Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes Skull and Face
Uploaded by
Kaye Cor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views1 pageHA
Original Title
notEs skull and face
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views1 pageNotes Skull and Face
Uploaded by
Kaye CorHA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
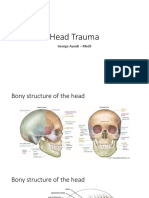
Head size as related to age and stature Scalp:
Diseases altering head size Similar to disease of the skin.
Diseases of scalp and hair o Lighter in color than the
complexion.
Normal: · Can be moist or oily.
The head is symmetrical. Size varies with · No scars noted.
age and body stature. · Free from lice, nits and dandruff.
Male pattern hair loss is common. · No lesions should be noted.
Minor undulations are normal for the skull. · No tenderness nor masses on
palpation.
Size o Cysts
o Enlarged: (Hydrocephalus, o Nevi
Acromegaly, Paget's disease) o Nevus flammeus: (Vascular birth
o Smaller: (Microcephaly) mark at posterior base of skull
and neck)
Skull symmetry and evenness o Moles
o Generally round, with o Loose white flakes: (Dandruff)
prominences in the frontal and o Tiny white ovoid nits: (Lice
occipital area. (Normocephalic). infestation)
· No tenderness noted upon o Redness and scaling: (Seborrheic
palpation. dermatitis, psoriasis)
o o Fungal infection
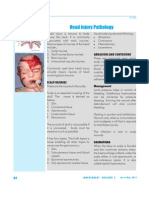
o Bumps: (Healed fractures, the superficial temporal artery is one of the
hematoma, Paget's disease) largest blood vessels in the neck. Branching
o Depressions (Fractures, post- off from the external carotid, it assists in
surgical, burr holes) delivering oxygenated blood from the heart
Hair to regions within the neck and head. The
o Can be black, brown or burgundy other branch of the external carotid
depending on the race. includes the maxillary artery.
· Evenly distributed covers the This artery begins around the mandible, or
whole scalp (No evidences of lower jawbone, and the parotid gland — a
Alopecia) gland located in front of the ear, which
· Maybe thick or thin, coarse or produces saliva for use in the mouth.
smooth. Toward the end of its course, the superficial
· Neither brittle nor dry temporal artery splits into the frontal and
o parietal branches.
o Hair loss During its course, the artery travels over the
Diffuse Hair loss: zygomatic process, the area of bone that
(Chemotherapy, Following an lies under the cheeks. There, the auricularis
acute serious illness) muscle covers it. Two branches of the facial
Well circumcised coin shaped nerve also cross the artery at the zygomatic
area of hair loss. Alopecia process.
areata (SLE) Since it is a major artery within the neck
o Texture and head, damage to or blockage of this
Diffuse hair thinning Fine artery could pose serious health problems.
hair: (Thyrotoxicosis, Iron def, The superficial temporal artery, along with
stress, syphilis) the occipital artery, has been associated
Coarse hair: with chronic migraine headaches.
(Hypothyroidism)
You might also like
- FM Lecture Notes DR - Pavan Pathology of AsphyxiaDocument6 pagesFM Lecture Notes DR - Pavan Pathology of AsphyxiaMituran IshwarNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Assessment: Common Symptoms and Examination TechniquesDocument72 pagesHead and Neck Assessment: Common Symptoms and Examination TechniquesBulajyo Pangngay JolinaNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment PortfolioDocument25 pagesHealth Assessment PortfolioGEN ERIGBUAGASNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On COntusion Parietal L and Cerebral ConcussionDocument49 pagesCase Presentation On COntusion Parietal L and Cerebral ConcussionJon Gab PaquitNo ratings yet
- Disorders of HairDocument5 pagesDisorders of Hairعبدالعزيز احمد علي عتشNo ratings yet
- Newborn AssessmentDocument3 pagesNewborn AssessmentAfril CadagNo ratings yet
- BENIGN & MALIGNANT LESIONS OF THE SKIN by AlbraaDocument7 pagesBENIGN & MALIGNANT LESIONS OF THE SKIN by AlbraaZoi PapadatouNo ratings yet
- HEAD-and-NECKDocument44 pagesHEAD-and-NECKDanica DaniotNo ratings yet
- Macules - Week 1Document18 pagesMacules - Week 1Jordan ChuNo ratings yet
- RADIOLOGICAL SUPPORT Head InjuryDocument33 pagesRADIOLOGICAL SUPPORT Head InjuryNurul NajwaNo ratings yet
- Cong Anomalies and Tumors of SpineDocument120 pagesCong Anomalies and Tumors of SpineSunny SbaNo ratings yet
- 00 H&N NotesDocument16 pages00 H&N NotesHythem HashimNo ratings yet
- Neck Anatomy: Lymph NodesDocument5 pagesNeck Anatomy: Lymph NodesKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- Ipd B: Finals - Heent: Techniques of Examination For Head (From Bates')Document13 pagesIpd B: Finals - Heent: Techniques of Examination For Head (From Bates')Janica Marie Ragsac100% (1)
- Asphyxia and BarotraumaDocument10 pagesAsphyxia and BarotraumadeevoncNo ratings yet
- Head & Neck: Clinical AnatomyDocument42 pagesHead & Neck: Clinical Anatomycheckmate100% (1)
- Presentation 1Document55 pagesPresentation 1shiviraghuNo ratings yet
- salivary neoplasmDocument20 pagessalivary neoplasmTicky TomNo ratings yet
- Blumenfeld Neuroanatomy Ch. 5 SummaryDocument5 pagesBlumenfeld Neuroanatomy Ch. 5 SummaryMeeraNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma: George Ayoub - Med3Document23 pagesHead Trauma: George Ayoub - Med3Joe KhdeirNo ratings yet
- Review To CNS Radiology Including SSDocument52 pagesReview To CNS Radiology Including SSBisher Al-halabiNo ratings yet
- Headache, SkinDocument4 pagesHeadache, SkinNadia SalwaniNo ratings yet
- SalivaryDocument20 pagesSalivaryTicky TomNo ratings yet
- Assessment Procedure Actual Findings Normal Findings Clinical Significance Integumenta RY Pallor Skin Is Seen inDocument13 pagesAssessment Procedure Actual Findings Normal Findings Clinical Significance Integumenta RY Pallor Skin Is Seen inPaul Loujin LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 14 NotesRhianon Annie McDowellNo ratings yet
- Head Neck Lymph NodesDocument17 pagesHead Neck Lymph NodesEreka LoretoNo ratings yet
- Head InjuriesDocument9 pagesHead InjuriesQasim HaleimiNo ratings yet
- Cranial Meninges)Document78 pagesCranial Meninges)Mustafa IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Newborn AssessmentDocument3 pagesNewborn AssessmentangelaclaireramosNo ratings yet
- Boards' Fodder: HypertrichosisDocument3 pagesBoards' Fodder: HypertrichosisJack MiguelNo ratings yet
- ENT Deferential Diagnosis MEDADDocument22 pagesENT Deferential Diagnosis MEDADReham AshourNo ratings yet
- 3rd Case StudyDocument8 pages3rd Case StudyDezerie GranfilNo ratings yet
- Neck and Head MassesDocument13 pagesNeck and Head MassesGhaiidaa khhNo ratings yet
- Head Injury-Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis and ManagementDocument48 pagesHead Injury-Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis and ManagementLuther ThengNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT OF THE EARSDocument65 pagesPHYSICAL ASSESSMENT OF THE EARSDeeeeeNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous system (自动保存的)Document36 pagesCentral Nervous system (自动保存的)Wai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- 008 Skin Hair NailsDocument35 pages008 Skin Hair NailsPauline An Toni CapurihanNo ratings yet
- Head Injury PathologyDocument12 pagesHead Injury Pathologyimilosavljev@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Skin and Bones 1Document6 pagesSkin and Bones 1Joseph John HiladoNo ratings yet
- Parotid Gland and Temporal Region AnatomyDocument43 pagesParotid Gland and Temporal Region AnatomyMohammad HilmiNo ratings yet
- Spine Notes: By: Dr. Abdullah NouhDocument14 pagesSpine Notes: By: Dr. Abdullah NouhHythem HashimNo ratings yet
- Neck Masses: Triangles of The NeckDocument5 pagesNeck Masses: Triangles of The NeckDuncan89No ratings yet
- 6.head Injuries 2Document41 pages6.head Injuries 2Hasabo AwadNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma - 5 Juli 2014 - by Robby HermawanDocument79 pagesHead Trauma - 5 Juli 2014 - by Robby Hermawandewi rahmanNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgical EmergenciesDocument25 pagesNeurosurgical EmergenciesFarah Wahidah Abd RazakNo ratings yet
- SOL PresentationDocument11 pagesSOL Presentationvony wirawatiNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Examination FiryaLDocument3 pagesThyroid Examination FiryaLFiryal Balushi100% (1)
- Carotid Artery DiseaseDocument48 pagesCarotid Artery DiseaseAdeleye John AdebolaNo ratings yet
- MeningiomaDocument51 pagesMeningiomaarushijha2000No ratings yet
- Imaging of Disorders of Cortical Formation: by Mamdouh Mahfouz MD Professor of Radiology Cairo UniversityDocument71 pagesImaging of Disorders of Cortical Formation: by Mamdouh Mahfouz MD Professor of Radiology Cairo UniversityDr KhanNo ratings yet
- 14 - CNS - 2Document22 pages14 - CNS - 2Saman SarKoNo ratings yet
- Bell's PalsyDocument36 pagesBell's Palsylejie*100% (6)
- Surgery FinalDocument225 pagesSurgery FinalKhoiam IslamNo ratings yet
- ACTB كوزشنيرDocument3 pagesACTB كوزشنيرnwxwgvqkscNo ratings yet
- Head Shape Abnormalities & HydrocephalusDocument7 pagesHead Shape Abnormalities & HydrocephalusZweNo ratings yet
- CT ScanDocument84 pagesCT ScanHafiz Wajid SadiqNo ratings yet
- Internal Diseases Review: Key Systems and FindingsDocument409 pagesInternal Diseases Review: Key Systems and FindingsPatrick Igbinoba - MFNo ratings yet
- Neck Swellings (Compatibility Mode)Document49 pagesNeck Swellings (Compatibility Mode)vihang146No ratings yet
- Dermatology Atlas for Medical StudentsFrom EverandDermatology Atlas for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Structuring Meaning and Humanbecoming PrinciplesDocument23 pagesStructuring Meaning and Humanbecoming PrinciplesKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Tecnicas para Cartas de Amor U OdioDocument4 pagesTecnicas para Cartas de Amor U OdioChristian Gabriel Stampacchio100% (16)
- Nursing Health History /nursing Process/Physical AsessmentDocument2 pagesNursing Health History /nursing Process/Physical AsessmentKaye CorNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Course OutlineDocument3 pagesNCM 103 Course OutlineKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Facts About Antianxiety and Sedative Medications Veteran and Family HandoutDocument3 pagesFacts About Antianxiety and Sedative Medications Veteran and Family HandoutKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Which of The Following Goals Is Correctly WrittenDocument13 pagesWhich of The Following Goals Is Correctly WrittenKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Emrpub 2012 en 1362 PDFDocument82 pagesEmrpub 2012 en 1362 PDFachysfNo ratings yet
- Diff Roles of A NurseDocument1 pageDiff Roles of A NurseKaye CorNo ratings yet
- OxygenationDocument3 pagesOxygenationKaye CorNo ratings yet
- TFNDocument8 pagesTFNKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Nursing Health HistoryDocument12 pagesNursing Health HistoryKaye Cor100% (3)
- Which of The Following Goals Is Correctly WrittenDocument13 pagesWhich of The Following Goals Is Correctly WrittenKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Nurses Guide To Family Assessment and InterventionDocument9 pagesNurses Guide To Family Assessment and InterventionKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Coping With Loss, Grieving and DeathDocument2 pagesCoping With Loss, Grieving and DeathKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Structuring Meaning and Humanbecoming PrinciplesDocument23 pagesStructuring Meaning and Humanbecoming PrinciplesKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Chest Trauma Treatment and ManagementDocument9 pagesChest Trauma Treatment and ManagementKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Occupational Lung Diseases: Causes, Treatments, and PreventionDocument5 pagesOccupational Lung Diseases: Causes, Treatments, and PreventionKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Pharma Task 1Document2 pagesPharma Task 1Kaye CorNo ratings yet
- 14bdfd PDFDocument9 pages14bdfd PDFKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Nots Skull and FaceDocument1 pageNots Skull and FaceKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Quiz 04 Unit .3 Introduction of Nursing Theory & Model: BSCN 2 Semseter 2016Document2 pagesQuiz 04 Unit .3 Introduction of Nursing Theory & Model: BSCN 2 Semseter 2016Kaye Cor80% (5)
- I-PPT - I-Fundamentals-1-31-2020Document61 pagesI-PPT - I-Fundamentals-1-31-2020Kaye Cor0% (1)
- Henderson Activity WorksheetDocument2 pagesHenderson Activity WorksheetKaye CorNo ratings yet
- HOW Nursing INformaticsDocument61 pagesHOW Nursing INformaticsKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2 PC Components Lesson 2Document57 pagesLesson 1.2 PC Components Lesson 2Kaye CorNo ratings yet
- HOW Nursing INformaticsDocument61 pagesHOW Nursing INformaticsKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Electronic Health Records in Public Health CentersDocument14 pagesElectronic Health Records in Public Health CentersKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document27 pagesLesson 1Kaye CorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1.nursing InformaticsDocument15 pagesLesson 1.1.nursing InformaticsKaye CorNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Effective Communication in NursingDocument23 pagesThe Importance of Effective Communication in NursingKaye CorNo ratings yet
- CHARACTERISTICS and ROLE OF A PSYCHIATRIC NURSEDocument3 pagesCHARACTERISTICS and ROLE OF A PSYCHIATRIC NURSESareno PJhēaNo ratings yet
- Hiata 2Document21 pagesHiata 2AnnJenn AsideraNo ratings yet
- DR L M KhanDocument9 pagesDR L M KhanHomoeopath Aamir Saleem100% (4)
- Dance TherapyDocument2 pagesDance TherapyXimena OrdonezNo ratings yet
- Scars PDFDocument9 pagesScars PDFMichaely NataliNo ratings yet
- Icd 10 CodeDocument3 pagesIcd 10 Codecheryll duenasNo ratings yet
- COPD Patient Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesCOPD Patient Nursing Care PlanNicole SimoneNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument25 pagesCase PresentationGaurav TanwarNo ratings yet
- Informed Consent SampleDocument7 pagesInformed Consent SampleArjuna BuduhNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Infiltrative TB of the LungDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan for Infiltrative TB of the LungMargarette Mae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis (Age)Document37 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis (Age)Jay Ar SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 12 Neha Dahiya 2017 Knowledge and Practices Related To Screening For Breast Cancer Among Women in Delhi IndiaDocument5 pages12 Neha Dahiya 2017 Knowledge and Practices Related To Screening For Breast Cancer Among Women in Delhi IndiaArick Frendi AndriyanNo ratings yet
- The Legalities of Nursing DocumentationDocument6 pagesThe Legalities of Nursing DocumentationCandace FlowersNo ratings yet
- Revisiting Structural Family TherapyDocument2 pagesRevisiting Structural Family TherapyKim ScottNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH Tìm từ sai-TOEFL- Bài số 1Document5 pagesENGLISH Tìm từ sai-TOEFL- Bài số 1iey ranaNo ratings yet
- Histological Features of Candidiasis: By:Mamdouh Dagsh Alshrifi ID:321103259Document14 pagesHistological Features of Candidiasis: By:Mamdouh Dagsh Alshrifi ID:321103259Mamdouh D AlrwailiNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologyDocument4 pagesMedical Terminologyflordeliza magallanesNo ratings yet
- Ingelvac Provenza: Description: Directions and DosageDocument2 pagesIngelvac Provenza: Description: Directions and DosageDrivailaNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Engineering Maintenance Services - Presentation 1Document8 pagesBiomedical Engineering Maintenance Services - Presentation 1ishoneyNo ratings yet
- Prince Price Alide Price Printer Sr. No Books Author Edition QT Y KinesiologyDocument9 pagesPrince Price Alide Price Printer Sr. No Books Author Edition QT Y KinesiologyNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- 15 - CCLS - PharmacologyDocument32 pages15 - CCLS - PharmacologyVENKATESH RAMSALINo ratings yet
- Sepmate ProtocolDocument2 pagesSepmate ProtocolZil PatelNo ratings yet
- Drug Ana Rifampicin Isoniazid Pyrazinamide Ethambutol StreptomycinDocument4 pagesDrug Ana Rifampicin Isoniazid Pyrazinamide Ethambutol StreptomycinLatoja, Lyndon Sixto Jr. C.No ratings yet
- Errors of Proline and Serine Metabolism DisordersDocument29 pagesErrors of Proline and Serine Metabolism DisordersHannah CokerNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (FLUoxetine)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (FLUoxetine)Diana Villanueva100% (1)
- Aha Guidelinedriven Management of Hypertension An Evidencebased UpdateDocument56 pagesAha Guidelinedriven Management of Hypertension An Evidencebased UpdateNanda Gopal Reddy AnamNo ratings yet
- Follow The Instructions For R.I.C.EDocument2 pagesFollow The Instructions For R.I.C.Eayatolla ayatollaTMNo ratings yet
- About Critical Care Nursing PDFDocument3 pagesAbout Critical Care Nursing PDFKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Diseases and Disorders (Gnv64)Document482 pagesEncyclopedia of Diseases and Disorders (Gnv64)Florin Ciobanu100% (12)
- GINA Strategy 2021pocket GuideDocument16 pagesGINA Strategy 2021pocket GuideHossam HamzaNo ratings yet