Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment #4: Problema Stabilitas Dalam Geoteknik (Si-5222)
Uploaded by
kikisakinahr_Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment #4: Problema Stabilitas Dalam Geoteknik (Si-5222)
Uploaded by
kikisakinahr_Copyright:
Available Formats
Assignment #4:
PROBLEMA STABILITAS DALAM GEOTEKNIK (SI-5222)
Instructor : Prof. I Wayan Sengara, Ph.D.
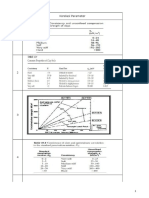
1. A series of triaxial tests was carried out on a clay soil, the cell pressure in each being
constant at 200 kN/m2. The shear strength parameters were to be c’ = 0 and ’ = 24o.
(a) If, in the undrained test, the pore water pressure at failure was 124 kN/m 2, what was
the maximum deviatoric stress?
(b) If, in the consolidated-undrained test, the maximum deviator stress was 160 kN/m2,
what was the pore water pressure at failure?
(c) What was the maximum deviatoric stress in the drained test, if the back pressure was
kept constant at 80 kN/m2?
2. A cohesive soil is found to have undrained shear strength parameters of cu= 35 kN/m2,
and u= 17o.
(a) In an undrained triaxial test, a specimen of the soil failed at a total axial stress of 360
kN/m2. What was the cell pressure?
(b) What value for the undrained shear strength would be indicated by an unconfined
compression test on a specimen of this soil?
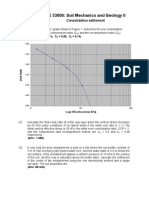
3. A specimen of a clay was fully consolidated under a cell pressure of 200 kN/m2 and then,
with the drainage valve closed, the cell pressure was raised to 400 kN/m 2. As the axial
load was increased the following data were recorded.
Deviatoric
stress 0 30 60 90 120 150 210 224(*)
(kN/m2)
Pore water
pressure 183 207 224 238 250 264 263 259
(kN/m2)
(*)
Failure
(a) Plot the effective and total stress paths.
(b) Compute pore water pressure parameters, Af and B.
(c) In another test on the same soil, the following values were recorded at failure: p’=
685 kN/m2 and q = 253 kN/m2. Plot the Kf-line and determine a’, ‘, c’, and ‘.
You might also like
- Principles of Soil Mechanics by Ronald F. Scott. - Compressed PDFDocument572 pagesPrinciples of Soil Mechanics by Ronald F. Scott. - Compressed PDFkikisakinahr_100% (2)
- Principles of Soil Mechanics by Ronald F. Scott. - Compressed PDFDocument572 pagesPrinciples of Soil Mechanics by Ronald F. Scott. - Compressed PDFkikisakinahr_100% (2)
- Co-Relations of N-Value and Relative Density DRDocument34 pagesCo-Relations of N-Value and Relative Density DRUmer WaheedNo ratings yet
- Lateral Earth PressureDocument15 pagesLateral Earth PressureLingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- Expansive Soils-Problems and RemediesDocument7 pagesExpansive Soils-Problems and Remediesrizu23No ratings yet
- Seed e Idriss 1970Document46 pagesSeed e Idriss 1970joake spas100% (3)
- Deep FoundationsDocument47 pagesDeep Foundationsipman99No ratings yet
- PROBLEMS Holtz and KovacsDocument3 pagesPROBLEMS Holtz and KovacsDaniel L. Blanco Pérez0% (2)
- A Brief Guide To Design of Bored Piles Under Axial CompressionDocument15 pagesA Brief Guide To Design of Bored Piles Under Axial Compressiondanielsu87No ratings yet
- Tunnel Lining Design GuideDocument195 pagesTunnel Lining Design GuideJasminka Vilotijevic Bozinovic100% (8)
- Investigation of The Resistance of Pile Caps To Lateral LoadingDocument322 pagesInvestigation of The Resistance of Pile Caps To Lateral LoadingJorge Luis Gutierrez100% (1)
- Daftar Korelasi Parameter TanahDocument18 pagesDaftar Korelasi Parameter Tanahadrian100% (1)
- J2910R1 Factual Report Pakubuwono Menteng PDFDocument175 pagesJ2910R1 Factual Report Pakubuwono Menteng PDFayumarysaNo ratings yet
- Efficiency of Horizontal Drains On Slope StabilityDocument6 pagesEfficiency of Horizontal Drains On Slope StabilityCristiano Reffatti rochaNo ratings yet
- Foundation Design Using Standard Penetration Test (SPT) N-ValueDocument39 pagesFoundation Design Using Standard Penetration Test (SPT) N-Valueneilmark undagNo ratings yet
- 2 Compressibility of SoilsDocument96 pages2 Compressibility of SoilsAyato KamisatoNo ratings yet
- Consolidation TutorialDocument6 pagesConsolidation TutorialJavidaNo ratings yet
- Plaxis Tutorial Manual - 3DFoundation v15Document94 pagesPlaxis Tutorial Manual - 3DFoundation v15krainajackaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7Document4 pagesTutorial 7Seanam DMNo ratings yet
- Shear Strength & Mohr Circle ProblemsDocument24 pagesShear Strength & Mohr Circle ProblemsNIKHIL BANDWALNo ratings yet
- Drillef Shaft Manual FHWA NHI 10 016Document973 pagesDrillef Shaft Manual FHWA NHI 10 016nicthegreek100% (3)
- Fundamentals of Soil Behavior (J.K. Mitchell & K. Soga)Document560 pagesFundamentals of Soil Behavior (J.K. Mitchell & K. Soga)EmílioFariasVaz100% (4)
- Session 5 - 6 Bearing Capacity of Shallow Foundation: Course: S0484/Foundation Engineering Year: 2007: 1/0Document41 pagesSession 5 - 6 Bearing Capacity of Shallow Foundation: Course: S0484/Foundation Engineering Year: 2007: 1/0rasputin0780803494No ratings yet
- PLAXIS 3D Tutorial Manual 2018Document138 pagesPLAXIS 3D Tutorial Manual 2018arpitNo ratings yet
- REPORT Soil Test Sondir Dan BoringDocument10 pagesREPORT Soil Test Sondir Dan BoringRento ChotanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Plaxis 2d AeDocument176 pagesTutorial Plaxis 2d AeJonathan Mendoza ChavezNo ratings yet
- Modul Pelatihan Software PlaxisDocument26 pagesModul Pelatihan Software PlaxisTeguh Setyo PurwantoNo ratings yet
- Soil Nail EffectsDocument8 pagesSoil Nail EffectsKingsley OchiengNo ratings yet
- SONDIRDocument39 pagesSONDIRSyafrizalNo ratings yet
- ASTM Agregat PDFDocument180 pagesASTM Agregat PDFVina OktavianaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document5 pagesTutorial 2WHfamilyNo ratings yet
- Iss34 Art2 - Validation of The Embeded Pile Row in PLAXIS 2DDocument4 pagesIss34 Art2 - Validation of The Embeded Pile Row in PLAXIS 2DhapsinteNo ratings yet
- Tugas 4 StabilitasDocument5 pagesTugas 4 StabilitasHanli WijayaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 (Permeability And Seepage) : i= h S hcosα SDocument11 pagesExercise 1 (Permeability And Seepage) : i= h S hcosα SMuhammad Abi Rafdi100% (1)
- Materi Kuliah III - Triaxial CU Dan CD Versi 2Document75 pagesMateri Kuliah III - Triaxial CU Dan CD Versi 2Lambok J SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Axial Pile Capacity Based On Statics MethodDocument17 pagesAxial Pile Capacity Based On Statics MethodhakamNo ratings yet
- 08-02 Rekayasa Pondasi Dalam IntroductionDocument48 pages08-02 Rekayasa Pondasi Dalam Introductionfirmen designNo ratings yet
- Identifications and Clasifications of Clay Shale Oke BanaDocument30 pagesIdentifications and Clasifications of Clay Shale Oke BanarullyirwandiNo ratings yet
- 18 Analysis and Settlement of A Pile GroupDocument10 pages18 Analysis and Settlement of A Pile GroupjasamnajNo ratings yet
- Ce 382 Soil Compaction 1442Document70 pagesCe 382 Soil Compaction 1442Princess Sandoval100% (1)
- Pengantar Dinamika Tanah Dan Rekayasa Gempa - Pertemuan Ke 6Document26 pagesPengantar Dinamika Tanah Dan Rekayasa Gempa - Pertemuan Ke 6Aprizian YogaNo ratings yet
- Assignment #1Document1 pageAssignment #1Aly Arquillano JrNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity of Mat FoundationsDocument7 pagesBearing Capacity of Mat FoundationsConstructora Ingenieria AlemanNo ratings yet
- PLAXIS 2D CE V20.00 Tutorial Lesson 08Document19 pagesPLAXIS 2D CE V20.00 Tutorial Lesson 08Safwat El RoubyNo ratings yet
- Griffith TheoryDocument8 pagesGriffith TheoryKarthick RamNo ratings yet
- (E) Chapter 1 - Shallow FoundationDocument27 pages(E) Chapter 1 - Shallow FoundationMoses HonNo ratings yet
- Gy Q y E Gy Q y E: Chapter 2: Energy - SolutionsDocument121 pagesGy Q y E Gy Q y E: Chapter 2: Energy - SolutionsCarol Espinoza BerrospiNo ratings yet
- Specific Energy and Depth RelationshipsDocument4 pagesSpecific Energy and Depth RelationshipsCindhy Ade HapsariNo ratings yet
- 005 Perbaikan Tanah PreloadingDocument140 pages005 Perbaikan Tanah PreloadingIntan YuniartiNo ratings yet
- Final Report Soil InvestiGationDocument255 pagesFinal Report Soil InvestiGationFungky King100% (2)
- Perhitungan Penurunan Menggunakan AllpileDocument1 pagePerhitungan Penurunan Menggunakan AllpileSu NarkoNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Engineering Properties of Soils From Field SPT Using Random Number Generation - SpringerLinkDocument22 pagesEstimation of Engineering Properties of Soils From Field SPT Using Random Number Generation - SpringerLinkMunicipal Engineer KothamangalamNo ratings yet
- Solved - Three Groups of Students From The Geotechnical EngineerDocument5 pagesSolved - Three Groups of Students From The Geotechnical Engineerabdullahiomar2020100% (1)
- Dispersive Characteristics of Clay Soil by Double HydrometerDocument3 pagesDispersive Characteristics of Clay Soil by Double Hydrometerโก อู๋No ratings yet
- 2a Balok Komposit Baja Berselubung BetonDocument11 pages2a Balok Komposit Baja Berselubung BetonPramugo AndiNo ratings yet
- Hatanaka, M., and A. Uchida, 1996, Internal Friction Angle of Sandy Soil.Document9 pagesHatanaka, M., and A. Uchida, 1996, Internal Friction Angle of Sandy Soil.Yutong LuNo ratings yet
- Triaxial Compression Test CU Dan CD Test: 22 Februari 2010Document75 pagesTriaxial Compression Test CU Dan CD Test: 22 Februari 2010Antariksa PrianggaraNo ratings yet
- Two-Dimensional Flow of Water Through Soils: ImportanceDocument31 pagesTwo-Dimensional Flow of Water Through Soils: ImportanceAngieNo ratings yet
- MATERI - 2 Saluran Komposite & GabunganDocument14 pagesMATERI - 2 Saluran Komposite & GabunganSandro Nainggolan BrabNo ratings yet
- Webinar Series 1B Hutama Karya Masyhur Permasalahan Geoteknik TanahDocument31 pagesWebinar Series 1B Hutama Karya Masyhur Permasalahan Geoteknik Tanahantonius satrioNo ratings yet
- Preconsolidation Pressure From Soil Indez and Plasticity PropertiesDocument5 pagesPreconsolidation Pressure From Soil Indez and Plasticity PropertiesSamuel Laura HuancaNo ratings yet
- Form Direct ShearDocument3 pagesForm Direct Sheardimas syahputraNo ratings yet
- Konstanta Pegas Dan Interaksi Struktur TanahDocument10 pagesKonstanta Pegas Dan Interaksi Struktur Tanahlimara65No ratings yet
- CE 366 - SITE INVESTIGATION (Problems & Solutions) : Depth of ExplorationDocument9 pagesCE 366 - SITE INVESTIGATION (Problems & Solutions) : Depth of Explorationbrianmanson78No ratings yet
- Preloading and Vertical DrainsDocument27 pagesPreloading and Vertical Drainsfery kustiawanNo ratings yet
- Assignment#1 SI5222 S2BUMN 2021Document1 pageAssignment#1 SI5222 S2BUMN 2021didiet noer affendiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - 5 - CE 1403 Geotechnical Engineering - 230426 - 092421Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet - 5 - CE 1403 Geotechnical Engineering - 230426 - 092421imamadnan69No ratings yet
- Module 7 - Tutorial 1 (Shear Strength) (OK)Document2 pagesModule 7 - Tutorial 1 (Shear Strength) (OK)Asfin HaqueNo ratings yet
- Consolidated-Undrained Tri-Axial Test (Cu - Test) : Problem 1Document14 pagesConsolidated-Undrained Tri-Axial Test (Cu - Test) : Problem 1Jemuel FloresNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Resistencia - CraigDocument2 pagesEjercicios Resistencia - Craigsebastian huerfanoNo ratings yet
- Literatur Anchor BlockDocument4 pagesLiteratur Anchor Blockkikisakinahr_No ratings yet
- Efficiency of Pile Groups in Clay Under DifferentDocument7 pagesEfficiency of Pile Groups in Clay Under Differentkikisakinahr_No ratings yet
- Price List: Programs Personal License Flexible License Lease Perpetual Lease PerpetualDocument1 pagePrice List: Programs Personal License Flexible License Lease Perpetual Lease Perpetualkikisakinahr_No ratings yet
- Wika CLTDocument2 pagesWika CLTYuly Elizabeth AryatnieNo ratings yet
- 1 BrosursetDocument36 pages1 BrosursetAde ChakraNo ratings yet
- 1 BrosursetDocument36 pages1 BrosursetAde ChakraNo ratings yet
- Tugas 4. Mektan PDFDocument5 pagesTugas 4. Mektan PDFkikisakinahr_No ratings yet
- (Jonathan T. H. Wu, Kevin Z. Z. Lee, Sam B. Helwan (B-Ok - Xyz) PDFDocument206 pages(Jonathan T. H. Wu, Kevin Z. Z. Lee, Sam B. Helwan (B-Ok - Xyz) PDFmahdNo ratings yet
- Tugas 4. MektanDocument5 pagesTugas 4. Mektankikisakinahr_No ratings yet
- Piecewise, Odd, Dan Even Continuous Periodic Function GraphsDocument2 pagesPiecewise, Odd, Dan Even Continuous Periodic Function Graphskikisakinahr_No ratings yet