission lines that permit most efficient transfer of microwave energy are
a. Cavity resonators b. faraday screen c. waveguide d. coaxial cable
7. Determine the characteristic impedance of a coaxial cable with an inductance of 0.2uH/ft and
capacitance of 16pF/ft.
a. 50 ohms b. 60 ohms c. 81.2 ohms d. 111.8 ohms
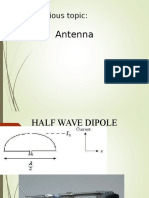
8. If the 2 towers of a 2MHz antenna are separated by 120 electrical degrees, what is the tower
separation in feet?
a. 150 b. 250 c. 500 d. 650
9. Which of the following is a major source of loss in a transmission line?
a. Dielectric heating b. radiation c. conductor heating d. all of these
10. The tendency of electrons to confine their travel near the surface of the solid conductor as the
frequency of operation increases.
a. Capture effect b. Doppler effect c. skin effect d. flywheel effect
11. The fixed voltage and current wave patterns that result in a resonant transmission line due to
the vector addition of the incident and reflected travelling waves.
a. Radio waves b. electric waves c. magnetic waves d. standing waves
12. It is the ratio of the maximum voltage to the minimum voltage of a standing wave on a
transmission line
a. SWR b. TDR c. Reflection Coefficient d. F/B ratio
13. A flat line is considered to have an SWR of
a. 1:1 b. 1:2 c. 1:0 d. 1:infinity
14. What is the reflection coefficient for a transmission line with incident voltage of 4 v and
reflected voltage of 0.75v?
a. 20 b. 2 c. 0.2 d. 5
15. If a 75 ohm transmission line is terminated with the load resistance of 50 ohms, what is the SWR
along the line?
a. 1.5 b. 0.67 c. 5 d. 12
16. Voltage minima are called
a. Anti nodes b. nodes c. peak d. lowest value
17. A transmission line is connected to a mismatch load. Calculate the VSWR decibel equivalent if
the reflection coefficient is 0.25.
a. 2.15 dB b. 4.44 dB c. 8.6 dB d. 5 dB
18. The person responsible in publishing graphical device for solving transmission line problems.
a. Charles Smith b. Philip Smith c. Smith Chart d. James Smith
19. For the coaxial line, the thickness of the outer conductor is 0.125” while the outer conductor
diameter is 1.25” and the diameter of the inner conductor is 0.75”. Solve for the characteristic
Impedance of the line.
a. 17.24 ohms b. 30.6 ohms c. 75 ohms d. 74.5 ohms
20. Determine the characteristic impedance of a quarter wave matching section which will eliminate
standing waves and thereby provide a matched condition for a 300 ohm resistive load fed from
a 72 ohm transmission line.
a. 50 ohms b. 75 ohms c. 150 ohms d. 300 ohms
21. A transformer used to match a balanced transmission line to an unbalanced line
a. Auto transformer b. stub c. quarter wave stub d. balun
22. A form of transmission line used at high UHF and microwave frequencies sandwiched between 2
ground planes and separated from each by a dielectric.
a. Stripline b. microstrip c. coaxial line d. twin lead
23. A shorted transmission line less than quarter wavelength will exhibit ____ reactance
a. Inductive b. capacitive c. series LC d. parallel LC
24. A transmission line consisting of center conductor, a plastic insulation, a fine wire braid shield
and outer plastic insulation as a jacket.
a. Coaxial cable b. twin lead c. waveguide d. twisted pair
25. RJ45 is the common connector used in what type of transmission line?
a. Flat wire b. twisted pair c. coaxial cable d. shielded pair
26. SWR stands for:
a. Shorted Wave Radiation c. Shorted Wire Region
b. Sine Wave Response d. none of the above
27. An example of an unbalanced line is:
a. a coaxial cable c. an open-wire-line cable
b. 300-ohm twin-lead TV cable d. all of the above
28. The characteristic impedance of a cable depends on:
a. the resistance per foot of the wire used
b. the resistance per foot and the inductance per foot
c. the resistance per foot and the capacitance per foot
d. the inductance per foot and the capacitance per foot
29. For best matching, the load on a cable should be:
a. lower than Z0 b. equal to Z0 c. higher than Z0 d. 50 ohms
30. The characteristic impedance of a cable:
a. increases with length c. increases with voltage
b. increases with frequency d. none of the above
31. The velocity factor of a cable depends mostly on:
a. the wire resistance c. the inductance per foot
b. the dielectric constant d. all of the above
32. The optimum value for SWR is:
a. zero b. as large as possible c. one d. there is no optimum value
33. A non-optimum value for SWR will cause:
a. standing waves c. higher voltage peaks on cable
b. loss of power to load d. all of the above
34. VSWR stands for:
a. variable SWR b. voltage SWR c. vacuum SWR d. none of the above
35. A Smith Chart is used to calculate:
a. transmission line impedances c. optimum length of a transmission line
b. propagation velocity d. transmission line losses
36. A balanced load can be connected to an unbalanced cable:
a. directly b. by using a "balun" c. by using a filter d. cannot be connected
37. Parallel lines are usually operated as ____________________ lines since both wires are
symmetrical with respect to ground.
a. Open wire b. unbalanced c. symmetrical d. balanced
38. Normally, a transmission line is terminated with a load equal to its ____________________
impedance.
a. characteristic b. balanced c. unbalanced d. symmetrical
39. Twisted-pair cables are transmission lines for relatively ____________________ frequencies.
a. high b. low c. radio d. microwave
40. The increase of a wire's resistance with frequency is called the ____________________ effect.
a. capture b. flywheel c. skin d. end
41. The inductance and capacitance of a cable are given per unit ____________________.
a. meter b. frequency c. foot d. length
42. A cable that is terminated in its characteristic impedance is called a ____________________
line.
a. resistive b. matched c. non resonant d. all of these
43. The ideal value for SWR is ____________________.
a. one b. zero c. infinity d. none of these
44. Short transmission-line sections called ____________________ can be used as capacitors or
inductors.
a. wave impedances b. quarter wave lines c. stubs d. short circuits
45. A ____________________ wavelength transmission line can be used a transformer.
a. one quarter b. one half c. full d. one fourth
46. A transmission line has 2.5 pF of capacitance per foot and 100 nH of inductance per foot.
Calculate Its characteristic impedance.
a. 300 ohms b. 150 ohms c. 175 ohms d. 200 ohms
47. Two wires with air as a dielectric are one inch apart. The diameter of the wire is .04 inch.
Calculate, approximately, its characteristic impedance.
a. 300 ohms b. 200 ohms c. 400 ohms d. 386 ohms
48. If a coaxial cable uses plastic insulation with a dielectric constant r = 2.6 , what is the velocity
factor for the cable?
a. 0.75 b. 1.3 c. 0.5 d. 0.62
49. A cable has a VSWR of 10. If the minimum voltage along the cable is 20 volts, what is the
maximum voltage along the cable?
a. 200 volts b. 100 volts c. 80 volts d. 400 volts
50. A lossless line has a characteristic impedance of 50 ohms, but is terminated with a 75-ohm
resistive load. What SWR do you expect to measure?
a. 1.25 b. 1.5 c. 1.75 d. 2
51. If a cable has an SWR of 1.5, what will be the absolute value of its voltage coefficient of
reflection?
a. 2 b. 1.5 c. 0.2 d. 0.1
52. The most commonly used transmission line is a
a. two-wire balanced line b. single wire c. three-wire line d. coax
53. The characteristic impedance of a transmission line does not depend upon its
a. length b. conductor diameter c. conductor spacing d. none of the above
54. Which of the following is not a common transmission line impedance?
a. 50 Ω b. 75 Ω c. 120 Ω d. 300 Ω
55. For maximum absorption of power at the antenna, the relationship between the characteristic
impedance of the line ZO and the load impedance Zl should be
a. ZO = Zl b. ZO > Zl c. ZO < Zl d. ZO = 0
56. The mismatch between antenna and transmission line impedances cannot be corrected for by
a. using an LC matching network b. adjusting antenna length
c. using a balun d. adjusting the length of transmission line
57. A pattern of voltage and current variations along a transmission line not terminated in its
characteristic impedance is called
a. an electric field b. radio waves c. standing waves d. a magnetic field
58. The desirable SWR on a transmission line is
a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. infinity
59. A 50 Ω coax is connected to a 73 Ω antenna. The SWR is
a. 0.685 b. 1 c. 1.46 d. 2.92
60. The most desirable reflection coefficient is
a. 0 b. 0.5 c. 1 d. infinity
61. A ratio expressing the percentage of incident voltage reflected on a transmission line is known
as the
a. velocity factor b. standing wave ratio c. reflection coefficient d. line efficiency
62. The minimum voltage along a transmission line is 260 V, while the maximum voltage is 390 V.
The SWR is
a. 0.67 b. 1.0 c. 1.2 d. 1.5
63. Three feet is one wavelength at a frequency of
a. 100 MHz b. 164 MHz c. 300 MHz d. 328 MHz
64. At very high frequencies, transmission lines are used as
a. tuned circuits b. antennas c. insulators d. resistors
65. A shorted quarter-wave line at the operating frequency acts like a(n)
a. series resonant circuit b. parallel resonant circuit c. capacitor d. inductor
66. A shorted half-wave line at the operating frequency acts like a(n)
a. capacitor b. inductor c. series resonant circuit d. parallel resonant circuit
67. The chief advantage of coaxial cable over open-wire line is
a. Minimized radiation losses b. Low cost
c. Low noise pick up d. Low resistive losses
68. The ratio of actual velocity to free-space velocity is called
a. Velocity factor b. Relative dielectric constant
c. Velocity of propagation d. Delay time
69. In a balanced line, the same current flows in each line but is
a. 45º out of phase b. 90º out of phase
c. 180º out of phase d. 270º out of phase
70. What is the length of a quarter-wavelength section of RG-8A/U coaxial cable at a frequency of
144.2 Mhz if its velocity factor is 0.69.
a. 52.1 cm b. 35.9 cm c. 143.6 cm d. 2.08 m
71. A nonlossy transmission line that is terminated with a resistive load that is equal to the
characteristic impedance of the line
a. Has the same impedance at all points along the line
b. Has a VSWR of 1:1
c. d. Has a reflection coefficient at the load equal to zero
d. All the above
72. A flat line indicates
a. No reflection b. VSWR = 1 c. No physical imperfections d. a and b
73. A nonlossy transmission line terminated with a short circuit has an
a. In-phase reflected voltage that is equal in magnitude to the incident voltage
b. Opposite-phase reflected voltage that is equal in magnitude to the incident voltage
c. In-phase reflected voltage that is smaller in magnitude than the incident voltage
d. Opposite-phase reflected voltage that is smaller in magnitude than the incident voltage
74. A 50-Ω transmission line that has a load impedance of 300 Ω has a VSWR of
a. 6:1 b. 1:6 c. 0.666:1 d. 1.5:1
75. The input impedance of a quarter-wavelength section of a 50-Ω transmission line that is
terminated with a short is
a. 50 Ω b. 0 Ω(a short) c. Infinite (open) d. 100 Ω
76. A device that is used to match an unbalanced transmission line to a balanced transmission line is
called a
a. Quarter-wavelength matching transformer b. Balun
c. Shorted-stub section d. Slotted line
77. In practice, the transmission lines are almost connected to antennas that have a _________.
a. resistive load whose resistance is greater than the characteristic impedance of the line
b. resistive load whose resistance is less than the characteristic impedance of the line
c. resistive load at the resonant frequency
d. capacitive load
78. When the transmission line is matched to the load, it
a. transfers maximum current to the load c. transfers maximum voltage to the load
b. transfers maximum power to the load d. reduces the load current
79. Conventional transmission media include
a. twisted cable pair b. waveguide c. fiber optic cable d. all of these
80. To couple a coaxial line to a parallel wire line, it is best to use a _____
a. slotted line b. directional coupler c. balun d. quarter wavelength transformer
81. Impedance inversion may be obtained with
a. an open circuited stub c. a short circuited stub
b. a quarterwave line d. a half-wave line
82. To be properly matched, the ratio of maximum to minimum voltage along a transmission line
should be equal to
a. 50 b. 10 c. 2 d. 1
83. When ZL Zo, the power sent down the line toward the load is called the
a. the incident power c. the reflected power
b. the power dissipation d. the carrier power
84. For transmission line load matching over a range of frequencies, it is best to use a
a. Balun c.broadband directional coupler
b. double stub d. single adjustable stub
85. A short section of a transmission line, open or shorted that is used to match the impedance of
the line to that of an antenna or transmitter.
a. slotted line b. stub c. wavetrap d. lecher wire
86. The property of a material that determines how much electrostatic energy can be stored per
unit volume when voltage is applied.
a. Permeability b. magnetic effect c. capacitance d. permittivity
87. The value of the total opposition of the transmission media to the flow of electromagnetic field
energy is called
a. characteristic impedance b. velocity factor c. standing waves d. reflected waves
88. When mismatch is great, this power actually cause damage to the transmitter or the line itself.
a. the incident power c. the reflected power
b. the power dissipation d. the carrier power
89. The measure of the superiority of a material over vacuum as a path for magnetic lines of force is
a. Permittivity b. permeability c. conductivity d. resistivity
90. The number of standing waves on the wire is equal to the length of the wire divided by a half
wavelength. The principle which allows antennas to operate at different frequencies which are
integral multiples of the fundamental frequency is called __________.
a. harmonic operation c. decimonic operation
b. electromagnetic reverberation d. asynchronous operation
91. A coax line has an attenuation of 2.4 dB per 100 ft. The attenuation for 2.75 ft. is ____ dB.
a. 2.4 b. 4.8 c. 3.3 d. 6.6
92. When a quarter wave stub is used to match a 600 ohm antenna to a line of 52 ohms, the
impedance of the matching stub must be ________ ohms.
a. 176 b. 200 c. 150 d. 300
93. The characteristic impedance of a transmission line is determined by
a. its length c. its height above ground
b. its physical construction d. the operating frequency
94. When the diameter of two conductors of a two-wire transmission line is held constant, the
effect of decreasing the distance between the conductors is to
a. decrease the impedance c. increase the surge impedance
b. increase radiation resistance d. decrease SWR
95. Considering a coaxial transmission line, maximum voltage on the line divided by the minimum
voltage equals the
a. characteristic impedance b. ISWR c. VSWR d. inductive reactance
96. In a transmission line, if the SWR or maximum current to a minimum current ratio of 2:1, the
ratio of the maximum voltage to the minimum voltage is
a. 1:4 b. 4:1 c. 1:2 d. 2:1
97. Transmission lines are either balanced or unbalanced with respect to
a. negative terminal b. input c. ground d. positive terminal
98. The radiation resistance of a quarterwave antenna is
a. 49 ohms b. 288 ohms c. 72 ohms d. 144 ohms
99. A radio transmission line of 500 ohms impedance is to be connected to an antenna having an
impedance of 200 ohms. What is the impedance of a quarter wave matching line?
a. 300 b. 316 c. 316.5 d. 361
100. Which of the following is used to measure SWR?
a. Multimeter b. reflectometer c. spectrum analyzer d. oscilloscope
You might also like
- BJT NotesDocument110 pagesBJT NotesHardesh Chauhan100% (1)
- Amplitude ModulationDocument89 pagesAmplitude Modulationelyk herreraNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line 101Document6 pagesTransmission Line 101George Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- Microwave CommunicationsDocument58 pagesMicrowave CommunicationsJesmar Enerio0% (1)
- Solved Problems in Microwave EngineeringDocument11 pagesSolved Problems in Microwave EngineeringTunde EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- HV Protection Relays Setting Calculation Rev-4Document58 pagesHV Protection Relays Setting Calculation Rev-4raza23988% (16)
- MCQ in Radiation and Wave Propagation PDFDocument106 pagesMCQ in Radiation and Wave Propagation PDFAaron EstacionNo ratings yet
- Geas 1Document84 pagesGeas 1Mariz-Elaine Noceja Rodriguez100% (7)
- Antennas Questions With ExplainationDocument43 pagesAntennas Questions With ExplainationmeetsanthoshNo ratings yet
- Excel Review Center Refresher Course EST: Give Your Best Shot !Document4 pagesExcel Review Center Refresher Course EST: Give Your Best Shot !Nida Bagoyboy NatichoNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave PropagationDocument81 pagesRadio Wave PropagationJoseph JeremyNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave PropagationDocument92 pagesRadio Wave PropagationFufa OdaNo ratings yet
- Emf (Electromotive Force)Document44 pagesEmf (Electromotive Force)shirley_ling_15No ratings yet
- COMMS 6 - Trans Line AnswersDocument4 pagesCOMMS 6 - Trans Line AnswersJerina Jeneth Cruz FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Pinoybix WADocument28 pagesPinoybix WAKenNo ratings yet
- COMMS 2 - Antenna & RadiowaveANSWERSDocument4 pagesCOMMS 2 - Antenna & RadiowaveANSWERSRovina LacunaNo ratings yet
- Elecs Ref 2019Document8 pagesElecs Ref 2019Hary KrizNo ratings yet
- Excel Review Center ECE Refresher/Coaching Course Estth1Document10 pagesExcel Review Center ECE Refresher/Coaching Course Estth1Al-ajim HadjiliNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument5 pagesReviewerRejg MendozaNo ratings yet
- Solved Problem in Microwave Engineering Part 2Document15 pagesSolved Problem in Microwave Engineering Part 2Tunde EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Antenna & Wave GuidesDocument53 pagesAntenna & Wave Guideshafiz azmanNo ratings yet
- Transmi Finals Set BDocument10 pagesTransmi Finals Set BKerwin TejucoNo ratings yet
- Preboard EST 2ndbatch April2015 SetBDocument15 pagesPreboard EST 2ndbatch April2015 SetBLopez Shian ErvinNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Chapter 4Document6 pagesQuestion Bank Chapter 4duppal35No ratings yet
- BE Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering PDFDocument670 pagesBE Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering PDFRahul TadeNo ratings yet
- Transmi Finals Set BDocument10 pagesTransmi Finals Set BKerwin TejucoNo ratings yet
- MicrowaveDocument24 pagesMicrowavejm m100% (1)
- Transmission MCQ Pinoy Bix 400Document23 pagesTransmission MCQ Pinoy Bix 400kathrineNo ratings yet
- Testatika Princip PDFDocument0 pagesTestatika Princip PDFmanos306No ratings yet
- MCQ in Communications Engineering by Lomboy & VillanuevaDocument114 pagesMCQ in Communications Engineering by Lomboy & VillanuevaSheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- Cellular TelephonyDocument88 pagesCellular TelephonySheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- Antenna and WaveguidesDocument5 pagesAntenna and WaveguidesRenz Dave Attos SiyNo ratings yet
- Microwave Communications - Mcqs (1-300)Document43 pagesMicrowave Communications - Mcqs (1-300)Abdul Hameed100% (1)
- PINOYBIX NoiseDocument50 pagesPINOYBIX NoiseNida Bagoyboy NatichoNo ratings yet
- Group Study - Microwaves Answer KeyDocument10 pagesGroup Study - Microwaves Answer KeySheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Transmission FundamentalsDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 1 Transmission FundamentalsDarwin Lajato Tipdas0% (1)
- Iecep Compilation EsatDocument10 pagesIecep Compilation Esatjanno2101No ratings yet
- COMMS 3 Microwave AnswersDocument5 pagesCOMMS 3 Microwave AnswersClyde Ann CantagoNo ratings yet
- Sand NotesDocument226 pagesSand NotesHGFLJJ0% (1)
- Road To EngineerDocument73 pagesRoad To EngineerDwight Eizen CristobalNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Modulation Part 1 ECE Board ExamDocument13 pagesMCQ in Modulation Part 1 ECE Board ExamXyNo ratings yet
- Wave PropagationDocument47 pagesWave PropagationFerdausi HatabNo ratings yet
- Comms Assignment MCQsDocument25 pagesComms Assignment MCQschristine geronimoNo ratings yet
- Periodic Exam 6Document5 pagesPeriodic Exam 6Inah RamosNo ratings yet
- MCQ AntennaDocument26 pagesMCQ AntennaRadha Nandhini100% (5)
- NEC3203 Geminiano Assignment-6Document13 pagesNEC3203 Geminiano Assignment-6JOSEFCARLMIKHAIL GEMINIANONo ratings yet
- 519 - Transmission Line Theory by VishnuDocument24 pages519 - Transmission Line Theory by VishnuSairam SairamNo ratings yet
- AWP NotesDocument76 pagesAWP NotesSebastin SureshNo ratings yet
- Henry Dave D. Demorito Problem Set 1Document4 pagesHenry Dave D. Demorito Problem Set 1Henry Dave DemoritoNo ratings yet
- TranslinepptDocument89 pagesTranslinepptJohn Brix BalisterosNo ratings yet
- Transient of R.C. CircuitDocument9 pagesTransient of R.C. CircuitArinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Amplitude ModulationDocument92 pagesAmplitude ModulationjjaazzmmNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Basic Concepts in Power ElectronicsDocument7 pagesTutorial 1 - Basic Concepts in Power ElectronicsJohn Appleseed100% (1)
- Frenzel Exam Sheet (Key To Correction)Document22 pagesFrenzel Exam Sheet (Key To Correction)Patrick James De LeonNo ratings yet
- Iecep EsatDocument29 pagesIecep EsatIvy Cee100% (1)
- EST Super Compiled (IECEP)Document54 pagesEST Super Compiled (IECEP)kurte moyoNo ratings yet
- EST For CorrectionDocument2 pagesEST For CorrectionCaurelou PitocNo ratings yet
- 1AT3 Microwave Communications and Satellite CommunicationsDocument1 page1AT3 Microwave Communications and Satellite CommunicationsNicholson ZapantaNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER in Electronic Communications System by Wayne TomasiDocument112 pagesREVIEWER in Electronic Communications System by Wayne TomasiSheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- COMMS 6 - Trans Line AnswersDocument4 pagesCOMMS 6 - Trans Line Answersurfriend_jjn05No ratings yet
- 04.transmission Lines - 05.wave PropagationDocument15 pages04.transmission Lines - 05.wave PropagationAchilles Aldave100% (1)
- RQS 6 - Transmission Lines - AnswersDocument6 pagesRQS 6 - Transmission Lines - AnswersRenz Benhar Ocon BobadillaNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines - RefresherDocument9 pagesTransmission Lines - RefresherShebNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument15 pagesTransmission LinesTalitha Cumi CruzNo ratings yet
- TX LineDocument10 pagesTX LineJonathan Zabala JrNo ratings yet
- Ece 511final Exam - Oct2017printingDocument3 pagesEce 511final Exam - Oct2017printingLoryliza M DeiparineNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument2 pagesTransmission LinesMaria Deborah Vivas BaluranNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line MCQ 2Document49 pagesTransmission Line MCQ 2Briely Briz100% (2)
- PERCDCDocument10 pagesPERCDCSheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER in Electronic Communications System by Wayne TomasiDocument112 pagesREVIEWER in Electronic Communications System by Wayne TomasiSheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- Group Study - Wave Propagation - QuestionnaireDocument8 pagesGroup Study - Wave Propagation - QuestionnaireSheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- Group Study - Wave Propagation - QuestionnaireDocument8 pagesGroup Study - Wave Propagation - QuestionnaireSheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- Group Study - Satcom Answer KeyDocument9 pagesGroup Study - Satcom Answer KeySheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- A. A. B. A. A. A.: Group Study - Op Amps and Ic'S Digital Electronics Answer KeyDocument6 pagesA. A. B. A. A. A.: Group Study - Op Amps and Ic'S Digital Electronics Answer KeyLorenz ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Group Study - Vac Tubes and Semicon Theory Diodes and ApplicationsDocument7 pagesGroup Study - Vac Tubes and Semicon Theory Diodes and ApplicationsSheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- Group Study - Transistors and Amplifiers Answer KeyDocument7 pagesGroup Study - Transistors and Amplifiers Answer KeySheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- Group Study - Instrumentation QuestionnaireDocument7 pagesGroup Study - Instrumentation QuestionnaireSheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- TLRF QB UNIT Full QBDocument54 pagesTLRF QB UNIT Full QBSri Nisha Tharani S100% (1)
- Quick Manual v1.5: Advanced CAT M1/GSM/GNSS/BLE Terminal With Flexible Inputs ConfigurationDocument16 pagesQuick Manual v1.5: Advanced CAT M1/GSM/GNSS/BLE Terminal With Flexible Inputs ConfigurationAlvaro ManosalvaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.5 Thevenin's Theorem: 1.1 ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExperiment No.5 Thevenin's Theorem: 1.1 ObjectiveNAJMUL HASSAN SARKARNo ratings yet
- Cable Shield Grounded at One End OnlyDocument4 pagesCable Shield Grounded at One End OnlyJoseph PoplingerNo ratings yet
- Motorola Maxtrac 100-300 User ManualDocument37 pagesMotorola Maxtrac 100-300 User ManualSabina RosuNo ratings yet
- Manual Motores Do Ferro Velho SanyoDocument64 pagesManual Motores Do Ferro Velho SanyoanclamixNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits 2008 Question PaperDocument6 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits 2008 Question Paperelimelek100% (3)
- Pullen - Conductance Curve Design Manual (1958)Document127 pagesPullen - Conductance Curve Design Manual (1958)Michele FelipeNo ratings yet
- Principles of Mechanical Measurements Prof. R.Raman Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 05Document18 pagesPrinciples of Mechanical Measurements Prof. R.Raman Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 05Abhinav SinglaNo ratings yet
- Elmo Servo DrivesDocument21 pagesElmo Servo DrivesjuliangoalNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits - 1 Unit - 3 Small Signal Analysis of JFET and MOSFET Amplifiers Biasing of Fet Amplifiers Fixed BiasDocument17 pagesElectronic Circuits - 1 Unit - 3 Small Signal Analysis of JFET and MOSFET Amplifiers Biasing of Fet Amplifiers Fixed BiasMutharasu SNo ratings yet
- Antennas and Circuits For Ambient Energy Harvesting in Wireless Body Area NetworksDocument6 pagesAntennas and Circuits For Ambient Energy Harvesting in Wireless Body Area NetworksMaritza NuñezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Analog Electronics Session-2: Unit 1Document15 pagesIntroduction To Analog Electronics Session-2: Unit 1SAHIL SATYAMNo ratings yet
- 8GE02 0e Active Antennas For RadiomonitoringDocument35 pages8GE02 0e Active Antennas For RadiomonitoringMostafa hdghNo ratings yet
- PMM-MD-53030-10 5 Phase Stepper DriverDocument18 pagesPMM-MD-53030-10 5 Phase Stepper DriverrobNo ratings yet
- An 903 Line TerminationDocument10 pagesAn 903 Line Terminationder_gaertnerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Op-Amp-Unit-IiiDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Op-Amp-Unit-IiiAnvesh MagantiNo ratings yet
- 4.-Especificaciones Tecnicas Del Equipo GPS FMU130-D0O835Document19 pages4.-Especificaciones Tecnicas Del Equipo GPS FMU130-D0O835Luis Meza ArevaloNo ratings yet
- RX Inverter Manual enDocument414 pagesRX Inverter Manual enMunja KlanaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For ExaminationDocument4 pagesImportant Questions For ExaminationSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit: Version 2 EE IIT, KharagpurDocument36 pagesDC Circuit: Version 2 EE IIT, KharagpurMuhammed UmarNo ratings yet
- OP-AMP SheetDocument14 pagesOP-AMP SheetAye Thein MaungNo ratings yet
- DG K 5120001Document65 pagesDG K 5120001Jimmy R. Calderon GualeNo ratings yet
- A Wideband Monopole Antenna DesignDocument67 pagesA Wideband Monopole Antenna DesignMohammad AlamsyahNo ratings yet
- Duo Series DU350, DU351: Product DescriptionDocument17 pagesDuo Series DU350, DU351: Product DescriptionEduardo NúñezNo ratings yet