Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M M T T H H: Water Benzene Water Water 2 2 Water 2 2 Benzene
Uploaded by
Rachita Prakash SarafOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
M M T T H H: Water Benzene Water Water 2 2 Water 2 2 Benzene
Uploaded by
Rachita Prakash SarafCopyright:
Available Formats
https://www.chegg.
com/homework-help/questions-and-answers/-q36611219
Answer:
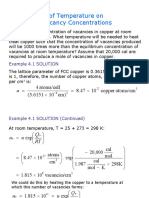
To calculate the ebullioscopic constant (Kb) for water and benzene, their molecular weight (Mw),
boiling point (Tb), and enthalpy of vaporization (ΔHvap) are needed which are taken from the
standard table for pure substances.
M w water 0.0180 kg mol
M w benzene 0.0781 kg mol
Tb water 373.2 K
Tb water 353.2 K
H vap water 40650 kg m2 s2 mol
H vap benzene 30720 kg m 2 s2 mol
Value of R to be used is
8.314 kg m 2 s 2
mol K .
Now, use the given theoretical expression for ebullioscopic constant (Kb) to calculate its values
for water and benzene as:
M w water R Tb 2water
Kb water
H vap water
kg kg m 2
373.2 K
2
0.0180 8.314 2
mol s mol K
kg m 2
40650 2
s mol
kg K
0.513
mol
M w benzene R Tb benzene
2
Kb benzene
H vap benzene
kg kg m 2
353.2 K
2
0.0781 8.314 2
mol s mol K
kg m 2
30720 2
s mol
kg K
2.637
mol
Therefore, the calculated theoretical values of ebullioscopic constant (Kb) for water and benzene
are 0.513 and 2.637 respectively which confirms the given experimental values of 0.51 and 2.63
respectively.
You might also like
- High Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Volume 2From EverandHigh Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Volume 2No ratings yet
- CHE 402 Omar's Notes (211) 2Document93 pagesCHE 402 Omar's Notes (211) 2mohammedNo ratings yet
- Conductivity ExerciseDocument1 pageConductivity ExerciseMr. Gamingo ChallengiNo ratings yet
- In Class Exercise For Chapter 13 KeyDocument2 pagesIn Class Exercise For Chapter 13 KeyJennifer TabitaNo ratings yet
- In Class Exercise For Chapter 13 KeyDocument2 pagesIn Class Exercise For Chapter 13 KeyfardNo ratings yet
- Solubility and Complex-Ion Equilibria: Practice ExamplesDocument33 pagesSolubility and Complex-Ion Equilibria: Practice Exampleskennethleo69No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Solution - Revision Session - NEET & AIIMS 2019Document4 pagesBasic Concepts of Chemistry and Solution - Revision Session - NEET & AIIMS 2019P.S.S AmulyaNo ratings yet
- Capitulo-4 Felder CHDocument73 pagesCapitulo-4 Felder CHJavier ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Principles of Modern Chemistry 8th Edition Oxtoby Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesPrinciples of Modern Chemistry 8th Edition Oxtoby Solutions Manualronne.cartouchuq4udNo ratings yet
- Principles of Modern Chemistry 8th Edition Oxtoby Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesPrinciples of Modern Chemistry 8th Edition Oxtoby Solutions Manualrainfalldrunkeny1tn2f100% (22)
- Materi 6 Teori Kinetik Versi Bhs InggrisDocument7 pagesMateri 6 Teori Kinetik Versi Bhs InggrisNur Budi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- CHM524 Chapter 2 Part B TutoDocument1 pageCHM524 Chapter 2 Part B TutoAnis SofeaNo ratings yet
- New Tutorial 5 With SolutionDocument4 pagesNew Tutorial 5 With SolutionNaveed AhmadNo ratings yet
- 7 Quantum+Theory+IIDocument44 pages7 Quantum+Theory+IIKashif KhanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Modern Chemistry 8th Edition Oxtoby Solutions ManualDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Modern Chemistry 8th Edition Oxtoby Solutions Manualjosephbrowntdnebozsrw93% (14)
- 12.1 Thermodynamics 01 SolutionsDocument15 pages12.1 Thermodynamics 01 SolutionsAldren Barrina DelanteNo ratings yet
- Solutions Set12Document18 pagesSolutions Set12Frank CañasNo ratings yet
- Aim of The ExperimentDocument3 pagesAim of The ExperimentPooja PadhanNo ratings yet
- Effects of Europium Concentration On Luminescent and Scintil - 2022 - Journal ofDocument5 pagesEffects of Europium Concentration On Luminescent and Scintil - 2022 - Journal ofShuNo ratings yet
- New-Problems-Chapter-21 Convective Mass TransferDocument2 pagesNew-Problems-Chapter-21 Convective Mass TransferKhanh NhiNo ratings yet
- DisplayArticleForFree CFMDocument3 pagesDisplayArticleForFree CFMCarolina TorresNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Sol PDFDocument5 pagesTest 1 Sol PDFabhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 (3 Edition) : Moles of Solute Molality Mass of Solvent (KG) 1.08 G Mass of 1 L Soln 1000 ML 1080 G 1 MLDocument4 pagesChapter 13 (3 Edition) : Moles of Solute Molality Mass of Solvent (KG) 1.08 G Mass of 1 L Soln 1000 ML 1080 G 1 MLOmar RefeNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Operations 1: Solution of Problem 2.2 (B) From Mass-Transfer Operations by Robert E. TreybalDocument8 pagesMass Transfer Operations 1: Solution of Problem 2.2 (B) From Mass-Transfer Operations by Robert E. TreybalZaid MansuriNo ratings yet
- Solution Koretsky Completo PDFDocument738 pagesSolution Koretsky Completo PDFBruna P100% (3)
- Hajer Alotaibi Hw1Document7 pagesHajer Alotaibi Hw1Hajer AlotaibiNo ratings yet
- Unit Eight Homework Solutions, November 2, 2010: M KG M KG M KG M C V C V C V V XDocument7 pagesUnit Eight Homework Solutions, November 2, 2010: M KG M KG M KG M C V C V C V V XShainee Delle PalmeraNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry HomeworkDocument4 pagesAnalytical Chemistry HomeworkNemo Cyzar LiisNo ratings yet
- ME 231 Gomes Whharris 2-28-18 SOLUTIONDocument5 pagesME 231 Gomes Whharris 2-28-18 SOLUTIONAzaki SeiryoNo ratings yet
- Curved Surface Boosts Electrochemical CO2 Reduction To Formate Via Bismuth Nanotubes in A Wide Potential Window - SuppDocument21 pagesCurved Surface Boosts Electrochemical CO2 Reduction To Formate Via Bismuth Nanotubes in A Wide Potential Window - SuppSantosh Srinivas NNo ratings yet
- Exercise - 4: Previous Year Jee Advanced Question: Solutions 43Document6 pagesExercise - 4: Previous Year Jee Advanced Question: Solutions 43Shweta AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Engineering and Chemical Thermodynamics: Chapter 1 SolutionsDocument24 pagesEngineering and Chemical Thermodynamics: Chapter 1 SolutionsBrandon SmithNo ratings yet
- An Ideal Gas Mixture Consists of 2kmol of N2 and 6 Kmol of CO2. The Mass Fraction of CO2 IsDocument9 pagesAn Ideal Gas Mixture Consists of 2kmol of N2 and 6 Kmol of CO2. The Mass Fraction of CO2 IsLance Andrew LagmanNo ratings yet
- Problem39 10Document1 pageProblem39 10IENCSNo ratings yet
- ch4 ExamplesDocument11 pagesch4 ExamplesSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- Aq Aq Aq L: 4: Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions 4.5: Quantitative Chemical AnalysisDocument4 pagesAq Aq Aq L: 4: Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions 4.5: Quantitative Chemical AnalysisLee JonesNo ratings yet
- Chem 340 Hw2 Key 2011 Physical Chemistry For Biochemists 1Document7 pagesChem 340 Hw2 Key 2011 Physical Chemistry For Biochemists 1krishnaswamy9No ratings yet
- Craig-Bampton Method For A Two Component System: This Is A Work in ProgressDocument15 pagesCraig-Bampton Method For A Two Component System: This Is A Work in ProgressnemaderakeshNo ratings yet
- Solution Stoichiometry Notes PDFDocument4 pagesSolution Stoichiometry Notes PDFAria MandalikaNo ratings yet
- Chap 08 Soln PDFDocument26 pagesChap 08 Soln PDFsoma sundaramNo ratings yet
- Principles of Chemical Equilibrium: BG BGDocument30 pagesPrinciples of Chemical Equilibrium: BG BGkennethleo69No ratings yet
- Assumptions Properties The Properties of Nitrogen at Room Temperature Are R 0.2968 Kpa.MDocument1 pageAssumptions Properties The Properties of Nitrogen at Room Temperature Are R 0.2968 Kpa.MFelipeEscobarNo ratings yet
- Ch7 HM 3 1Document2 pagesCh7 HM 3 1Najmul Puda PappadamNo ratings yet
- CH434 Assignment 1 2007Document1 pageCH434 Assignment 1 2007Zulfahmi FerdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Example CH 2 PDFDocument6 pagesExample CH 2 PDFRojan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Example 2.1: DP DP P P or P PDocument6 pagesExample 2.1: DP DP P P or P PEzanaLordNo ratings yet
- PIPE Constants and ConversionsDocument2 pagesPIPE Constants and ConversionsJames Joseth ArceoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2pointsDocument4 pagesChemistry 2pointsjovanniNo ratings yet
- Property Calculations: Virial Equation of StateDocument9 pagesProperty Calculations: Virial Equation of Statesalman hussainNo ratings yet
- hw3 PDFDocument2 pageshw3 PDFRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aqueous Solution Chemistry-ExercisesDocument7 pagesAqueous Solution Chemistry-ExercisesragustochemNo ratings yet
- Ch10 2022Document2 pagesCh10 2022810003No ratings yet
- 2.simple Hormonic Motion (SHM) - FinalDocument13 pages2.simple Hormonic Motion (SHM) - Finaldrishyakumar1234No ratings yet
- D T V T TDocument2 pagesD T V T TRachita Prakash SarafNo ratings yet
- Supercapacitors Based on Carbon or Pseudocapacitive MaterialsFrom EverandSupercapacitors Based on Carbon or Pseudocapacitive MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Endohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideFrom EverandEndohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideNo ratings yet
- D T V T TDocument2 pagesD T V T TRachita Prakash SarafNo ratings yet
- Ducdt DW PDV C Is The Constant Volume Heat Capacity,: DqdudwDocument3 pagesDucdt DW PDV C Is The Constant Volume Heat Capacity,: DqdudwRachita Prakash SarafNo ratings yet
- At RT P VBVVB: Calculate Z, GR, HR and SR For Co2 at 325 K and 60 Bar Using R-K Eos. AnswerDocument2 pagesAt RT P VBVVB: Calculate Z, GR, HR and SR For Co2 at 325 K and 60 Bar Using R-K Eos. AnswerRachita Prakash SarafNo ratings yet
- I I inDocument3 pagesI I inRachita Prakash SarafNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicsRachita Prakash Saraf0% (1)
- ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicsRachita Prakash SarafNo ratings yet