Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electronic Mechanic 3 RD Semester NSQFQBCTS
Uploaded by
Wasim SKOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electronic Mechanic 3 RD Semester NSQFQBCTS
Uploaded by
Wasim SKCopyright:
Available Formats
Electronic Mechanic 3rd Semester - Module 1: Digital Storage Oscilloscope
Questions: Level 1
1 What is the full form of the abbreviation
D.S.O?
A Dual System Oscillator
B Dual Storage Oscillator
C Digital System Oscilloscope
D Digital Storage Oscilloscope
2 What type of wave form is available at pin
number 2 of function generator IC 8038?
A Sine wave
B Square wave
C Triangular wave
D Modulated wave
3 What is the name of the circuit?
A Astable multivibrator
B Bistable multivibrator
C RC coupled amplifier
D Monostable multivibrator
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 4
Questions: Level 2 7 What is the name of the factory setup done
to the Digital Storage Oscilloscope?
1 Which function makes a stable waveform A Normal setup
displayed on the DSO screen? B Factory setup
A Auto set function C Default setup
B Triggering function D Measurement setup
C Saving a setup function 8 Which IC is used in the Astable multivibrator
D Recalling a setup function circuit?
2 Which acquisition mode is used by the DSO
to sample the highest and lowest values of
the input signal?
A Auto mode
B Sample mode
C Average mode
D Peak detect mode
3 What is the purpose of sampling in DSO
operation?
A Control time base signal
A IC 324
B Convert analog signal to digital
B IC 555
C Convert digital signal to analog
C IC 723
D Visualize the signal on screen.
D IC 741
4 How the overall operation of DSO is
9 Which type of waveform is available in pin
controlled?
number 3 of IC 8038 function generator?
A Using microprocessors
A Sine wave
B Using ICs and transistors
B Square wave
C Using discrete components
C Triangle wave
D Using diodes and transistors
D Modulated wave
5 Which function is performed by the sample /
10 What is the advantage of the Digital Storage
Hold circuit along with the ADC in Digital
Oscilloscope?
Storage Oscilloscope?
A Process signals in analog format
A Storage
B Make measurement of digital data
B Data display
C Stores digital data for later viewing
C Data acquisition
D Electron beam moves across the screen
D Upload to computer
11 Which part of the DSO stores the processed
6 What is the name of the circuit built with IC
data of input signal voltage?
8038?
A Memory
B Screen display
C Analog to digital converter
D Digital to analog converter
A Pulse generator
B Sine wave generator
C Square wave generator
D Function generator
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 4
12 What is the name of waveform displayed on
the DSO screen?
A DC waveform
B Pulse waveform
C Ringing waveform
D Sawtooth waveform
13 How the digital equipment works with the
input voltage samples?
A Constant output voltage
B Continuously variable voltage
C Continuously variable current
D Convert it to Binary numbers
14 Which circuit is used in Digital Storage
Oscilloscope (DSO) to convert the input
sample voltage into digital information?
A Rectifier circuit
B Inverter circuit
C Digital to Analog converter circuit
D Analog to Digital converter circuit
15 Which type of waveform is available at pin
number 9 of function generator IC 8038?
A Sine wave
B Square wave
C Triangular wave
D Modulated wave
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 4
Module 1 : Digital Storage Oscilloscope - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2
SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 D 1 A
2 A 2 D
3 A 3 B
4 A
5 C
6 D
7 C
8 B
9 C
10 C
11 A
12 C
13 D
14 D
15 B
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 4
Electronic Mechanic 3rd Semester - Module 2 : 1.Basic SMD - I
Questions: Level 1 6 Which type of hot air pencil tip is used in
SMD soldering?
1 What is the type of SMD IC package?
A Oval type
A PGA pack
B Round type
B TSOP pack
C Angled type
C Flat pack
D Fine / jet type
D Quad flat pack
2 What is the acceptable resistance value limit
for the ESD wrist strap?
A 1Ω
B 1 kΩ
C 1 MΩ
D 10 MΩ
3 What is the type of SMD IC package?
A LCC
B PLCC
C MLCC
D TSOP
4 What is the power rating of soldering iron
used in electrical and electronics work?
A 15 to 35 watts
B 40 to 65 watts
C 75 to 100 watts
D 85 to 135 watts
5 What is the full form of the abbreviation
PGA used in SMD IC package?
A Package Grid Array
B Pin Grid Array
C Perfect Grid Array
D Popular Grid Array
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 5
Questions: Level 2 6 What is the name of SMD tool?
1 What is the range of temperature setting on
soldering work station for soldering SMD
ICs?
A 100°C to 200°C
B 200°C to 250°C
C 250°C to 280°C
D 280°C to 400°C A 90° forming tool
2 How does the desoldering braid removes B Monocole magnifier
the molten solder from the joint on the PCB? C Heated tweezers
A By capillary action D Soldering pumps
B By heating the joint 7 Which type of leads constructed in SOIC
C By hardening the solder package?
D By increasing the temperature A Padsin leads
3 Which method is effective to control ESD, B Gull wing leads
during manufacturing the devices? C Flat leads
A Use helmet D Pitch ball leads
B Use metal chain 8 Which SMD IC needs lead forming
C Use ESD wrist strap equipment to cut and bent into gull wing
D Use tables type?
4 Which technology is used to place the A TSOP
components directly on the printed circuit B FLAT Package
boards? C Pin grid array
A Solder Mount Technology D Leaded chip carrier
B Surface Mount Technology 9 Which is alternative to ceramic SMD IC
C Safety Metaphor Technology packages?
D Silicon multiplayer Technology A Glass packages
5 What is the name of the device? B Plastic packages
C Metal packages
D Fiber packages
10 What is the purpose of bumpered corners of
the Bumpered Quad Flat Pack?
A Prevent Vibration
B Dissipate heat
C Protects the IC leads
D Gives mechanical strength
A Microcontroller 11 What is the full form of the abbreviation
B Signal generator SOIC?
C SMD workstation A Surface Optimised Internal Circuits
D Insulation tester B Small Outline Integrated Circuits
C Service Outline Internal Circuits
D Solder Oriented Integrated Circuits
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 5
12 What is the name of the IC package?
A CQFP
B PQFP
C BQFP
D LQFP
13 What is the full form of the abbreviation
SMT?
A Specific Multipin Technology
B Small Metalised Technology
C Surface Mount Technology
D Solder Mount Technology
14 What is the use of Bench top Ionisers?
A To control moisture in atmosphere
B To control ESD in work environment
C To control voltage
D To eleminate molecules
15 What is called ‘tinning’ in soldering?
A Clean the tip of the iron
B Change the tip of the iron
C Melt a little solder on the tip of the iron
D Remove the tip of the iron
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 5
Questions: Level 3
1 What is the name of the defect caused due
to ESD event?
A Mechanical defect
B Dripping defect
C Latent defect
D Tombstone defect
2 How to minimize the cause of ESD during
the manufacturing of devices?
A Used for heel groundings
B Used ESD controlled footwear
C Used normal footmat
D Wear plastic dress material
3 What is the percentage of defect caused to
devices due to ESD?
A 10 to 20
B 25 to 30
C 35 to 50
D 60 to 90
4 Which material is used to make conductive
shoe covers to protect from static charges?
A Fibre
B Copper
C Plastic
D Polypropylene
5 What is the cause of ‘Voiding’ in SMT?
A Damaged wiring
B Damaged component
C Damaged joint strength
D Restricted voltage level
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 5
Module 2: 1.Basic SMD - I - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Questions: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 A 1 C 1 C
2 C 2 A 2 B
3 A 3 C 3 D
4 A 4 B 4 D
5 B 5 C 5 C
6 C 6 C
7 B
8 B
9 B
10 C
11 B
12 C
13 C
14 B
15 C
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 5
Electronic Mechanic - 3rd Semester - Module 2 : 2. Basic SMD - II
Questions: Level 1
1 What is the composition of solder paste
used for reflow soldering process?
A Tin and Lead
B Tin, Lead and flux
C Powdered solder and flux
D Rosin cored solder and flux
2 Which conformal coating material is used as
two part thermosetting mixture?
A Epoxy resin
B Acrylic resin
C Silicone resin
D Polyurethane resin
3 Which material is used to make the drill bits
for drilling PCB holes?
A Stainless steel
B High speed steel
C High carbon steel
D Solid coated Tungsten carbide
4 What is the size of pad width for soldering
resistors, capacitors and diodes on the
PCB?
A 50 Thou
B 60 Thou
C 70 Thou
D 80 Thou
5 Which colour of solder mask is used on
PCBs?
A Brown
B Orange
C Green
D Violet
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 5
Questions: Level 2 8 What is the ramp-up rate of temperature in
the preheat zone of reflow soldering
1 What is the shape of pad used to solder process?
Dual In Line (DIL) components on PCB? A 1°C to 3°C / sec
A Oval B 4°C to 5°C / sec
B Round C 6°C to 10°C / sec
C Square D 11°C to 20°C / sec
D Rectangle 9 Which is the common method of attaching
2 Which method of conformal coating is used surface mount components to a printed
for epoxy coated on PCBs? circuit board?
A Solvent A Wave soldering
B Peeling off B Manual soldering
C Microblasting C Soldering station
D Mechanical removal D Reflow soldering
3 Which conformal coating is easy to apply 10 What is the purpose of providing solder
and remove with low moisture absorption? mask on the PCBs?
A Epoxy resin A Easy soldering
B Acrylic resin B Remove conformal coating
C Silicon resin C Provide conformal coating
D Polyparaxylylene D Prevent solder bridges
4 Which protective chemical coating is applied 11 How the solder mask is removed on the
on the PCB? PCB for replacement of components?
A Shellac A Microblasting
B PVC coating B Grinding and scraping
C Enamel varnish C Conformal coating peeled off
D Polymer film coating D Photolithography
5 Which is the last zone on the reflow 12 What is the range of peak temperature
soldering? reached at reflow zone of reflow soldering
A Preheat zone process?
B Reflow zone A 10°C to 15°C
C Cooling zone B 20°C to 40°C
D Thermal soak zone C 41°C to 60°C
6 Which is the second stage in the reflow D 61°C to 80°C
soldering process? 13 How the fine grain structure of soldered joint
A Reflow zone is achieved by using reflow soldering
B Cooling zone process?
C Preheat zone A Fast cooling rate
D Thermal soak zone B Slow cooling rate
7 Which zone is the lengthiest in the reflow C Oven temperature change
soldering process? D Higher thermal soak time
A Reflow zone 14 What is the typical temperature range of
B Cooling zone cooling zone in flow soldering process?
C Preheat zone A 5° to 10°C
D Thermal soak zone B 11° to 15°C
C 16° to 25°C
D 30° to 100°C
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 5
15 Which fabrication technology is used for the
assembly of the circuit board?
A Microchip fabrication
B Single layer fabrication
C Double sided fabrication
D Plated through hole fabrication
16 What is the name of technology used to
mount components on multilayer PCBs?
A Microblasting
B Peeling technique
C Joining technique
D Plated through hole
17 Which type of coating process is used to
apply para-xylylene as conformal coating on
PCB?
A Dipping
B Brushing
C Spraying
D Chemical vapour deposition
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 5
Questions: Level 3 7 What causes a decrease in cleaning by flux
leads to poor wetting and defective solder
1 What is the effect on the solder paste, when joint in reflow soldering process?
the ramp-up rate exceeds the maximum A Higher ramp-up rate
slope in reflow soldering process? B Longer preheat zone time
A Poor wetting C More thermal soak exposure
B Fire and gases D Insufficient time/temperature
C Blow hole effect 8 How the damaged Vias in PTH circuit
D Spattering effect boards are repaired?
2 What is the effect on components, after the A Replace PCB
ramp-up rate exceeds the maximum slope B Use jumpers
in the heat zone of reflow soldering C Use eyelets
process? D Connectors
A Burnt
B Cracking
C No change
D Desoldered
3 At which zone the maximum allowable
temperature of the reflow soldering process
is reached?
A Reflow
B Cooling
C Preheat
D Thermal soak
4 What is the purpose of apply polymer
coating on the PCB?
A To improve circuit connectivity
B To prevent corrosion
C To prevent temperature
D To prevent resistance
5 What is the cooling rate suggested for
reflow soldering process?
A 3°C/second
B 4°C/second
C 5°C/second
D 10°C/second
6 What is the effect on excessive intermetallic
growth caused by wetting time above
liquidus in reflow soldering process?
A Poor wetting
B Flux oxidation
C Joint brittleness
D Solder spattering
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 5
Module 2 : 2.Basic SMD - II - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 C 1 A 1 D
2 A 2 C 2 B
3 D 3 B 3 A
4 C 4 D 4 B
5 C 5 C 5 B
6 D 6 C
7 C 7 D
8 A 8 C
9 D
10 D
11 D
12 B
13 A
14 D
15 A
16 D
17 D
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 5
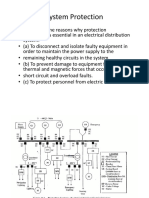
Electronic Mechanic 3rd Semester - Module 3 : Protection Devices
Questions: Level 1 6 What is the current rating of tinned copper
wire 40 SWG used for rewireable fuse?
1 What is the fusing factor of rewireable HRC A 1.0 A
fuse? B 1.5 A
A 1.0 C 2.5 A
B 1.1 D 4.0 A
C 1.2 7 What is the name of the fuse cartridge part
D 1.5 marked as ‘X’?
2 What is the current rating of cartridge fuse
used for domestic wiring?
A 1250 Ampere
B 1350 Ampere
C 1450 Ampere
D 1550 Ampere
3 What is the current rating of rewireable fuse
used for domestic wiring? A Heat contact
A 200 A B Fuse wire
B 300 A C Sand filling
C 400 A D Break indicator
D 500 A 8 What is the full form of the abbreviation
4 What is the name of the part marked as ‘X’ ELCB used in Electrical circuit?
in the MCB? A Earth Lead Circuit Breakers
B Electrical Live Contact Breakers
C Equipment Load Circuit Breakers
D Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers
9 What is the type of relay?
A Latch
B Plunger A Thermal relay
C Solenoid B Dry reed relay
D Contact C Impulse relay
D Latch relay
5 What is the name of the relay used in
electrical circuit? 10 Which series MCB is used for protection of
motor?
A ‘L’ series MCBs
B ‘F’ series MCBs
C ‘G’ series MCBs
D ‘DC’ series MCBs
A Latching relay
B Ferreed relay
C Dry reed relay
D Voltage sensing relay
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 6
11 What is the breaking capacitor of a DC
series MCB?
A 6 kA
B 8 kA
C 10 kA
D 12 kA
12 What is the maximum voltage rating for ‘DC’
series MCBs?
A 110 VDC
B 220 VDC
C 415 VDC
D 440 VDC
13 What is the maximum current rating for 4
pole MCB?
A 50 A
B 60 A
C 70 A
D 80 A
14 What is the fusing factor of a rewireable
fuse selected for over current protection in a
circuit?
A 1.1
B 1.2
C 1.3
D 1.4
15 What is the name of the current interrupted
by the circuit breaker?
A Rated current
B Residual current
C Earth leakage current
D Prospective fault current
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 6
Questions: Level 2 7 What is the fusing current for a rewireable
fuse?
1 Which relay has contact arrangement to A 1.2
break make or transfer contact B 1.5
combination? C 2.2
A Dry reed relay D 1.4 to 1.7
B Latching relay 8 Which parameter opens the fuse element
C Mercury wetted contact relay under fault, without damaging the load?
D Clapper type armature relay A Current rating
2 Which relay functions whenever the current B Voltage rating
in the coil reaches on upper limit? C Power rating
A Latching relay D Rupturing capacity
B Under current relay 9 Which relay is used for the time delay
C Current sensing relay purpose?
D Voltage sensing relay A Reed relay
3 Which device is used in electrical B Impulse relay
installations to protect from electric shock? C Thermal relay
A MCB D Electromagnetic relay
B MCCB 10 Which relay is operating with very low
C ELCB power?
D Insulator A Reed relay
4 Which type of relay is used in voltage B Impulse relay
stabilizer? C Thermal relay
A Latching relay D Electromagnetic relay
B Under current relay 11 What is the current rating of cartridge fuse
C Current sensing relay with brown colour code?
D Voltage sensing relay A 1A
5 What is the name of device? B 2A
C 4A
D 5A
12 How much time is taken by overload relay to
open motor contact at 500 percentage of full
load current?
A 5 sec
B 10 sec
C 15 sec
D 20 sec
A Starter
B Relay
C Contactor
D Switch
6 What is the maximum earth fault loop
impedance if an ELCB with a rated tripping
current of 30 mA?
A 900 Ω
B 1200 Ω
C 1666 Ω
D 2666 Ω
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 6
13 What is the type of miniature circuit breaker
(MCB)?
A 2 pole MCB
B 3 pole MCB
C 4 pole MCB
D Single pole MCB
14 Which device opens and closes an auxiliary
circuit?
A Fuse
B Relay
C Starter
D Circuit breaker
15 What is the current rating of copper colour
fuse cartridge?
A 25 ampere
B 35 ampere
C 50 ampere
D 63 ampere
16 Which function is performed by the isolator
in an electrical circuit?
A As a fuse
B As a switch
C Over loaded cut off
D Earth leakage cut off
17 Which condition the MCB is breaking open
of the electrical circuit?
A Low current
B High voltage
C Short circuit
D Earth leakage
18 What is the trip for clearing short circuits in
MCB combination circuit breaker?
A 1 milli second
B 3 milli second
C 4 milli second
D 5 milli second
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 6
Questions: Level 3
1 What is the cause of motor starts with
chattering noise?
A High voltage
B No volt coil burnt
C Control circuit of relay open
D Dust between the contacts in electromagnet
2 Which formula is used to find the fusing
factor?
Minimum fusing current
A Fusing formula =
Rated current
Rated current
B Fusing formula =
Minimum fusing current
C Fusing factor = Minimum fusing current –
Rated current
D Fusing factor = Minimum fusing current +
Rated current
3 What is the cause of humming noise from
the starter?
A Low voltage
B Open no volt coil
C Auxiliary contact not closing
D Meeting on the no - volt coil
4 What is the factor for time taken a fuse to
interrupt the circuit in the event of fault?
A Power factor
B Fusing factor
C Cut off factor
D Paralleling factor
5 What is the cause of failure of contactor due
to too much heating of the no-volt coil?
A Low voltage
B Higher incoming supply
C Control circuit of relay open
D Open in no-volt coil circuit
6 Why the AC relay connected to DC supply
draw more current?
A High voltage
B High current
C High resistance
D Absence of inductive reactance
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 6
Module 3: Protection Devices - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Questions: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 B 1 D 1 D
2 A 2 C 2 A
3 A 3 C 3 A
4 C 4 D 4 C
5 C 5 C 5 B
6 B 6 C 6 D
7 D 7 D
8 D 8 D
9 C 9 C
10 C 10 A
11 A 11 C
12 B 12 B
13 B 13 B
14 D 14 B
15 D 15 D
16 B
17 C
18 B
- NIMI Question Bank - Page6/ 6
Electronic Mechanic - 3rd Semester - Module 4 : Electrical Control Circuits
Questions: Level 1 5 Which type of switch is used in the capacitor
start, induction run motor?
1 Which single phase induction motor is rated A SPST switch
for less then 1HP? B Rotary switch
A Commutator motor C Centrifugal switch
B Permanent capacitor motor D Push button switch
C Split-phase induction motor 6 Which motor is characterised by low rotor
D Fractional horse power motor circuit resistance and reactance?
2 What is the name of the centrifugal switch A Class - A
part marked ‘X’? B Class - B
C Class - C
D Class - D
A Contacts
B Governor
C Insulator ring
D Governor weight
3 What is the name of the torque speed
characteristics curve of the motor?
A Split phase motor
B Permanent capacitor motor
C Capacitor-start capacitor motor
D Capacitor-start induction run motor
4 How many watts is equal to 1 Horse power
(HP)?
A 726 watts
B 746 watts
C 756 watts
D 786 watts
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 5
Questions: Level 2 7 What is the name of the permanent
capacitor motor part marked ‘X’?
1 What is the class of squirrel cage induction
motor according to the starting
characteristics?
A Main winding
A Class - A B Series winding
B Class - B C Shunt winding
C Class - C D Auxiliary winding
D Class - D 8 Which test is conducted through the circuit?
2 How much starting torque is achieved by the
Class-D type squirrel cage motor?
A 200%
B 300%
C 500%
D 600%
3 How the centrifugal switch is connected in a
capacitor start, induction-run motor?
A Across the starting winding
B Across the running winding A Capacity test on Capacitor
C Series with the starting winding B Charge test on Capacitor
D Series with the running winding C Discharge test on Capacitor
4 What is the starting torque of Class-C type D Insulation test on Capacitor
squirrel cage motor in the rated speed? 9 What is determined by the way of
A 200% connecting main winding and auxiliary
B 300% winding in a split-phase motor?
C 500% A Torque created
D 600% B Coil resistance
5 What is the purpose of capacitor used in the C Direction of rotation
single phase motor? D Maximum flux produced
A To split current 10 Why the main and starting windings of split-
B To split voltage phase motor connected across the supply
C To split phase only at the time of starting?
D To split resistance A Minimise current flow
6 Which induction motor is preferred for B Decrease the magnetic flux
constant speed with high efficiency C Combine the magnetic flux
performance? D Produce rotating magnetic field
A Slip ring Im
B Split phase Im
C Shaded pole Im
D Squirrel cage Im
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 5
11 Which synchronous speed of the motor, the 16 Which class of squirrel case induction motor
starting winding is opened by the centrifugal is taking normal starting torque and used for
switch? general purpose?
A 30 to 45% A Class - A
B 50 to 70% B Class - B
C 75 to 80% C Class - C
D 81 to 90% D Class - D
12 How the overload relay in a manual D.O.L 17 What is the synchronous speed (Ns) of a
starter is activated during heavy load 3phase induction motor with 8 poles working
current? at 50 Hz?
A Manual switch off A 600 rpm
B Electromagnetic relay is off B 750 rpm
C Short circuit relay is on C 900 rpm
D Bimetallic strip get heated up D 1200 rpm
13 Which force is used capacitor-start,
induction-run motor to disconnect the
starting winding?
A Centripetal force
B Centrifugal force
C Gravitational force
D Electromagnetic force
14 What is the full load current of a 10 HP,
three phase, 415 V squirrel-cage motor?
A 5A
B 10 A
C 15 A
D 20 A
15 Which test is conducted through the circuit?
A Capacity test on capacitor
B Discharge test on capacitor
C Charge test on capacitor
D Insulation test on capacitor
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 5
Questions: Level 3
1 What is the result on the split-phase motor
by changing the main winding terminals?
A Speed increases
B Speed decreases
C No charge in rotation
D Direction of rotation reversed
2 Why squirrel cage induction motor is
preferred for efficient performance?
A Increased torque
B Decreased torque
C Variable speed
D Constant speed
3 Which motors are used on loads having
high inertia and long acceleration period?
A Commutator motor
B Split-phase motor
C Star-delta motor
D Resistance start-induction run motor
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 5
Module 4 : Electrical Control Circuits - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 D 1 B 1 D
2 B 2 B 2 D
3 A 3 C 3 C
4 B 4 A
5 C 5 C
6 A 6 D
7 D
8 B
9 C
10 D
11 C
12 D
13 B
14 C
15 A
16 B
17 B
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 5
Electronic Mechanic 3rd Semester - Module 5 : Electronic Cables and Connectors
Questions: Level 1 7 What is the full form of the abbreviation PTZ
cable used in security camera?
1 What is the size of thinnet type coaxial cable A Purpose Technique Zoom
used in network installations? B Phase Terminal Zoom
A 0.15 inch C Pan Tilt Zoom
B 0.25 inch D Pattern Type Zoom
C 0.35 inch 8 What is the name of cable?
D 0.45 inch
2 What is the distributed capacitance value
between the core and screen of coaxial
cable per meter?
A 120 pF
B 220 pF
C 320 pF
D 420 pF A Audio cable
3 What is the data transmission speed of USB B PTZ combo cable
3.0 for interfacing computers? C Micro phase cable
A 225 Mbps D 2 core power CCTV cable
B 625 Mbps 9 Which purpose BNC connector with 75
C 725 Mbps Ohms is used?
D 825 Mbps A Roof top to TV receivers
4 What is the full form of the abbreviation B Low power RF equipments
DVI? C Carry video Signals
A Digital Video Interface D Interconnect the cables
B Digital Visual Interface 10 What is the data transmission speed of
C Digital Versatile Interface category 4 twisted pair Network cables?
D Digital Vector Interface A 14 mbps
5 What is the maximum data transfer speed of B 15 mbps
coaxial cable? C 16 mbps
A 5 Mbps D 17 mbps
B 8 Mbps 11 Which types of cables are used for balanced
C 10 Mbps signal circuits?
D 12 Mbps A Double core screened cables
6 What is the audible frequency range in B Single core screened cables
communication? C Flat ribbon cable
A 20 Hz to 20 kHz D Twisted pair cable
B 30 kHz to 400 kHz
C 452 kHz to 455 kHz
D 550 kHz to 1600 kHz
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 5
Questions: Level 2 8 What is the purpose of shielded wire used in
audio signal cable?
1 What is the purpose of heavy-duty audio A Mechanical strength
cable four core individually screened B Grounds interference signal
7x0.2mm? C Increase frequency response
A For microphone use D Improve noise signal
B For line amplifiers 9 Which connector is used specifically to
C For data transmission provide DC power connection to devices?
D For main line usage A F-connector
2 Which cable supports the data, power and B TRS connector
video signals in security camera C XLR connector
application? D Barrel connector
A RG 8 10 Which part of the signal cable is crimped to
B RG 59 the outer conductor of F-connector?
C PTZ combo cable A Central conductor
D RG 400 B Outer insulation
3 Which type of RF cable is used for higher C Inner insulation
power applications? D Shield of the cable
A RG 8 11 How many channels of uncompressed PCM
B RG 60 audio signals are carried by the S/PDIF
C RG 174 cable?
D RG 213 A Two
4 Which cable is used for lower power B Four
application? C Six
A RG 60 D Eight
B RG 58 12 Which cable is used in S/PDIF
C RG 213 interconnecting home theatre and digital
D RG 174 audio systems?
5 What is the purpose of screen wire used in A Coaxial cable
audio cables? B Fiber optic cable
A To increase the quality C Multi core cable
B Reject unwanted signal D Multi strand cable
C To increase the flexibility 13 Which purpose the two core individually
D To provide mechanical strength screened heavy duty cables are used?
6 What is the use of F-connector? A Micro phones
A Telephone circuits B Audio consoles
B Power supply circuits C Data transmission
C Cable TV circuits D Program amplifiers
D Audio circuits only 14 What is the characteristics impedance of
7 What is the advantage of twisted copper RG 6U cable used for long line cable TV
wire in single transmission? transmission?
A Reduces cross talk A 25 Ω
B Increase cross talk B 50 Ω
C Carry wideband signal C 75 Ω
D Increase signal emissions D 100 Ω
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 5
15 What is the maximum length of UTP cable
used from node to Hub connection?
A 15 meters
B 25 meters
C 50 meters
D 100 meters
16 Which speed of maximum data signal is
carried by the CAT-6 twisted pair network
cable?
A 250 MHz
B 550 MHz
C 650 MHz
D 750 MHz
17 What is the full form of the abbreviation
HDMI?
A High Digital Multimedia Input
B Hybrid Digital Multifunction Interface
C High Definition Multimedia Interface
D Hybrid Design Multifunction Interconnect
18 Which tool is used to connect the cable
ends to lug terminals for firm contact and
avoid breaking of leads?
A Wire stripper
B Crimping tool
C Soldering iron
D Flat nose pliers
19 Which type of cable is used in satellite
receiver?
A RG 6
B RG 9
C RG 59
D CT 100
20 What is the characteristics impedance (Z0)
of BNC connector?
A 25 Ω
B 30 Ω
C 60 Ω
D 75 Ω
21 Which connector is used on unbalanced
audio cables?
A RCA plug
B BNC plug
C F - connector
D TRS connector
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 5
Questions: Level 3
1 What is the effect of mismatch in
characteristic impedance (Z0) with 50Ω to
75Ω coaxial cable?
A No video signal
B RF circuit fails
C Heating of components
D Coaxial cable burnt
2 Why the cotton braid is provided in between
the leads and shield of audio cables?
A Mechanical strength
B Protection from weather
C Flexibility to the cable
D Prevent unwanted interference signal
3 Why more number of strands and thicker
gauge wire is used for high power amplifier
to connect another location?
A To increase power
B To avoid line loss
C Reject unwanted signals
D To increase signal strength
4 What is the effect of using bare coaxial
cables without end connectors?
A Current increase
B Voltage reduce
C Mismatch the loads
D Wire resistance increase
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 5
Module 5: Electronic Cables and Connectors - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Questions: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 B 1 C 1 C
2 C 2 C 2 C
3 B 3 A 3 B
4 B 4 B 4 C
5 C 5 B
6 A 6 C
7 C 7 A
8 B 8 B
9 A 9 D
10 C 10 D
11 A 11 A
12 B
13 C
14 C
15 D
16 B
17 C
18 B
19 C
20 D
21 A
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 5
Electronic Mechanic - 3rd Semester - Module 6 : Communication Electronics
Questions: Level 1 5 What is the name of the signal used in
digital modulation?
1 What is the range of frequency for short
wave (SW) band?
A 550 kHz to 1650 kHz
B 3 MHz to 30 MHz
C 30 MHz to 100 MHz A ASK signal
D 200 MHz to 300 MHz B PSK signal
2 What is the name of block diagram? C FSK signal
D QAM signall
6 What is the range of frequency for Medium
Wave (MW) in AM broadcasting?
2nd
A 20 Hz to 20 kHz
B 452 Hz to 456 kHz
C 530 Hz to 1650 kHz
A TRF receiver
D 3 MHz to 26 MHz
B FM receiver
7 What is the speed of light?
C Satellite receiver
A 3 x 103 meters per second
D Superheterodyne receiver
B 3 x 106 meters per second
3 What is fidelity of receiver circuits?
C 3 x 108 meters per second
A Generated automatic gain
D 3 x 1010 meters per second
B Stability of amplifier
C Accuracy of reproduction
D Mixing complicated signals
4 What is the name of the section marked ‘X’
in the digital communication system?
A Amplifier
B Modulator
C Rectifier
D Multiplexer
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 5
Questions: Level 2 5 What is the modulation index of the
Amplitude modulated waveform?
1 What is the function of analog multiplier IC
AD 633?
A Generate FM signal
B Generate AM signal
C Demodulate AM signal
D Demodulate FM signal
2 Which antenna is used for Medium Wave
A 0.5
band in AM receiver?
B 5.0
A Loop antenna
C 10
B Wire antenna
D 50
C Telescopic antenna
6 What is the function of capacitor (C) in the
D Ferrite rod antenna
envelope detector circuit?
3 Which types of modulation techniques is
A Detects the signal
used to produce the wave form?
B Stores the signal
C Opposes the signal
D Grounds the signal
7 Which circuit is used to process the
demodulation of Amplitude modulated
signal?
A PSK A Ratio detector
B ASK B Slope detector
C FSK C Envelope detector
D QAM D Quadrature detector
4 What is the name of radio receiver? 8 Which type of FM detector concept
produces the frequency response
characteristics curve?
A FM receiver
B TRF receiver
C Reflectional receiver
D Superheterodyne receiver
A Ratio detector
B Foster-seeley FM detector
C FM slope detector
D Quadrature FM detector
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 5
9 Which instrument is necessary to align the
FM detector in receiver circuit?
A Ammeter
B Voltmeter
C Distortion Analyser
D Ohmmeter
10 Which type of modulation uses the signal
superimposed over the carrier waves?
A Amplitude modulation
B Frequency modulation
C Phase modulation
D Voice modulation
11 Which modulation method is used in binary
phase shift keying applications?
A Pulse Position Modulation
B Pulse Amplitude Modulation
C Amplitude Modulation
D Phase Modulation
12 What is the expansion of AFC?
A Automatic Function Control
B Automatic Frequency Control
C Automatic Filter Control
D Automatic Format Control
13 What is the range of frequency for FM
broadcasting?
A 3 MHz to 26 MHz
B 30 MHz to 75 MHz
C 88 MHz to 108 MHz
D 530 kHz to 1650 kHz
14 Which amplifier is first matches the output
impedance of the carrier oscillator with the
input impedance?
A Buffer amplifier
B Power amplifier
C Audio amplifier
D Video amplifier
15 Which type of antenna is used for point-to-
point communication of radio waves?
A Parabolic antenna
B Omnidirectional
C Dipole antenna
D Yasi antenna
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 5
Questions: Level 3
1 Why the modulation index is kept within
limits in amplitude modulated signal
transmission?
A Reduce distortion
B Improve signal strength
C Reduce fidelity of the signal
D Increase signal coverage area
2 What is the effect of increasing the
modulation depth to 100% in Amplitude
modulation process?
A No modulation
B Over modulation
C Low-level modulation
D Reduce distortion and interference
3 How the image frequency is prevented in
radio receiver circuits?
A Envelope Detector
B More IF amplifiers
C Low noise audio amplifier
D Highly selective RF amplifier
4 How the over modulation of carrier signal is
prevented by the broadcast station?
A Cut lower side band
B Limit upper side band
C Limiter circuits provided
D Use manual audio gain control
5 What is the effect on the AM transmitter
output if the modulation index value
exceeds unity?
A Output increases
B Weak signal
C No signal output
D Produces erroneous distortion
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 5
Module 6 : Communication Electronics - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 B 1 B 1 A
2 A 2 D 2 B
3 C 3 C 3 D
4 B 4 C 4 C
5 B 5 A 5 D
6 C 6 B
7 C 7 C
8 C
9 C
10 A
11 D
12 B
13 C
14 A
15 A
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 5
Electronic Mechanic - 3rd Semester - Module 7 : Microcontroller (8051)
Questions: Level 1
1 Which pin is marked as the master reset
(RST) function in microcontroller IC 8051?
A Pin No 9
B Pin No 20
C Pin No 30
D Pin No 40
2 What is the name of device marked ‘X’?
A Computer
B Microcontroller
C Microprocessor
D Traffic light control
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 5
Questions: Level 2 8 How the logic operations performed by the
MCS 51 family microcontroller?
A Bit operand
1 Which circuits uses microcontroller?
B Opcode format
A Computers
C Function mnemonic
B Multimeters
D Bits and Byte operands
C Microprocessors
D Embedded systems 9 What is the Vcc supply pin number for the
microcontroller IC 8051?
2 Which is developed to overcome the
A 21
drawback of the microprocessor?
B 30
A JFET
C 38
B MOSFET
D 40
C IGBT
D Microcontroller 10 What is the use of microcontroller?
A Small systems
3 Expand the abbreviation CISC used in
B Large and complex system
microcontroller?
C General purpose systems
A Complete Instruction Set Computer
D Automatically controlled devices
B Compact Instruction Set Computer
C Complex Integer Set Computer 11 What is produced by the DC motor,
D Complex Instruction Set Computer interfaced with 8051 microcontroller?
A Heat
4 Which electronic component is connected in
B Torque
pin number 18 and 19 of the IC 8051
C AC current
microcontroller?
D Electric field
A Sensor
B Crystal 12 What is the bit length of upcounting timers in
C Resistor 8051 microcontroller?
D Zener diode A 8 Bits
B 16 Bits
5 How many bits are numbered from OOH to
C 32 Bits
7FH for general-purpose addressable
D 64 Bits
locations in 8051 microcontroller?
A 32 bits 13 What is the name of the section that counts
B 64 bits a predefined number of processor clock
C 128 bits pulses, to generate a programmable delay?
D 256 bits A Timer
B Counter
6 Which instruction set, the accumulator
C Clock signal
specific instructions are grouped?
D Clock generate
A Logic
B Arithmetic 14 Which section in IC 8051 is running on
C Data transfer external clock source?
D Control transfer A Timer
B Counter
7 How many instructions available in the
C Clock signal
microcontroller family instruction set?
D Clock generator
A 17
B 45 15 What is the maximum delay possible using a
C 49 single 8051-microcontroller timer running at
D 111 12 MHz frequency?
A 8192 µS
B 16384 µS
C 32768 µS
D 65536 µS
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 5
16 Which is the timer input frequency for the
8051 microcontroller running at 12 MHz?
A 1 MHz
B 2 MHz
C 3 MHz
D 4 MHz
17 What is the purpose of using divide by 12
network in 8051 microcontroller oscillator
output to feed the timer?
A Clock signal
B Amplifier input signal
C Loading initial value
D Special function register
18 How the longer delays in basic program
using timer in 8051 microcontroller is
implemented?
A Modify component values
B Change microcontroller
C Rewrite the program
D Looping number of times
19 What is the minimum delay possible using a
single 8051 microcontroller timer running at
12 MHz frequency?
A 1 µS
B 5 µS
C 10 µS
D 100 µS
20 Which chip is versatile to use from simple
consumer electronics to high-end
applications?
A Chip on board
B Logic gate ICs
C Microprocessors
D Microcontrollers
21 What is the full form of the abbreviation SFR
used in microcontroller?
A Serial Function Register
B Safety Function Relay
C Special Function Register
D System Function Register
22 Which lens is fitted on the yellow light to
produce green light in the traffic light control
interfaced with the 8051 microcontroller?
A Red lens
B Blue lens
C Green lens
D Orange lens
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 5
Questions: Level 3
1 Which device protects the microcontroller
from high current drawn by DC motor circuit
interfaced with it?
A Fuse
B Over load relay
C Opto isolator
D Miniature circuit breaker
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 5
Module 7 : Microcontroller (8051) - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 A 1 D 1 C
2 B 2 D
3 D
4 B
5 C
6 C
7 D
8 D
9 D
10 D
11 B
12 B
13 A
14 B
15 D
16 A
17 A
18 D
19 A
20 D
21 C
22 B
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 5
Electronic Mechanic - 3rd Semester
Module 8 : Sensors, Transducers and Applications
Questions: Level 1
1 What is the name of the device?
A Thermistor
B Strain gauge
C Inductive transducer
D Temperature detector
2 What is the name of device used to convert
a physical quantity into its corresponding
electrical signal?
A Amplifier
B Transducer
C Oscillator
D Modulator
3 What is the full form of the abbreviation RTD
used as a sensor?
A Remote Transistor Detector
B Repulsion Type Detector
C Reluctance Transmitter Detector
D Resistance Temperature Detector
4 What is the maximum temperature of
platinum RTD device?
A 500°C
B 650°C
C 800°C
D 950°C
5 What is the range of temperature
measurement using thermocouples?
A 4° to 100°C
B 101° to 250°C
C 270° to 3000°C
D 3001° to 3500°C
- NIMI Question Bank - Page1/ 5
Questions: Level 2 7 What is the application of LVDT?
A To reduce temperature
1 Which sensor detect the presence of objects B To measure displacement
without any physical contact? C To measure residual stress
A LVDT D To measure speed
B Load cell 8 Which is functioning as the active type
C Strain gauge transducer?
D Proximity sensor A Thermocouple
2 Which device is used to convert force into B Potentiometer
electrical signal? C Dielectric gauge
A Load cell D Variable capacitance pressure gauge
B Thermistor 9 Which working principle is used in the
C Thermocouple proximity sensor?
D Photoelectric sensor A High voltage source
3 Which sensor is suitable for process B Low temperature source
temperature measurement of steel? C Low frequency signal
A Thermistor D Electromagnetic field
B Strain gauge 10 What is the application of thermistor in
C Thermocouple sensing circuit?
D capacitive transducer A To measure displacement
4 Which test is conducted through the circuit B To measure pressure
diagram? C To measure temperature
D To measure light intensity
11 Which signal is used by the passive
transducer to produce output signal?
A Magnetic signal
B Excitation signal
C Self-generating signal
D Light radiation signal
12 Which type of sensor gives quick and
precise measurements?
A Loadcell
A Sound control test
B Electrical strain gauge
B Speed control test
C Mechanical strain gauge
C Temperature control test
D Hydraulic strain gauge
D Light level control test
13 Which type of strain gauge is the most
5 What is the use of resistance hygrometer?
sensitive and reliable?
A To measure light intensity
A Hydraulic
B To measure humidity
B Mechanical
C To measure temperature
C Piezoelectric
D To measure pressure
D Electrical resistance
6 What is the application of strain gauge?
A Temperature measurement
B Pressure and displacement
C Radiation measurement
D Compression and tension measurement
- NIMI Question Bank - Page2/ 5
14 Which measurement is carried out by this
test?
A Vibration measurement
B Temperature measurement
C Strain measurement
D Displacement measurement
15 What is the function of resistance strain
gauge?
A Measurement of power
B Measurement of torque
C Measurement of voltage
D Measurement of ampere
16 Which component is used as the transducer
in the measurement of displacement?
A Resistor
B Inductor
C Capacitor
D Quartz crystal
17 What is the use of load cell?
A Converts force into linear movement
B Converts force into optical light rays
C Converts force into mechanical vibration
D Converts force into electrical signal
- NIMI Question Bank - Page3/ 5
Questions: Level 3
1 How the increase in temperature affects the
resistance value of the positive temperature
coefficient (PTC) component?
A Resistance value decreases
B Resistance value increases
C Resistance value remains the same
D Resistance value becomes infinity
- NIMI Question Bank - Page4/ 5
Module 8 : Sensors, Transducers and Applications - Key paper
Questions: Level 1 Questions: Level 2 Question: Level 3
SL.No Key SL.No Key SL.No Key
1 B 1 D 1 B
2 B 2 A
3 D 3 C
4 B 4 C
5 C 5 B
6 D
7 B
8 A
9 D
10 C
11 B
12 A
13 C
14 C
15 B
16 B
17 D
- NIMI Question Bank - Page5/ 5
You might also like
- C Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemFrom EverandC Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemNo ratings yet
- Project On Ic TesterDocument14 pagesProject On Ic TesterDebashish PalNo ratings yet
- BCD To 7 Segment Display ProjectDocument10 pagesBCD To 7 Segment Display ProjectPravin Gareta88% (16)
- Digital Voltmeter Using PIC MicrocontrollerDocument7 pagesDigital Voltmeter Using PIC MicrocontrollerbecemNo ratings yet
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxFrom EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Ground Fault Protection GuideDocument56 pagesGround Fault Protection Guidewilliamb285No ratings yet
- Bharati Vidyapeeth Institute of Technology Question Bank: Unit Test-I (Shift:-I)Document14 pagesBharati Vidyapeeth Institute of Technology Question Bank: Unit Test-I (Shift:-I)Shr3yasNo ratings yet
- C15 Adapter Board A612 PDFDocument22 pagesC15 Adapter Board A612 PDFOleg KuryanNo ratings yet
- Components of Control PanelDocument17 pagesComponents of Control PanelHarish Padmanaban100% (1)
- Ep1 en PDFDocument13 pagesEp1 en PDFAnonymous YjfIzg7No ratings yet
- Emerging Trends in Electronics MCQ PDF: Question BankDocument42 pagesEmerging Trends in Electronics MCQ PDF: Question BankHarshad Bhong43% (7)
- 3 RD Semester NSQFQBCTSDocument45 pages3 RD Semester NSQFQBCTSKiran AithalNo ratings yet
- CRO Multiple Choice Practice QuestionsDocument66 pagesCRO Multiple Choice Practice QuestionsAbcNo ratings yet
- De Thi AVCN1 - 7-2022Document7 pagesDe Thi AVCN1 - 7-2022vu965796No ratings yet
- Fiber Optical Communication DPMDocument46 pagesFiber Optical Communication DPMKiran AithalNo ratings yet
- MCQ From PICT College of EngineeringDocument14 pagesMCQ From PICT College of EngineeringSyket HossainNo ratings yet
- De Thi AVCN2 - 7-2022Document7 pagesDe Thi AVCN2 - 7-2022vu965796No ratings yet
- Pir Intruder Alarm Internship Report Sa Polytechnic CollegeDocument16 pagesPir Intruder Alarm Internship Report Sa Polytechnic Collegetaru22iloveyouNo ratings yet
- CSS Summative 1-3Document3 pagesCSS Summative 1-3koiNo ratings yet
- Microtips 01 27 2021 REX012832AWPP3N00000 RevD 201-1984173Document28 pagesMicrotips 01 27 2021 REX012832AWPP3N00000 RevD 201-1984173vicio tarNo ratings yet
- ELectrician 4 Thsem NSQFDocument38 pagesELectrician 4 Thsem NSQFAbhimanyu Kilania100% (3)
- Lab Manual: Syllabus Micro Project Final Year Projec MCQ With Answer Model Answer Sample QuestionDocument46 pagesLab Manual: Syllabus Micro Project Final Year Projec MCQ With Answer Model Answer Sample QuestionSOURABHNo ratings yet
- (22636) Emerging Trends in Electronics (EJ)Document47 pages(22636) Emerging Trends in Electronics (EJ)413 YASH MANENo ratings yet
- Linear and Digital IC Applications (III EEE MID II) QuizDocument5 pagesLinear and Digital IC Applications (III EEE MID II) Quizprathap kumarNo ratings yet
- BCD To 7 Segment LED Display Decoder Circuit Diagram and WorkingDocument19 pagesBCD To 7 Segment LED Display Decoder Circuit Diagram and WorkingAashish KumarNo ratings yet
- BCD To 7 Segment Display ProjectDocument11 pagesBCD To 7 Segment Display ProjectNeel UnadkatNo ratings yet
- Adc F09Document61 pagesAdc F09abdala67No ratings yet
- Logic Design Lab ManualDocument22 pagesLogic Design Lab ManualAzarkhan Mokashi100% (1)
- Logic Circuits I Study Guide For Ch6-7Document23 pagesLogic Circuits I Study Guide For Ch6-7Alexandre Guerreiro100% (1)
- Objective Type Question For Adc/Dac: A. B. C. DDocument6 pagesObjective Type Question For Adc/Dac: A. B. C. DsuryaNo ratings yet
- Amplifier 1Document37 pagesAmplifier 1Pawan VermaNo ratings yet
- Raystar Optronics OLED Module Specification SheetDocument28 pagesRaystar Optronics OLED Module Specification Sheetmarius.chitigaNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives:: Topic 2.2.3 - BCD Counter Topic 2.2.4 - Decade CounterDocument35 pagesLearning Objectives:: Topic 2.2.3 - BCD Counter Topic 2.2.4 - Decade CountersuriantoNo ratings yet
- Analog-Digital Converters: Types, Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument62 pagesAnalog-Digital Converters: Types, Characteristics and Applicationsparth bhardwajNo ratings yet
- ETE MCQ-QB CwipediaDocument42 pagesETE MCQ-QB CwipediaRAVI kumar100% (1)
- Study Guide M4Document4 pagesStudy Guide M4Dylan CosepNo ratings yet
- 202015Document7 pages202015Shubham TayadeNo ratings yet
- Nagindas Khandwala College of Commerce, Arts & Management Studies & Shantaben Nagindas Khandwala College of Science Malad (W), Mumbai - 64Document35 pagesNagindas Khandwala College of Commerce, Arts & Management Studies & Shantaben Nagindas Khandwala College of Science Malad (W), Mumbai - 64127fyitvanshnagdaNo ratings yet
- 9V To 22V: Level Translator Output DriverDocument2 pages9V To 22V: Level Translator Output DriverMutharasu SNo ratings yet
- EE610: CMOS Analog EE610: CMOS Analog Circuits: L0: IntroductionDocument23 pagesEE610: CMOS Analog EE610: CMOS Analog Circuits: L0: IntroductionEpili Rajkiran SarabaNo ratings yet
- A1821910492 19390 10 2019 MCQsWithAnsDocument94 pagesA1821910492 19390 10 2019 MCQsWithAnsJatin PawarNo ratings yet
- BCD To 7 Segment Display PDFDocument18 pagesBCD To 7 Segment Display PDFRobertoRodríguezNo ratings yet
- Digital and MPMC QuizDocument17 pagesDigital and MPMC QuiznjparNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document51 pagesChapter 6ezekiel makandwaNo ratings yet
- ADAC1030 Data Acquisition and Control SystemDocument43 pagesADAC1030 Data Acquisition and Control Systemnanasilva2325No ratings yet
- PTS Arduino Kunci JawabanDocument7 pagesPTS Arduino Kunci JawabanAzukni ElshyrazieNo ratings yet
- Test I. Instructions: Read The Questions Carefully and Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The SpaceDocument4 pagesTest I. Instructions: Read The Questions Carefully and Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The SpaceTrending 2019No ratings yet
- Alaziz Pre Lab 2Document2 pagesAlaziz Pre Lab 2Hamid NasirNo ratings yet
- CS302 - Analog and DigitalDocument5 pagesCS302 - Analog and DigitalGaitonde GaneshNo ratings yet
- MCQ EEE (All 6 Units)Document49 pagesMCQ EEE (All 6 Units)SantoshNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsJames GuevaraNo ratings yet
- EENG484 Midterm SampleDocument9 pagesEENG484 Midterm SampleZeina Al AnoutiNo ratings yet
- 74FCT3574-3.3V CMOS Octal D Register (Obsolete)Document7 pages74FCT3574-3.3V CMOS Octal D Register (Obsolete)Lau LauNo ratings yet
- Design and build gray code and BCD convertersDocument3 pagesDesign and build gray code and BCD convertersmarkjesterNo ratings yet
- 1/10'' Vga Cmos Image Sensor Gc0310: Galaxycore IncDocument38 pages1/10'' Vga Cmos Image Sensor Gc0310: Galaxycore Inciingos088No ratings yet
- Second Periodic Exam in Elective 10Document3 pagesSecond Periodic Exam in Elective 10cresel.alcantaraNo ratings yet
- 11-ch-1 complete short questionDocument1 page11-ch-1 complete short questiontaimoorriaz101No ratings yet
- AAI Jr. Executive Electronics Answer 2009Document2 pagesAAI Jr. Executive Electronics Answer 2009Paritam SoniNo ratings yet
- Exp-10 COLabDocument7 pagesExp-10 COLabAdarsh DwivediNo ratings yet
- Application Notes Guide of IGBT Driver 2019: I. Product Overview 1Document21 pagesApplication Notes Guide of IGBT Driver 2019: I. Product Overview 1eluy ledezmaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Unit - V: Registers & Counters Part - A (Each Question Carries 1 Mark)Document9 pagesQuestion Bank Unit - V: Registers & Counters Part - A (Each Question Carries 1 Mark)Nithya SNo ratings yet
- Demonstration of Digital Optical D Flip Flop Based On Photonic Micro-Ring ResonatorDocument3 pagesDemonstration of Digital Optical D Flip Flop Based On Photonic Micro-Ring ResonatorMark LawNo ratings yet
- DE LAB ManualC-18 FinalDocument85 pagesDE LAB ManualC-18 FinalBRAGPW,Karimnagar 087No ratings yet
- B 7 Segment Display DecoderDocument8 pagesB 7 Segment Display Decoderlokesh krapaNo ratings yet
- 143Document5 pages143Wasim SKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document22 pagesChapter 4Wasim SKNo ratings yet
- C SDocument27 pagesC SWasim SKNo ratings yet
- PG6Document1 pagePG6Wasim SKNo ratings yet
- C SDocument21 pagesC SWasim SKNo ratings yet
- PG7Document2 pagesPG7Wasim SKNo ratings yet
- Project OnDocument1 pageProject OnWasim SKNo ratings yet
- P 9Document1 pageP 9Wasim SKNo ratings yet
- PG 8Document2 pagesPG 8Wasim SKNo ratings yet
- PG 8Document2 pagesPG 8Wasim SKNo ratings yet
- S2212567114002111 - 1 s2.0 S2212567114002111 MainDocument14 pagesS2212567114002111 - 1 s2.0 S2212567114002111 MainEkta Saraswat VigNo ratings yet
- S2212567114002111 - 1 s2.0 S2212567114002111 MainDocument14 pagesS2212567114002111 - 1 s2.0 S2212567114002111 MainEkta Saraswat VigNo ratings yet
- Draft SPEC NO 0013-2011-19.06.14 PDFDocument37 pagesDraft SPEC NO 0013-2011-19.06.14 PDFKatikareddy Sreenu100% (1)
- Manual Service MMED6000DP-M7Document28 pagesManual Service MMED6000DP-M7wilmerNo ratings yet
- Electrical Control For Machines 7th Edition Lobsiger Solutions ManualDocument3 pagesElectrical Control For Machines 7th Edition Lobsiger Solutions Manualbrandicarrilloretfdampgw100% (14)
- British 100 Watt ManualDocument6 pagesBritish 100 Watt ManualVitor RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Circuit QuestionsDocument8 pagesElectrostatics Circuit Questions6C09 FUNG CHI LAMNo ratings yet
- Sharp r-8270 PDFDocument56 pagesSharp r-8270 PDFJulio AndresNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Electrical Code: P) E I T P A R Y Q W D T M O ODocument9 pagesThe Philippine Electrical Code: P) E I T P A R Y Q W D T M O Ojay garciaNo ratings yet
- Pectra: Reference, Installation and ProgrammingDocument20 pagesPectra: Reference, Installation and ProgrammingimasemozeseNo ratings yet
- VM405 PBBD2 52317 PDFDocument51 pagesVM405 PBBD2 52317 PDFpechnicNo ratings yet
- Esm-4450 Man Env11Document125 pagesEsm-4450 Man Env11Cristian SerbanoiuNo ratings yet
- DelixicatDocument354 pagesDelixicatRobert TiinNo ratings yet
- Fanuc10 140611214409 Phpapp02Document8 pagesFanuc10 140611214409 Phpapp02rotimi olalekan fataiNo ratings yet
- Protection DevicesDocument11 pagesProtection DevicesjishnusajiNo ratings yet
- Pre Heating Control CircuitDocument7 pagesPre Heating Control CircuitImam JavaNo ratings yet
- Cahier Technique No 212: The Neutral: A Live and Unique ConductorDocument32 pagesCahier Technique No 212: The Neutral: A Live and Unique ConductorDiego AraújoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety CheckDocument6 pagesElectrical Safety CheckFawaaz KhurwolahNo ratings yet
- Abb KatalogeditDocument60 pagesAbb KatalogeditSherinSyafarinaSuryanaNo ratings yet
- APX2180 APX4360 DPX2250 DPX1800 DPX11500: Owner's ManualDocument28 pagesAPX2180 APX4360 DPX2250 DPX1800 DPX11500: Owner's ManualDaniel CatherallNo ratings yet
- BA - KUKA flexFELLOW - V03 - en PDFDocument102 pagesBA - KUKA flexFELLOW - V03 - en PDFEdel WeissNo ratings yet
- Powerteam 2 Stage PumpDocument24 pagesPowerteam 2 Stage PumpdestroNo ratings yet
- Vapro 5600 BrochureDocument4 pagesVapro 5600 Brochurerajesh_rbpNo ratings yet
- Installation Guide for Wall Mounted Package Air ConditionersDocument26 pagesInstallation Guide for Wall Mounted Package Air ConditionersMukti AwanNo ratings yet
- Atr-Mix: Metal Enclosed SwitchgearDocument20 pagesAtr-Mix: Metal Enclosed SwitchgearMarco PoliNo ratings yet
- Material Plant Valuation DataDocument752 pagesMaterial Plant Valuation DataVikas Kulasri SharmaNo ratings yet
- Model Sr850: DSP Lock-In AmplifierDocument290 pagesModel Sr850: DSP Lock-In AmplifieralexNo ratings yet
- Acti9 India-Technical-Catalogue PDFDocument296 pagesActi9 India-Technical-Catalogue PDFAmit NagNo ratings yet