Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BLOW MOLDING (Film Sheets)
Uploaded by
Nemo Cyzar LiisOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BLOW MOLDING (Film Sheets)
Uploaded by
Nemo Cyzar LiisCopyright:
Available Formats
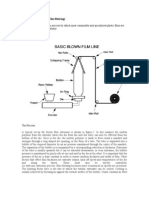
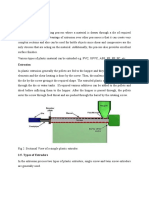
FILM BLOWING PROCESS
Typically, blown film extrusion is carried out vertically upwards, however horizontal and downward
extrusion processes are now becoming more common.
FOUR MAIN STEPS:
1. PELLET MELTING: The polymer material starts in a pellet form, which are successively
compacted and melted to form a continuous, viscous liquid [4]. This molten plastic is then
forced, or extruded, through an annular die.
2. EXTRUSION OR EXPANSION: Air is injected through a hole in the center of the die, and the
pressure causes the extruded melt to expand into a bubble. The air entering the bubble replaces
air leaving it, so that even and constant pressure is maintained to ensure uniform thickness of
the film.
3. COOLING: The bubble is pulled continually upwards from the die and a cooling ring blows air
onto the film. The film can also be cooled from the inside using internal bubble cooling. This
reduces the temperature inside the bubble, while maintaining the bubble diameter.
4. WINDING: After solidification at the frost line, the film moves into a set of nip rollers which
collapse the bubble and flatten it into two flat film layers. The puller rolls pull the film onto
windup rollers. The film passes through idler rolls during this process to ensure that there is
uniform tension in the film. Between the nip rollers and the windup rollers, the film may pass
through a treatment centre, depending on the application. During this stage, the film may be slit
to form one or two films, or surface treated
ADVANTAGES:
1. Blown film generally has a better balance of mechanical properties than cast or extruded
films because it is drawn in both the transverse and machine directions. Mechanical
properties of the thin film include tensile and flexural strength, and toughness. The nearly
uniform properties in both directions allow for maximum toughness in the film
2. Blown film extrusion can be used to make one large film, two smaller ones, or tubes that can
be made into bags.
3. Also, one die can make many different widths and sizes without significant trimming
DISADVANTAGES
1. Blown film has a less effective cooling process than flat film.
2. The resins used for casting typically have a lower melt flow index, which is the amount of
polymer that can be forced through a standard die in 10 minutes according to a standard
procedure. The melt flow index for cast film is about 5.0 g/10 min whereas for blown film it
is about 1.0 g/10 min
3. The production rates for cast film are higher
4. Cast film has better optical properties, including transparency, haze, and gloss
You might also like
- Blown Film ExtrusionDocument3 pagesBlown Film Extrusionchoirunissa setyaningrumNo ratings yet
- Plastics Extrusion ProcessDocument27 pagesPlastics Extrusion Processjaiprakash saini100% (5)
- Film Sheets (Polymer)Document5 pagesFilm Sheets (Polymer)Nemo Cyzar LiisNo ratings yet
- Blown FilmDocument4 pagesBlown Filmwahyutrisutrisno91No ratings yet
- Blown FilmDocument4 pagesBlown FilmAdinda LNo ratings yet
- Film Sheet PresentationDocument24 pagesFilm Sheet PresentationNemo Cyzar Liis100% (1)
- Olymer Rocessing: The Main Goal of Polymer Processing Is To Produce A Usable ObjectDocument59 pagesOlymer Rocessing: The Main Goal of Polymer Processing Is To Produce A Usable ObjectChaitanya PatelNo ratings yet
- Report BengkelDocument11 pagesReport BengkelMuhammad Nasri Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- FilmDocument2 pagesFilmDhileepan KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Blown Film Extrusion ReportDocument12 pagesBlown Film Extrusion ReportAbdul Razak RahmatNo ratings yet
- Blown FilmDocument18 pagesBlown Filmahsan888100% (2)
- Extrusion Blow MoldingDocument55 pagesExtrusion Blow MoldingnabilNo ratings yet
- Clase 7. Blown Film ExtrusionDocument37 pagesClase 7. Blown Film ExtrusionJuan Carlos Amaro ReyesNo ratings yet
- Polymer Procession Term Test-1Document90 pagesPolymer Procession Term Test-1সাইদুর রহমানNo ratings yet
- Injection Molding AssignmentDocument8 pagesInjection Molding AssignmentaakshusabhNo ratings yet
- How Importance of Cell Structure For Viscoelastic Foams PolyuretgabDocument13 pagesHow Importance of Cell Structure For Viscoelastic Foams PolyuretgabajoilhamNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Fabrication Process of PolymerDocument10 pages2.4 Fabrication Process of Polymersalmie_77No ratings yet
- Processing of PolymersDocument15 pagesProcessing of PolymersK Sruti RaniNo ratings yet
- Polymer Processing: ME 318 Manufacturing TechniquesDocument17 pagesPolymer Processing: ME 318 Manufacturing TechniquesSulOgikpcNo ratings yet
- Fluid Bed PPT End Ar - pptx1Document20 pagesFluid Bed PPT End Ar - pptx1Yaqeen MutanNo ratings yet
- 02 Multilayercompositefilms 110322072335 Phpapp02Document48 pages02 Multilayercompositefilms 110322072335 Phpapp02naveenjeswaniNo ratings yet
- Plastics: ThermoformingDocument36 pagesPlastics: ThermoformingMahesh KarpeNo ratings yet
- PP4&5Document60 pagesPP4&5daddarioalexander01No ratings yet
- POLYMER PROCESSING HandoutDocument4 pagesPOLYMER PROCESSING HandoutAmabelle SantosNo ratings yet
- The Tubular Film Blowing ProcessDocument9 pagesThe Tubular Film Blowing ProcessAlmir MachadoNo ratings yet
- Injection Blow MoldingDocument3 pagesInjection Blow MoldingMaximiliano RiccaNo ratings yet
- 202004032240236827nksingh Polymer ProcessingDocument9 pages202004032240236827nksingh Polymer ProcessingMuhammad Umair Akbar GujjarNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process DiagramDocument3 pagesManufacturing Process DiagramCris Diane G. DatingginooNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Plastic Processing: 1. State The General Properties of PlasticsDocument13 pagesUnit 3: Plastic Processing: 1. State The General Properties of PlasticsSagar DhageNo ratings yet
- Plastics ExtrusionDocument9 pagesPlastics ExtrusionFITIWINo ratings yet
- Plastic Film - WikipediaDocument5 pagesPlastic Film - WikipediaHimanshuNo ratings yet
- RIL BoppDocument14 pagesRIL BoppSaurabh PariharNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8-Extrusion-Sheets+filmsDocument20 pagesLecture 8-Extrusion-Sheets+filmsAhmed WaelNo ratings yet
- Injection MouldingDocument76 pagesInjection MouldingYohannesNo ratings yet
- Tablet CompressionDocument34 pagesTablet Compressionايناس ماجدNo ratings yet
- Blow Molding 1Document21 pagesBlow Molding 1prashant_cool_4_u100% (1)
- Injection MoldingDocument5 pagesInjection MoldingFAIZ RASOOLNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 (BCHE-602)Document14 pagesUnit 4 (BCHE-602)Garima TamtaNo ratings yet
- Plastics ProcessingDocument19 pagesPlastics ProcessingAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNo ratings yet
- Blow Moulding by HammahDocument28 pagesBlow Moulding by HammahAdnan JavedNo ratings yet
- Forming of PlasticDocument25 pagesForming of PlasticAzhar AliNo ratings yet
- Foam Mat DryingDocument28 pagesFoam Mat DryingASHUTOSH TRIPATHYNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Lesson 5Document41 pagesModule 5 Lesson 5Jayamma R NiranjanNo ratings yet
- 2.end Seal Tape - 1 Jul 2012 - PDSDocument3 pages2.end Seal Tape - 1 Jul 2012 - PDSUbaidah JarrahNo ratings yet
- Plastic Processing TechniquesDocument8 pagesPlastic Processing TechniquesSohail Anwar KhanNo ratings yet
- CLB21103 Process Instrumentation Mini Project: Process & Instrumentation in Yakult (M) SDN BHD, Negeri Sembilan (Critical Instrument Part)Document3 pagesCLB21103 Process Instrumentation Mini Project: Process & Instrumentation in Yakult (M) SDN BHD, Negeri Sembilan (Critical Instrument Part)Siti Hajar MohamedNo ratings yet
- Microencapsulation FinalDocument17 pagesMicroencapsulation FinalHuma Hameed DogarNo ratings yet
- High Speed Blow Molding MachineDocument64 pagesHigh Speed Blow Molding MachineSandip LadNo ratings yet
- Polymers PPT PDFDocument47 pagesPolymers PPT PDFShivani RajeevNo ratings yet
- The Many Benefits of Plastic Injection MouldingDocument3 pagesThe Many Benefits of Plastic Injection MouldingmelvinNo ratings yet
- Notes - Injection MoldingDocument10 pagesNotes - Injection MoldingNaveen VasanthNo ratings yet
- Module V - Blow and Transfer Molding ProcessesDocument17 pagesModule V - Blow and Transfer Molding ProcessesAntonius PrakosaNo ratings yet
- Textile Composites III-composite MFGDocument10 pagesTextile Composites III-composite MFGYared FikreNo ratings yet
- Blown FilmDocument11 pagesBlown FilmMarc Romero100% (1)
- Extrusion of PlasticDocument6 pagesExtrusion of Plasticdasani93No ratings yet
- Plastic Processing: Extrusion Compression MouldingDocument88 pagesPlastic Processing: Extrusion Compression MouldingBhushan Shankar Kamble100% (2)
- Injection MoldingDocument46 pagesInjection MoldingBeer with FriendsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Sugar Industry WastewaterDocument2 pagesIntroduction To The Sugar Industry WastewaterNemo Cyzar LiisNo ratings yet
- Film Sheet PresentationDocument24 pagesFilm Sheet PresentationNemo Cyzar Liis100% (1)
- Answers To Study Questions in The Above Experiment, Why Do You Have To Use CO2-free Water in All Your Solution Preparations?Document1 pageAnswers To Study Questions in The Above Experiment, Why Do You Have To Use CO2-free Water in All Your Solution Preparations?Nemo Cyzar LiisNo ratings yet
- Sedimentation ExperimentDocument31 pagesSedimentation ExperimentNemo Cyzar Liis100% (2)
- Analytical Chemistry HomeworkDocument4 pagesAnalytical Chemistry HomeworkNemo Cyzar LiisNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry HomeworkDocument4 pagesAnalytical Chemistry HomeworkNemo Cyzar LiisNo ratings yet
- Paint Manufacturing and NomenclatureDocument4 pagesPaint Manufacturing and NomenclatureNemo Cyzar LiisNo ratings yet
- Gas Absorption Column-Mass Transfer Experiment ADocument22 pagesGas Absorption Column-Mass Transfer Experiment ANemo Cyzar Liis100% (1)
- Gas AbsorptionDocument26 pagesGas AbsorptionNemo Cyzar LiisNo ratings yet
- Gas Absorption Column-Mass Transfer Experiment ADocument22 pagesGas Absorption Column-Mass Transfer Experiment ANemo Cyzar Liis100% (1)
- Impregnation MechanismDocument3 pagesImpregnation MechanismNemo Cyzar LiisNo ratings yet
- Appendix E Answers To QuestionsDocument2 pagesAppendix E Answers To QuestionsNemo Cyzar LiisNo ratings yet
- IRS Guidelins HPCDocument12 pagesIRS Guidelins HPCsaritasohamNo ratings yet
- 6 2 3 6 1 Polybond SBR PDFDocument2 pages6 2 3 6 1 Polybond SBR PDFHtun ZarniNo ratings yet
- SBS Basalt 101Document4 pagesSBS Basalt 101kelvinyeohNo ratings yet
- SS 332-2007+amd 1&2 - Preview PDFDocument10 pagesSS 332-2007+amd 1&2 - Preview PDFEe JoNo ratings yet
- BDA Free Standing WallsDocument7 pagesBDA Free Standing WallsEnginerdouglasNo ratings yet
- 419 TDS LataskimDocument3 pages419 TDS LataskimTomtom YabayabNo ratings yet
- Basic Material Science Lecture - 1Document22 pagesBasic Material Science Lecture - 1Mustafa Enes KırmacıNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Using Coconut Fibre To Concrete AsphaltDocument13 pagesThe Effect of Using Coconut Fibre To Concrete AsphaltLembaga Pendidikan100% (2)
- Specification.: Steel ScrapDocument24 pagesSpecification.: Steel ScrapKalpeshNo ratings yet
- Metal Properties and Destructive TestingDocument84 pagesMetal Properties and Destructive Testingtuvu100% (3)
- Revb Piping Class PetrobrasDocument87 pagesRevb Piping Class PetrobrasJessica SisalemaNo ratings yet
- Mainline Works: Project NameDocument32 pagesMainline Works: Project NameCorrtech TrichyNo ratings yet
- Laton Ms58 - CuZn39Pb3 - Original FusiblesDocument4 pagesLaton Ms58 - CuZn39Pb3 - Original FusiblesLuis CeronNo ratings yet
- SKF Materials For Bearing Rings and Rolling ElementsDocument2 pagesSKF Materials For Bearing Rings and Rolling ElementsKamolwan WeerachatsakulNo ratings yet
- Product Description Sheet 8009 Heavy Duty Anti-Seize: March 2002Document2 pagesProduct Description Sheet 8009 Heavy Duty Anti-Seize: March 2002Fabio ParceroNo ratings yet
- AOT 4-1/2" & 5-1/2" "TS-100" MANUAL SPIDER: Aot# Description # REQ. WTDocument1 pageAOT 4-1/2" & 5-1/2" "TS-100" MANUAL SPIDER: Aot# Description # REQ. WTRICHARDNo ratings yet
- Home Biogas System (Philippine BioDigesters) - Appropedia - The Sustainability Wiki PDFDocument9 pagesHome Biogas System (Philippine BioDigesters) - Appropedia - The Sustainability Wiki PDFel jeoNo ratings yet
- Bruchure Metal SolutionDocument10 pagesBruchure Metal Solutionanibal rey brito lopezNo ratings yet
- Survey of Precast Concrete Method and Cast-in-Situ Concrete MethodDocument4 pagesSurvey of Precast Concrete Method and Cast-in-Situ Concrete MethoderpublicationNo ratings yet
- M157Document6 pagesM157FRANZ RICHARD SARDINAS MALLCONo ratings yet
- Aluminco Crystal-Line-Product-Brochure en FR Rev072017Document74 pagesAluminco Crystal-Line-Product-Brochure en FR Rev072017irena34No ratings yet
- Tandard: Figure 5.12-Flush-Type Cleanout Fittings (See Tables 5.9a, 5.9b, 5.10a, 5.10b, 5.11a, and 5.11b)Document2 pagesTandard: Figure 5.12-Flush-Type Cleanout Fittings (See Tables 5.9a, 5.9b, 5.10a, 5.10b, 5.11a, and 5.11b)dedenNo ratings yet
- Standard - en 1555-5Document16 pagesStandard - en 1555-5ured cizminNo ratings yet
- Treatment of A Liquid AluminumDocument55 pagesTreatment of A Liquid AluminumLilian Jefferson Malavazi100% (1)
- UNDP - SZ - Environment - Doors-Windows Schedule PDFDocument1 pageUNDP - SZ - Environment - Doors-Windows Schedule PDFA MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Brick WorkDocument17 pagesChapter 6 Brick WorkFaisal KhanNo ratings yet
- Bitugum: SmoothDocument2 pagesBitugum: Smoothsr2011glassNo ratings yet
- Bunnings CatalogDocument21 pagesBunnings CatalogStratos Tsiavis100% (1)
- ConnectorsDocument36 pagesConnectorsSherif El Sayed100% (2)
- Plasticbrick 190603072205Document24 pagesPlasticbrick 190603072205NUR SYAFIQAH BINTI FISAL MET211031No ratings yet