EMG (Electromyograph)
Electromyography is the technique for calculating and recording the action potential of
muscles. EMG is taken using a device called electromyography and the record obtained
is known as electromyogram. The electrical activity of muscle cells when they are active
and at rest can be analysed using an EMG. The measured EMG potentials range from
50 µ Volt to 30 millivolts.
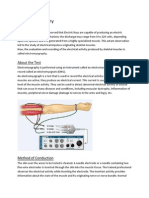
Mainly there are two kinds of EMG measurements. The first method is using surface
electrodes and the second one is using needle electrodes. The Surface EMG electrodes
are used to monitor the electrical activity of muscles generally whereas the needle
electrodes are used to observe the electrical activity of only few fibers.
A trained expert can observe the electrical activity of muscles when the needle is inserted.
There is a normal electrical activity for the muscle fibers at rest. The physician or
concerned expert examines the normal activity of muscles when the needle is inserted.
There is a normal electrical activity for the muscle fibers at rest. The physician or
concerned expert examines the normal activity of muscles. The abnormal spontaneous
activity indicates that some nerve or muscle cells are damaged. At a time potentials from
different electrodes are taken. So the needle electrodes have to be placed at different
locations to obtain an accurate EMG. So the intramuscular EMG is considered to be too
invasive.
So in order to obtain the general activity of the muscle cells we use surface electrodes
which need to be placed only on the concerned area. So no insertion is required. This
technique is commonly used in many applications such as in a physiotherapy clinic where
the muscle activity is monitored by the surface EMG electrodes and the patients can have
visual stimulus when they activating the muscles.
So when the motor neuron or muscle fiber is stimulated, the action potential is transmitted
across the muscle it is passed to the connected nerve fibers. Actually during EMG we are
evaluating this bioelectric potential from different cells. This potential is collectively called
motor unit action potential (MUAP). EMG signals are made up of superimposed MUAPs.
Hence the shape of the electromyogram is affected by factors such as number of muscle
fibers under consideration, the metabolic type of muscle fibers etc.
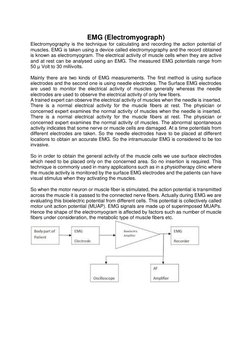
�EMG Block Diagram Explanation:
1. EMG electrode: As told earlier, the electrode used for EMG recording can be of surface
type or needle type depending on the area from which the EMG is to be obtained and the
type of measurement. If we need to have EMGs from many individual muscle cells rather
than from the surface as a group, needle electrodes are the best choice. But if the general
activity of a muscle is to be analysed the surface electrodes can give the accurate values.
2. Bioelectric amplifier: As the name implies, the bioelectric amplifiers are used to
amplify the bioelectric signals obtained from EMG electrodes.
3. AF amplifier: At rest under normal condition the sound does not undergo large
variations. But abnormal and spontaneous activity may be distinguished by the sudden
change in sound and this can be analyzed by the physician. The abnormal activity usually
indicates muscle damage and they can easily find out the nerve or muscle damage. So
physicians normally use AF amplifiers during EMG measurement so as to distinguish there
sounds clearly.
4. Oscilloscope: The measured EMG can be connected to the oscilloscope to visualize
the EMG. The abnormalities in the working of nerves and muscle cells can be identified
by a physician by analyzing the EMG waveform. The EMG can also be stored using
special oscilloscopes such as DSO (Digital Storage Oscilloscope) for future analysis.
5. EMG recorder: Unlike ECG, EMG cannot be recorded in a low speed chart paper
recorders because of its extreme low frequencies. So it will be less useful. Normally we
use the photographic recording of EMG. For this a light sensitive paper is moved over the
recording CRT.
Frequency Limitations:
1. The normal EMG is in the range of 60 – 70 Hz. The EMG appear as a random noise
signal the shape of the waveform may vary based on the part of the body from which EMG
is taken.
2. Due to the low frequency limitation, EMG cannot be recorded on a strip chart recorder
because it cannot give a clear idea of the waveform.
Applications of EMG:
1. EMG can be used to diagnose two main categories of diseases. They are neuropathies
and myopathies. In EMG representation, an increase in duration of action potential is an
indication of neuropathic disease and a decrease in duration of action potential is an
indication of myopathic disease.
2. EMG is utilized as a diagnostic instrument for detecting neuromuscular diseases.
3. EMG can be utilized for silent speech detection which identifying the speech by
examining the EMG activity of muscles related with speech.