Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Course Content
Uploaded by
Berkay Çakır0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Course_Content.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views2 pagesCourse Content
Uploaded by
Berkay ÇakırCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
CE- 376 HYDROMECHANICS
2017-2018 SUMMER
Course Instructor: Assoc.Prof.Dr. Kerem TAŞTAN (Office Number= 202)
COURSE OUTLINE
1. FLOW IN CLOSED CONDUITS
1.1. General Characteristics of Flow in Closed Conduits
1.1.1. Definition of Laminar and Turbulent Flows
1.1.2. Entrance Region and Fully Developed Flow
1.1.3. Head Losses in Pipes
1.2. Fully Developed Flow in Closed Conduits
1.2.1. Derivation of Darcy-Weisbach Equation
1.2.2. Laminar Flow in Pipes
1.2.3. Turbulent Flow in Pipes
1.2.4. Moody Chart
1.3. Computation of Flow in Single Pipes
1.3.1. Calculation of Head Loss (Type I)
1.3.2. Calculation of Velocity (Discharge) (Type II)
1.3.3. Calculation of Pipe Diameter (Type III)
1.4. Minor Losses
1.4.1. Minor loss and its formula, loss coefficient
1.4.2. Common structures, causing minor loss
(cross-section changes, valves, elbows, etc.)
1.5. Pipeline Systems
1.5.1. Pipes in Series
1.5.2. Pipes in Parallel
1.5.3. Branching Pipes, Multiple Reservoir and Junction Problems
1.5.4. Hydraulics and Operation of Pumped Discharge Lines
2. OPEN CHANNEL FLOW
2.1. General Characteristics of Open Channel Flow
2.1.1. Classification of Open Channel Flows
2.1.2. Pressure Distribution in Open Channel Flows
2.1.3. Velocity Distribution in Open Channel Flows
2.2. Uniform Flow
2.2.1. Resistance in Open Channel Flow
2.2.2. Uniform Flow Equations
2.2.3. Composite and Compound Sections
2.3. Specific-Energy Concept
2.3.1. Specific Energy and Alternate Depth
2.3.2. Critical Flow
2.3.3. Channel Transitions and Chocking Problems
2.4. Rapidly Varied Flow, Specific Force Concept
2.4.1. Specific Force
2.4.2. Hydraulic Jump
2.5. Gradually Varied Flow
2.5.1. General Equation of Gradually Varied Flow
2.5.2. Types of Slopes
2.5.3. Longitudinal Flow Profiles
2.6. Design of Open Channels for Uniform Flow
2.6.1. Hydraulic Efficiency of Cross-Sections
3. FLOW MEASUREMENTS
3.1.Common flow measuring devices
3.2.Flow measurement for pipe flows
3.3.Flow measurement for open channel flows
4. DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS
4.1. Importance of dimensional analysis
4.2. Buckhingham’s -Theorem and Power Product Method
4.3. Basic dimensionless parameters in hydraulic
4.4. Modeling, simulation and principles of hydraulic
REFERENCE BOOKS
1) Munson, B. R., Young, D. F., and Okiishi, T. H., 'FUNDEMENTALS OF FLUID
MECHANICS', John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
2) Munson, B. R., Young, D. F., Okiishi, T. H., (Çevirmenler : Prof.Dr. Haşmet Türkoğlu,
Prof.Dr. Nuri Yücel, Prof.Dr. Zekeriya Altaç, Doç.Dr. Nureddin Dinler) Akışkanlar
Mekaniğine Giriş (A Brief Introduction to Fluid Mechanics) Nobel Yayınevi, 2013.
3) Fox, R.W., McDonald, A.T., and Pritchard, P.J., “INTRODUCTION TO FLUID
MECHANICS, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
4) White, F.M., “FLUID MECHANICS” , McGraw Hill
5) Çengel Y.A, Cımbala J.M, "Akışkanlar Mekaniği- Temelleri ve Uygulamaları" Palme
Yayınevi
6) Shames I., 'MECHANICS OF FLUIDS', McGraw Hill.
7) Streeter V.L. and Wylie B., 'FLUID MECHANICS', McGraw Hill.
8) Ilgaz C., Karahan E., Bulu A., 'Akışkanlar Mekaniği ve Hidrolik Problemleri' Çağlayan
Yayınevi.
9) Sümer M., Unsal İ., Bayazıt M., 'Hidrolik', Birsen Yayınevi.
10) Sümer A. ve Sümer M., 'Hidrolik Problemleri', Birsen Yayınevi.
11) Ronalds V.G., 'Akışkanlar Mekaniği ve Hidrolik', Sanem Çözümlü Serisi.
12) Douglas J.F., Janusz M.G. and Swaffield J.A., 'FLUID MECHANICS', Prentice Hall.
13) Şekerdağ, N. “Akışkanlar Mekaniği ve Hidrolik Problemleri” Nobel Yayın Dağıtım
14) Yıldırım, N., Taştan, K., “Pompalar ve Pompalı Boru Hatları (Çözümlü Problemler)”,
Nobel Yayınevi, 2014.
Grading:
2 Midterms = 60% of total grade
Final Examination = 40% of total grade
You might also like
- Technical Career Institute (Tci) Hvac Interview QuestionsDocument2 pagesTechnical Career Institute (Tci) Hvac Interview QuestionsSYED MUDASSIR NAZARNo ratings yet
- Spare Part List: Milli-Q Reference Milli-Q Reference A+Document12 pagesSpare Part List: Milli-Q Reference Milli-Q Reference A+Yassine AzzouzNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Diploma in Civil Engineering Semester: 3Document4 pagesGujarat Technological University: Diploma in Civil Engineering Semester: 3krunal sutharNo ratings yet
- Intro WK1Document30 pagesIntro WK1Amir Al-AimanNo ratings yet
- Open Channel Hydraulics Lecture NotesDocument59 pagesOpen Channel Hydraulics Lecture Notessikarwar22No ratings yet
- Syllabus Hydraulics IDocument4 pagesSyllabus Hydraulics IDiego GarfiasNo ratings yet
- He-2 Coarse OutlineDocument1 pageHe-2 Coarse OutlineQawdhan MahamoudNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pagesFluid MechanicsVipin KallingalNo ratings yet
- River HydraulicsDocument70 pagesRiver HydraulicsRicha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - 1989208478open ChannelDocument3 pagesCourse Outline - 1989208478open ChannelAlfatah muhumedNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: CHAPTER ONE (0.5 Week)Document4 pagesCourse Outline: CHAPTER ONE (0.5 Week)nimcanNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fluid (UCE03B03) Total Credit: 03 Contact Periods: 03 (2L+1T+0P)Document5 pagesMechanics of Fluid (UCE03B03) Total Credit: 03 Contact Periods: 03 (2L+1T+0P)David HumphreyNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument90 pagesHydraulicsilhammkaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics PDFDocument3 pagesHydraulics PDFAnil MarsaniNo ratings yet
- Madawalabu University Open Channel Hydraulics CourseDocument2 pagesMadawalabu University Open Channel Hydraulics Coursedawana samuelNo ratings yet
- Ka30902 Hydraulic: Lecturer: Nazaruddin Bin Abdul Taha / Siti Jahara Matlan Sesi: Sem 1 2016/2017Document54 pagesKa30902 Hydraulic: Lecturer: Nazaruddin Bin Abdul Taha / Siti Jahara Matlan Sesi: Sem 1 2016/2017hyuriyyNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY 5thDocument3 pagesENGINEERING HYDROLOGY 5thRahim ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Course Content: Chapter 1 Fundamental Concepts of River EngineeringDocument1 pageCourse Content: Chapter 1 Fundamental Concepts of River EngineeringTemesgen DemessieNo ratings yet
- HYDRAULICS-I CourseoutlineDocument1 pageHYDRAULICS-I CourseoutlinegolhoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Hydraulics-2022Document118 pagesEngineering Hydraulics-2022olingxjcNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Course OutlineDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics Course Outlinemeku44No ratings yet
- 3rd Sem SyllabusDocument33 pages3rd Sem SyllabusSUHOTRA guptaNo ratings yet
- Hire 1990Document683 pagesHire 1990CarlosDavidMuñicoCapuchoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics - CEng 2161 Course OutlineDocument2 pagesHydraulics - CEng 2161 Course Outlinehannahmelaku7773No ratings yet
- Water PDFDocument290 pagesWater PDFSam BarotillaNo ratings yet
- Phase Inversion in Dispersed Liquid-Liquid Pipe Flow: Kwun Ho NganDocument234 pagesPhase Inversion in Dispersed Liquid-Liquid Pipe Flow: Kwun Ho NgansaifoaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline CivilDocument2 pagesCourse Outline CivilgemadogelgaluNo ratings yet
- DFM NtuDocument31 pagesDFM NtuVimal RajNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Course OverviewDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics Course OverviewJoe NjoreNo ratings yet
- sem-3Document29 pagessem-3rajindermechNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FluidmechanicsDocument28 pagesIntroduction To FluidmechanicsSomnath SwamyNo ratings yet
- Module in Mech 141-1-20Document20 pagesModule in Mech 141-1-20Patrick Nikolai 01No ratings yet
- Fluid Characteristics: Doc. Ref. No Issue Date Uon-Stc-Cs 1 Oct 2010Document8 pagesFluid Characteristics: Doc. Ref. No Issue Date Uon-Stc-Cs 1 Oct 2010SreedharReddySajjalaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Design Manual (AUS)Document68 pagesHydraulic Design Manual (AUS)rotciv132709100% (1)
- FLUID MECHANICS LECTURE NOTESDocument64 pagesFLUID MECHANICS LECTURE NOTESswapneshNo ratings yet
- (Civil Engineering Hydraulics) Robert H. J. Sellin B.SC., Ph.D. (Auth.) - Flow in Channels-Macmillan Education UK (1969) PDFDocument159 pages(Civil Engineering Hydraulics) Robert H. J. Sellin B.SC., Ph.D. (Auth.) - Flow in Channels-Macmillan Education UK (1969) PDFLuis David Lopez BuitragoNo ratings yet
- Summary KH2134 Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pagesSummary KH2134 Fluid MechanicsAzman SamerNo ratings yet
- CE74.12: Hydrodynamics 3 (3-0) Course Objectives:: School of Engineering and Technology, (SET)Document3 pagesCE74.12: Hydrodynamics 3 (3-0) Course Objectives:: School of Engineering and Technology, (SET)Danna ValdezNo ratings yet
- Fakulti Kejuruteraan Universiti Malaysia Sarawak SESI 2-2008/2009 Course PlanDocument3 pagesFakulti Kejuruteraan Universiti Malaysia Sarawak SESI 2-2008/2009 Course PlanOng George SammyNo ratings yet
- UTM Mechanical Engineering Fluid Mechanics CourseDocument4 pagesUTM Mechanical Engineering Fluid Mechanics CoursesdcsdcdcwNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Hydraulic Engineering Section CE-213 Fluid Mechanics Course Category: DC L - T - P: 3 - 1-0 Credit: 4Document35 pagesSyllabus of Hydraulic Engineering Section CE-213 Fluid Mechanics Course Category: DC L - T - P: 3 - 1-0 Credit: 4subxaanalahNo ratings yet
- Fluid Properties and FundamentalsDocument46 pagesFluid Properties and FundamentalsnazreenNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Structures LN9Document69 pagesHydraulic Structures LN9Nijaz Lukovac100% (5)
- Course Title: Irrigation Engineering Course Code: 4012 Course Category: A Periods/Week: 5 Periods/Semester: 65 Credits: 4Document5 pagesCourse Title: Irrigation Engineering Course Code: 4012 Course Category: A Periods/Week: 5 Periods/Semester: 65 Credits: 4VaisakVenugopalNo ratings yet
- NPTEL Fluid Mechanics SyllabusDocument4 pagesNPTEL Fluid Mechanics SyllabusPradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- (International Centre For Mechanical Sciences 270) C. M. Rodkiewicz (Eds.) - Arteries and Arterial Blood Flow-Springer-Verlag Wien (1983)Document425 pages(International Centre For Mechanical Sciences 270) C. M. Rodkiewicz (Eds.) - Arteries and Arterial Blood Flow-Springer-Verlag Wien (1983)Narendra DesaiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Course Code, Name, CreditsDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics Course Code, Name, CreditsParmeshwarPaulNo ratings yet
- 4me3 Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pages4me3 Fluid MechanicsGautam GunjanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics II (MEng 3306)Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics II (MEng 3306)Addisu DagneNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa University Thermo-fluid Systems Design Course SyllabusDocument1 pageAddis Ababa University Thermo-fluid Systems Design Course SyllabusAddisu AyeleNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lect Notes With Sample QuesDocument96 pagesFluid Mechanics Lect Notes With Sample QuesMahin Samuel John 74No ratings yet
- C5 HH223 Fluid Mechanics IDocument2 pagesC5 HH223 Fluid Mechanics IArturo AnticonaNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps Hydraulics Seals CourseDocument3 pagesCentrifugal Pumps Hydraulics Seals CourseSebas FreireNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Systems of Groundwater FloDocument311 pagesGravitational Systems of Groundwater FloDaniel Alexi Avilez MaciasNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument3 pagesPDFMonu singhNo ratings yet
- E. M. Wilson PH.D., M.SC., F.I.C.E. (Auth.) - Engineering Hydrology-Macmillan Education UK (1969)Document192 pagesE. M. Wilson PH.D., M.SC., F.I.C.E. (Auth.) - Engineering Hydrology-Macmillan Education UK (1969)hailuNo ratings yet
- Me (Wre&gis)Document15 pagesMe (Wre&gis)Mohamed Nageeb SalemNo ratings yet
- Course Description:: University of Technology Civil Engineering Department Sanitary Engineering BranchDocument1 pageCourse Description:: University of Technology Civil Engineering Department Sanitary Engineering BranchMuna AzizNo ratings yet
- Stream Restoration in Dynamic Fluvial Systems: Scientific Approaches, Analyses, and ToolsFrom EverandStream Restoration in Dynamic Fluvial Systems: Scientific Approaches, Analyses, and ToolsNo ratings yet
- Yağ-Meme Kanseri PDFDocument1 pageYağ-Meme Kanseri PDFBerkay ÇakırNo ratings yet
- News & Views: A Heated Response To DangerDocument2 pagesNews & Views: A Heated Response To DangerBerkay ÇakırNo ratings yet
- Chess Problems: The Exposition of 1851Document1 pageChess Problems: The Exposition of 1851Berkay ÇakırNo ratings yet
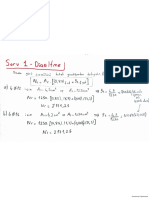
- Course ContentDocument2 pagesCourse ContentBerkay ÇakırNo ratings yet
- Ödev-1-Son Hali PDFDocument2 pagesÖdev-1-Son Hali PDFBerkay ÇakırNo ratings yet
- Ödev 1 Düzeltme PDFDocument1 pageÖdev 1 Düzeltme PDFBerkay ÇakırNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow in Porous MediaDocument26 pagesFluid Flow in Porous MediaksndknsnNo ratings yet
- Scrubbers PDFDocument8 pagesScrubbers PDFTAREK ALMAHDYNo ratings yet
- TS-2026 Tsunami CatalogDocument11 pagesTS-2026 Tsunami CatalogIrfan GhaniNo ratings yet
- Open Feedwater Heaters Closed Feedwater HeatersDocument22 pagesOpen Feedwater Heaters Closed Feedwater HeatersM.Thirunavukkarasu100% (1)
- A Two Phase Model CavitationDocument11 pagesA Two Phase Model CavitationThePrius0% (1)
- Experimental Process Technology Textbook Version 6Document116 pagesExperimental Process Technology Textbook Version 6Sara AlrubaiiNo ratings yet
- IB 3 Thermal QPDocument9 pagesIB 3 Thermal QPraghava vadhiyarNo ratings yet
- Flow Through Pipes LabDocument15 pagesFlow Through Pipes LabLauren MNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Vaporization DrawingsDocument3 pagesAmmonia Vaporization DrawingsEdenson Flores TrujilloNo ratings yet
- ESAB ExtractPage35-36DDocument16 pagesESAB ExtractPage35-36DDries VandezandeNo ratings yet
- SymgenicsTQ Automation Gas Start Up - SI UnitsDocument28 pagesSymgenicsTQ Automation Gas Start Up - SI UnitscahyaNo ratings yet
- 10.... 50 DS51.5Document4 pages10.... 50 DS51.5tinhNo ratings yet
- Energy WoodDocument2 pagesEnergy WoodMag FhearadhaighNo ratings yet
- 1.12 Fluor Sunil Singhal Lead Process EngineerDocument23 pages1.12 Fluor Sunil Singhal Lead Process Engineerrameshkarthik810No ratings yet
- 31 Underground Hydrocarbon Storage in TexasDocument130 pages31 Underground Hydrocarbon Storage in Texasrachmad_irwanto100% (1)
- Fired HeatersDocument40 pagesFired HeatersAhmad Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Chapter 2Document24 pagesRefrigeration Chapter 2predmarkjNo ratings yet
- Argonite FFES Uses Safe Nitrogen-Argon MixDocument4 pagesArgonite FFES Uses Safe Nitrogen-Argon MixJoel Shelton LasradoNo ratings yet
- Autocad Aca User Guide SpanishDocument554 pagesAutocad Aca User Guide Spanishjol87No ratings yet
- FranksDocument3 pagesFranksNawab Muhammad Ibrahim100% (1)
- Rectisol PDFDocument12 pagesRectisol PDFAna-Maria HodorogeaNo ratings yet
- 02 Feedstocks & ProductsDocument135 pages02 Feedstocks & ProductsciclointermedioNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Mechanical Seal Piping PlansDocument2 pages4.4 Mechanical Seal Piping PlansNikhil UdainiyaNo ratings yet
- Flare Gas Recovery Helpful InformationDocument2 pagesFlare Gas Recovery Helpful InformationKalai SelvanNo ratings yet
- Safe Chart Kinanti Field Rev 0Document2 pagesSafe Chart Kinanti Field Rev 0ZakyAlFatonyNo ratings yet
- BS en 126-2004-03Document39 pagesBS en 126-2004-03Abey VettoorNo ratings yet
- F1 Chapter 5 MatterDocument13 pagesF1 Chapter 5 Matteralya sophiaNo ratings yet
- Art's Process Spec SheetsDocument19 pagesArt's Process Spec Sheetsjdaig17No ratings yet