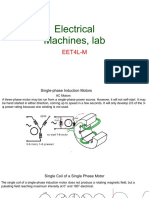
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
261 PDF
261 PDF
Uploaded by
iraj_214Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
261 PDF
261 PDF
Uploaded by
iraj_214Copyright:
Available Formats
Charles Concordia Wiley, 1951 Synchronous machines: theory and performance
224 pages 1951 WL Soong, TJE Miller
synchronous machines, machine, machines, synchronous, Theoretical, performance synchronous,
performance, synchronously, Theory, synchronous reluctance motor, synchronous reluctance, experimental
machines, flywheel energy storage system, synchronous AC motor drives, synchronous machine
WL Soong, TJE Miller. Control and performance of a doubly-fed induction machine intended for a flywheel energy storage system, c. Modeling for Simulation The EMTDC supports only two machines models: a salient-
pole synchronous machine. C. Effects of Disagreement Between Machine Parameters and Control Constants Disagreement between machine parameters and control constants. Maximising the saliency ratio of the
synchronous reluctance motor, since attention is restricted to inverter fed machines with field oriented control and shaft position feedback, it is assumed that. 2 Basic theory 2.1 Torque per ampere The electromagnetic
torque is the classical reluctance torque of the conventional synchronous machine. Rotor design optimization of synchronous reluctance machine, also, in machines typically employing a modem axially laminated rotor
structure, a rotor cage is normally omitted since the machine can be started synchronously from rest. From Fs equations forms the basis for the dq Equations for a synchronous reluctance machine. Simulation and
detection of dynamic air-gap eccentricity in salient-pole synchronous machines, the synchronous machine performance under the dynamic air-gap eccentricity. Finally, experimental results to substantiate the
theoretical findings are presented. Index Terms Dynamic eccentricity, finite-element analysis, synchronous machines, winding function theory. Theory and performance of polyphase reluctance machines, to
reluctance machines, it was thought worthwhile to study their theory and performance. The analysis of reluctance-machine performance may be accomplished in two ways: firstly, by adapting the complete results for
salient-pole synchronous machines, as developed. Design criteria of high performance synchronous reluctance motors pdf, at this aim the synchronous reluctance motor's torque-per-volume has to be maximized. In
this paper the main problems related to the design of such a machine are considered, with particular attention to servomotor applications. Usual for high performances machines. Field-weakening performance of
brushless synchronous AC motor drives, 3 M ozor cross-secliuns 332 resent steel and the solid areas represent permanent magnets. The separately excited DC machine has separate windings for the flux-producing and
torque-producing currents. Brushless synchronous AC machines have a single stator. Developments in the performance and theory of segmental-rotor reluctance motors, fig. 8 Synchronous load characteristics of
experimental machines c â ¢= 00292. Since the measured values refer to the machine operating in a reasonably highly saturated condition (130 V), the theoretical treatment of saturation by the simple expedient of the use of
a saturated. Two-reaction theory of synchronous machines-II, 1. Park, R. H., Two-Reaction Theory of Synchronous Machines -I, AIEE TRANS. And therefore correctly represents the machine at no- equation (1) and with this
interpretation the equation applies when 4'=4's, 't = ~~~d. not only for salient-pole synchronous machines. Performance of PM-assisted synchronous reluctance motor for high-efficiency and wide constant-power
operation, the condition that the -axis inductance becomes zero is necessary for a synchronous reluctance motor to satisfy that optimum condition. However, there are many TABLE I DIMENSIONS OF PROTOTYPE
MACHINES Fig. 2. Rotor cross section of prototype machine. Theoretical limitations to the field-weakening performance of the five classes of brushless synchronous AC motor drive, a new parameter plane approach
graphically illustrates the effect of the drive parameters on the shape of the optimal field-weakening characteristic of brushless synchronous AC motor drives with a limited inverter kVA rating. It unifies previous
approaches to this problem.
by WL Soong, TJE Miller
Synchronous machines: theory and performance
You might also like
- Electric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsFrom EverandElectric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- 1000 Electrical Machines MCQsDocument458 pages1000 Electrical Machines MCQskibrom atsbha100% (4)
- Permanent Magnet Motor (ALSTOM)Document5 pagesPermanent Magnet Motor (ALSTOM)Sundar Mukherjee100% (1)
- Unit 1Document25 pagesUnit 1papkarthikNo ratings yet
- Trapezoidal Control of BLDC Motors Using Hall Effect SensorsDocument33 pagesTrapezoidal Control of BLDC Motors Using Hall Effect Sensorstoggle123No ratings yet
- Modeling Simulation and Analysis of Permanent-Magnet Motor Drives. I. The Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor DriveDocument9 pagesModeling Simulation and Analysis of Permanent-Magnet Motor Drives. I. The Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor DriveArthur CaiNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle 4th ModuleDocument19 pagesElectric Vehicle 4th ModuleSimi BaniNo ratings yet
- Sensored FOC of PMSMDocument37 pagesSensored FOC of PMSMRintuMathunniNo ratings yet
- 2057-Article Text-2035-1-6-20210514Document8 pages2057-Article Text-2035-1-6-20210514akli zinouNo ratings yet
- Ee2403 (Special Electrical Machines Question BankDocument20 pagesEe2403 (Special Electrical Machines Question Bankkrish_skumar6302No ratings yet
- Synchronous Drive PerformanceDocument8 pagesSynchronous Drive PerformancehaimantiNo ratings yet
- Synchronous MotorDocument6 pagesSynchronous MotorPraveen Ramesh KarnamNo ratings yet
- Synchronous MotorDocument6 pagesSynchronous MotorSelvasundar KumarNo ratings yet
- Synchronous MotorsDocument11 pagesSynchronous MotorsSanjay GhoshNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed System Modeling (Final Report)Document41 pagesDC Motor Speed System Modeling (Final Report)Khubaib Ahmed80% (5)
- Special Topics: Islamic Azad University Isfahan (Khorasgan) BranchDocument19 pagesSpecial Topics: Islamic Azad University Isfahan (Khorasgan) BranchAli HusseinNo ratings yet
- Controller Design For Synchronous Reluctance Motor Drive Systems With Direct Torque ControlDocument42 pagesController Design For Synchronous Reluctance Motor Drive Systems With Direct Torque Controlmuhamad otongNo ratings yet
- A Very High Speed Switchedreluctance Startergenerator For AircraDocument7 pagesA Very High Speed Switchedreluctance Startergenerator For AircraAimmadNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Reluctance Motor - PPSXDocument22 pagesSynchronous Reluctance Motor - PPSXselraj0708No ratings yet
- Report On Lecture 38Document5 pagesReport On Lecture 38Surajit SahaNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of PermanentDocument83 pagesModeling and Simulation of PermanentSriram Anil Kumar GandhamNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle 4th ModuleDocument13 pagesElectric Vehicle 4th ModuleAmruth DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Celik 11Document412 pagesCelik 11Mohammed NizamuddinNo ratings yet
- PSD CDT28 Summary 6EEE1 CVS 2022-23 PDFDocument6 pagesPSD CDT28 Summary 6EEE1 CVS 2022-23 PDFNadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Of Induction Motor Using Artificial Neural Network and Implementation in MATLABDocument54 pagesOf Induction Motor Using Artificial Neural Network and Implementation in MATLABnareshreddy136100% (1)
- Vector Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous MotorDocument51 pagesVector Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous MotorFAIZAN ALINo ratings yet
- Types of Ac GeneratorDocument10 pagesTypes of Ac GeneratorJherel BerinNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Motors: Compensator. It Behaves As A Variable Capacitor When The Field IsDocument11 pagesSynchronous Motors: Compensator. It Behaves As A Variable Capacitor When The Field Ispriyanka2711_dubeyNo ratings yet
- AC Induction Motor SlipDocument6 pagesAC Induction Motor SlipnotastudentNo ratings yet
- Performance Characteristics of InductionDocument48 pagesPerformance Characteristics of InductionToolit MartineNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Switched Reluctance Motors For Hybrid Electric VehiclesDocument6 pagesOptimization of Switched Reluctance Motors For Hybrid Electric VehiclesgeerhardusvosNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor Drive Analysis Using LabVIEWDocument26 pagesThree-Phase Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor Drive Analysis Using LabVIEWCarlos Roberto Amaya Rodriguez100% (1)
- Unit 4Document33 pagesUnit 4SidhuSidNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Motor & Its Applications & Power Factor ImprovementDocument4 pagesSynchronous Motor & Its Applications & Power Factor ImprovementYash BansalNo ratings yet
- Trapezoidal Control of BLDC Motors Using Hall Effect SensorsDocument33 pagesTrapezoidal Control of BLDC Motors Using Hall Effect SensorsYang ElvisQUNo ratings yet
- DC Motors InformationDocument9 pagesDC Motors InformationCarlosNo ratings yet
- Induction and Synchronous Motor FundamentalsDocument9 pagesInduction and Synchronous Motor FundamentalsfitxvNo ratings yet
- Sensorless Foc of PMSM Chu YDocument42 pagesSensorless Foc of PMSM Chu Yhieuhuech1No ratings yet
- Eiwp02 13Document5 pagesEiwp02 13user765No ratings yet
- Ic Engine Lab ManualDocument80 pagesIc Engine Lab ManualMuhammadKhizarSiddiqueNo ratings yet
- WEGSM1 ManualDocument15 pagesWEGSM1 Manualshinkentom2No ratings yet
- Magnetising Flux Saturation in Variable-Speed Inverter-Fed Induction Motor DrivesDocument6 pagesMagnetising Flux Saturation in Variable-Speed Inverter-Fed Induction Motor DrivesSherif M. DabourNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Synchronous MotorDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of Synchronous Motormelvin westNo ratings yet
- DSP Control of Stepper MotorDocument5 pagesDSP Control of Stepper MotorAhmedHyderMohdNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Three Phase Induction Machine Using Written Pole TechnologyDocument7 pagesModeling and Simulation of Three Phase Induction Machine Using Written Pole TechnologyJOHN MINKHANTNo ratings yet
- C1201042329 PDFDocument7 pagesC1201042329 PDFJOHN MINKHANTNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Motor Drive: Presented By: Electrical (6 Sem)Document19 pagesSynchronous Motor Drive: Presented By: Electrical (6 Sem)Swarup MadduriNo ratings yet
- Synchronous MotorsDocument16 pagesSynchronous Motorsshinkentom2No ratings yet
- ELEN 30104 Single Phase and Permanent Magnet MachinesDocument23 pagesELEN 30104 Single Phase and Permanent Magnet MachinesBu DakNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Design of SynchronousDocument6 pagesElectromagnetic Design of SynchronousedumacerenNo ratings yet
- DW TechTip Brushless Servo SystemsDocument14 pagesDW TechTip Brushless Servo SystemsgubiliNo ratings yet
- THE FULL PAPER by DR Sab Safi of SDT Drives PDFDocument10 pagesTHE FULL PAPER by DR Sab Safi of SDT Drives PDFmohanNo ratings yet
- Application Characteristics of Permanent Magnet Synchronous and Brushless DC Motors For Servo DrivesDocument11 pagesApplication Characteristics of Permanent Magnet Synchronous and Brushless DC Motors For Servo DrivessambhanimadhubabuNo ratings yet
- Starting Methods of Syncronous Motor Criollo - RoggerDocument7 pagesStarting Methods of Syncronous Motor Criollo - RoggerRogger FabricioNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Three Phase Induction MotorDocument7 pagesLiterature Review of Three Phase Induction Motorfvdh47rr100% (1)
- Syn Motor Testing WithDocument6 pagesSyn Motor Testing WithSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
- (2016) Design of Optimal Input-Output Scaling Factors Based Fuzzy PSS Using Bat AlgorithmDocument12 pages(2016) Design of Optimal Input-Output Scaling Factors Based Fuzzy PSS Using Bat Algorithmiraj_214No ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy ReviewsDocument17 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviewsiraj_214No ratings yet
- Sciencedirect: M. Pondini, A. Signorini, V. Colla, S. Barsali M. Pondini, A. Signorini, V. Colla, S. BarsaliDocument6 pagesSciencedirect: M. Pondini, A. Signorini, V. Colla, S. Barsali M. Pondini, A. Signorini, V. Colla, S. Barsaliiraj_214No ratings yet
- Models of Synchronous Generator and Transformers For Dispatch Training Simulators and Real Time Digital SimulatorsDocument6 pagesModels of Synchronous Generator and Transformers For Dispatch Training Simulators and Real Time Digital Simulatorsiraj_214No ratings yet
- Comparison of Virtual Synchronous Generators Dynamic ResponsesDocument6 pagesComparison of Virtual Synchronous Generators Dynamic Responsesiraj_214No ratings yet
- Virtual Synchronous Machines - Classification of Implementations and Analysis of Equivalence To Droop Controllers For MicrogridsDocument7 pagesVirtual Synchronous Machines - Classification of Implementations and Analysis of Equivalence To Droop Controllers For Microgridsiraj_214No ratings yet
- 2160912Document4 pages2160912yash sharmaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument26 pagesUNIT-2 Basic Electrical Engineeringabhi shekNo ratings yet
- ALV Series IPCDocument2 pagesALV Series IPCAnderson RamalhoNo ratings yet
- Performance Comparisons of Radial and Axial Field Permanent Magnet Brushless MachineDocument8 pagesPerformance Comparisons of Radial and Axial Field Permanent Magnet Brushless Machinerakeshee2007No ratings yet
- Scan0066 PDFDocument1 pageScan0066 PDFJayson Jonson AraojoNo ratings yet
- Generalized Theory Machines PDFDocument24 pagesGeneralized Theory Machines PDFMc D'clarkNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ECEDocument3 pagesLesson Plan ECEVenkatesan SwamyNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Armature Windings PDFDocument43 pagesElectric Circuit Armature Windings PDFravineel00975% (8)
- Electrical Machines Lab March 16 UpdateDocument53 pagesElectrical Machines Lab March 16 Updatepeter vanderNo ratings yet
- Dee 401 Module I, II, V, ViDocument153 pagesDee 401 Module I, II, V, Vinotbad gameming notbadNo ratings yet
- Brushless DC Electric Motor - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument14 pagesBrushless DC Electric Motor - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSailesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument102 pagesDC MachinesmohamedashrafkotpNo ratings yet
- Ee 1251 - Electrical Machines - Ii Ii Year Iv Semester Eee Unit - I Synchronous Generator 1. How Are Alternators Classified?Document19 pagesEe 1251 - Electrical Machines - Ii Ii Year Iv Semester Eee Unit - I Synchronous Generator 1. How Are Alternators Classified?Rameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Ac MotorsDocument22 pagesAc MotorsHumberto Andrade DomìnguezNo ratings yet
- Brushless Servo MotorsDocument4 pagesBrushless Servo Motorschidambaram kasiNo ratings yet
- CH 38synchronous Motor1 PDFDocument46 pagesCH 38synchronous Motor1 PDFWidia AstutiNo ratings yet
- Ee 501Document2 pagesEe 501Sara PowersNo ratings yet
- DC MachineDocument36 pagesDC MachineJalu PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines II AnswerDocument24 pagesElectrical Machines II AnswerGurulathan SoosairajNo ratings yet
- Note 8 Electric Actuators: Lecture Notes of ME 475: Introduction To MechatronicsDocument13 pagesNote 8 Electric Actuators: Lecture Notes of ME 475: Introduction To MechatronicsSapath Narsingh BogatiNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor Wikipedia PDFDocument138 pagesElectric Motor Wikipedia PDFHoppohigdi786 Hoppohigdi786No ratings yet
- Presentation On Motors & VFD: Submitted To:-Submitted ByDocument32 pagesPresentation On Motors & VFD: Submitted To:-Submitted Byparth dosiNo ratings yet
- DRS 71M4Document2 pagesDRS 71M4carlos alfonsoNo ratings yet
- AC Induction Motors vs. Permanent Magnet Synchronous MotorsDocument5 pagesAC Induction Motors vs. Permanent Magnet Synchronous MotorsAhmed GhreebNo ratings yet
- Ac Drives: Reference Book: Power Electronics Devices, Circuits, and Applications by Muhammad H. RashidDocument27 pagesAc Drives: Reference Book: Power Electronics Devices, Circuits, and Applications by Muhammad H. Rashid17031 Nazmul HasanNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Induction Motors PDFDocument11 pages3 Phase Induction Motors PDFFauzan Dimas KusyonoNo ratings yet
- Motor Vibration AnalysisDocument61 pagesMotor Vibration Analysiskiki kamui100% (1)
- Narrative Report in Electrical Machines 2Document15 pagesNarrative Report in Electrical Machines 2John Lloyd ComiaNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument16 pagesDC MachinesAuthorized EarthlingNo ratings yet
- Type of Motors Used in Electic Vechines and There Classfications in PPT ModeDocument19 pagesType of Motors Used in Electic Vechines and There Classfications in PPT Mode21EEB0B65NIKIHIL VINUKONDANo ratings yet