Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Light Shallow Drizzle Mist Dust/sand Whirls: Locations Stations
Uploaded by
Adrian QuahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Light Shallow Drizzle Mist Dust/sand Whirls: Locations Stations
Uploaded by
Adrian QuahCopyright:
Available Formats
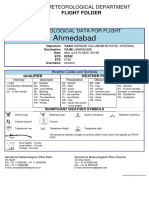
TAF - Terminal Aerodrome Forecast
A detailed forecast of expected weather elements at an aerodrome that
significantly affects the movement of aircraft.
A TAF has the following basic format:
TAF CCCC DDHHmmZ DDFMTL DDDSSGSSKT VVVV WW NNNhhh (VVhhh )
TXTtTt/HHZTNTtTt/HHZ { BECMG HHHH / FMHHmm / TEMPO HHHH }
{PROB % HHHH} =
Explanation of Terms:
CCCC - Location or Place
Four letter ICAO ID's designators are is used. (see: Locations and Stations )
DDHHmmZ - Date/time of compilation
DD - Day, HH - Hour, mm - Minutes
Z - Time Zone, Z=Zulu or GMT.
AUTO - Used when the observation is done by an automatic weather station.
DDDSSGSSKT - Wind (see: VRB )
DDD - Wind Direction in degrees
SS - Wind Speed, G - GUST, KT - Knots
Wind direction from True North, wind speed is measured in knots(KT).
Gust is added only if the average wind speed is exceeded by 10KT or
more of the mean windspeed for previous 10 minutes. (1KT = 1.85 Km/h)
Other units that may be used to measure wind speed are:
KMH - Kilometres per hour, MPS - Metres per second.
WW - weather (see: NSW )
Used to report significant weather. The table below shows the abbreviations .
Sign Present and Forecast Weather
Qualifier Weather Phenomena
Intensity of
Descriptor Precipitation Obscuration Other
Proximity
2 3 4 5
1
MI Shallow PO
- Light DZ Drizzle BR Mist
Dust/sand
BC Patches whirls
RA Rain FG Fog
PR Partial SQ Squalls
SN Snow FU Smoke
(Covering part of
the aerodrome) SG Snow Grains VA Volcanic FC Funnel
Moderate
Ash Clouds
(no qualifier)
DR Low Drifting IC Ice crystals (tornado or
(diamond dust) DU waterspout)
BL Blowing
Widespread
PE Pellets Dust SS
SH Shower(s) Sandstorm
+ Heavy GR Hail SA Sand
TS DS Duststorm
Thunderstorm GS Small hail HZ Haze
and/or
FZ Freezing
VC Vicinity snow pellets
(supercooled)
VVVV - Horizontal Visibility (see: CAVOK , RVR - Runway visual range)
measured in meters.
The following increments are used:
10m - below 100m
100m - below 1000m
500m - between 1000m and 5000m
1000m - between 5000m and 9000m
9999 - 10Km and above.
Some countries use statute mile(SM) as a unit to measure visibility.
D - Direction
When the horizontal visibility is not the same in all directions, a minimum
and maximum visibility may be given followed the direction.
Values for D are:
N - North, NE - Northeast, E - East, SE - Southeast, S - South,
SW - Southwest, W - West, NW - Northwest.
..top of page
NNNhhh - Clouds (see: CAVOK , NSC , Cloud Type, Cloud Atlas)
NNN - Cloud amount, shown by the following abbreviations:
FEW - 1 to 2 octas
SCT - 3 to 4 octas
BKN - 5 to 7 octas
OVC - 8 octas
hhh - Cloud height in feet above station level (or AGL).
VVhhh - Vertical visibility
When the sky is obscured and instrumentation is available to measure
vertical visibility, hhh is given in increments of 100ft.
TT/TdTd - Temperatures
TT - Temperature, Td - Dewpoint Temperature
Temperatures in South Africa are measured in Celsius.
QPPPP - QNH
Q - indicator for QNH, PPPP - Pressure value.
Measured in hecto Pascal (HPa), 1 Hpa = 1 mB(millibar)
REWW - Recent Significant Weather (see: WW , NSW )
TTTTT - Trend Forecast
This type of forecast is used to indicate significant changes in the weather
expected within a two hour period from the time of issue of the Metar.
RMK - Remark
Used supply additional information that do fall within the boundaries of
the general code. One such example is the tops of CB that are visible
from the point of observation but the cloud may be 200Km away.
Eg. RMK CB DISTANT SW.
= - Indicates the end of the report/bulletin
..top of page
CAVOK
Visibility greater than 10Km, no cloud below 5000 ft or minimum sector altitude,
whichever is the lowest and no CB or over development and no significant
weather.
NOSIG - No Significant Change
Nosig is added to the METARs of locations where no forecaster is available
to give trend forecast. It is omitted with Auto METARs and those from
smaller locations.
RD/VVVV - Runway visual range
At aerodromes where instruments are used to measure visibility this group
will be included in the METAR when significant.
RD/ - Runway designator/point where the visibility is measured.
VVVV - Visibility.
RD/VVVV vVVVV - This format is used when the visibility fluctuates at a
runway point. The fluctuation is considered significant when the visibility
during the last 5 seconds changes by 50m or 20% of the mean visibility
of the previous 10 minutes.
v - tendency for the visibility to change by 100m or more from the mean,
terms used are: U - upward, D - downward, N - no tendency.
..top of page
NSW - No significant Weather (TAF only)
NSC - No Significant Cloud.
NOBS - No Observation. Appears at the end of a TAF when no surface
observation is available for the location at the time when the TAF is issued.
VRB - Variable
Used when windspeed is less than 3KT or during a violent thunderstorm
when wind direction can not be determined.
Cloud Type
Abbreviations for cloud used in METAR, TAF and Sigwx Charts.
CB - Cumulonimbus
TCU - Towering Cumulus
Abbreviations used only in Sigwx Charts.
ST - Stratus
SC - Stratocumulus
CU - Cumulus
NS - Nimbo Stratus
AC - Alto Cumulus
AS - Alto Stratus
The following cloud types are not considered to be significant to aviation
and therefore not in any aviation forecasts:
Ci - Cirrus
Cs - Cirrostratus
Cc - Cirrocumulus
..top of page
DDFMTL - Period of validity
DD - Day, FM - Hour, start of the period, TL - Hour, end of period
Eg 120312 - Taf is valid for the 12th day of the month, from 03:00z until 12:00z.
Two sets of TAFs are issued in South Africa:
FC-TAF: TAF valid for 6 to 9 hours, updated in 3 hour intervals.
FT-TAF: Valid for 18 to 24 hours, updated at 6 hour intervals.
Note: Not all locations have FT-TAFs.
TXTtTt/HHZTNTtTt/HHZ - Forecast Max and Min temperature
TX - Indicator for Maximum temperature
TtTt - Temperature value in Celsius
TN - Indicator for Minimum temperature
HH - Forecast hour, i.e. the time(hour) when the temperature is expected
Z - Time Zone indicator, Z=GMT.
{ BECMG HHHH / FMHHmm / TEMPO HHHH (TLHHmm)}
{PROB % HHHH}
HHHH - Period of validity
HH on the left is the hour indicating the start of time while HH on the
right will be the end of the period.
Eg. 1317 - a change from 13:00Z to 17:00Z.
BECMG - Becoming
Used to indicate a gradual change in some of the forecast elements.
TAF - BECMG is always followed by a time group(HHHH) and does not exceed 4
hours.
TREND(METAR) - This forecast is only 2 hours and need not be followed by a
time.
FMHHmm - From
HH - Hour, mm - minute from when the change is expected.
TAF - Used when a significant change in all elements is expected at a specific
time.
TREND(METAR) - Used with BECMG and may be used to indicate a change in
some or all the elements, e.g. BECMG FM2015.
..top of page
TEMPO - Temporary fluctuation in some of the elements lasting for periods of
30 minutes or more but not longer than one hour with each instance and does
not cover more than half of the total period indicated by HHHH .
TLHHmm - Until (used in METAR only)
HH - Hour, mm - minute until when the change is expected to stop.
TL may be used with FM.
PROB % - Probability
% - percentage, only 30 or 40 is used. If a higher probability is expected
TEMPO is used.
..top of page
SPECI - Special METAR
A SPECI is the same as a METAR but issued when the following criteria is met:
1. Mean surface wind direction has changed by 30 degrees or more, the mean
wind speed before and/or after the change being 20Kt or more.
2. Mean surface wind speed has change by 10Kt or more, the wind speed
before and/or after the change be 30Kt or more.
3. Wind Gusts have increased by 10Kt or more, the mean wind speed before
and/or after the change being 15Kt or more.
4. Visibility changes to or pass:
a. 1500 or 3000m (SPECI) - 150, 350, 600, 800,1500, 3000m (TAF)
b. 5000m where significant numbers of VFR flights are operating.
5. Runway visual range changes to or pass 150, 350, 600, 800m.
6. When any combination of weather in the significant weather table begins,
ends or changes intensity.
7. Height of the base of the lowest cloud layer of BKN or OVC extent,
changes to or passes:
a. 100, 200, 500 or 1000ft.
b. 1500ft where significant numbers of VFR flights are operating.
8. When the amount of cloud below 1500ft changes from:
a. SKC, FEW, SCT to BKN or OVC
b. BKN or OVC to SKC, FEW, SCT
9. When the sky is obscured and vertical visibility changes to or pass
100, 200, 500, 1000ft.
10. Increase in temperature of 2 degrees Celsius or more.
..top of page
You might also like
- Navigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsFrom EverandNavigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsNo ratings yet
- Metar code formatsDocument3 pagesMetar code formatsJoão MartinhoNo ratings yet
- SAWS AviationCodesDocument17 pagesSAWS AviationCodes294rahulNo ratings yet
- Decode a European METAR weather reportDocument6 pagesDecode a European METAR weather reportAhmeed BadiiNo ratings yet
- METAR in TAF Decoding PDFDocument6 pagesMETAR in TAF Decoding PDFDaniel MkenyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Met Reports DecoderDocument7 pagesBasic Met Reports Decodera_v71No ratings yet
- Metar HelpDocument5 pagesMetar HelpNelson GonzàlezNo ratings yet
- MetarDocument3 pagesMetarA320viator100% (1)
- Metar y Sus CódigosDocument3 pagesMetar y Sus CódigosRolo Fallas100% (1)
- METARTAF AbbreviationsDocument1 pageMETARTAF Abbreviationsshaddjd25No ratings yet
- U.S. Metar Observation ReportDocument43 pagesU.S. Metar Observation ReportAmirAli MohebbiNo ratings yet
- Metar - Taf - PirepDocument2 pagesMetar - Taf - PirepSantosh Raj KhanalNo ratings yet
- METARDocument7 pagesMETARjitansh singhNo ratings yet
- METAR TAF Code Glossary Under 40Document4 pagesMETAR TAF Code Glossary Under 40Yeison Chavez100% (1)
- 6 Règles D'or Pour Que Votre Cerveau Continue de Fabriquer de Nouveaux Neurones - SciencesetavenirDocument2 pages6 Règles D'or Pour Que Votre Cerveau Continue de Fabriquer de Nouveaux Neurones - SciencesetaveniradsrjmNo ratings yet
- What Is A Metar? A Basic ExampleDocument12 pagesWhat Is A Metar? A Basic ExampleTim RolandNo ratings yet
- Sigmet PDFDocument4 pagesSigmet PDFlim huivoonNo ratings yet
- 41 Gamet Airmet EngDocument6 pages41 Gamet Airmet EngEriks GrazulisNo ratings yet
- METAR Decode PDFDocument2 pagesMETAR Decode PDFazx72No ratings yet
- Weather SymbolsDocument1 pageWeather SymbolsAl GRUNERNo ratings yet
- Rules of Thumb: Local WindsDocument5 pagesRules of Thumb: Local WindsPintuNo ratings yet
- Airport Metar CardDocument2 pagesAirport Metar CardtalonmiesNo ratings yet
- METAT and TAF Weather Report 1612262538Document12 pagesMETAT and TAF Weather Report 1612262538cplowhangNo ratings yet
- METAR TAFDocument12 pagesMETAR TAFcplowhangNo ratings yet
- Meteo Manual DraftDocument14 pagesMeteo Manual DraftAlejandro García MeleroNo ratings yet
- Ehlw 201702020823Document18 pagesEhlw 201702020823Filipe RosaNo ratings yet
- METARTAF AbbreviationsDocument9 pagesMETARTAF Abbreviationsstalin13No ratings yet
- Mampu B737 RLT COMPANION Rev Jul 2011 PDFDocument298 pagesMampu B737 RLT COMPANION Rev Jul 2011 PDFJoey Marks100% (1)
- US METAR AbbreviationsDocument4 pagesUS METAR AbbreviationsalinarochaNo ratings yet
- Metar AbbreviationsDocument3 pagesMetar AbbreviationsLidiaEstanNo ratings yet
- Metar/Taf List of Abbreviations and AcronymsDocument6 pagesMetar/Taf List of Abbreviations and AcronymsOsama KhalilNo ratings yet
- .PK055 202210210518Document11 pages.PK055 202210210518roms.monteiro27No ratings yet
- ANALISIS PARAMETER KONVEKTIF UNTUK PRAKIRAAN CUACA LOKALDocument20 pagesANALISIS PARAMETER KONVEKTIF UNTUK PRAKIRAAN CUACA LOKALTitis Angger PangestuNo ratings yet
- Mark.E.Fo X@faa - Gov: Key To Aerodrome Forecast (TAF) and Aviation Routine Weather Report (METAR) (Front)Document2 pagesMark.E.Fo X@faa - Gov: Key To Aerodrome Forecast (TAF) and Aviation Routine Weather Report (METAR) (Front)郭芛宏No ratings yet
- METAR and TAF Weather Reports Area ForecastDocument11 pagesMETAR and TAF Weather Reports Area Forecastajcd110No ratings yet
- TAF CardDocument2 pagesTAF CardRichard LundNo ratings yet
- WS SIGMET Quick Reference GuideDocument4 pagesWS SIGMET Quick Reference GuideflotterotterNo ratings yet
- ATC MetarDocument6 pagesATC MetarTito PratistaNo ratings yet
- METAR (Aviation Routine Weather Report) / TAF Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMETAR (Aviation Routine Weather Report) / TAF Cheat SheetOscar UracilNo ratings yet
- Template For Taf, SigmetawlfDocument10 pagesTemplate For Taf, Sigmetawlfchinna rajaNo ratings yet
- METAR DECODEDocument6 pagesMETAR DECODEPeter ChanceNo ratings yet
- Abb Meanings 2Document13 pagesAbb Meanings 2IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Awp MetarspeciDocument4 pagesAwp Metarspecic_poliNo ratings yet
- Decode aerodrome weather forecasts and reportsDocument5 pagesDecode aerodrome weather forecasts and reportsOvidiu LambruNo ratings yet
- MetarDocument22 pagesMetaravcafeNo ratings yet
- PARAMETER KONVEKTIF UNTUK ANALISIS AWAN CB DAN THUNDERSTORMDocument19 pagesPARAMETER KONVEKTIF UNTUK ANALISIS AWAN CB DAN THUNDERSTORMgrazieNo ratings yet
- Week 3 TutorialDocument23 pagesWeek 3 TutorialMatthew WongNo ratings yet
- Significant Weather (SIGWX) ChartsDocument55 pagesSignificant Weather (SIGWX) ChartsGenesis AeroNo ratings yet
- Aviation ConceptsDocument4 pagesAviation ConceptsStasNo ratings yet
- METAR and SPECI DecodingDocument4 pagesMETAR and SPECI Decodingvikash_kumar_thakurNo ratings yet
- Area Forecasts: Aviation Weather ProductsDocument4 pagesArea Forecasts: Aviation Weather ProductsAmernurfitra Andi RusdinNo ratings yet
- UTAA Trip Kit PDFDocument38 pagesUTAA Trip Kit PDFgiganticvisNo ratings yet
- Flight Doc NotationsDocument1 pageFlight Doc Notationsdard100% (1)
- Section 10 TB MeteorologyDocument45 pagesSection 10 TB MeteorologylunefiekertNo ratings yet
- Zse Weather Watch: Tempo Groups in TafsDocument4 pagesZse Weather Watch: Tempo Groups in TafsChenyu WangNo ratings yet
- Met Report AhmDocument8 pagesMet Report Ahmabhishek tewariNo ratings yet
- Metar CodeDocument6 pagesMetar CodeAhmed SharafeldinNo ratings yet
- Aerodrome WarningDocument36 pagesAerodrome WarningNARENSH NAIRNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Jet Stream: Clash of the TitansFrom EverandUnderstanding the Jet Stream: Clash of the TitansRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Model Characteristics 110062221Document2 pagesModel Characteristics 110062221Adrian QuahNo ratings yet
- A Reef in The Sky: Are You Mounting Your Frags To The Best Substrate?Document48 pagesA Reef in The Sky: Are You Mounting Your Frags To The Best Substrate?Adrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Jecod - dp-2 - Manual 2Document3 pagesJecod - dp-2 - Manual 2Adrian QuahNo ratings yet
- A Reef in The Sky: Are You Mounting Your Frags To The Best Substrate?Document48 pagesA Reef in The Sky: Are You Mounting Your Frags To The Best Substrate?Adrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Oegc Basic Teachersnotes 01Document4 pagesOegc Basic Teachersnotes 01Chiosa AdinaNo ratings yet
- Inside A Predator'S Reef: Astronaut Food For Your ReefDocument48 pagesInside A Predator'S Reef: Astronaut Food For Your ReefAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Inside A Predator'S Reef: Astronaut Food For Your ReefDocument48 pagesInside A Predator'S Reef: Astronaut Food For Your ReefAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Algae-management-Program Multilanguage-Manual GB de FR SE NL SP PT JP CH 17ADocument129 pagesAlgae-management-Program Multilanguage-Manual GB de FR SE NL SP PT JP CH 17AAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Cup RamineDocument2 pagesCup RamineAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocument15 pagesDownloaded From Manuals Search EngineAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Cup RamineDocument2 pagesCup RamineAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocument15 pagesDownloaded From Manuals Search EngineAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- First UkuleleDocument14 pagesFirst Ukuleleadrianomarqs68% (19)
- Jecod - dp-2 - Manual 2Document3 pagesJecod - dp-2 - Manual 2Adrian QuahNo ratings yet
- App Usage - IOS V1.3.464Document20 pagesApp Usage - IOS V1.3.464Adrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Flight International 2021-05Document84 pagesFlight International 2021-05Valery GagichNo ratings yet
- Algae-management-Program Multilanguage-Manual GB de FR SE NL SP PT JP CH 17ADocument129 pagesAlgae-management-Program Multilanguage-Manual GB de FR SE NL SP PT JP CH 17AAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- App Usage - IOS V1.3.464Document20 pagesApp Usage - IOS V1.3.464Adrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Mobilise Hotspots IOS App GuideDocument10 pagesMobilise Hotspots IOS App GuideAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- App Usage - Android V1.3.446Document23 pagesApp Usage - Android V1.3.446Adrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Connect to in-flight Wi-Fi using iPass app or web loginDocument1 pageConnect to in-flight Wi-Fi using iPass app or web loginAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Mobilise Hotspots User Guide How To Subscribe To Our SerivceDocument5 pagesMobilise Hotspots User Guide How To Subscribe To Our SerivceAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Mobilise Hotspots User Guide How To Subscribe To Our SerivceDocument5 pagesMobilise Hotspots User Guide How To Subscribe To Our SerivceAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- User Guide: Grming MonitorDocument41 pagesUser Guide: Grming MonitorAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- User Guide: Grming MonitorDocument41 pagesUser Guide: Grming MonitorAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Hoo Too Nano Travel PDFDocument45 pagesHoo Too Nano Travel PDFAlexandru ȘtefănițăNo ratings yet
- Mobilise Hotspots IOS App GuideDocument10 pagesMobilise Hotspots IOS App GuideAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- MS-17E9 v1.0 EnglishDocument60 pagesMS-17E9 v1.0 EnglishAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- By Matt Leacock: 7 Role Cards 59 Player Cards 4 Reference Cards 7 PawnsDocument8 pagesBy Matt Leacock: 7 Role Cards 59 Player Cards 4 Reference Cards 7 PawnsL'Homme RévoltéNo ratings yet
- MS-17E9 v1.0 EnglishDocument60 pagesMS-17E9 v1.0 EnglishAdrian QuahNo ratings yet
- Notam MetarDocument26 pagesNotam MetarAdiyanto PamungkasNo ratings yet
- 8896 Meteo Practice Manual PDFDocument156 pages8896 Meteo Practice Manual PDFVitor M R CoelhoNo ratings yet
- AIP INDIA GEN 2.2 - Abbreviations Used in AIS PublicationDocument11 pagesAIP INDIA GEN 2.2 - Abbreviations Used in AIS PublicationitsrijoNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Flying Club Cessna Incident ReportDocument24 pagesGujarat Flying Club Cessna Incident ReportjaiNo ratings yet
- In-033-2018 Final ReportDocument36 pagesIn-033-2018 Final ReportOguzhanNo ratings yet
- 050 MeteorologyDocument27 pages050 MeteorologyΑγγελική ΜπρNo ratings yet
- Atpl - Meteorology SetDocument5 pagesAtpl - Meteorology SetHamidK.FarhatNo ratings yet
- Weather AbbreviationsDocument26 pagesWeather Abbreviationskiki100% (1)
- DPA Part 107 Cheat SheetDocument35 pagesDPA Part 107 Cheat Sheetmrstudios010100% (4)
- Briefing FCPP - FCBB (Created 27 Oct 045321Z)Document6 pagesBriefing FCPP - FCBB (Created 27 Oct 045321Z)carine DIABAKANANo ratings yet
- UTAA Trip Kit PDFDocument38 pagesUTAA Trip Kit PDFgiganticvisNo ratings yet
- AVIATION ROUTINE WEATHER REPORT (Metar-Codes)Document26 pagesAVIATION ROUTINE WEATHER REPORT (Metar-Codes)tdr250100% (5)
- MANOBSDocument479 pagesMANOBSBia239No ratings yet
- VaisalaDocument3 pagesVaisalaRiza FahLeviNo ratings yet
- Aviation Meteorology Lecture NotesDocument208 pagesAviation Meteorology Lecture NotesJatin Udwadia100% (2)
- Aviation Weather Services GuideDocument56 pagesAviation Weather Services Guideemdcad3790100% (1)
- VTBS RJTT PDFDocument7 pagesVTBS RJTT PDFhatefreefire CasterNo ratings yet
- Aircrew Quick Reference to METAR and TAF CodesDocument36 pagesAircrew Quick Reference to METAR and TAF CodesSudhir ChandranNo ratings yet
- Aviation Meteorology IntroductionDocument15 pagesAviation Meteorology IntroductionViplav Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- OptiMET-Message Software User Guide 5v1Document25 pagesOptiMET-Message Software User Guide 5v1Nguyễn Văn TrungNo ratings yet
- Metar - Taf - PirepDocument2 pagesMetar - Taf - PirepSantosh Raj KhanalNo ratings yet
- User Manual XEnviroDocument14 pagesUser Manual XEnvirospectrumNo ratings yet
- Mampu B737 RLT COMPANION Rev Jul 2011 PDFDocument298 pagesMampu B737 RLT COMPANION Rev Jul 2011 PDFJoey Marks100% (1)
- UTAM Trip Kit PDFDocument24 pagesUTAM Trip Kit PDFgiganticvisNo ratings yet
- Manual de Abbreviations, METAR, TAF, NOTAM para PPLDocument20 pagesManual de Abbreviations, METAR, TAF, NOTAM para PPLEurico RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Basic MET TD 1004107Document198 pagesBasic MET TD 1004107sandro5avantaggiato100% (1)
- Decode TAFs and METARsDocument4 pagesDecode TAFs and METARsDouglas AlvarezNo ratings yet
- AIP New Zealand AbbreviationsDocument38 pagesAIP New Zealand Abbreviationstracon900100% (2)