Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fuel Oil System
Uploaded by
LawLietOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fuel Oil System
Uploaded by
LawLietCopyright:
Available Formats
1/C Galvez, Francis James A.
C/E Tomas
S4 CHARLIE MAR-E 03/18/20
PASGT
RESEARCH WORK: EXPLAIN THE FUEL OIL SYSTEM FOR MARINE DIESEL
ENGINE
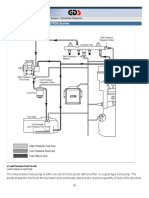
A. FUEL SUPPLY SYSTEM
A fuel supply system mainly consists of a fuel tank, fuel filters, a fuel
pump/compressor, a heat exchanger, valves and connecting pipes. The functions of
the fuel supply system are to store and supply natural gas to the fuel injector(s)
under a predetermined pressure and temperature at the desired rate. The natural gas
is in the form of either compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas
(LNG). The components of a fuel supply system could differ from one to another
substantially, depending on whether the gas is stored in the form of CNG or LNG.
B. FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
The purpose of the fuel injection system is to deliver fuel into the engine cylinders,
while precisely controlling the injection timing, fuel atomization, and other
parameters. The main types of injection systems include pump-line-nozzle, unit
injector, and common rail. Modern injection systems reach very high injection
pressures, and utilize sophisticated electronic control methods.
C. SAFETY DEVICES OF FUEL SYSTEM
Various safety devices in a fuel system for a diesel engine are:
Quick closing valves on settling/service tanks
relief valves on 2 pumps/heaters
quick closing valve on mixing/vent tank
pipes lagged/save-alls under pumps and heaters
low fuel oil pressure alarm
high fuel oil pressure alarm
low fuel oil temperature alarm
high fuel oil temperature alarm
emergency remote stops for pumps
High pressure pipes between fuel injection pump and injector are double
skinned.
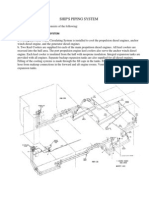
D. DIFFERENT PIPING ARRANGEMENT
There are two principal types of pipes that carry fuel and they are categorised by the
pressure the pipe is designed to withstand. Low-pressure pipes are used to move
fuel from a storage tank to a service tank to an injection pump; high-pressure pipes
are used to deliver fuel from an injection pump to an engine combustion chamber.
Ships’ fuel is usually stored in double-bottom tanks, deep tanks, side bunker tanks,
settling tanks or service tanks. Piping between a service tank and a fuel transfer or
1/C Galvez, Francis James A. C/E Tomas
S4 CHARLIE MAR-E 03/18/20
booster pump is rated as low pressure. However, between each pumping stage,
pressure increases.
It is a mistake to assume that even if a pipe’s pressure is relatively low, fuel will not
spray from a crack or small hole. Pipes from fuel tanks can pass through ballast
tanks and pipes serving ballast tanks can pass through fuel tanks. Because of
pollution risks, classification societies have stringent rules restricting the length of
any oil pipe passing through a ballast tank (and vice versa); it must be short, have
increased wall thickness and stronger flanges.
Here’s a diagram of a fuel oil system for marine diesel engine
You might also like
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Fuel SystemDocument58 pagesUnit 3 Fuel SystemuthiraNo ratings yet
- Fuel Oil PDFDocument5 pagesFuel Oil PDFJayadevDamodaranNo ratings yet
- PLTT TranlateDocument4 pagesPLTT Tranlatesabrila wandaNo ratings yet
- Piping System: Group 3Document25 pagesPiping System: Group 3Aaron NakpilNo ratings yet
- Resumen Power Point .L.Document8 pagesResumen Power Point .L.Manoa Aguilar ReyesNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Job TrainingDocument14 pagesProject Report On Job TrainingAakash DodiyaNo ratings yet
- SHIP Piping SystemDocument5 pagesSHIP Piping Systemsurnaik100% (1)
- Fuel Gas System - Candidate PDFDocument11 pagesFuel Gas System - Candidate PDFbelil206No ratings yet
- Dash8 200 300 Fuel PDFDocument13 pagesDash8 200 300 Fuel PDFCarina Ramo LakaNo ratings yet
- Discovery Fuel ServiceDocument65 pagesDiscovery Fuel Serviceshafeek mshahNo ratings yet
- Gasoline and Diesel Fuel Injection: Operation, Diagnosis, and ServiceDocument37 pagesGasoline and Diesel Fuel Injection: Operation, Diagnosis, and Servicemohamad1010No ratings yet
- Aircraft Fuel SystemDocument64 pagesAircraft Fuel SystemAbinashMahapatraNo ratings yet
- Carburetor SystemDocument6 pagesCarburetor SystemMina BadratNo ratings yet
- All About Marine Enginnering OralsDocument76 pagesAll About Marine Enginnering OralsUdana Hettiarachchi100% (3)
- Furnace Design and Operation: Fuel Handling SystemsDocument45 pagesFurnace Design and Operation: Fuel Handling SystemskINGNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Fuel SystemDocument32 pagesUnit 3 Fuel SystemuthiraNo ratings yet
- Handout - Fuel SystemDocument20 pagesHandout - Fuel System김종환No ratings yet
- AMT Module 1 - PartB-1Document12 pagesAMT Module 1 - PartB-1PrathikNo ratings yet
- LNG Fuel Gas SystemsDocument2 pagesLNG Fuel Gas SystemsMoanquileNo ratings yet
- DUEL Fuel EnginesDocument11 pagesDUEL Fuel EnginesMohamed Al NazooqueNo ratings yet
- Crdi System 1 Hyundai H1Document2 pagesCrdi System 1 Hyundai H1Ra Aranzaso100% (5)
- General Engineering Knowledge For Marine EngineersDocument31 pagesGeneral Engineering Knowledge For Marine EngineersSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- Lubricant System of Power PlantsDocument12 pagesLubricant System of Power PlantsPaulNo ratings yet
- Design Consideration of Hot Oil SystemDocument24 pagesDesign Consideration of Hot Oil SystemOmar EzzatNo ratings yet
- Bosch Fuel System Common RailDocument4 pagesBosch Fuel System Common RailAlaa saidNo ratings yet
- Tite Ni Kip Mahaba at MatabaDocument5 pagesTite Ni Kip Mahaba at MatabaKobe Alcantara ReyesNo ratings yet
- EvapEmission PDFDocument8 pagesEvapEmission PDFpivillamilNo ratings yet
- High Rise Building Fuel Systems 01 0Document11 pagesHigh Rise Building Fuel Systems 01 0eimrehNo ratings yet
- Ppt:-Piping SystemDocument35 pagesPpt:-Piping Systemaimri_cochin64% (11)
- FPS - MS9001Document3 pagesFPS - MS9001shravani mangalpalliNo ratings yet
- AircraftSystems Week 10 11 MergedDocument45 pagesAircraftSystems Week 10 11 MergedJake BarettoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of HydraulicsDocument101 pagesFundamentals of HydraulicsLuis Nunes100% (1)
- 05-737-800 Ramp & Transit FuelDocument90 pages05-737-800 Ramp & Transit FuelNicolas SalNo ratings yet
- Welcome Common Rail Diesel Fuel Systems: To A Technical Overview ofDocument61 pagesWelcome Common Rail Diesel Fuel Systems: To A Technical Overview ofMuhammad DinataNo ratings yet
- TankerDocument31 pagesTankerpushkarsidhayeNo ratings yet
- AKTraining DesbloqueadoDocument61 pagesAKTraining DesbloqueadoJUAN JOSE LOPEZ LOJANo ratings yet
- EFI - Fuel Delivery System: Richard E. Ramos Richard E. RamosDocument44 pagesEFI - Fuel Delivery System: Richard E. Ramos Richard E. RamosBiruk TilahunNo ratings yet
- P 0087Document6 pagesP 0087CopyMaster2No ratings yet
- Jeep+2.5 TD PDFDocument38 pagesJeep+2.5 TD PDFMiguel ChaconNo ratings yet
- Fuel SystemDocument7 pagesFuel SystemখালিদহাসানNo ratings yet
- The Design and Operation of Offshore Relief - Venting SystemsDocument24 pagesThe Design and Operation of Offshore Relief - Venting SystemsMichael HaiseNo ratings yet
- Technical Training SeriesDocument8 pagesTechnical Training SeriesMubashiryyy mehmoodNo ratings yet
- Mar PowerDocument29 pagesMar PowerSeilfred SanggoNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Fuel SystemDocument63 pagesAircraft Fuel SystemsushantreshmaNo ratings yet
- The Fleet Type Submarine - Chapter 16Document5 pagesThe Fleet Type Submarine - Chapter 16nisfun nahar smrityNo ratings yet
- Basics of Hydralic SystemDocument101 pagesBasics of Hydralic SystemNikhil MalhotraNo ratings yet
- PumpsDocument6 pagesPumpsiqtorresNo ratings yet
- Cascade Filling System: Principle of Operation UsesDocument3 pagesCascade Filling System: Principle of Operation Usesmiguek clementsNo ratings yet
- Ledm0126 01Document9 pagesLedm0126 01Djebali MouradNo ratings yet
- Diesel Pump Check ListDocument3 pagesDiesel Pump Check Listபிரபாகரன் மீண்டும் வருவான்No ratings yet
- 43-4002 - Fuel Oil SupplyDocument4 pages43-4002 - Fuel Oil Supplydebu1985No ratings yet
- Hot Oil System Design Consideration-LibreDocument28 pagesHot Oil System Design Consideration-LibreAdel Chelba100% (2)
- Bosch CP3 OperationDocument6 pagesBosch CP3 OperationGianfranco Danna Gálvez100% (2)
- Fuel System JTEC ChryslerDocument56 pagesFuel System JTEC ChryslerkeiwerkasNo ratings yet
- As LPG Bottle Filling EDocument9 pagesAs LPG Bottle Filling EGerson AsmNo ratings yet
- Naval Mechanical Engineering: Gas Turbine Propulsion, Auxiliary, and Engineering Support SystemsFrom EverandNaval Mechanical Engineering: Gas Turbine Propulsion, Auxiliary, and Engineering Support SystemsNo ratings yet
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingFrom EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SFrom EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNo ratings yet
- Electronic Unit Injector - Install: Disassembly and AssemblyDocument4 pagesElectronic Unit Injector - Install: Disassembly and AssemblysxturboNo ratings yet
- 4045DF158 POWERTECH SPECIFICATIONS For Gen Set ApplicationsDocument2 pages4045DF158 POWERTECH SPECIFICATIONS For Gen Set ApplicationsMohammed ShafekNo ratings yet
- Brochure TAD760VE VolvoDocument2 pagesBrochure TAD760VE VolvoNoer RachNo ratings yet
- 10 GeneralSpecs PDFDocument59 pages10 GeneralSpecs PDFFabian BarajasNo ratings yet
- Diesel Fuel : Click On The Applicable Bookmark To Selected The Required Model YearDocument13 pagesDiesel Fuel : Click On The Applicable Bookmark To Selected The Required Model Yearrolly abantoNo ratings yet
- Apt 190 Martillo NeumaticoDocument1 pageApt 190 Martillo NeumaticoGerman Ortega100% (1)
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument37 pagesChapter 1 Introductionfaris iqbalNo ratings yet
- 4 Versus 8 Counterweights For An I4Document10 pages4 Versus 8 Counterweights For An I4cyberjuanNo ratings yet
- ENGINE 6.7L Diesel - Service Information - Ram Pickup PDFDocument317 pagesENGINE 6.7L Diesel - Service Information - Ram Pickup PDFcharles100% (2)
- TIS - Lexus 2013 LX570 Repair Manual (RM19F0U)Document18 pagesTIS - Lexus 2013 LX570 Repair Manual (RM19F0U)Celis TabaresNo ratings yet
- ECU List 7 3 0 New Features ListDocument46 pagesECU List 7 3 0 New Features ListOscar AfonsoNo ratings yet
- MotoStruct Engine Enhancer - Lighthouse EmporiumDocument6 pagesMotoStruct Engine Enhancer - Lighthouse EmporiumPieter SteenkampNo ratings yet
- Board Diploma Examination, (C-20) MAY-2023 Dme - Fourth Semester ExaminationDocument3 pagesBoard Diploma Examination, (C-20) MAY-2023 Dme - Fourth Semester ExaminationRkrishna ANo ratings yet
- Ce T200 1D eDocument4 pagesCe T200 1D edassdsr5No ratings yet
- Lubrication and Oil SystemDocument6 pagesLubrication and Oil SystemIzz BaharNo ratings yet
- dSPACE ASM Product Information 2018-01 English PDFDocument40 pagesdSPACE ASM Product Information 2018-01 English PDFkkkprotNo ratings yet
- VP44 Install PDFDocument6 pagesVP44 Install PDFAlberto AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Isuzu Flash CodeDocument3 pagesIsuzu Flash CodeTam87% (30)
- Hatz Diesel 1D Workshop ManualDocument193 pagesHatz Diesel 1D Workshop ManualОлег Медак67% (3)
- Quiz: Wind Energy Technology ConceptsDocument6 pagesQuiz: Wind Energy Technology ConceptsPedro Galvani63% (8)
- Section 13E - Engine Fuel System PDFDocument18 pagesSection 13E - Engine Fuel System PDFrobbertmdNo ratings yet
- TATA ACE-EX-2 Parts CatalogueDocument95 pagesTATA ACE-EX-2 Parts CatalogueAnbarasanNo ratings yet
- Chery Carry A18 ENGINE ELECTRICAL SYSTEM - E PDFDocument89 pagesChery Carry A18 ENGINE ELECTRICAL SYSTEM - E PDFEduar SevillaNo ratings yet
- Mack T13 Engine Lubricant TestDocument2 pagesMack T13 Engine Lubricant TestFrank FareNo ratings yet
- Catalogue ACDelco FuelPumpsDocument45 pagesCatalogue ACDelco FuelPumpsAnonymous J1sELDp7No ratings yet
- Pump CalculationsDocument6 pagesPump CalculationsAshenafi Gebremeskel MezgeboNo ratings yet
- SSP 117 Skoda Karoq Vehicle Presentation Part IIDocument64 pagesSSP 117 Skoda Karoq Vehicle Presentation Part IIJose Ramón Orenes ClementeNo ratings yet
- Motorna Kosa FS 350 2019 812989473Document58 pagesMotorna Kosa FS 350 2019 812989473Marinko PetrovićNo ratings yet
- Wiseco 2019 Catalog AutoDocument130 pagesWiseco 2019 Catalog AutoFelix VeraNo ratings yet